Abstract
In the title compound, C11H10N3O4S+·Br−, the benzene ring makes an angle of 88.4 (2)° with the pyridinium ring. The dihedral angle between the nitro group and the benzene ring is 16.5 (2)°. The ions in the crystal structure are linked by a combination of intermolecular N—H⋯Br and non-conventional C—H⋯Br and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For zwitterionic forms of N-arylbenzenesulfonamides, see: Li et al. (2007 ▶); Yu & Li (2007 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For non-conventional hydrogen bonds, see: Desiraju & Steiner (2001 ▶). For the use of pyridinium derivatives in the construction of supramolecular architectures, see: Damiano et al. (2007 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H10N3O4S+·Br−
M r = 360.19
Monoclinic,

a = 38.242 (8) Å
b = 5.2852 (11) Å
c = 13.941 (3) Å
β = 108.18 (3)°
V = 2677.0 (11) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.24 mm−1
T = 113 (2) K
0.10 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.710, T max = 0.938
10460 measured reflections
3174 independent reflections
2635 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.050
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.033
wR(F 2) = 0.076
S = 1.05
3174 reflections
189 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035265/si2122sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035265/si2122Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯Br1i | 0.89 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.195 (2) | 173 (3) |
| N2—H2A⋯Br1 | 0.84 (3) | 2.38 (3) | 3.225 (3) | 174 (2) |
| C10—H10⋯O3ii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.301 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5⋯Br1iii | 0.95 | 2.75 | 3.676 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Organic pyridinium salts have been widely used in the construction of supramolecular architectures (Damiano et al., 2007). As part of our ongoing studies of supramolecular chemistry involving the pyridinium rings (Li et al., 2007), an X-ray structure analysis of the title compound has been performed. In the cations of the title compound the short C—N distance [N2—C3 = 1.387 (3) Å] has a value between those of a typical C=N double and C—N single bond (1.34–1.38 Å and 1.47–1.50 Å, respectively; Allen et al., 1987). This might be indicative of a slight conjugation of the sulphonamide π electrons N with those of the pyridinium ring. The benzene ring makes an angle of 88.4 (2) ° with the pyridinium ring. The dihedral angle between the nitro group and the benzene ring is 163.5 (2) °. The S atom has a tetrahedral geometry and the Br anion link the cationic molecule into chains along the c axis. The ions in the crystal structure are linked by a combination of intermolecular N—H···Br and non-conventional C—H···Br and C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) to form a three-dimensional network (Desiraju & Steiner, 2001).
Experimental
A solution of 4-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride (2.2 g, 10 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (10 ml) was added dropwise to a suspension of 4-aminopyridine (0.9 g, 10 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (10 ml) at room temperature with stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight. The yellow solid obtained was washed with warm water to obtain the title compound in a yield of 60.6%. A colorless single-crystal suitable for X-ray analysis was obtained by slow evaporation of an hydrobromic acid (5%) solution at room temperature over a period of a week. Analysis calculated for C11H10N3O4SBr: C 36.68, H 2.80, N 11.67%; found: C 36.70, H 2.52, N 11.98%.
Refinement
The N-bound H atoms were located in a difference map and their coordinates were refined with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). The C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H =0.95 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
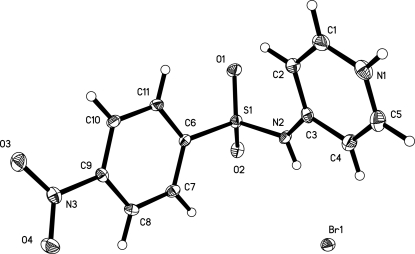
Fig. 1.
View of one molecule of the title compound showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 35% probability level (arbitrary spheres for the H atoms).
Crystal data
| C11H10N3O4S+·Br– | F000 = 1440 |
| Mr = 360.19 | Dx = 1.787 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 3479 reflections |
| a = 38.242 (8) Å | θ = 2.2–27.9º |
| b = 5.2852 (11) Å | µ = 3.24 mm−1 |
| c = 13.941 (3) Å | T = 113 (2) K |
| β = 108.18 (3)º | Needle, colorless |
| V = 2677.0 (11) Å3 | 0.10 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3174 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2635 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: confocal | Rint = 0.050 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9º |
| T = 113(2) K | θmin = 2.2º |
| ω and φ scans | h = −45→50 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) | k = −6→4 |
| Tmin = 0.710, Tmax = 0.938 | l = −18→18 |
| 10460 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.076 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0332P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3174 reflections | Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3 |
| 189 parameters | Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.038458 (6) | −0.03831 (5) | 0.156635 (19) | 0.02228 (9) | |
| S1 | 0.134013 (15) | −0.12886 (11) | 0.40908 (5) | 0.01823 (14) | |
| O1 | 0.14776 (4) | −0.1752 (3) | 0.51529 (13) | 0.0248 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.12760 (4) | −0.3323 (3) | 0.33820 (13) | 0.0240 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.25567 (5) | 0.7285 (4) | 0.36991 (13) | 0.0304 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.21939 (5) | 0.7239 (3) | 0.21551 (13) | 0.0277 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.05972 (6) | 0.5912 (4) | 0.53090 (18) | 0.0279 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.09433 (5) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.38299 (17) | 0.0191 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.22900 (5) | 0.6463 (4) | 0.30319 (16) | 0.0207 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.09132 (7) | 0.4746 (5) | 0.5789 (2) | 0.0271 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.1046 | 0.5230 | 0.6460 | 0.033* | |
| C2 | 0.10479 (6) | 0.2877 (5) | 0.53330 (18) | 0.0227 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.1277 | 0.2101 | 0.5672 | 0.027* | |
| C3 | 0.08437 (6) | 0.2113 (5) | 0.43571 (18) | 0.0196 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.05109 (6) | 0.3348 (5) | 0.38843 (19) | 0.0261 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.0365 | 0.2863 | 0.3224 | 0.031* | |
| C5 | 0.03964 (7) | 0.5254 (5) | 0.4376 (2) | 0.0304 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.0173 | 0.6115 | 0.4053 | 0.036* | |
| C6 | 0.16392 (6) | 0.0923 (4) | 0.37923 (18) | 0.0165 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.16066 (6) | 0.1306 (5) | 0.27787 (18) | 0.0192 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.1436 | 0.0342 | 0.2268 | 0.023* | |
| C8 | 0.18247 (6) | 0.3099 (5) | 0.25237 (17) | 0.0186 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.1808 | 0.3389 | 0.1838 | 0.022* | |
| C9 | 0.20687 (6) | 0.4465 (4) | 0.32927 (18) | 0.0164 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.21101 (6) | 0.4056 (5) | 0.43050 (18) | 0.0188 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.2285 | 0.4995 | 0.4815 | 0.023* | |
| C11 | 0.18912 (6) | 0.2252 (5) | 0.45572 (17) | 0.0193 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.1914 | 0.1931 | 0.5244 | 0.023* | |
| H1A | 0.0529 (8) | 0.723 (6) | 0.561 (2) | 0.040 (8)* | |
| H2A | 0.0799 (8) | −0.010 (5) | 0.324 (2) | 0.018 (7)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.02226 (14) | 0.02479 (15) | 0.01857 (15) | −0.00186 (10) | 0.00461 (11) | −0.00007 (10) |
| S1 | 0.0162 (3) | 0.0167 (3) | 0.0210 (3) | 0.0022 (2) | 0.0046 (2) | 0.0039 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0270 (10) | 0.0216 (10) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0025 (7) | 0.0111 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0323 (10) | 0.0006 (7) | 0.0085 (8) | −0.0030 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0290 (9) | 0.0333 (11) | 0.0296 (11) | −0.0136 (8) | 0.0099 (8) | −0.0083 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0260 (10) | 0.0230 (10) | −0.0022 (8) | 0.0105 (8) | 0.0055 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0323 (12) | 0.0243 (12) | 0.0317 (14) | −0.0043 (10) | 0.0170 (11) | −0.0065 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0224 (11) | 0.0182 (12) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0010 (9) | −0.0021 (9) |
| N3 | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0248 (12) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0124 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0280 (14) | 0.0316 (15) | 0.0234 (15) | −0.0087 (11) | 0.0104 (12) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0209 (12) | 0.0261 (13) | 0.0209 (13) | −0.0024 (10) | 0.0063 (11) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0186 (11) | 0.0182 (12) | 0.0250 (13) | −0.0050 (10) | 0.0109 (10) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0203 (12) | 0.0310 (15) | 0.0256 (15) | 0.0033 (11) | 0.0052 (11) | −0.0009 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0246 (13) | 0.0292 (15) | 0.0398 (17) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0136 (13) | 0.0012 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0182 (12) | 0.0163 (12) | 0.0017 (9) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0013 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0204 (11) | 0.0185 (12) | 0.0162 (13) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0022 (10) | −0.0038 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0226 (11) | 0.0208 (12) | 0.0129 (11) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0063 (10) | −0.0005 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0172 (11) | 0.0146 (11) | 0.0194 (13) | 0.0029 (9) | 0.0087 (10) | 0.0011 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0160 (11) | 0.0232 (12) | 0.0149 (12) | 0.0011 (9) | 0.0015 (10) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0175 (11) | 0.0246 (13) | 0.0146 (12) | 0.0042 (10) | 0.0032 (9) | 0.0037 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O2 | 1.4288 (18) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| S1—O1 | 1.4292 (18) | C3—C4 | 1.399 (3) |
| S1—N2 | 1.637 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.366 (4) |
| S1—C6 | 1.773 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| O3—N3 | 1.226 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O4—N3 | 1.232 (3) | C6—C11 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C5 | 1.333 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.394 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.335 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.380 (3) |
| N1—H1A | 0.89 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C3 | 1.387 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.385 (3) |
| N2—H2A | 0.84 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C9 | 1.468 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.387 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.359 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.385 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.400 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| O2—S1—O1 | 121.05 (11) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.6 (3) |
| O2—S1—N2 | 104.58 (11) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| O1—S1—N2 | 109.04 (11) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| O2—S1—C6 | 108.52 (10) | N1—C5—C4 | 120.3 (2) |
| O1—S1—C6 | 107.48 (11) | N1—C5—H5 | 119.8 |
| N2—S1—C6 | 105.09 (11) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 121.6 (2) | C11—C6—C7 | 121.8 (2) |
| C5—N1—H1A | 120.0 (19) | C11—C6—S1 | 119.90 (17) |
| C1—N1—H1A | 118.3 (19) | C7—C6—S1 | 118.27 (18) |
| C3—N2—S1 | 128.28 (19) | C8—C7—C6 | 119.4 (2) |
| C3—N2—H2A | 115.5 (17) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| S1—N2—H2A | 114.9 (18) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| O3—N3—O4 | 123.7 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 118.3 (2) |
| O3—N3—C9 | 118.3 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.9 |
| O4—N3—C9 | 117.9 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.9 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 121.1 (3) | C8—C9—C10 | 122.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 119.4 | C8—C9—N3 | 119.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.4 | C10—C9—N3 | 118.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.1 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 118.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C11—C10—H10 | 120.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.7 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 117.2 (2) | C10—C11—C6 | 119.0 (2) |
| N2—C3—C2 | 124.6 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.2 (2) | C6—C11—H11 | 120.5 |
| O2—S1—N2—C3 | 172.9 (2) | O1—S1—C6—C7 | 167.55 (17) |
| O1—S1—N2—C3 | 42.1 (2) | N2—S1—C6—C7 | −76.4 (2) |
| C6—S1—N2—C3 | −72.9 (2) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | −1.6 (3) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 1.7 (4) | S1—C6—C7—C8 | 177.10 (17) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −2.3 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.2 (3) |
| S1—N2—C3—C4 | 168.56 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.9 (3) |
| S1—N2—C3—C2 | −13.2 (3) | C7—C8—C9—N3 | −177.11 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—N2 | −177.1 (2) | O3—N3—C9—C8 | −164.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.1 (3) | O4—N3—C9—C8 | 16.1 (3) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 178.9 (2) | O3—N3—C9—C10 | 16.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (4) | O4—N3—C9—C10 | −162.90 (19) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.0 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −1.1 (4) | N3—C9—C10—C11 | 177.23 (19) |
| O2—S1—C6—C11 | −146.30 (18) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 0.0 (3) |
| O1—S1—C6—C11 | −13.8 (2) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | 1.7 (3) |
| N2—S1—C6—C11 | 102.3 (2) | S1—C6—C11—C10 | −176.96 (17) |
| O2—S1—C6—C7 | 35.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···Br1i | 0.89 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.195 (2) | 173 (3) |
| N2—H2A···Br1 | 0.84 (3) | 2.38 (3) | 3.225 (3) | 174 (2) |
| C10—H10···O3ii | 0.95 | 2.44 | 3.301 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5···Br1iii | 0.95 | 2.75 | 3.676 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (iii) −x, y+1, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SI2122).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Damiano, T., Morton, D. & Nelson, A. (2007). Org. Biomol. Chem.5, 2735–2752. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Desiraju & Steiner (2001). The Weak Hydrogen Bond in Structural Chemisty and Biology IUCr Monographs on Crystallography, Vol. 9. Oxford Science Publications.
- Li, J. S., Chen, L. G., Zhang, Y. Y., Xu, Y. J., Deng, Y. & Huang, P. M. (2007). J. Chem. Res.6, 350–352.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear and CrystalStructure Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-J. & Li, J.-S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3399.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035265/si2122sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035265/si2122Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report