Abstract
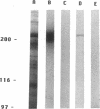
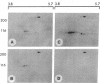
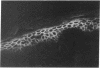
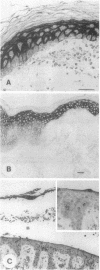
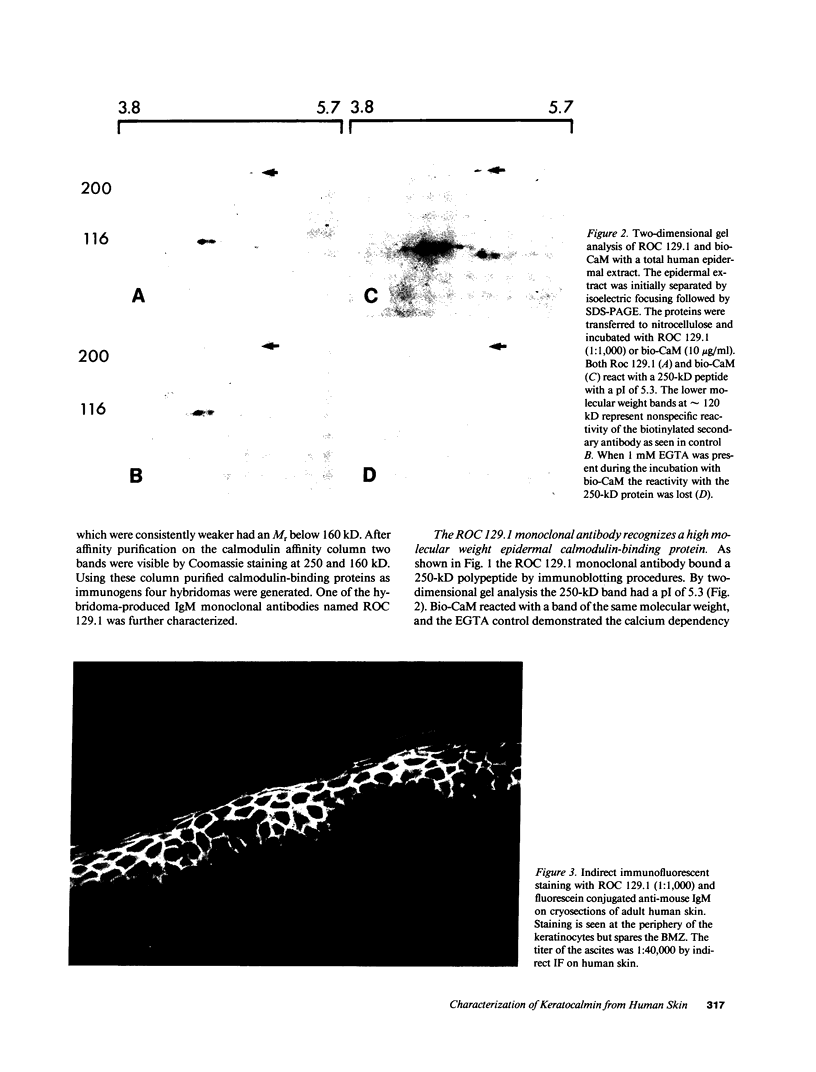
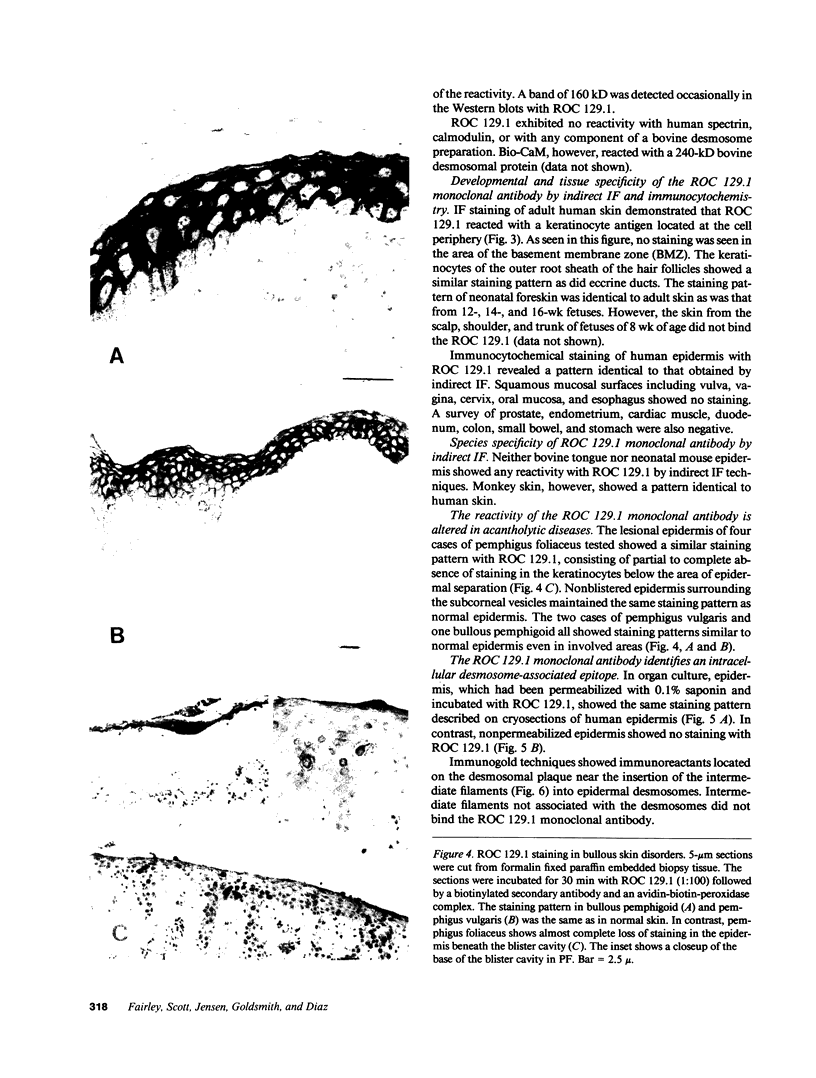
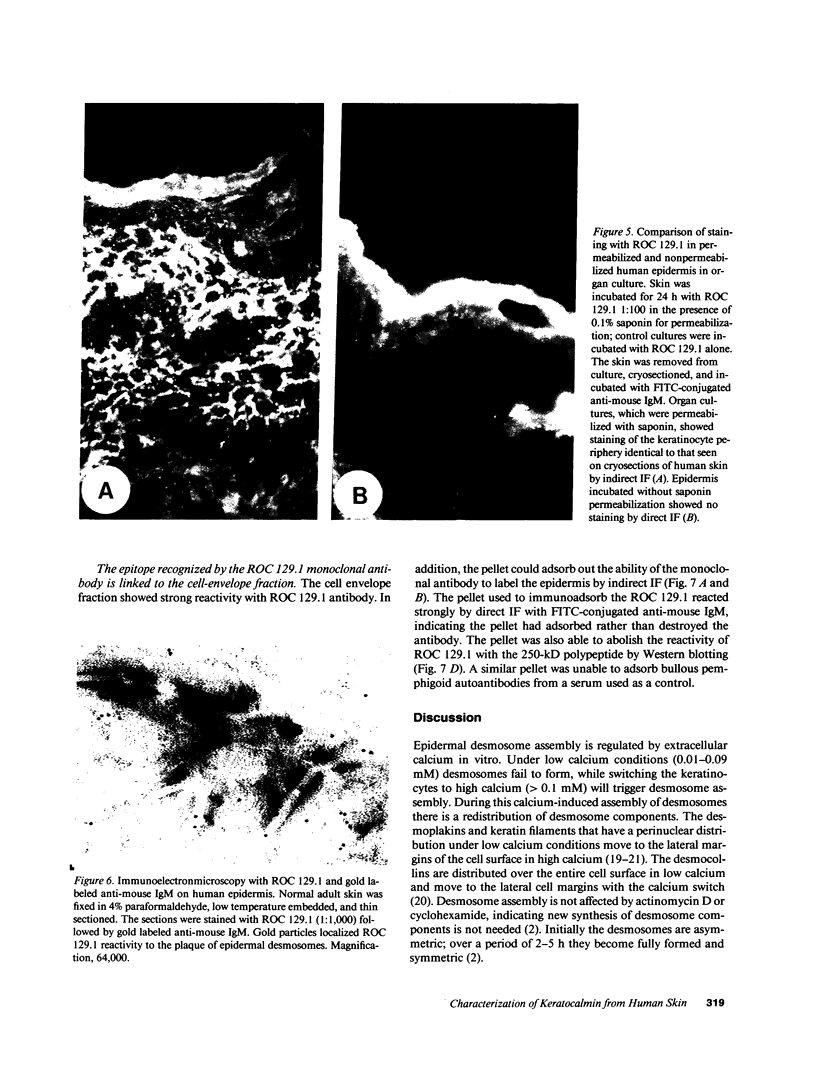
Using affinity-purified calmodulin-binding proteins from human epidermis we have developed a monoclonal IgM antibody, ROC 129.1, to a human desmosomal calcmodulin-binding protein. This antibody reacts with a submembranous 250-kD protein from human keratinocytes and stains human epidermis in a "cell-surface pattern". Permeability studies indicated that the epitope with which this monoclonal reacts is on the inner surface of the cell membrane. Immunoelectronmicroscopy localized the antigen to the desmosome. The epitope is restricted to stratified squamous epithelia and arises between 8-12 wk of fetal development. This desmosomal calmodulin-binding protein, which we have termed keratocalmin, may be involved in the calcium-regulated assembly of desmosomes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutner E. H., Prigenzi L. S., Hale W., Leme C. de A., Bier O. G. Immunofluorescent studies of autoantibodies to intercellular areas of epithelia in Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):81–86. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingsley M. L., Pennypacker K. R., Hoover C. G., Brigati D. J., Kincaid R. L. A rapid and sensitive method for detection and quantification of calcineurin and calmodulin-binding proteins using biotinylated calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7585–7589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce S. T., Ham R. G. Calcium-regulated differentiation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in chemically defined clonal culture and serum-free serial culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):33s–40s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin: an overview. Fed Proc. 1982 May;41(7):2253–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Garrod D. R. Antibodies to epithelial desmosomes show wide tissue and species cross-reactivity. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):148–150. doi: 10.1038/302148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre R. W., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal protein complex with a calcium-sensitive epitope are characteristic of pemphigus foliaceus patients. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1719–1724. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farb R. M., Dykes R., Lazarus G. S. Anti-epidermal-cell-surface pemphigus antibody detaches viable epidermal cells from culture plates by activation of proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Parry D. A., Steinert P. M., Virata M. L., Wagner R. M., Angst B. D., Nilles L. A. Structure of the human desmoplakins. Implications for function in the desmosomal plaque. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2603–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Holbrook K. A. Calcium regulation of cell-cell contact and differentiation of epidermal cells in culture. An ultrastructural study. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jan;143(1):127–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Steinert P., Buxman M. M. Calcium induction of transglutaminase and the formation of epsilon(gamma-glutamyl) lysine cross-links in cultured mouse epidermal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 30;102(2):739–745. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaken S., Yuspa S. H. Early signals for keratinocyte differentiation: role of Ca2+-mediated inositol lipid metabolism in normal and neoplastic epidermal cells. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Jun;9(6):1033–1038. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.6.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman A. E., Steinert P. M., Yuspa S., Goldman R. D. Dynamic aspects of the supramolecular organization of intermediate filament networks in cultured epidermal cells. Cell Motil. 1982;2(3):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cm.970020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments and the initiation of desmosome assembly. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):506–517. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Geoghegan W. D., Jordon R. E. Complement fixation by pemphigus antibody. II. Complement enhanced detachment of epidermal cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Sep;61(3):517–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana S., Geoghegan W. D., Jordon R. E. Complement fixation by pemphigus antibody. III. Altered epidermal cell membrane integrity mediated by pemphigus antibody and complement. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Jan;86(1):29–33. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12283762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koulu L., Kusumi A., Steinberg M. S., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal core protein in pemphigus foliaceus. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1509–1518. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib R. S., Camargo S., Futamura S., Martins C. R., Rock B., Anhalt G. J., Diaz L. A. Pemphigus foliaceus antigen: characterization of a keratinocyte envelope associated pool and preparation of a soluble immunoreactive fragment. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Aug;93(2):272–279. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane A. T., Helm K. F., Goldsmith L. A. Identification of bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus, laminin, and anchoring fibril antigens in human fetal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jan;84(1):27–30. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattey D. L., Suhrbier A., Parrish E., Garrod D. R. Recognition, calcium and the control of desmosome formation. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;125:49–65. doi: 10.1002/9780470513408.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller H., Franke W. W. Biochemical and immunological characterization of desmoplakins I and II, the major polypeptides of the desmosomal plaque. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):647–671. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Ono T., VanBerkum M. F., Means A. R. Functional significance of the central helix in calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11242–11249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe J. T., Diaz L., Sampaio S. A., Castro R. M., Labib R. S., Takahashi Y., Patel H., Anhalt G. J. Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies are pathogenic to BALB/c mice by passive transfer. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Dec;85(6):538–541. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B., Papay R. Appearance of "pemphigus acantholysis factor" in human skin cultured with pemphigus antibody. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Dec;73(6):575–581. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B., Papay R. Pemphigus antibody interaction with human epidermal cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):778–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI109189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheu H. M., Kitajima Y., Yaoita H. Involvement of protein kinase C in translocation of desmoplakins from cytosol to plasma membrane during desmosome formation in human squamous cell carcinoma cells grown in low to normal calcium concentration. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Nov;185(1):176–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Koulu L., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinberg M. S. A monoclonal antibody to the desmosomal glycoprotein desmoglein I binds the same polypeptide as human autoantibodies in pemphigus foliaceus. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1227–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M. S., Shida H., Giudice G. J., Shida M., Patel N. H., Blaschuk O. W. On the molecular organization, diversity and functions of desmosomal proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1987;125:3–25. doi: 10.1002/9780470513408.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W., Ziboh V. A., Isseroff R., Martinez D. Turnover of inositol phospholipids in cultured murine keratinocytes: possible involvement of inositol triphosphate in cellular differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jan;90(1):37–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12462536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkaus-Randall V., Gipson I. K. Role of calcium and calmodulin in hemidesmosome formation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1565–1571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Tsukita S. Desmocalmin: a calmodulin-binding high molecular weight protein isolated from desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2070–2080. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Lynch T. J., Tallant E. A., Cheung W. Y. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein of brain adenylate cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M., Mattey D. L., Garrod D. R. Calcium-induced reorganization of desmosomal components in cultured human keratinocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A., Isseroff R. R., Pandey R. Phospholipid metabolism in calcium-regulated differentiation in cultured murine keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1234–1240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]