Abstract
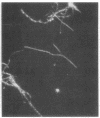
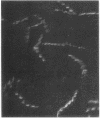
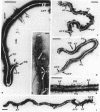
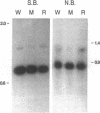
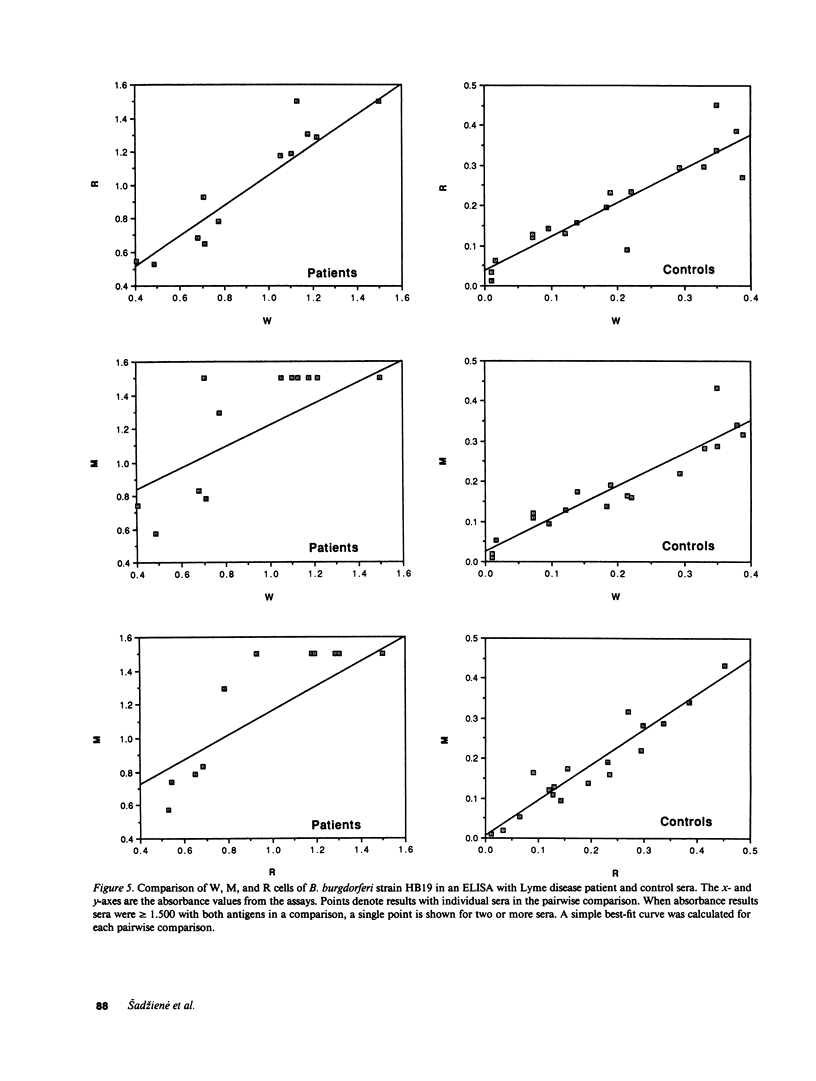
A nonmotile mutant of Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease, was isolated and characterized. The mutant was compared with the wild-type predecessor as well as with a motile back-revertant of the same genetic background. The mutant lacked, by morphologic, biochemical, and immunologic criteria, the major structural protein of flagella, flagellin. This mutation was not associated with major DNA rearrangements or with failure of transcription. An apparent consequence of a loss of flagella was reduced ability to penetrate human endothelial cell layers in vitro. In another assessment of functional significance, the flagella-less mutant was equal if not superior to flagella-bearing, isogenic isolates when examined in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for anti-B. burgdorferi antibodies in the sera of Lyme disease patients. These studies of a mutant, the first among pathogenic Borrelia spp. to be characterized, indicate that the flagellum and motility it confers play a role in B. burgdorferi's invasion of human tissues. A flagella-less B. burgdorferi may be useful as the basis of a more specific immunoassay and a vaccine for protection against Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberer E., Brunner C., Suchanek G., Klade H., Barbour A., Stanek G., Lassmann H. Molecular mimicry and Lyme borreliosis: a shared antigenic determinant between Borrelia burgdorferi and human tissue. Ann Neurol. 1989 Dec;26(6):732–737. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Grunwaldt E., Steere A. C. Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):504–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI110998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Stoenner H. G. Variable major proteins of Borrellia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1312–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley D. B., Charon N. W. Axial filament involvement in the motility of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1406–1412. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1406-1412.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundoc V. G., Barbour A. G. Clonal polymorphisms of outer membrane protein OspB of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2733–2741. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2733-2741.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell M. B., Guerry P., Lee E. C., Burans J. P., Walker R. I. Reversible expression of flagella in Campylobacter jejuni. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):941–943. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.941-943.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsiotis M., Stocker B. A., Weinstein D. L., O'Brien A. D. A Salmonella typhimurium virulence gene linked to flg. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3276–3280. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3276-3280.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. L., Benach J. L. Isolation of antigenic components from the Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):756–765. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Penetration of endothelial cell monolayers by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1626–1628. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1626-1628.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann G. S., Kramer M., Göbel U. B., Wallich R. Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3590–3590. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. F., Charon N. W. Motility of the spirochete Leptospira. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;9(2):101–110. doi: 10.1002/cm.970090202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicki R. L., Steere A. C. Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):790–797. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Motility as a virulence factor for Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):890–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.890-897.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Asbrink E. Serodiagnosis of erythema migrans and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans by the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.545-551.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Hindersson P., Pedersen N. S. Measurement of antibodies to the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.338-346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch J., Bergström S., Barbour A. G. Cloning and sequence analysis of linear plasmid telomeres of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):811–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Iino T., Yamaguchi S. Hook-associated proteins essential for flagellar filament formation in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):100–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.100-108.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Freter R. Adhesive properties of Vibrio cholerae: nature of the interaction with isolated rabbit brush border membranes and human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):240–245. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.240-245.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Treponema phagedenis has at least two proteins residing together on its periplasmic flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.105-112.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockman H. A., Curtiss R., 3rd Salmonella typhimurium mutants lacking flagella or motility remain virulent in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):137–143. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.137-143.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for the detection of class-specific immunoglobulins to Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Epidemiol. 1988 Apr;127(4):818–825. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. T., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Antigenic variation is associated with DNA rearrangements in a relapsing fever Borrelia. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montie T. C., Doyle-Huntzinger D., Craven R. C., Holder I. A. Loss of virulence associated with absence of flagellum in an isogenic mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the burned-mouse model. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):1296–1298. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.1296-1298.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Vejtorp M., Axelsen N. H. Serodiagnosis of syphilis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies against the Reiter treponeme flagellum. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Apr;15(4):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadallah F., Brighouse G., Del Giudice G., Drager-Dayal R., Hocine M., Lambert P. H. Production of specific monoclonal antibodies to Salmonella typhi flagellin and possible application to immunodiagnosis of typhoid fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):59–64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Dwyer E., Winchester R. Association of chronic Lyme arthritis with HLA-DR4 and HLA-DR2 alleles. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):219–223. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Comstock L. E. Interaction of Lyme disease spirochetes with cultured eucaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1324–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1324-1326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
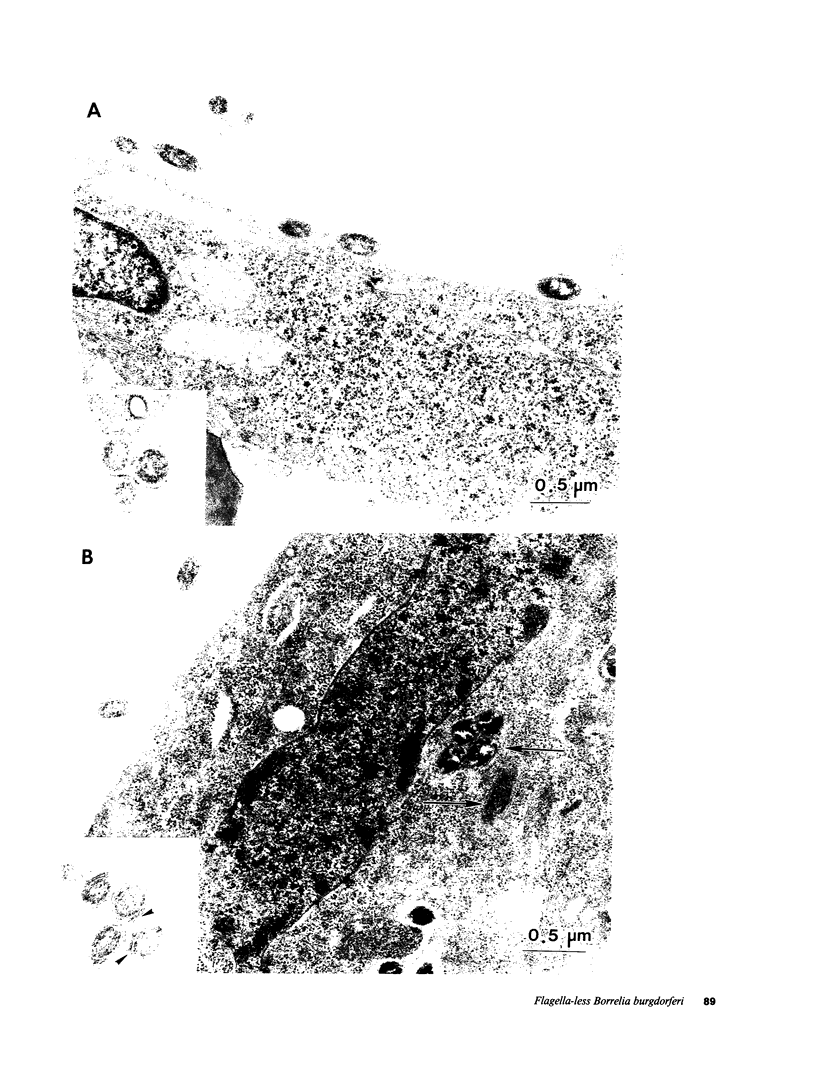
- Wallich R., Moter S. E., Simon M. M., Ebnet K., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. The Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum-associated 41-kilodalton antigen (flagellin): molecular cloning, expression, and amplification of the gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1711-1719.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Gueye W., Herzer P., Weber K. Immunochemische Analyse der Immunantwort bei Spätmanifestationen der Lyme Borreliose. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Mar;267(4):549–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]