Abstract
In the title compound [systematic name: (1R,3S,5R,6S)-8-methyl-3-(4-methylphenylsulfonyloxy)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-6-yl acetate], C17H23NO5S, the fused piperidine ring exists in a chair conformation with the N atom and one C atom displaced by 0.876 (2) and −0.460 (3) Å, respectively, on opposite sides of the mean plane defined by the other four atoms. The fused pyrrolidine ring adopts an envelope conformation with the N atom deviating by 0.644 (3) Å from the mean plane of the other four atoms.
Related literature
For the synthesis, see: Yang & Wang (1998 ▶); Xie et al. (2005 ▶). For the pharmacological activity, see: Zhu et al. (2008 ▶).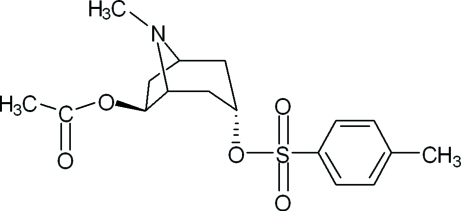
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H23NO5S
M r = 353.42
Orthorhombic,

a = 6.9241 (6) Å
b = 15.5069 (14) Å
c = 16.1020 (15) Å
V = 1728.9 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.21 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.47 × 0.41 × 0.31 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.751, T max = 1.000 (expected range = 0.702–0.935)
10216 measured reflections
3770 independent reflections
3238 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.066
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 0.97
3770 reflections
221 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1671 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.01 (7)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035800/ng2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035800/ng2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fund of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (grant No. 06DZ19001) and the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission Foundation (grant No. 06BZ009). We thank the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry for the X-ray data collection and analysis.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
6β-Acetoxy-3α-paramethylbenzene sulfonyloxytropane, a racemic analog of Baogongteng A, prepared in our laboratory (Yang et al., 1998), is a potent muscarinic receptor agonist and has been shown to be a promising candidate as a new antiglaucoma agent in our previous preclinical studies. Recently, we resolved the racemates and investigated the pharmacological characteristics of both enantiomers. The enantiomer (1R,3S,5R,6S) elicited agonistic activity on muscarinic receptors (Zhu et al., 2008). We report here the crystal structure of the bioactive enantiomer. The three-dimensional structure of the title compound is shown in Fig.1. The absolute stereochemistry has been confirmed by the structure determination, with absolute structure parameter -0.01 (7) (Flack, 1983). The tropane ring system adopts a conformation typical of 3α-substituted derivatives, with the piperidine ring in a chair-like shape and the pyrrolidine ring in an envelope form with nitrogen atom as the flap. Atoms N and C3 are displaced by 0.8762(0.0024) and 0.4602(0.0031) Å on opposite sides of the plane containing four atoms C1,C2, C4 and C5 (plane I), and N is deviated by 0.6435 (0.0029)Å from the mean plane through the other four atoms C1,C5,C6,C7 (plane II). The phenyl group C12 to C17 is planar to within 0.0078 (plane III). The dihedral angles between planes I—II and planes I-III are 67.58 (0.09)° and 28.67 (0.08)° respectively.
Experimental
Preparation of the title compound has been described previously (Yang et al.,1998). 6β-Acetoxy-3 α-tropanol (11 g, 0.06 mol) was dissolved in 20 ml CHCl3, and 4-toluene sulfonyl chloride (13 g, 0.07 mol) in 8 ml pyridine were added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 72 h. The solvent was evaporated in vacou. The residue was dissolved in anhydrous ethanol and recrystallized to give the hydrochloride of racemates of the title compound. Then it was dissolved in 20% ammonium hydroxide, extracted with dichloromethane and the organic phase was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated in vacou to give racemates of the title compound. The racemates (9.8 g, 0.03 mol) and (-)-2,3-dibenzoyl-L-tartaric acid (11 g, 0.03 mol) were dissolved in methanol for 2 h. After disposing at room temperature for 3 h, the (-)-2,3-dibenzoyl-L-tartarate as precipitate was collected by filtration and recrystallized from anhydrous ethanol. The salt was converted into the title compound as colorless crystals, 30% yield, m.p. 403–405 K, [α]D20 -11.42 (c = 0.1313, CHCl3), by treatment with 20% ammonium hydroxide as described above. The enantiomeric excess of the title compound was 98.05% (Xie et al., 2005). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow crystallization from acetone.
Refinement
The absolute configuration was assigned after refining the Flack parameter (Flack, 1983), using 1671 measured Friedel pairs. H atoms were placed in idealized positions, and refined as riding to their carrier atoms. with Uĩso(H) = 1.5Ueq(methyl C) and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(methylene and methine C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Ellipsoid plot.
Crystal data
| C17H23NO5S | Dx = 1.358 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 353.42 | Melting point: 405 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 3847 reflections |
| a = 6.9241 (6) Å | θ = 2.5–26.2º |
| b = 15.5069 (14) Å | µ = 0.21 mm−1 |
| c = 16.1020 (15) Å | T = 293 (2) K |
| V = 1728.9 (3) Å3 | P{rism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.48 × 0.41 × 0.31 mm |
| F000 = 752 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART area-detector diffractometer | 3770 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3238 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.066 |
| T = 293(2) K | θmax = 27.0º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 1.8º |
| Absorption correction: Multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000) | h = −6→8 |
| Tmin = 0.751, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −19→18 |
| 10216 measured reflections | l = −20→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Least-squares matrix: full | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0451P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| S = 0.97 | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 3770 reflections | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 221 parameters | Extinction coefficient: 0.0065 (11) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1671 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: −0.01 (7) |
| Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.96500 (8) | 0.56721 (3) | 0.57026 (3) | 0.04821 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.83603 (18) | 0.75864 (9) | 0.86913 (8) | 0.0433 (3) | |
| O2 | 1.1550 (2) | 0.76965 (12) | 0.85445 (11) | 0.0663 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.8477 (2) | 0.62594 (8) | 0.63122 (8) | 0.0476 (4) | |
| O4 | 1.1038 (2) | 0.61718 (11) | 0.52631 (10) | 0.0613 (4) | |
| O5 | 1.0274 (3) | 0.49732 (10) | 0.62094 (11) | 0.0692 (5) | |
| N8 | 0.6078 (2) | 0.83046 (10) | 0.71495 (11) | 0.0423 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.5182 (3) | 0.74438 (13) | 0.70783 (12) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.3790 | 0.7481 | 0.7183 | 0.053* | |
| C2 | 0.5559 (3) | 0.71277 (14) | 0.61955 (13) | 0.0482 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.5003 | 0.6558 | 0.6130 | 0.058* | |
| H2B | 0.4918 | 0.7511 | 0.5807 | 0.058* | |
| C3 | 0.7683 (3) | 0.70892 (12) | 0.59874 (13) | 0.0447 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.7838 | 0.7103 | 0.5383 | 0.054* | |
| C4 | 0.8843 (3) | 0.78262 (13) | 0.63697 (12) | 0.0429 (5) | |
| H4A | 1.0190 | 0.7657 | 0.6405 | 0.051* | |
| H4B | 0.8762 | 0.8326 | 0.6010 | 0.051* | |
| C5 | 0.8130 (3) | 0.80705 (12) | 0.72301 (12) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.8878 | 0.8554 | 0.7453 | 0.046* | |
| C6 | 0.8169 (3) | 0.72949 (12) | 0.78367 (12) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.9185 | 0.6882 | 0.7689 | 0.046* | |
| C7 | 0.6163 (3) | 0.68959 (13) | 0.77502 (14) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| H7A | 0.5459 | 0.6928 | 0.8270 | 0.053* | |
| H7B | 0.6250 | 0.6297 | 0.7579 | 0.053* | |
| C9 | 0.5348 (3) | 0.87927 (14) | 0.78624 (13) | 0.0528 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.5454 | 0.8448 | 0.8355 | 0.079* | |
| H9B | 0.4019 | 0.8940 | 0.7771 | 0.079* | |
| H9C | 0.6094 | 0.9310 | 0.7929 | 0.079* | |
| C10 | 1.0149 (3) | 0.77628 (12) | 0.89615 (13) | 0.0434 (5) | |
| C11 | 1.0125 (3) | 0.80429 (14) | 0.98486 (14) | 0.0530 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.9534 | 0.7603 | 1.0182 | 0.079* | |
| H11B | 0.9402 | 0.8568 | 0.9899 | 0.079* | |
| H11C | 1.1425 | 0.8137 | 1.0035 | 0.079* | |
| C12 | 0.7863 (3) | 0.53147 (12) | 0.50065 (13) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.6276 (3) | 0.48904 (15) | 0.53244 (15) | 0.0596 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.6197 | 0.4778 | 0.5891 | 0.072* | |
| C14 | 0.4820 (3) | 0.46356 (14) | 0.48051 (16) | 0.0593 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.3746 | 0.4357 | 0.5025 | 0.071* | |
| C15 | 0.4917 (3) | 0.47852 (12) | 0.39596 (14) | 0.0463 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.6542 (3) | 0.51942 (13) | 0.36492 (14) | 0.0490 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.6642 | 0.5288 | 0.3080 | 0.059* | |
| C17 | 0.8019 (3) | 0.54657 (12) | 0.41651 (12) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| H17 | 0.9096 | 0.5745 | 0.3949 | 0.054* | |
| C18 | 0.3260 (4) | 0.45457 (15) | 0.33942 (17) | 0.0645 (7) | |
| H18A | 0.2196 | 0.4930 | 0.3490 | 0.097* | |
| H18B | 0.2863 | 0.3964 | 0.3508 | 0.097* | |
| H18C | 0.3667 | 0.4590 | 0.2826 | 0.097* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0516 (3) | 0.0486 (3) | 0.0444 (3) | 0.0070 (2) | −0.0010 (3) | −0.0041 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0631 (8) | 0.0300 (7) | −0.0006 (6) | −0.0012 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0381 (8) | 0.0992 (13) | 0.0617 (10) | −0.0063 (9) | 0.0096 (8) | −0.0149 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0639 (9) | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0072 (7) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0006 (6) |
| O4 | 0.0454 (9) | 0.0769 (10) | 0.0615 (10) | −0.0050 (8) | 0.0070 (8) | −0.0094 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0832 (12) | 0.0597 (9) | 0.0645 (11) | 0.0239 (9) | −0.0145 (10) | −0.0013 (8) |
| N8 | 0.0422 (9) | 0.0490 (9) | 0.0358 (9) | 0.0084 (7) | 0.0006 (8) | −0.0016 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0341 (10) | 0.0591 (12) | 0.0400 (11) | 0.0006 (9) | −0.0015 (9) | −0.0016 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0490 (12) | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0406 (11) | 0.0020 (10) | −0.0097 (10) | −0.0017 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0588 (13) | 0.0453 (11) | 0.0301 (9) | 0.0059 (9) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0026 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0467 (11) | 0.0474 (11) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0078 (9) | 0.0048 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0385 (11) | 0.0415 (10) | 0.0341 (10) | −0.0026 (8) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0459 (10) | 0.0304 (9) | 0.0017 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0026 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0538 (12) | 0.0361 (10) | −0.0082 (9) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0032 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0546 (13) | 0.0579 (12) | 0.0458 (12) | 0.0143 (10) | 0.0057 (11) | −0.0063 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0411 (12) | 0.0453 (11) | 0.0439 (11) | −0.0006 (9) | −0.0037 (9) | 0.0036 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0530 (14) | 0.0634 (13) | 0.0426 (12) | −0.0007 (11) | −0.0101 (11) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0497 (12) | 0.0388 (10) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0039 (9) | 0.0068 (10) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0732 (16) | 0.0603 (14) | 0.0453 (13) | −0.0174 (12) | 0.0081 (12) | 0.0037 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0588 (15) | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0636 (15) | −0.0159 (11) | 0.0146 (13) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0481 (13) | 0.0327 (9) | 0.0581 (12) | 0.0053 (9) | 0.0031 (10) | −0.0041 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0544 (13) | 0.0507 (11) | 0.0420 (11) | 0.0044 (10) | 0.0067 (10) | −0.0022 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0444 (11) | 0.0463 (11) | 0.0433 (12) | 0.0013 (9) | 0.0126 (9) | −0.0023 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0541 (14) | 0.0594 (14) | 0.0800 (18) | −0.0012 (11) | −0.0065 (13) | 0.0006 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—O4 | 1.4231 (16) | C6—H6 | 0.9800 |
| S1—O5 | 1.4239 (16) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| S1—O3 | 1.5663 (14) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| S1—C12 | 1.759 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| O1—C10 | 1.341 (2) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| O1—C6 | 1.454 (2) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| O2—C10 | 1.184 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.493 (3) |
| O3—C3 | 1.494 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| N8—C9 | 1.465 (2) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| N8—C5 | 1.472 (2) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| N8—C1 | 1.476 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.379 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.526 (3) | C12—C17 | 1.379 (3) |
| C1—C7 | 1.534 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.368 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9800 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.510 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.383 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.385 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.527 (3) | C15—C18 | 1.511 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9800 | C16—C17 | 1.383 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.519 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.550 (3) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9800 | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.526 (3) | ||
| O4—S1—O5 | 119.62 (11) | C5—C6—H6 | 111.5 |
| O4—S1—O3 | 110.21 (9) | C6—C7—C1 | 104.05 (16) |
| O5—S1—O3 | 103.94 (9) | C6—C7—H7A | 110.9 |
| O4—S1—C12 | 109.26 (10) | C1—C7—H7A | 110.9 |
| O5—S1—C12 | 109.81 (10) | C6—C7—H7B | 110.9 |
| O3—S1—C12 | 102.57 (9) | C1—C7—H7B | 110.9 |
| C10—O1—C6 | 117.04 (15) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.0 |
| C3—O3—S1 | 118.18 (12) | N8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C9—N8—C5 | 113.03 (17) | N8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C9—N8—C1 | 112.53 (16) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C5—N8—C1 | 100.92 (14) | N8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N8—C1—C2 | 106.91 (17) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| N8—C1—C7 | 105.06 (16) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 113.78 (17) | O2—C10—O1 | 123.71 (19) |
| N8—C1—H1 | 110.3 | O2—C10—C11 | 125.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 110.3 | O1—C10—C11 | 111.09 (18) |
| C7—C1—H1 | 110.3 | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 112.71 (17) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.1 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.1 | C10—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.1 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.1 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.8 | C13—C12—C17 | 120.5 (2) |
| O3—C3—C2 | 108.34 (16) | C13—C12—S1 | 118.30 (17) |
| O3—C3—C4 | 108.07 (16) | C17—C12—S1 | 121.17 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 113.17 (17) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.9 (2) |
| O3—C3—H3 | 109.1 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 109.1 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 109.1 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.2 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 112.55 (16) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.4 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.1 | C14—C15—C16 | 118.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.1 | C14—C15—C18 | 121.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.1 | C16—C15—C18 | 120.8 (2) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.8 | C17—C16—C15 | 121.6 (2) |
| N8—C5—C4 | 107.15 (17) | C17—C16—H16 | 119.2 |
| N8—C5—C6 | 105.28 (15) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 112.08 (16) | C12—C17—C16 | 118.72 (19) |
| N8—C5—H5 | 110.7 | C12—C17—H17 | 120.6 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 110.7 | C16—C17—H17 | 120.6 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 110.7 | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C7 | 107.18 (16) | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C5 | 110.90 (16) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 103.96 (15) | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—H6 | 111.5 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 111.5 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O4—S1—O3—C3 | 47.59 (16) | N8—C5—C6—C7 | 24.8 (2) |
| O5—S1—O3—C3 | 176.95 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −91.32 (19) |
| C12—S1—O3—C3 | −68.65 (15) | O1—C6—C7—C1 | 120.02 (17) |
| C9—N8—C1—C2 | 162.61 (17) | C5—C6—C7—C1 | 2.53 (19) |
| C5—N8—C1—C2 | −76.63 (18) | N8—C1—C7—C6 | −29.1 (2) |
| C9—N8—C1—C7 | −76.2 (2) | C2—C1—C7—C6 | 87.5 (2) |
| C5—N8—C1—C7 | 44.6 (2) | C6—O1—C10—O2 | 0.3 (3) |
| N8—C1—C2—C3 | 57.9 (2) | C6—O1—C10—C11 | −179.30 (16) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −57.6 (2) | O4—S1—C12—C13 | −173.64 (16) |
| S1—O3—C3—C2 | 128.33 (15) | O5—S1—C12—C13 | 53.3 (2) |
| S1—O3—C3—C4 | −108.70 (15) | O3—S1—C12—C13 | −56.72 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | 82.9 (2) | O4—S1—C12—C17 | 5.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −36.9 (2) | O5—S1—C12—C17 | −127.77 (18) |
| O3—C3—C4—C5 | −83.20 (19) | O3—S1—C12—C17 | 122.19 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 36.8 (2) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | −1.7 (3) |
| C9—N8—C5—C4 | −162.88 (16) | S1—C12—C13—C14 | 177.25 (17) |
| C1—N8—C5—C4 | 76.72 (17) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.9 (4) |
| C9—N8—C5—C6 | 77.6 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.6 (3) |
| C1—N8—C5—C6 | −42.76 (19) | C13—C14—C15—C18 | −176.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N8 | −57.7 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 57.3 (2) | C18—C15—C16—C17 | 175.95 (18) |
| C10—O1—C6—C7 | 164.05 (16) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 0.9 (3) |
| C10—O1—C6—C5 | −83.1 (2) | S1—C12—C17—C16 | −177.98 (15) |
| N8—C5—C6—O1 | −90.05 (18) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 0.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—O1 | 153.80 (16) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NG2508).
References
- Bruker (2001). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2000). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y., Yang, L. & Lu, Y. (2005). Acta Univ. Med. Sec. Shanghai, 25, 229–231.
- Yang, L. & Wang, H. (1998). Acta Pharm. Sin.33, 832–835.
- Zhu, L., Yang, L., Cui, Y., Zheng, P., Niu, Y., Wang, H., Lu, Y., Ren, Q., Wei, P. & Chen, H. (2008). Acta Pharmacol. Sin.29, 177–184. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035800/ng2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808035800/ng2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



