Abstract
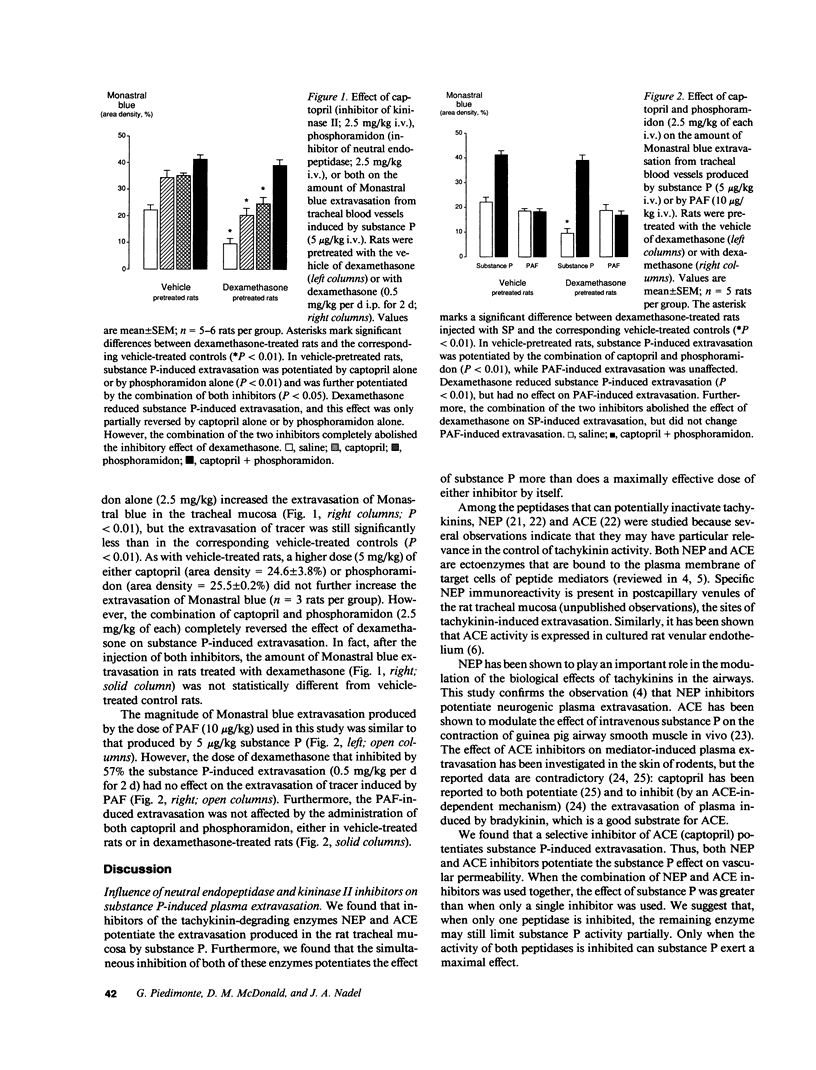
Glucocorticoids inhibit plasma extravasation induced in the rat tracheal mucosa by substance P and other tachykinins released from sensory nerves. This study was performed to determine whether this antiinflammatory effect of glucocorticoids is mediated by the tachykinin-degrading enzymes neutral endopeptidase (NEP) and kininase II (angiotensin converting enzyme, ACE). In addition, we studied the effect of dexamethasone on a nonpeptide inflammatory mediator, platelet-activating factor (PAF), which is not degraded by NEP or ACE. Adult male pathogen-free F344 rats were treated for 2 d with dexamethasone (0.5 mg/kg per d i.p.), or with the vehicle used to dissolve the steroid. The magnitude of plasma extravasation produced by an intravenous injection of substance P (5 micrograms/kg) or PAF (10 micrograms/kg) was then assessed by using Monastral blue pigment as an intravascular tracer. The role of NEP and ACE activities in the changes produced by dexamethasone was investigated by examining the effect of the selective inhibitors of these enzymes, phosphoramidon and captopril. Dexamethasone reduced the substance P-induced extravasation by 57% but did not affect the PAF-induced extravasation. The suppressive effect of dexamethasone on substance P-induced extravasation was completely reversed by simultaneously inhibiting NEP and ACE activities, but the inhibition of these enzymes had no effect on PAF-induced extravasation, regardless of whether the rats were pretreated with dexamethasone or not. These results suggest that NEP and ACE mediate a selective inhibitory effect of glucocorticoids on neurogenic plasma extravasation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Asthma as an axon reflex. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):242–245. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90777-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Gruenert D. C. Glucocorticoids induce neutral endopeptidase in transformed human tracheal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):L83–L89. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.2.L83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boura A. L., Svolmanis A. P. Converting enzyme inhibition in the rat by captopril is accompanied by potentiation of carrageenin-induced inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 May;82(1):3–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnuccio R., Di Rosa M., Guerrasio B., Iuvone T., Sautebin L. Vasocortin: a novel glucocorticoid-induced anti-inflammatory protein. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;90(3):443–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. W., Chung K. F., Rogers D. F., Barnes P. J. Effect of platelet-activating factor on airway vascular permeability: possible mechanisms. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):479–484. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantone J. C., Schrier D., Weingarten B. Inhibition of vascular permeability changes in rats by captopril. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1207–1211. doi: 10.1172/JCI110559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J., Setton C., Silverstein E. Angiotensin converting enzyme: induction by steroids in rabbit alveolar macrophages in culture. Science. 1977 Jul 1;197(4298):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.194311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Charleson S. E., Zimmerman M., Mumford R., Wood P. L. Enkephalinase: selective peptide inhibitors. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2593–2601. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris I., DeGirolami U., Wortham K., Majno G. Vascular labelling with monastral blue B. Stain Technol. 1982 May;57(3):177–183. doi: 10.3109/10520298209066611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Brodin E., Rosell S., Folkers K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E., SCHOEFL G. I. Studies on inflammation. II. The site of action of histamine and serotonin along the vascular tree: a topographic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:607–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majno G., Shea S. M., Leventhal M. Endothelial contraction induced by histamine-type mediators: an electron microscopic study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):647–672. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M. Neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. I. Changes in venules, leucocytes and epithelial cells. J Neurocytol. 1988 Oct;17(5):583–603. doi: 10.1007/BF01260988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D. M. Respiratory tract infections increase susceptibility to neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1432–1440. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A., Lloyd C. J., Kachel C., Funder J. W. Induction by glucocorticoids of angiotensin converting enzyme production from bovine endothelial cells in culture and rat lung in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):684–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI110663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer C. F., Dennis P. A., Majno G., Joris I. Venular endothelium in vitro: isolation and characterization. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;24(4):359–368. doi: 10.1007/BF02628839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyanagui Y. Physiological regulation of vascular permeability by endogenous glucocorticoids and active oxygen. Inflammation. 1983 Mar;7(1):81–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00918010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedimonte G., McDonald D. M., Nadel J. A. Glucocorticoids inhibit neurogenic plasma extravasation and prevent virus-potentiated extravasation in the rat trachea. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1409–1415. doi: 10.1172/JCI114855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedimonte G., Nadel J. A., Umeno E., McDonald D. M. Sendai virus infection potentiates neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Feb;68(2):754–760. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.2.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Lundberg J. M., Skofitsch G., Lembeck F. Vascular protein linkage in various tissue induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;324(3):212–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00503897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saria A., Martling C. R., Yan Z., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Gamse R., Lundberg J. M. Release of multiple tachykinins from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves in the lung by bradykinin, histamine, dimethylphenyl piperazinium, and vagal nerve stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jun;137(6):1330–1335. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Coats S. R., Drazen J. M. Substance P-induced bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig. Enhancement by inhibitors of neutral metalloendopeptidase and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):331–336. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Engelbrecht S., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Hydrolysis of substance p and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Sugio K., Takemasa F. The role of glucocorticoid receptor and gene expression in the anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):408–410. doi: 10.1038/280408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno E., McDonald D. M., Nadel J. A. Hypertonic saline increases vascular permeability in the rat trachea by producing neurogenic inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1905–1908. doi: 10.1172/JCI114652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuk-Pavlović Z., Kreofsky T. J., Rohrbach M. S. Characteristics of monocyte angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) induction by dexamethasone. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jun;45(6):503–509. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.6.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



