Abstract
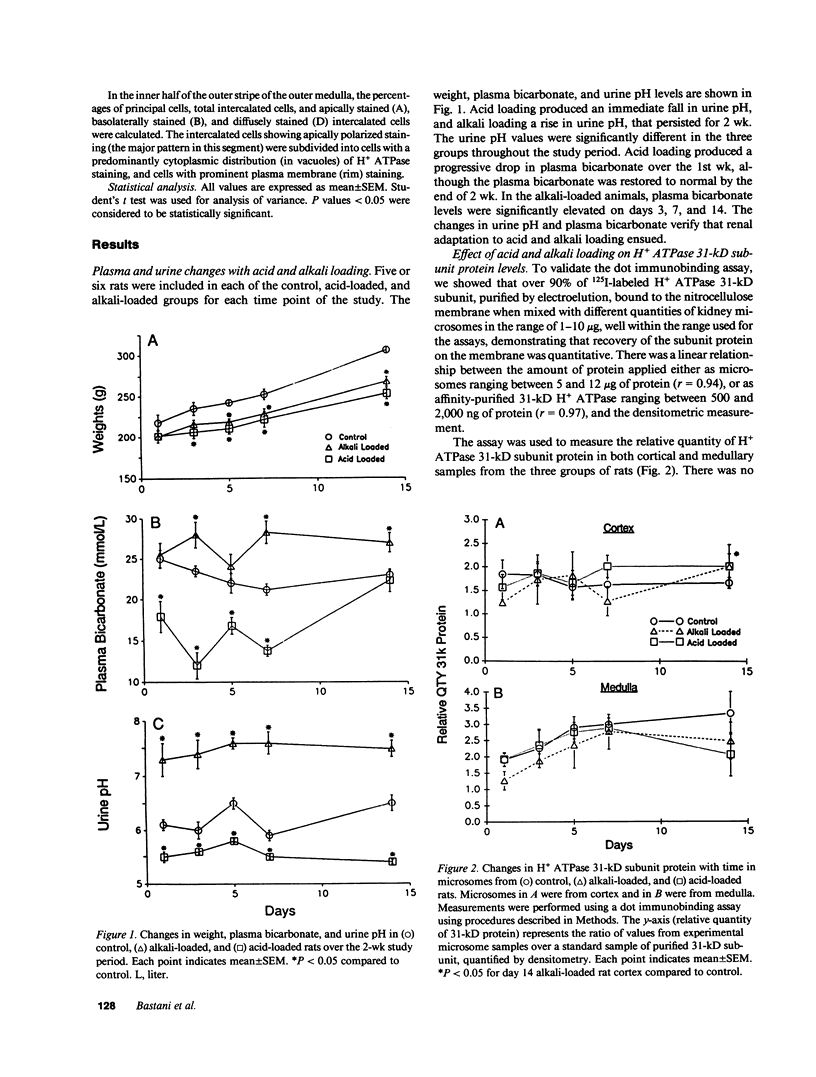
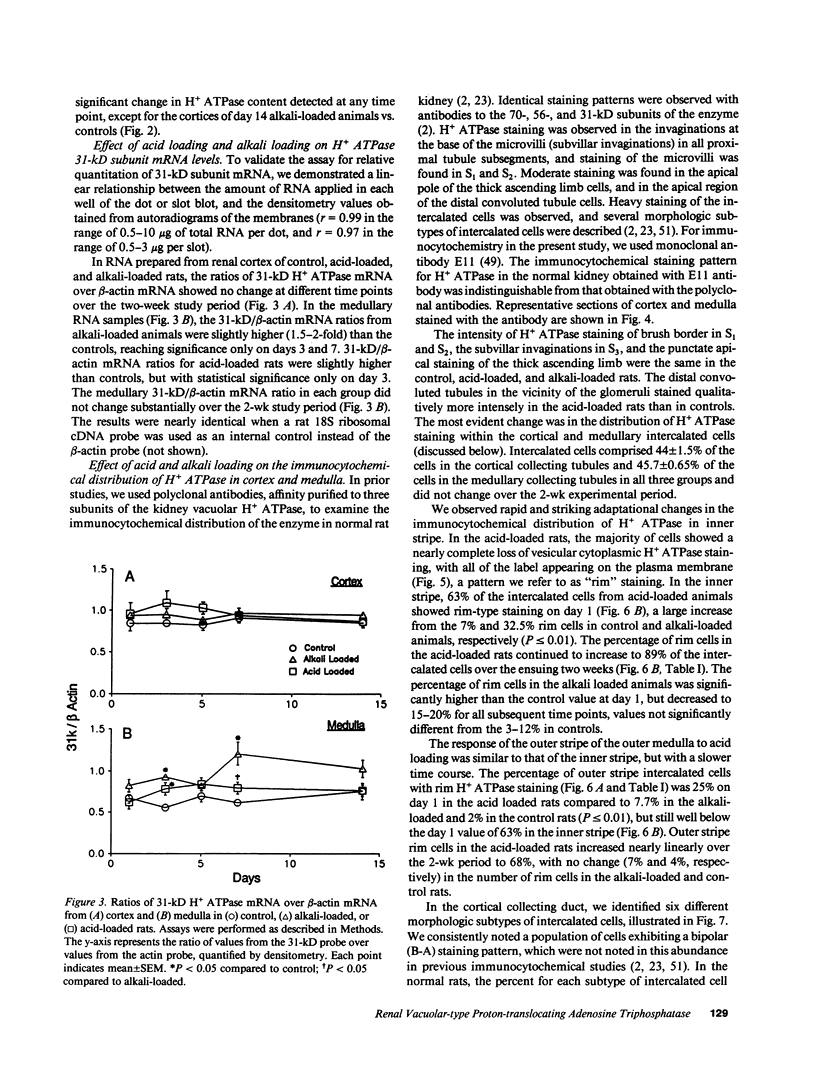
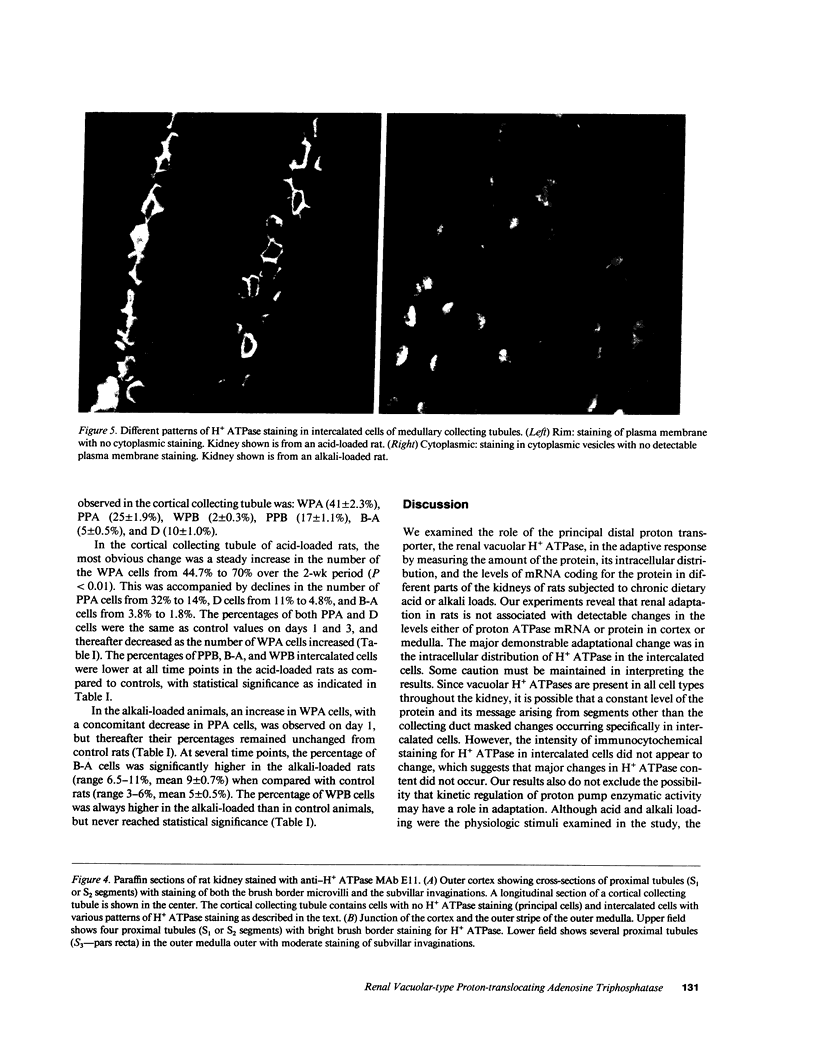
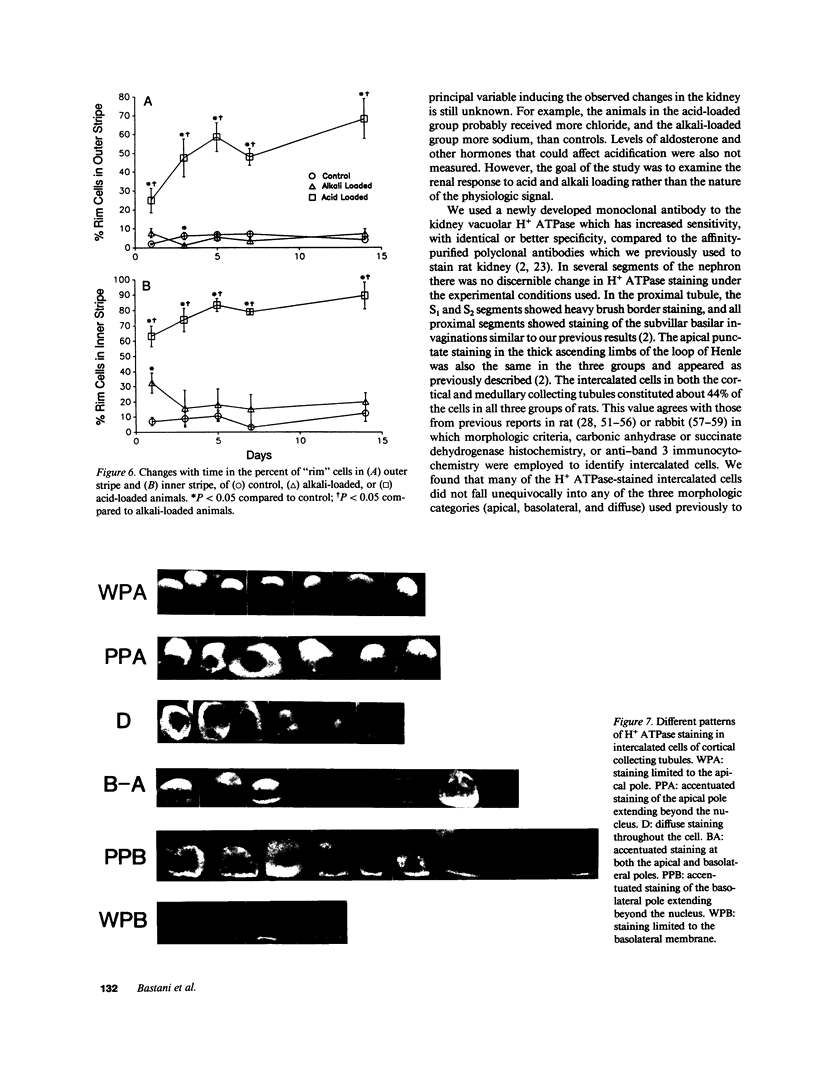
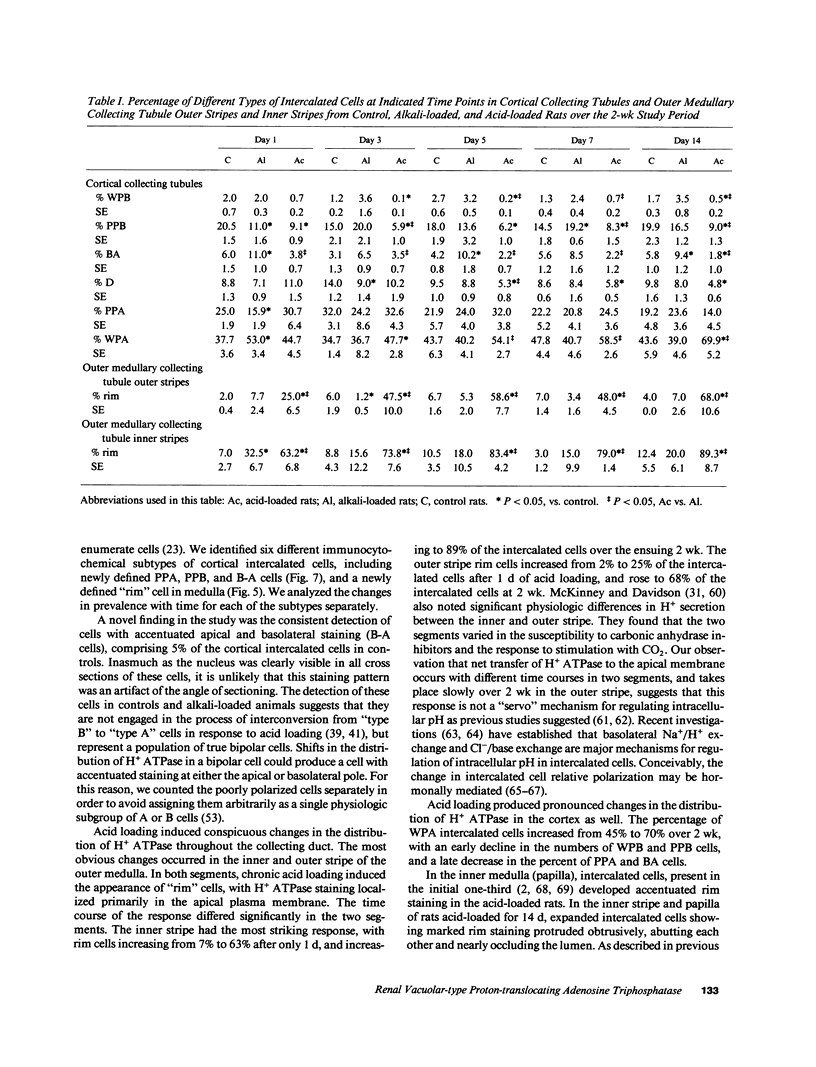
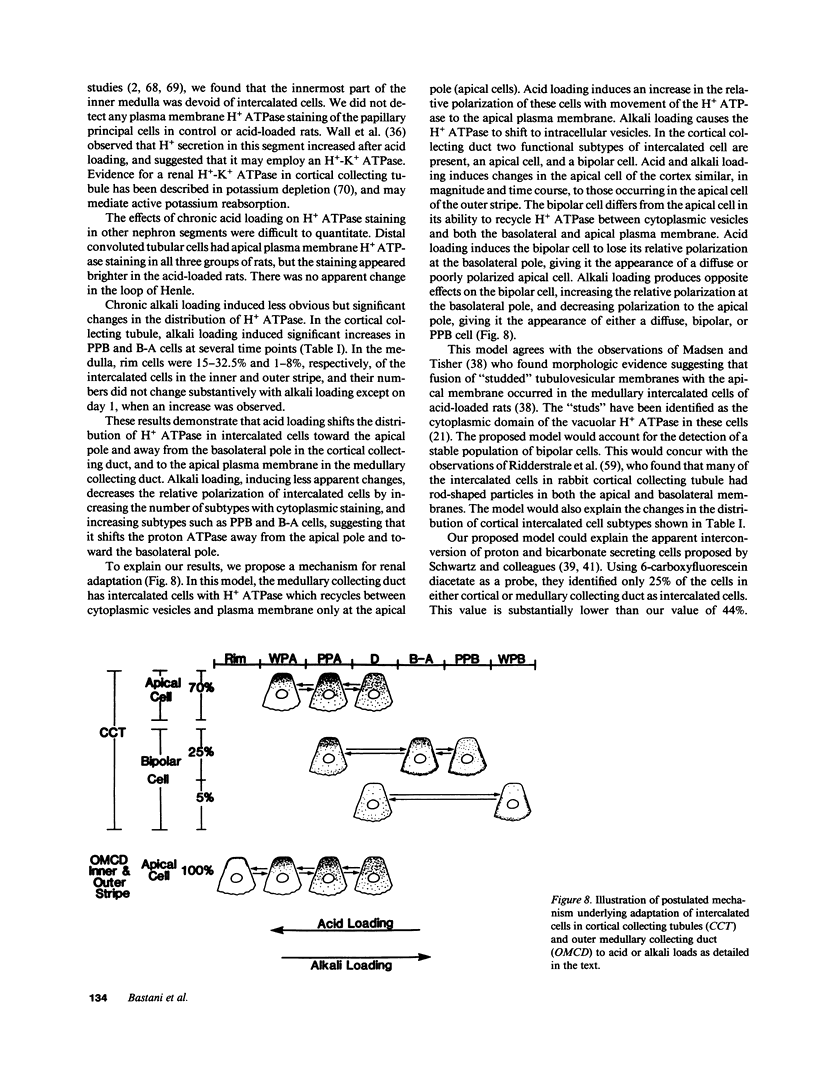
Renal hydrogen ion excretion increases with chronic acid loads and decreases with alkali loads. We examined the mechanism of adaptation by analyzing vacuolar proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase (H+ ATPase) 31-kD subunit protein and mRNA levels, and immunocytochemical distribution in kidneys from rats subjected to acid or alkali loads for 1, 3, 5, 7, and 14 d. Acid- and alkali-loaded rats exhibited adaptive responses in acid excretion, but showed no significant changes in H+ ATPase protein or mRNA levels in either cortex or medulla. In contrast, there were profound adaptive changes in the immunocytochemical distribution of H+ ATPase in collecting duct intercalated cells. In the medulla, H+ ATPase staining in acid-loaded rats shifted from cytoplasmic vesicles to plasma membrane, whereas in alkali-loaded rats, cytoplasmic vesicle staining was enhanced, and staining of plasma membrane disappeared. In the cortical collecting tubule, acid loading increased the number of intercalated cells showing enhanced apical H+ ATPase staining and decreased the number of cells with basolateral or poorly polarized apical staining. The results indicate that both medulla and cortex participate in the adaptive response to acid and alkali loading by changing the steady-state distribution of H+ ATPase, employing mechanisms that do not necessitate postulating interconversion of intercalated cells with opposing polarities.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ait-Mohamed A. K., Marsy S., Barlet C., Khadouri C., Doucet A. Characterization of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive proton pump in the rat kidney. Localization along the nephron. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12526–12533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiba T., Rocco V. K., Warnock D. G. Parallel adaptation of the rabbit renal cortical sodium/proton antiporter and sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):308–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI113074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper S. L., Natale J., Gluck S., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Subtypes of intercalated cells in rat kidney collecting duct defined by antibodies against erythroid band 3 and renal vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern R. J. Cell mechanisms of proximal tubule acidification. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):79–114. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. L., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate transport by isolated perfused rat collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 2):F485–F489. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.4.F485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank N., Aynedjian H. S., Mutz B. F. Proximal bicarbonate absorption independent of Na+-H+ exchange: effect of bicarbonate load. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):F577–F582. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.4.F577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengele H. H., Schwartz J. H., McNamara E. R., Alexander E. A. Chronic metabolic acidosis augments acidification along the inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 2):F690–F694. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.4.F690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breyer M. D., Jacobson H. R. Regulation of rabbit medullary collecting duct cell pH by basolateral Na+/H+ and Cl-/base exchange. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1172/JCI114264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Gluck S., Hartwig J. Structure of the novel membrane-coating material in proton-secreting epithelial cells and identification as an H+ATPase. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1637–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. An H+-ATPase in opposite plasma membrane domains in kidney epithelial cell subpopulations. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):622–624. doi: 10.1038/331622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. Localization of a proton-pumping ATPase in rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2114–2126. doi: 10.1172/JCI113833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon C., van Adelsberg J., Kelly S., Al-Awqati Q. Carbon-dioxide-induced exocytotic insertion of H+ pumps in turtle-bladder luminal membrane: role of cell pH and calcium. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):443–446. doi: 10.1038/314443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp W. L., Madsen K. M., Verlander J. W., Tisher C. C. Intercalated cells of the rat inner medullary collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1987 May;31(5):1080–1087. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. E., Klahr S., Hammerman M. R. Metabolic acidosis and parathyroidectomy increase Na+-H+ exchange in brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F217–F222. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Schlüter K., Allen D. P., Bennett V. Colocalization of band 3 with ankyrin and spectrin at the basal membrane of intercalated cells in the rat kidney. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1287–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.2933809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBose T. D., Jr, Caflisch C. R. Effect of selective aldosterone deficiency on acidification in nephron segments of the rat inner medulla. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1624–1632. doi: 10.1172/JCI113774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg L. C., Narang N. Stimulation of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive ATPase in the collecting duct segments of the rat nephron by metabolic acidosis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;63(10):1291–1296. doi: 10.1139/y85-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Al-Awqati Q. An electrogenic proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from bovine kidney medulla. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1704–1710. doi: 10.1172/JCI111378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Caldwell J. Immunoaffinity purification and characterization of vacuolar H+ATPase from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15780–15789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Caldwell J. Proton-translocating ATPase from bovine kidney medulla: partial purification and reconstitution. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 2):F71–F79. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.1.F71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Cannon C., Al-Awqati Q. Exocytosis regulates urinary acidification in turtle bladder by rapid insertion of H+ pumps into the luminal membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4327–4331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluck S., Kelly S., Al-Awqati Q. The proton translocating ATPase responsible for urinary acidification. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9230–9233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W. Adaptation of HCO-3 and NH+4 transport in rat MTAL: effects of chronic metabolic acidosis and Na+ intake. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1345–F1353. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm L. L., Hering-Smith K. S., Vehaskari V. M. Control of bicarbonate transport in collecting tubules from normal and remnant kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):F680–F687. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.4.F680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen G. P., Tisher C. C., Robinson R. R. Response of the collecting duct to disturbances of acid-base and potassium balance. Kidney Int. 1980 Mar;17(3):326–337. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Hormonal regulation of proton secretion in rabbit medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1279–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI112712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch S., Strauss A., Masood K., Lee S., Sukhatme V., Gluck S. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the 31-kDa subunit of bovine kidney vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson H. R. Medullary collecting duct acidification. Effects of potassium, HCO3 concentration, and pCO2. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2107–2114. doi: 10.1172/JCI111635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange activity in renal brush border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis: The role of glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):630–634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J., Cujdik T., Sacktor B. Na+-H+ exchange in isolated renal brush-border membrane vesicles in response to metabolic acidosis. Kinetic effects. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13224–13227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Helman S. I. Acidification of luminal fluid by the rabbit cortical collecting tubule perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F521–F531. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski M. E., Kurtzman N. A. Characterization of acidification in the cortical and medullary collecting tubule of the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2050–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI111170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z., Vandorpe D., Iacovitti M. Luminal chloride modulates rat distal tubule bidirectional bicarbonate flux in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1793–1798. doi: 10.1172/JCI114637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G., Ridderstråle Y. Intracellular distribution of carbonic anhydrase in the rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1980 Feb;17(2):162–174. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Clapp W. L., Verlander J. W. Structure and function of the inner medullary collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1988 Oct;34(4):441–454. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen K. M., Tisher C. C. Response of intercalated cells of rat outer medullary collecting duct to chronic metabolic acidosis. Lab Invest. 1984 Sep;51(3):268–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate secretion by rabbit cortical collecting tubules in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1421–1427. doi: 10.1172/JCI109061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate transport by rabbit cortical collecting tubules. Effect of acid and alkali loads in vivo on transport in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):766–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI108830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Davidson K. K. Bicarbonate transport in collecting tubules from outer stripe of outer medulla of rabbit kidneys. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 2):F816–F822. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.5.F816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Davidson K. K. Effects of respiratory acidosis on HCO3- transport by rabbit collecting tubules. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F656–F665. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier O., Bichara M., Delahousse M., Prigent A., Leviel F., Paillard M. Effects of glucagon on H(+)-HCO3- transport in Henle's loop, distal tubule, and collecting ducts in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):F1003–F1014. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup T. E., Garella S., Perticucci E., Cohen J. J. Acidemia alone does not stimulate rat renal Na+-H+ antiporter activity. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F237–F243. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard M., Bichara M. Peptide hormone effects on urinary acidification and acid-base balance: PTH, ADH, and glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F973–F985. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Alpern R. J. Chronic metabolic acidosis causes an adaptation in the apical membrane Na/H antiporter and basolateral membrane Na(HCO3)3 symporter in the rat proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1445–1453. doi: 10.1172/JCI113750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig P. A., Ives H. E., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr Role of the Na+/H+ antiporter in rat proximal tubule bicarbonate absorption. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):970–978. doi: 10.1172/JCI113190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridderstrale Y., Kashgarian M., Koeppen B., Giebisch G., Stetson D., Ardito T., Stanton B. Morphological heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1988 Nov;34(5):655–670. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini S., Laski M. E., Kurtzman N. A. NEM-sensitive ATPase activity in rat nephron: effect of metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 2):F297–F304. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.2.F297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satlin L. M., Schwartz G. J. Cellular remodeling of HCO3(-)-secreting cells in rabbit renal collecting duct in response to an acidic environment. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1279–1288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Bonsib S. M., Jennings M. L. Two types of collecting duct mitochondria-rich (intercalated) cells: lectin and band 3 cytochemistry. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C347–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-stimulated bicarbonate secretion in rabbit cortical collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2056–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI111925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Al-Awqati Q. Carbon dioxide causes exocytosis of vesicles containing H+ pumps in isolated perfused proximal and collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1638–1644. doi: 10.1172/JCI111871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Barasch J., Al-Awqati Q. Plasticity of functional epithelial polarity. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):368–371. doi: 10.1038/318368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Satlin L. M., Bergmann J. E. Fluorescent characterization of collecting duct cells: a second H+-secreting type. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F1003–F1014. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon B. J., Burckhardt G. Characterization of inside-out oriented H(+)-ATPases in cholate-pretreated renal brush-border membrane vesicles. J Membr Biol. 1990 Aug;117(2):141–151. doi: 10.1007/BF01868681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Star R. A., Burg M. B., Knepper M. A. Bicarbonate secretion and chloride absorption by rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Role of chloride/bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetson D. L., Steinmetz P. R. Correlation between apical intramembrane particles and H+ secretion rates during CO2 stimulation in turtle bladder. Pflugers Arch. 1986;407 (Suppl 2):S80–S84. doi: 10.1007/BF00584934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetson D. L., Steinmetz P. R. Role of membrane fusion in CO2 stimulation of proton secretion by turtle bladder. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C113–C120. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. J., Ives H. E., Alpern R. J., Yee V. J., Warnock D. G., Rector F. C., Jr Increased Vmax for Na+/H+ antiporter activity in proximal tubule brush border vesicles from rabbits with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F339–F343. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrini F., Sabolić I., Zimolo Z., Moewes B., Burckhardt G. Relation of ATPases in rat renal brush-border membranes to ATP-driven H+ secretion. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jan;107(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01871078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlander J. W., Madsen K. M., Low P. S., Allen D. P., Tisher C. C. Immunocytochemical localization of band 3 protein in the rat collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):F115–F125. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.1.F115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall S. M., Sands J. M., Flessner M. F., Nonoguchi H., Spring K. R., Knepper M. A. Net acid transport by isolated perfused inner medullary collecting ducts. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):F75–F84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Gluck S. Isolation and properties of bovine kidney brush border vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. A proton pump with enzymatic and structural differences from kidney microsomal H(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21957–21965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner I. D., Hamm L. L. Regulation of intracellular pH in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):274–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI114423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling L. W., Evan A. P., Welling D. J. Shape of cells and extracellular channels in rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Kidney Int. 1981 Aug;20(2):211–222. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingo C. S. Active proton secretion and potassium absorption in the rabbit outer medullary collecting duct. Functional evidence for proton-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):361–365. doi: 10.1172/JCI114165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurko M. A., Gluck S. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody to vacuolar H+ATPase of renal epithelia. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15770–15779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Adelsberg J., Al-Awqati Q. Regulation of cell pH by Ca+2-mediated exocytotic insertion of H+-ATPases. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1638–1645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]