Abstract
The title compound, [Cu2V4O12(C10H8N2)2]n, shows a two-dimensional copper–vanadate layer composed of eight-membered rings, each containing four corner-sharing VO4 tetrahedra; these are linked through six pentacoordinated CuII atoms with the 2,2′-bipyridine ligands attached and pointing above and below the plane of the layer. The Cu atom is coordinated by two N donors from the 2,2′-bipyridine ligand and three O atoms from three adjacent VO4 units to form a distorted tetragonal pyramid. These layers are further connected by π–π interactions between interleaving bipyridine ligands of adjacent layers [centroid–centroid distances = 3.63 (1) and 3.68 (1) Å] into a three-dimensional supramolecular structure.
Related literature
For related literature, see: DeBord et al. (1996 ▶); Kucsera et al. (2002 ▶); Lu et al. (2002 ▶); Yi et al. (2007 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu2V4O12(C10H8N2)2]
M r = 417.60
Triclinic,
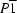
a = 8.1019 (4) Å
b = 8.3122 (5) Å
c = 10.3501 (4) Å
α = 72.332 (3)°
β = 84.562 (3)°
γ = 77.878 (3)°
V = 648.98 (6) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.06 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.33 × 0.31 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.379, T max = 0.469
4603 measured reflections
3114 independent reflections
2553 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.055
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.084
S = 0.99
3114 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.75 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067979/hy2113sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067979/hy2113Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Cu1—O1 | 2.012 (2) |
| Cu1—O4i | 2.054 (2) |
| Cu1—O6ii | 2.061 (2) |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.084 (2) |
| Cu1—N2 | 2.117 (2) |
| V1—O2 | 1.615 (2) |
| V1—O1 | 1.667 (2) |
| V1—O5iii | 1.824 (2) |
| V1—O3 | 1.833 (2) |
| V2—O4 | 1.655 (2) |
| V2—O6 | 1.670 (2) |
| V2—O5 | 1.774 (2) |
| V2—O3 | 1.790 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—O4i | 89.62 (9) |
| O1—Cu1—O6ii | 94.53 (9) |
| O4i—Cu1—O6ii | 121.32 (9) |
| O1—Cu1—N1 | 100.17 (9) |
| O4i—Cu1—N1 | 124.55 (9) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N1 | 112.18 (9) |
| O1—Cu1—N2 | 172.29 (9) |
| O4i—Cu1—N2 | 85.25 (9) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N2 | 93.05 (9) |
| N1—Cu1—N2 | 78.18 (10) |
| O2—V1—O1 | 108.65 (12) |
| O2—V1—O5iii | 109.43 (12) |
| O1—V1—O5iii | 111.53 (11) |
| O2—V1—O3 | 107.98 (12) |
| O1—V1—O3 | 110.08 (11) |
| O5iii—V1—O3 | 109.09 (10) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 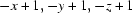 ; (ii)
; (ii) 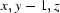 ; (iii)
; (iii) 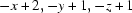 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the New Century Talent Program of the Chinese Ministry of Education and the Postdoctoral Foundation of Heilongjiang Province.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Considerable efforts have been devoted to the hydrothermal synthesis of solid-state inorganic–organic hybrid vanadate(V) species based on discrete clusters, infinite chain and layer structures, such as [Zn(phen)3][V2O6].10H2O and [Cu(bipy)V2O6] (Yi et al., 2007), [Cu(bipy)][V2O6] and [Cu(bipy)2][V2O6] (DeBord et al., 1996), [Mn(phen)2]2[V4O12].0.5H2O (Lu et al., 2002), and [Co(phen)2]2[V4O12].H2O (Kucsera et al., 2002), because of their diverse topologies and fascinating physical properties. We report here the crystal structure of a new complex, {[Cu(bipy)]2V4O12}n (bipy = 2,2'-bipyridine).
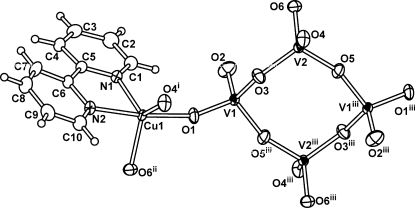
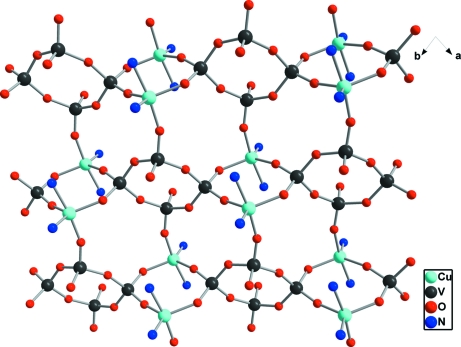
The asymmetric unit of the title compound consists of one CuII atom, one bipy molecule and a half of V4O12 unit (Fig. 1). The V4O12 units are linked through six square-pyramidal CuII atoms to six adjacent V4O12 rings (Fig. 2). Two of VO4 units in the V4O12 unit each connect with one square-pyramidal Cu unit, while the other two VO4 units each exhibit corner-sharing interactions with two Cu units. Each Cu unit links three V4O12 units through corner-sharing interactions. In this way, a two-dimensional layer is formed (Fig. 2). The CuII atom is coordinated by two pyridine N atoms and three tetravanadate O atoms (Fig. 1 and Table 1). The relative orientation of the bipy ligand with respect to the copper–vanadate layer is depicted by a dihedral angel of 84.6 (6)°. Furthermore, these bipy ligands interact with each other through π–π interactions between adjacent layers with centroid–centroid distances of 3.63 (1) and 3.68 (1) Å.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared hydrothermally from a mixture of V2O5 (0.73 g, 4.0 mmol), 2,2'-bipyridine dihydrate (0.38 g, 2.0 mmol), CuCl2.2H2O (0.34 g, 2.0 mmol) and water (18 ml) (molar ratio 2:1:1:500), adjusting pH to ca 6.1 with 4 M KOH, in a 25 ml Teflon-lined stainless steel reactor heated to 443 K for 7 d. After cooling to room temperature, green crystals were collected.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.93Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, extended to show the V4O12 unit. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. [Symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z; (ii) x, y - 1, z; (iii) 2 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z.]
Fig. 2.
A view of the copper–vanadate layer with C and H atoms of the bipy ligands omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Cu2V4O12(C10H8N2)2] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 417.60 | F000 = 410 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.137 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.1019 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 3811 reflections |
| b = 8.3122 (5) Å | θ = 2.1–28.3º |
| c = 10.3501 (4) Å | µ = 3.06 mm−1 |
| α = 72.332 (3)º | T = 298 (2) K |
| β = 84.562 (3)º | Block, green |
| γ = 77.878 (3)º | 0.33 × 0.31 × 0.25 mm |
| V = 648.98 (6) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 3114 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2553 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.055 |
| T = 298(2) K | θmax = 28.3º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 2.1º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −10→9 |
| Tmin = 0.379, Tmax = 0.469 | k = −10→7 |
| 4603 measured reflections | l = −13→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.084 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0438P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.99 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3114 reflections | Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmin = −0.75 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.59216 (4) | 0.14236 (4) | 0.28662 (3) | 0.01368 (10) | |
| V1 | 0.87679 (6) | 0.39002 (6) | 0.34998 (5) | 0.01604 (12) | |
| V2 | 0.73879 (6) | 0.72867 (6) | 0.47736 (5) | 0.01495 (12) | |
| O1 | 0.7741 (3) | 0.2421 (3) | 0.3367 (2) | 0.0249 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.9198 (3) | 0.5062 (3) | 0.1993 (2) | 0.0359 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.7425 (3) | 0.5317 (3) | 0.4394 (2) | 0.0259 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.5705 (3) | 0.7685 (3) | 0.5748 (2) | 0.0270 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.9278 (3) | 0.7084 (3) | 0.5595 (2) | 0.0285 (5) | |
| O6 | 0.7286 (3) | 0.8942 (3) | 0.3363 (2) | 0.0247 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.5900 (3) | 0.2590 (3) | 0.0777 (2) | 0.0191 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.3794 (3) | 0.0700 (3) | 0.2320 (2) | 0.0202 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.7065 (4) | 0.3461 (4) | 0.0041 (3) | 0.0242 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.7903 | 0.3671 | 0.0489 | 0.029* | |
| C2 | 0.7057 (4) | 0.4056 (4) | −0.1364 (3) | 0.0300 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.7869 | 0.4667 | −0.1848 | 0.036* | |
| C3 | 0.5828 (4) | 0.3731 (4) | −0.2037 (3) | 0.0270 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.5811 | 0.4107 | −0.2980 | 0.032* | |
| C4 | 0.4620 (4) | 0.2835 (4) | −0.1289 (3) | 0.0232 (6) | |
| H4 | 0.3787 | 0.2594 | −0.1722 | 0.028* | |
| C5 | 0.4675 (4) | 0.2303 (4) | 0.0120 (3) | 0.0192 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.3397 (4) | 0.1390 (4) | 0.1003 (3) | 0.0187 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.1878 (4) | 0.1270 (4) | 0.0534 (3) | 0.0288 (7) | |
| H7 | 0.1610 | 0.1775 | −0.0372 | 0.035* | |
| C8 | 0.0781 (4) | 0.0386 (4) | 0.1448 (4) | 0.0309 (7) | |
| H8 | −0.0237 | 0.0290 | 0.1160 | 0.037* | |
| C9 | 0.1209 (4) | −0.0351 (4) | 0.2786 (3) | 0.0274 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.0492 | −0.0962 | 0.3409 | 0.033* | |
| C10 | 0.2718 (4) | −0.0166 (4) | 0.3187 (3) | 0.0247 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.3001 | −0.0660 | 0.4091 | 0.030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.01353 (17) | 0.01631 (18) | 0.01260 (17) | −0.00306 (12) | −0.00204 (12) | −0.00563 (13) |
| V1 | 0.0140 (2) | 0.0172 (2) | 0.0183 (2) | −0.00322 (18) | −0.00335 (18) | −0.00613 (19) |
| V2 | 0.0127 (2) | 0.0155 (2) | 0.0177 (2) | −0.00107 (17) | −0.00215 (18) | −0.00696 (18) |
| O1 | 0.0202 (11) | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0335 (12) | −0.0079 (9) | −0.0034 (9) | −0.0167 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0332 (14) | 0.0428 (14) | 0.0249 (12) | −0.0122 (11) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0031 (11) |
| O3 | 0.0243 (12) | 0.0225 (11) | 0.0346 (13) | −0.0036 (9) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0154 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0201 (11) | 0.0366 (13) | 0.0301 (12) | −0.0050 (9) | 0.0047 (9) | −0.0201 (10) |
| O5 | 0.0228 (12) | 0.0308 (12) | 0.0346 (13) | −0.0013 (9) | −0.0112 (10) | −0.0128 (10) |
| O6 | 0.0245 (11) | 0.0204 (11) | 0.0266 (11) | −0.0018 (9) | −0.0051 (9) | −0.0034 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0195 (12) | 0.0206 (12) | 0.0179 (12) | −0.0040 (10) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0059 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0225 (13) | 0.0233 (13) | 0.0178 (12) | −0.0065 (10) | −0.0011 (10) | −0.0088 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0211 (15) | 0.0252 (16) | 0.0269 (16) | −0.0057 (12) | −0.0012 (12) | −0.0077 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0264 (17) | 0.0326 (18) | 0.0299 (17) | −0.0117 (14) | 0.0065 (14) | −0.0058 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0328 (18) | 0.0269 (16) | 0.0177 (15) | −0.0036 (13) | −0.0008 (13) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0261 (16) | 0.0256 (16) | 0.0199 (15) | −0.0037 (12) | −0.0050 (12) | −0.0090 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0181 (14) | 0.0190 (14) | 0.0211 (14) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0044 (11) | −0.0072 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0188 (14) | 0.0207 (14) | 0.0188 (14) | −0.0048 (11) | −0.0023 (11) | −0.0078 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0270 (17) | 0.0350 (18) | 0.0252 (16) | −0.0084 (14) | −0.0101 (13) | −0.0056 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0204 (16) | 0.0381 (19) | 0.0376 (19) | −0.0095 (14) | −0.0062 (14) | −0.0118 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0242 (16) | 0.0299 (17) | 0.0318 (18) | −0.0129 (13) | 0.0058 (13) | −0.0110 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0263 (17) | 0.0295 (17) | 0.0192 (14) | −0.0094 (13) | 0.0023 (12) | −0.0065 (12) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu1—O1 | 2.012 (2) | N2—C6 | 1.350 (4) |
| Cu1—O4i | 2.054 (2) | C1—C2 | 1.387 (4) |
| Cu1—O6ii | 2.061 (2) | C1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| Cu1—N1 | 2.084 (2) | C2—C3 | 1.381 (5) |
| Cu1—N2 | 2.117 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| V1—O2 | 1.615 (2) | C3—C4 | 1.388 (5) |
| V1—O1 | 1.667 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| V1—O5iii | 1.824 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.392 (4) |
| V1—O3 | 1.833 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| V2—O4 | 1.655 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.488 (4) |
| V2—O6 | 1.670 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.397 (4) |
| V2—O5 | 1.774 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.384 (5) |
| V2—O3 | 1.790 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O4—Cu1i | 2.054 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.379 (5) |
| O5—V1iii | 1.824 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O6—Cu1iv | 2.061 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.379 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.346 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.352 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C10 | 1.344 (4) | ||
| O1—Cu1—O4i | 89.62 (9) | C6—N2—Cu1 | 114.9 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—O6ii | 94.53 (9) | N1—C1—C2 | 122.1 (3) |
| O4i—Cu1—O6ii | 121.32 (9) | N1—C1—H1 | 118.9 |
| O1—Cu1—N1 | 100.17 (9) | C2—C1—H1 | 118.9 |
| O4i—Cu1—N1 | 124.55 (9) | C3—C2—C1 | 119.2 (3) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N1 | 112.18 (9) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| O1—Cu1—N2 | 172.29 (9) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 |
| O4i—Cu1—N2 | 85.25 (9) | C2—C3—C4 | 119.1 (3) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N2 | 93.05 (9) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 |
| N1—Cu1—N2 | 78.18 (10) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 |
| O2—V1—O1 | 108.65 (12) | C3—C4—C5 | 118.9 (3) |
| O2—V1—O5iii | 109.43 (12) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| O1—V1—O5iii | 111.53 (11) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 |
| O2—V1—O3 | 107.98 (12) | N1—C5—C4 | 121.9 (3) |
| O1—V1—O3 | 110.08 (11) | N1—C5—C6 | 115.6 (3) |
| O5iii—V1—O3 | 109.09 (10) | C4—C5—C6 | 122.5 (3) |
| O4—V2—O6 | 107.88 (11) | N2—C6—C7 | 121.6 (3) |
| O4—V2—O5 | 111.20 (11) | N2—C6—C5 | 114.8 (2) |
| O6—V2—O5 | 108.55 (11) | C7—C6—C5 | 123.6 (3) |
| O4—V2—O3 | 109.63 (11) | C8—C7—C6 | 118.6 (3) |
| O6—V2—O3 | 111.29 (11) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.7 |
| O5—V2—O3 | 108.30 (10) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.7 |
| V1—O1—Cu1 | 159.01 (14) | C9—C8—C7 | 119.6 (3) |
| V2—O3—V1 | 139.64 (14) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.2 |
| V2—O4—Cu1i | 162.64 (14) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.2 |
| V2—O5—V1iii | 160.20 (14) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| V2—O6—Cu1iv | 133.16 (13) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.6 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.7 (3) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.6 |
| C1—N1—Cu1 | 125.5 (2) | N2—C10—C9 | 122.5 (3) |
| C5—N1—Cu1 | 115.6 (2) | N2—C10—H10 | 118.7 |
| C10—N2—C6 | 118.8 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 118.7 |
| C10—N2—Cu1 | 125.7 (2) | ||
| O2—V1—O1—Cu1 | −60.3 (4) | N1—Cu1—N2—C10 | −175.0 (3) |
| O5iii—V1—O1—Cu1 | 179.0 (4) | O4i—Cu1—N2—C6 | 122.4 (2) |
| O3—V1—O1—Cu1 | 57.8 (4) | O6ii—Cu1—N2—C6 | −116.4 (2) |
| O4i—Cu1—O1—V1 | −68.8 (4) | N1—Cu1—N2—C6 | −4.4 (2) |
| O6ii—Cu1—O1—V1 | 169.8 (4) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −0.6 (5) |
| N1—Cu1—O1—V1 | 56.3 (4) | Cu1—N1—C1—C2 | 173.5 (2) |
| O4—V2—O3—V1 | −176.89 (19) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (5) |
| O6—V2—O3—V1 | 63.8 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (5) |
| O5—V2—O3—V1 | −55.4 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.5 (5) |
| O2—V1—O3—V2 | −51.5 (2) | C1—N1—C5—C4 | 2.0 (4) |
| O1—V1—O3—V2 | −169.94 (19) | Cu1—N1—C5—C4 | −172.6 (2) |
| O5iii—V1—O3—V2 | 67.4 (2) | C1—N1—C5—C6 | −177.8 (3) |
| O6—V2—O4—Cu1i | −84.8 (5) | Cu1—N1—C5—C6 | 7.5 (3) |
| O5—V2—O4—Cu1i | 34.1 (5) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | −2.0 (4) |
| O3—V2—O4—Cu1i | 153.8 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.9 (3) |
| O4—V2—O5—V1iii | 104.6 (4) | C10—N2—C6—C7 | 2.1 (4) |
| O6—V2—O5—V1iii | −136.9 (4) | Cu1—N2—C6—C7 | −169.2 (2) |
| O3—V2—O5—V1iii | −15.9 (5) | C10—N2—C6—C5 | −179.3 (3) |
| O4—V2—O6—Cu1iv | 17.23 (19) | Cu1—N2—C6—C5 | 9.5 (3) |
| O5—V2—O6—Cu1iv | −103.38 (17) | N1—C5—C6—N2 | −11.3 (4) |
| O3—V2—O6—Cu1iv | 137.53 (15) | C4—C5—C6—N2 | 168.8 (3) |
| O1—Cu1—N1—C1 | 11.4 (3) | N1—C5—C6—C7 | 167.3 (3) |
| O4i—Cu1—N1—C1 | 108.1 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −12.5 (5) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N1—C1 | −87.8 (3) | N2—C6—C7—C8 | −1.5 (5) |
| N2—Cu1—N1—C1 | −176.2 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 180.0 (3) |
| O1—Cu1—N1—C5 | −174.30 (19) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.0 (5) |
| O4i—Cu1—N1—C5 | −77.7 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.9 (5) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N1—C5 | 86.5 (2) | C6—N2—C10—C9 | −1.2 (5) |
| N2—Cu1—N1—C5 | −1.97 (19) | Cu1—N2—C10—C9 | 169.1 (2) |
| O4i—Cu1—N2—C10 | −48.2 (3) | C8—C9—C10—N2 | −0.3 (5) |
| O6ii—Cu1—N2—C10 | 73.0 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x, y−1, z; (iii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HY2113).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND Release 2.1c. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2002). SMART (Version 5.62), SAINT (Version 6.02) and SADABS (Version 2.03). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- DeBord, J. R. D., Zhang, Y., Haushalter, R. C., Zubieta, J. & O’Connor, C. J. (1996). J. Solid State Chem.122, 251–258.
- Kucsera, R., Gyepes, R. & Zurkvoa, L. (2002). Cryst. Res. Technol.37, 890–895.
- Lu, Y., Wang, E. B., Yuan, M., Li, Y. G., Hu, C. W., Hu, N. H. & Jia, H. Q. (2002). Solid State Sci.4, 449–453.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Yi, Z.-H., Cui, X.-B., Zhang, X., Yu, J.-H., Lu, J., Xu, J.-Q., Yang, G.-D., Wang, T.-G., Yu, H.-H. & Duan, W.-J. (2007). Dalton Trans. pp. 2115–2120. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067979/hy2113sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067979/hy2113Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report