Abstract
The structure analysis of the title compound, C16H19N3O3, has been undertaken in order to facilitate the interpretation of 1H and 13C NMR data and to determine the position of the morpholine residue in this nucleophilic substitution product. The main result is that the morpholine group, with a chair conformation, is connected at the 4-position of the pyridazine ring. The benzene and pyridazine rings make a dihedral angle of 62.17 (5)°. Molecules are linked into a two-dimensional network by non-classical C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, in which O atoms serve as double or triple acceptors.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶); Bałoniak & Melzer (1979 ▶); Katrusiak et al. (2002 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H19N3O3
M r = 301.34
Monoclinic,

a = 5.6246 (6) Å
b = 8.8923 (6) Å
c = 15.0842 (10) Å
β = 99.530 (7)°
V = 744.03 (11) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.78 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.38 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Kuma Diffraction KM-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.716, T max = 0.794
2796 measured reflections
2705 independent reflections
2646 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
2 standard reflections every 100 reflections intensity decay: <2%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.082
S = 1.06
2705 reflections
202 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶); 1249 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.07 (16)
Data collection: KM-4 Software (Kuma, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: KM-4 Software; data reduction: KM-4 Software; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808000111/cf2177sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808000111/cf2177Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17A⋯O15 | 0.97 | 2.21 | 2.8636 (18) | 124 |
| C10—H10⋯O15i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.3508 (19) | 148 |
| C14—H14C⋯O15i | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.419 (2) | 155 |
| C5—H5⋯O19ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.4124 (19) | 174 |
| C21—H21B⋯O19ii | 0.97 | 2.52 | 3.3036 (18) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 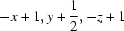 ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Treatment of 4-bromo-1-methyl-2-(4-methylphenyl)-3,6-pyridazinedione with morpholine in anhydrous ethanol gives a mixture of ipso and cine substitution products; one of them, labelled as (I), was found as a precipitate (Bałoniak & Melzer, 1979). The crystal structure determination of (I) was carried out in order to facilitate the interpretation of 1H and 13C NMR data, to determine the position of the morpholine residue on the pyridazinedione ring, and to study the nature of the hydrogen-bond formation in the crystalline state.
The X-ray analysis revealed the molecular structure of (I) and its conformation and distortions induced in the pyridazine ring by substituents.
The geometry of the molecule of (I) is illustrated in Fig. 1. The pyridazine ring is nearly planar with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.0211 Å. The methyl, p-methylphenyl and morpholine substituents are connected at N1, N2 and C4, respectively. The mean plane of the benzene ring is oriented at an angle of 62.17 (5)° to the mean plane of the pyridazine ring. The C4—C5 bond, 1.3500 (18) Å, belonging to the latter ring, is a double bond.
The ring bonds are conjugated, and the formally single bond C5—C6 is shorter by about 14 and the bond C3—C4 is longer by about 13σ than the normal (C?)Csp2—Csp2(?O) single bond [1.465 (1) Å; Allen et al., 1987]. The elongation of the latter is a result of the presence of the morpholine residue at C4. The last two observations are consistent with that reported for 2-methyl-4-morpholino-1-phenyl-3,6-pyridazinedione (Katrusiak et al., 2002).
The C3—N1 and C6—N1 distances are similar [1.3700 (18) and 1.3686 (17) Å, respectively] and are somewhat larger than a normal C—N tertiary amide distance [1.346 (5) Å; Allen et al., 1987]. The sums of valency angles around N1 and N2 atoms are 356.5 and 357.4°. Atom C7 of the methyl group has a mutual orientation of synperiplanar and synclinal with respect to the atom C8 of the benzene ring [torsion angle C7—N1—N2—C8 = -37.79 (18)°].
The molecules in the crystal structure of (I) are linked via non-classical C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1), forming a two-dimensional hydrogen-bond network parallel to the (101) plane (Figs. 2 and 3).
Experimental
Compound (I) was synthesized according to a literature procedure of Bałoniak & Melzer (1979). Crystals suitable for single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis were grown from ethanol by slow evaporation.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions and were refined with a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H. The methyl groups were refined as rigid groups, allowed to rotate. The crystal polarity of (I) was established by refinement of the Flack (1983) parameter. The relatively large s.u. of the Flack parameter is due to the small contribution of atoms with measurable anomalous dispersion effects.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing the atomic labelling scheme. Non-H atoms are drawn as 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing and hydrogen bonds (dotted lines); symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, 1/2 + y, 1 - z, (ii) 2 - x, 1/2 + y, -z. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 3.
Molecular packing and hydrogen bonds (dotted lines); symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, 1/2 + y, 1 - z, (ii) 2 - x, 1/2 + y, -z. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C16H19N3O3 | F(000) = 320 |
| Mr = 301.34 | Dx = 1.345 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Melting point = 475–476 K |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 5.6246 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 53 reflections |
| b = 8.8923 (6) Å | θ = 14.8–30.5° |
| c = 15.0842 (10) Å | µ = 0.78 mm−1 |
| β = 99.530 (7)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 744.03 (11) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.38 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Kuma Diffraction KM-4 diffractometer | 2646 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.025 |
| graphite | θmax = 70.1°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω–2θ scans | h = −6→6 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | k = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.716, Tmax = 0.794 | l = 0→18 |
| 2796 measured reflections | 2 standard reflections every 100 reflections |
| 2705 independent reflections | intensity decay: <2% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0538P)2 + 0.0723P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.07 | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 2705 reflections | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
| 202 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction coefficient: 0.0345 (18) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983); 1249 Fiedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: 0.07 (16) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against all reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.4950 (2) | 0.30562 (12) | 0.24834 (8) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.4743 (2) | 0.15882 (12) | 0.28125 (7) | 0.0339 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.5939 (3) | 0.03738 (15) | 0.25416 (8) | 0.0325 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.7375 (2) | 0.06485 (14) | 0.18118 (8) | 0.0300 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.7609 (3) | 0.20788 (15) | 0.15387 (9) | 0.0359 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.8658 | 0.2264 | 0.1135 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.6334 (3) | 0.33293 (15) | 0.18353 (9) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.3067 (3) | 0.41229 (19) | 0.25978 (12) | 0.0516 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.3504 | 0.4642 | 0.3159 | 0.077* | |
| H7B | 0.1577 | 0.3595 | 0.2596 | 0.077* | |
| H7C | 0.2876 | 0.4837 | 0.2114 | 0.077* | |
| C8 | 0.3819 (2) | 0.14755 (15) | 0.36480 (8) | 0.0326 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.4878 (3) | 0.22780 (18) | 0.43950 (9) | 0.0426 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.6209 | 0.2886 | 0.4367 | 0.051* | |
| C10 | 0.3942 (3) | 0.2170 (2) | 0.51839 (10) | 0.0450 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.4645 | 0.2717 | 0.5684 | 0.054* | |
| C11 | 0.1978 (3) | 0.12600 (18) | 0.52421 (9) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.0964 (3) | 0.04506 (18) | 0.44820 (10) | 0.0425 (3) | |
| H12 | −0.0346 | −0.0175 | 0.4510 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | 0.1868 (3) | 0.05591 (17) | 0.36881 (9) | 0.0381 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.1165 | 0.0018 | 0.3185 | 0.046* | |
| C14 | 0.0953 (4) | 0.1141 (2) | 0.61008 (11) | 0.0581 (5) | |
| H14A | 0.1592 | 0.0263 | 0.6427 | 0.087* | |
| H14B | −0.0771 | 0.1064 | 0.5961 | 0.087* | |
| H14C | 0.1385 | 0.2020 | 0.6461 | 0.087* | |
| O15 | 0.5897 (2) | −0.08309 (11) | 0.29241 (7) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| N16 | 0.8655 (2) | −0.05448 (13) | 0.15642 (7) | 0.0339 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.7617 (3) | −0.20541 (15) | 0.13920 (9) | 0.0369 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.6324 | −0.2196 | 0.1737 | 0.044* | |
| H17B | 0.8843 | −0.2807 | 0.1582 | 0.044* | |
| C18 | 0.6651 (3) | −0.22466 (16) | 0.04052 (10) | 0.0407 (3) | |
| H18A | 0.6047 | −0.3264 | 0.0299 | 0.049* | |
| H18B | 0.5311 | −0.1561 | 0.0234 | 0.049* | |
| O19 | 0.8440 (2) | −0.19668 (12) | −0.01424 (7) | 0.0444 (3) | |
| C20 | 0.9381 (3) | −0.04743 (17) | 0.00089 (9) | 0.0404 (3) | |
| H20A | 0.8098 | 0.0252 | −0.0157 | 0.049* | |
| H20B | 1.0604 | −0.0298 | −0.0363 | 0.049* | |
| C21 | 1.0461 (3) | −0.02754 (16) | 0.09851 (9) | 0.0386 (3) | |
| H21A | 1.1792 | −0.0972 | 0.1142 | 0.046* | |
| H21B | 1.1088 | 0.0738 | 0.1082 | 0.046* | |
| O22 | 0.6396 (2) | 0.46036 (12) | 0.15195 (8) | 0.0522 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0206 (5) | 0.0022 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0453 (7) | 0.0291 (5) | 0.0311 (5) | −0.0018 (5) | 0.0176 (5) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0313 (6) | 0.0260 (5) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0122 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0236 (5) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0458 (8) | 0.0327 (7) | 0.0332 (6) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0181 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0489 (8) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0362 (7) | −0.0036 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | −0.0004 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0578 (10) | 0.0419 (8) | 0.0617 (9) | 0.0102 (7) | 0.0289 (8) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0383 (7) | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0268 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0131 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0393 (7) | −0.0128 (6) | 0.0174 (6) | −0.0094 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0540 (8) | 0.0324 (6) | −0.0070 (7) | 0.0131 (6) | −0.0121 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0332 (7) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0399 (8) | 0.0488 (8) | 0.0418 (7) | −0.0085 (6) | 0.0153 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0385 (7) | 0.0445 (8) | 0.0319 (6) | −0.0063 (6) | 0.0082 (5) | −0.0042 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0687 (11) | 0.0728 (12) | 0.0394 (8) | −0.0065 (9) | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0017 (8) |
| O15 | 0.0746 (7) | 0.0334 (5) | 0.0418 (5) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0307 (5) | 0.0098 (4) |
| N16 | 0.0431 (6) | 0.0301 (6) | 0.0311 (5) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0140 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0264 (6) | 0.0363 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0165 (6) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C18 | 0.0489 (8) | 0.0350 (7) | 0.0415 (7) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0173 (6) | −0.0072 (6) |
| O19 | 0.0602 (7) | 0.0384 (6) | 0.0397 (5) | −0.0032 (5) | 0.0237 (5) | −0.0100 (4) |
| C20 | 0.0514 (8) | 0.0364 (7) | 0.0389 (7) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0234 (6) | −0.0009 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0373 (7) | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0435 (7) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0163 (5) | −0.0039 (6) |
| O22 | 0.0788 (8) | 0.0287 (5) | 0.0565 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0326 (6) | 0.0058 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C6 | 1.3686 (17) | C11—C14 | 1.5062 (18) |
| N1—N2 | 1.4083 (15) | C12—C13 | 1.3796 (18) |
| N1—C7 | 1.4530 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.930 |
| N2—C3 | 1.3700 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.930 |
| N2—C8 | 1.4440 (15) | C14—H14A | 0.960 |
| C3—O15 | 1.2188 (17) | C14—H14B | 0.960 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4897 (16) | C14—H14C | 0.960 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3500 (18) | N16—C21 | 1.4648 (15) |
| C4—N16 | 1.3685 (17) | N16—C17 | 1.4696 (17) |
| C5—C6 | 1.4344 (19) | C17—C18 | 1.507 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.930 | C17—H17A | 0.970 |
| C6—O22 | 1.2319 (18) | C17—H17B | 0.970 |
| C7—H7A | 0.960 | C18—O19 | 1.4256 (16) |
| C7—H7B | 0.960 | C18—H18A | 0.970 |
| C7—H7C | 0.960 | C18—H18B | 0.970 |
| C8—C13 | 1.376 (2) | O19—C20 | 1.4330 (18) |
| C8—C9 | 1.3826 (19) | C20—C21 | 1.507 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.3819 (18) | C20—H20A | 0.970 |
| C9—H9 | 0.930 | C20—H20B | 0.970 |
| C10—C11 | 1.384 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.970 |
| C10—H10 | 0.930 | C21—H21B | 0.970 |
| C11—C12 | 1.393 (2) | ||
| C6—N1—N2 | 120.42 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.4 |
| C6—N1—C7 | 118.75 (12) | C8—C13—C12 | 119.38 (12) |
| N2—N1—C7 | 117.31 (11) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.3 |
| C3—N2—N1 | 123.52 (11) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.3 |
| C3—N2—C8 | 118.10 (11) | C11—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| N1—N2—C8 | 115.76 (10) | C11—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O15—C3—N2 | 120.18 (11) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O15—C3—C4 | 123.32 (12) | C11—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N2—C3—C4 | 116.39 (11) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—N16 | 124.41 (12) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.17 (11) | C4—N16—C21 | 118.94 (11) |
| N16—C4—C3 | 116.66 (11) | C4—N16—C17 | 123.00 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 123.79 (12) | C21—N16—C17 | 109.79 (10) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.1 | N16—C17—C18 | 110.23 (11) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.1 | N16—C17—H17A | 109.6 |
| O22—C6—N1 | 119.68 (12) | C18—C17—H17A | 109.6 |
| O22—C6—C5 | 123.02 (12) | N16—C17—H17B | 109.6 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 117.28 (11) | C18—C17—H17B | 109.6 |
| N1—C7—H7A | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.1 |
| N1—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O19—C18—C17 | 112.26 (12) |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | O19—C18—H18A | 109.2 |
| N1—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18A | 109.2 |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | O19—C18—H18B | 109.2 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18B | 109.2 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 120.59 (12) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.9 |
| C13—C8—N2 | 118.96 (11) | C18—O19—C20 | 110.30 (10) |
| C9—C8—N2 | 120.45 (12) | O19—C20—C21 | 110.04 (12) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.45 (14) | O19—C20—H20A | 109.7 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.3 | C21—C20—H20A | 109.7 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.3 | O19—C20—H20B | 109.7 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.15 (14) | C21—C20—H20B | 109.7 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.4 | H20A—C20—H20B | 108.2 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.4 | N16—C21—C20 | 110.87 (11) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 118.17 (12) | N16—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C14 | 121.26 (14) | C20—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C14 | 120.57 (15) | N16—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.25 (13) | C20—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.4 | H21A—C21—H21B | 108.1 |
| C6—N1—N2—C3 | 2.4 (2) | N1—N2—C8—C9 | −53.57 (18) |
| C7—N1—N2—C3 | 160.94 (14) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (2) |
| C6—N1—N2—C8 | 163.62 (12) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | 179.08 (14) |
| C7—N1—N2—C8 | −37.79 (18) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.7 (3) |
| N1—N2—C3—O15 | 171.72 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (3) |
| C8—N2—C3—O15 | 10.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C14 | −179.93 (16) |
| N1—N2—C3—C4 | −4.50 (19) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.7 (2) |
| C8—N2—C3—C4 | −165.37 (11) | C14—C11—C12—C13 | 179.35 (15) |
| O15—C3—C4—C5 | −169.22 (15) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.3 (2) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 6.88 (19) | N2—C8—C13—C12 | −179.65 (13) |
| O15—C3—C4—N16 | 1.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 0.5 (2) |
| N2—C3—C4—N16 | 177.35 (12) | C5—C4—N16—C21 | 1.9 (2) |
| N16—C4—C5—C6 | −177.11 (13) | C3—C4—N16—C21 | −167.96 (11) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −7.4 (2) | C5—C4—N16—C17 | −143.29 (14) |
| N2—N1—C6—O22 | 176.13 (14) | C3—C4—N16—C17 | 46.90 (17) |
| C7—N1—C6—O22 | 17.8 (2) | C4—N16—C17—C18 | 93.59 (14) |
| N2—N1—C6—C5 | −2.2 (2) | C21—N16—C17—C18 | −54.29 (15) |
| C7—N1—C6—C5 | −160.51 (14) | N16—C17—C18—O19 | 55.96 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—O22 | −173.17 (15) | C17—C18—O19—C20 | −58.23 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 5.1 (2) | C18—O19—C20—C21 | 58.88 (15) |
| C3—N2—C8—C13 | −71.32 (17) | C4—N16—C21—C20 | −92.81 (14) |
| N1—N2—C8—C13 | 126.34 (14) | C17—N16—C21—C20 | 56.56 (15) |
| C3—N2—C8—C9 | 108.77 (16) | O19—C20—C21—N16 | −58.94 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17A···O15 | 0.97 | 2.21 | 2.8636 (18) | 124 |
| C10—H10···O15i | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.3508 (19) | 148 |
| C14—H14C···O15i | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.419 (2) | 155 |
| C5—H5···O19ii | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.4124 (19) | 174 |
| C21—H21B···O19ii | 0.97 | 2.52 | 3.3036 (18) | 137 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CF2177).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bałoniak, S. & Melzer, E. (1979). Acta Pol. Pharm.36, 147–154.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Katrusiak, A. A., Katrusiak, A., Bałoniak, S. & Zielińska, K. (2002). Pol. J. Chem.76, 45–56.
- Kuma (1996). KM-4 User’s Guide Version 8.0.1. Kuma Diffraction, Wrocław, Poland.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808000111/cf2177sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808000111/cf2177Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





