Abstract
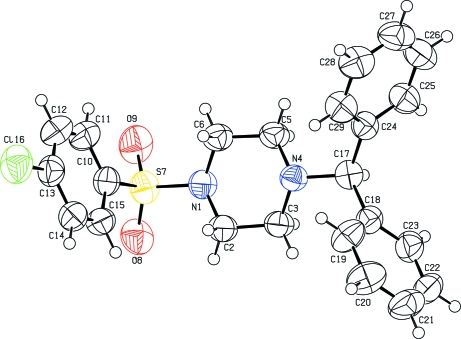
The title compound, C23H23ClN2O2S, was synthesized by the nucleophilic substitution of 1-benzhydrylpiperazine with 4-chlorophenylsulfonyl chloride. The piperazine ring is in a chair conformation. The geometry around the S atom is that of a distorted tetrahedron. There is a large range of bond angles around the piperazine N atoms. The dihedral angle between the least-squares plane (p1) defined by the four coplanar C atoms of the piperazine ring and the benzene ring is 81.6 (1)°. The dihedral angles between p1 and the phenyl rings are 76.2 (1) and 72.9 (2)°. The two phenyl rings make a dihedral angle of 65.9 (1)°. Intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are present.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Bassindale (1984 ▶); Berkheij et al. (2005 ▶); Campbell et al. (1973 ▶); Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶); Dinsmore & Beshore (2002 ▶); Humle & Cherrier (1999 ▶); Katzung (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C23H23ClN2O2S
M r = 426.94
Monoclinic,
a = 9.392 (7) Å
b = 13.114 (10) Å
c = 19.225 (11) Å
β = 113.645 (3)°
V = 2169 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
MacScience DIPLabo 32001 diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
7255 measured reflections
3818 independent reflections
2917 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.147
S = 1.08
3818 reflections
263 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3
Data collection: XPRESS (MacScience, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO and SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶) and ORTEPII (Johnson, 1976 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067888/hg2365sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067888/hg2365Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2A⋯O8 | 0.97 | 2.49 | 2.890 (3) | 105 |
| C6—H6B⋯O9 | 0.97 | 2.56 | 2.965 (3) | 105 |
| C11—H11⋯O9 | 0.93 | 2.53 | 2.905 (3) | 104 |
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to DST/CSIR, New Delhi, for financial support under the projects SP/I2/FOO/93 and 01(1904)/03/EMR-II 2004. The authors also acknowledge DST-FIST and UGC-SAP (phase I) for support with the collection of CHNS and IR data.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Piperazines are among the most important building blocks in today's drug discovery. The piperazine nucleus is capable of binding to multiple receptors with high affinity and therefore piperazine has been classified as a privileged structure (Dinsmore et al., 2002). They are found in biologically active compounds across a number of different therapeutic areas (Berkheij et al., 2005) such as antifungal, antibacterial, antimalarial, antipsychotic, antidepressant and antitumour activity against colon, prostate, breast, lung and leukemia tumors (Humle & Cherrier, 1999). 1-Benzylpiperazine was originally synthesized as a potential antihelminthic (Campbell et al., 1973) and these derivatives were found to possess excellent pharmacological activities such as vasodilator, hypotensive, antiviral activity and cerebral blood flow increasing actions, broad pharmacological action on central nerves system (CNS), especially on dopaminergic neurotransmission. Sulfonamides are among the most widely used antibacterial agents (Katzung et al., 1995). Piperazine sulfonamides exhibit diverse therapeutic activity such as antibacterial activity, MMP-3 inhibition and carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Encouraged by the above information, the title compound was synthesized and herein we report its crystal structure.
A perspective view of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. A study of torsion angles, asymmetry parameters and least-squares plane calculations reveal that the piperazine ring in the structure is in a chair conformation. This has been confirmed by the puckering paramaters q2=0.0291 (24) Å, q3=0.5969 (26) Å, QT=0.5977 (26) Å, θ=3.07 (23)° and φ=198 (5)° (Cremer & Pople, 1975). The conformation of the attachment of the diphenylmethyl and the sulfonyl groups to the piperazine ring are best described by the torsion angle values of 166.6 (2)° and -177.4 (2)° for S7—N1—C2—C3 and C17—N4—C5—C6, respectively; i.e. they adopt +antiperiplanar and -antiperiplanar conformations, respectively. The bonds N1—S7 and N4—C17 connecting the sulfonyl and the diphenyl groups make angles of 86.00 (11)° and 72.92 (14)°, respectively, with the Cremer and Pople plane of the piperazine ring and thus are in the equatorial plane of the piperazine ring.
The bond angles about the S atom shows significant deviation from that of a regular tetrahedron, with the largest deviations being observed for O9—S7—O8 [119.92 (12)°] and 09—S7—C10 [107.88 (12)°]. The widening of O8—S7—O9 is due to the repulsive interactions between the S?O bonds and the non-bonded interactions involving the two S?O bonds and the varied steric hindrance of the substituents. The structure thus has less steric interference. The reduction of the N1—S7—C10 angle from the ideal tetrahedral value is attributed to the Thorpe-Ingold effect (Bassindale, 1984). The sulfonyl O atoms, O8 and O9, are oriented in -synclinal and +synclinal conformations, respectively, as indicated by the torsion angle values of -42.1 (2)° and 53.96 (19)° for C2—N1—S7—O8 and C6—N1—S7—O9, respectively.
Experimental
A solution of 1-benzhydryl-piperazine (0.5 g, 1.98 mmol) in dry dichloromethane was taken, and cooled to 0–5° C in an ice bath. Then triethylamine (0.601 g, 5.94 mmol) was added to the cold reaction mixture and stirred for 10 minutes. Then 4-chloro-benzenesulfonyl chloride (0.417 g, 1.98 mmol) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 hrs. The reaction mixture was monitored by TLC. On completion of the reaction, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was taken in water and extracted with ethyl acetate. Finally water wash was given to organic layer and dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was evaporated to get crude product, which was purified by column chromatography over silica gel using hexane: ethyl acetate (8:2) as an eluent. Pure white crystals were obtained due to the slow evaporation of the solvent with a yield of 90%. M.p. 428.1 K.
1HNMR (DMSO, 400 MHz): δ 7.7–7.8 (m, 4H, Ar—H), 7.4 (d, 4H, Ar—H), 7.25(t, 4H, Ar—H), 7.16 (t, 2H, Ar—H), 4.32 (s, 1H, –CH), 3.32 (dd, 4H, –CH2), 2.41 (dd, 4H, –CH2).
MS (ESI + ion): m/z = 427.9
IR (KBr, cm1): 2961, 2889, 1350, 1279, 707.
Anal. Calcd.for C23H23ClN2O2S (in %): C-59.87, H-4.81, N-6.07, S-6.95. Found C-59.82, H-4.78, N-6.04, S-6.90%.
Refinement
H atoms were placed at idealized positions and allowed to ride on their parent atoms with C—H distances in the range 0.92–0.97 Å and O—H = 0.82 Å; Uiso(H) values were set equal to 1.2Ueq(carrier atom).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure, with atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C23H23ClN2O2S | F000 = 896 |
| Mr = 426.94 | Dx = 1.307 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2 ybc | Cell parameters from 7255 reflections |
| a = 9.392 (7) Å | θ = 2.3–25.0º |
| b = 13.114 (10) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| c = 19.225 (11) Å | T = 295 (2) K |
| β = 113.645 (3)º | Block, white |
| V = 2169 (3) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| MacScience DIPLabo 32001 diffractometer | 3818 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2917 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.024 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0º |
| T = 295(2) K | θmin = 2.3º |
| ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −15→15 |
| 7255 measured reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0781P)2 + 0.4503P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.147 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.08 | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 3818 reflections | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
| 263 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997), FC*=KFC[1+0.001XFC2Λ3/SIN(2Θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.065 (4) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All e.s.d.'s are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F^2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F^2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F^2. The observed criterion of F^2 > σ(F^2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F^2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl16 | 0.45997 (9) | 0.44356 (6) | 0.31602 (5) | 0.0932 (3) | |
| S7 | 0.02536 (7) | 0.06459 (5) | 0.20336 (3) | 0.0673 (2) | |
| O8 | −0.12416 (19) | 0.08971 (15) | 0.20131 (11) | 0.0815 (7) | |
| O9 | 0.0391 (2) | 0.02536 (16) | 0.13714 (9) | 0.0878 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.1012 (2) | −0.02030 (15) | 0.27063 (10) | 0.0592 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.28463 (19) | −0.12983 (14) | 0.40601 (10) | 0.0540 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.0814 (3) | −0.00363 (19) | 0.34202 (13) | 0.0639 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.1236 (3) | −0.09986 (19) | 0.38885 (13) | 0.0602 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.2974 (3) | −0.14861 (19) | 0.33344 (12) | 0.0611 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.2608 (3) | −0.05271 (19) | 0.28593 (13) | 0.0631 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.1441 (3) | 0.17362 (19) | 0.23278 (12) | 0.0601 (8) | |
| C11 | 0.2522 (3) | 0.1935 (2) | 0.20299 (16) | 0.0773 (10) | |
| C12 | 0.3485 (4) | 0.2768 (2) | 0.22841 (18) | 0.0847 (12) | |
| C13 | 0.3378 (3) | 0.3395 (2) | 0.28381 (14) | 0.0670 (8) | |
| C14 | 0.2302 (3) | 0.3203 (2) | 0.31371 (13) | 0.0652 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.1327 (3) | 0.23722 (19) | 0.28775 (13) | 0.0631 (8) | |
| C17 | 0.3273 (2) | −0.22232 (17) | 0.45406 (12) | 0.0563 (7) | |
| C18 | 0.3073 (3) | −0.20476 (18) | 0.52750 (12) | 0.0569 (7) | |
| C19 | 0.3666 (3) | −0.1188 (2) | 0.57137 (15) | 0.0762 (10) | |
| C20 | 0.3439 (4) | −0.1023 (3) | 0.63736 (15) | 0.0896 (11) | |
| C21 | 0.2629 (3) | −0.1724 (3) | 0.66053 (16) | 0.0884 (13) | |
| C22 | 0.2052 (3) | −0.2577 (3) | 0.61814 (18) | 0.0877 (11) | |
| C23 | 0.2268 (3) | −0.2744 (2) | 0.55178 (16) | 0.0725 (9) | |
| C24 | 0.4921 (2) | −0.25730 (17) | 0.46936 (12) | 0.0556 (7) | |
| C25 | 0.5204 (3) | −0.3596 (2) | 0.46298 (15) | 0.0710 (9) | |
| C26 | 0.6693 (4) | −0.3932 (2) | 0.47724 (17) | 0.0849 (11) | |
| C27 | 0.7892 (3) | −0.3270 (3) | 0.49653 (15) | 0.0819 (13) | |
| C28 | 0.7633 (3) | −0.2248 (3) | 0.50267 (15) | 0.0785 (10) | |
| C29 | 0.6157 (3) | −0.1903 (2) | 0.48981 (14) | 0.0700 (8) | |
| H2A | −0.02550 | 0.01470 | 0.33090 | 0.0770* | |
| H2B | 0.14780 | 0.05190 | 0.37020 | 0.0770* | |
| H3A | 0.11070 | −0.08900 | 0.43590 | 0.0720* | |
| H3B | 0.05410 | −0.15440 | 0.36130 | 0.0720* | |
| H5A | 0.22580 | −0.20230 | 0.30600 | 0.0730* | |
| H5B | 0.40200 | −0.17110 | 0.34290 | 0.0730* | |
| H6A | 0.33330 | 0.00080 | 0.31280 | 0.0760* | |
| H6B | 0.27090 | −0.06560 | 0.23850 | 0.0760* | |
| H11 | 0.26010 | 0.15100 | 0.16600 | 0.0930* | |
| H12 | 0.42120 | 0.29090 | 0.20820 | 0.1020* | |
| H14 | 0.22290 | 0.36260 | 0.35100 | 0.0780* | |
| H15 | 0.05880 | 0.22390 | 0.30740 | 0.0760* | |
| H17 | 0.25590 | −0.27700 | 0.42630 | 0.0680* | |
| H19 | 0.42240 | −0.07150 | 0.55640 | 0.0910* | |
| H20 | 0.38330 | −0.04380 | 0.66600 | 0.1080* | |
| H21 | 0.24770 | −0.16160 | 0.70490 | 0.1060* | |
| H22 | 0.15070 | −0.30520 | 0.63380 | 0.1050* | |
| H23 | 0.18670 | −0.33290 | 0.52340 | 0.0870* | |
| H25 | 0.43890 | −0.40610 | 0.44900 | 0.0850* | |
| H26 | 0.68700 | −0.46240 | 0.47350 | 0.1020* | |
| H27 | 0.88860 | −0.35040 | 0.50560 | 0.0980* | |
| H28 | 0.84530 | −0.17880 | 0.51550 | 0.0940* | |
| H29 | 0.59950 | −0.12130 | 0.49500 | 0.0840* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl16 | 0.0815 (5) | 0.0828 (5) | 0.1088 (6) | −0.0121 (4) | 0.0313 (4) | 0.0117 (4) |
| S7 | 0.0656 (4) | 0.0731 (4) | 0.0505 (4) | 0.0021 (3) | 0.0100 (3) | 0.0025 (3) |
| O8 | 0.0547 (10) | 0.0906 (13) | 0.0809 (12) | 0.0060 (9) | 0.0079 (8) | 0.0115 (10) |
| O9 | 0.1093 (14) | 0.0931 (13) | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0001 (12) | 0.0181 (9) | −0.0040 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0570 (11) | 0.0656 (11) | 0.0507 (10) | 0.0035 (9) | 0.0170 (8) | 0.0024 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0527 (10) | 0.0602 (11) | 0.0488 (9) | 0.0038 (8) | 0.0199 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0625 (13) | 0.0731 (15) | 0.0598 (13) | 0.0111 (11) | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0045 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0561 (13) | 0.0687 (14) | 0.0586 (13) | 0.0073 (11) | 0.0258 (10) | 0.0003 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0633 (14) | 0.0705 (14) | 0.0511 (12) | 0.0099 (11) | 0.0247 (10) | −0.0015 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0602 (14) | 0.0752 (16) | 0.0552 (13) | 0.0064 (11) | 0.0246 (10) | 0.0004 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0624 (13) | 0.0664 (14) | 0.0488 (12) | 0.0087 (11) | 0.0196 (10) | 0.0103 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0962 (19) | 0.0804 (18) | 0.0711 (16) | 0.0040 (15) | 0.0502 (15) | 0.0042 (15) |
| C12 | 0.091 (2) | 0.089 (2) | 0.096 (2) | −0.0023 (16) | 0.0603 (17) | 0.0113 (18) |
| C13 | 0.0623 (14) | 0.0679 (15) | 0.0674 (15) | 0.0039 (12) | 0.0226 (12) | 0.0163 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0719 (15) | 0.0680 (15) | 0.0563 (13) | 0.0042 (12) | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0023 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0621 (14) | 0.0718 (15) | 0.0606 (13) | 0.0049 (12) | 0.0299 (11) | 0.0057 (12) |
| C17 | 0.0547 (12) | 0.0559 (12) | 0.0539 (12) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0171 (9) | −0.0030 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0503 (12) | 0.0650 (14) | 0.0533 (12) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0186 (9) | 0.0083 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0865 (18) | 0.0880 (18) | 0.0602 (14) | −0.0231 (15) | 0.0359 (13) | −0.0095 (14) |
| C20 | 0.093 (2) | 0.118 (2) | 0.0596 (15) | −0.0119 (18) | 0.0325 (14) | −0.0179 (17) |
| C21 | 0.0703 (17) | 0.139 (3) | 0.0609 (15) | 0.0153 (18) | 0.0315 (13) | 0.0205 (19) |
| C22 | 0.0742 (18) | 0.112 (2) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0156 (17) | 0.0467 (16) | 0.040 (2) |
| C23 | 0.0617 (14) | 0.0716 (16) | 0.0852 (18) | 0.0061 (12) | 0.0305 (13) | 0.0190 (14) |
| C24 | 0.0558 (12) | 0.0585 (13) | 0.0482 (11) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0164 (9) | 0.0009 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0751 (16) | 0.0623 (14) | 0.0759 (16) | 0.0023 (12) | 0.0306 (13) | −0.0057 (13) |
| C26 | 0.087 (2) | 0.0782 (18) | 0.090 (2) | 0.0235 (16) | 0.0360 (16) | −0.0004 (16) |
| C27 | 0.0639 (16) | 0.113 (3) | 0.0660 (16) | 0.0199 (16) | 0.0230 (13) | −0.0014 (16) |
| C28 | 0.0571 (15) | 0.101 (2) | 0.0690 (16) | −0.0054 (14) | 0.0166 (12) | −0.0045 (15) |
| C29 | 0.0605 (14) | 0.0712 (15) | 0.0726 (15) | −0.0041 (12) | 0.0207 (12) | −0.0055 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl16—C13 | 1.730 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.385 (5) |
| S7—O8 | 1.427 (2) | C26—C27 | 1.351 (5) |
| S7—O9 | 1.4261 (18) | C27—C28 | 1.376 (6) |
| S7—N1 | 1.637 (2) | C28—C29 | 1.383 (4) |
| S7—C10 | 1.761 (3) | C2—H2A | 0.9692 |
| N1—C2 | 1.473 (3) | C2—H2B | 0.9704 |
| N1—C6 | 1.470 (4) | C3—H3A | 0.9701 |
| N4—C3 | 1.466 (4) | C3—H3B | 0.9700 |
| N4—C5 | 1.468 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9704 |
| N4—C17 | 1.479 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9705 |
| C2—C3 | 1.508 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9699 |
| C5—C6 | 1.511 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9687 |
| C10—C11 | 1.376 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9296 |
| C10—C15 | 1.384 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9296 |
| C11—C12 | 1.377 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.9305 |
| C12—C13 | 1.381 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9302 |
| C13—C14 | 1.372 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9806 |
| C14—C15 | 1.381 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.9291 |
| C17—C18 | 1.515 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9302 |
| C17—C24 | 1.526 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9305 |
| C18—C19 | 1.384 (4) | C22—H22 | 0.9297 |
| C18—C23 | 1.381 (4) | C23—H23 | 0.9291 |
| C19—C20 | 1.385 (4) | C25—H25 | 0.9300 |
| C20—C21 | 1.376 (5) | C26—H26 | 0.9306 |
| C21—C22 | 1.362 (5) | C27—H27 | 0.9303 |
| C22—C23 | 1.387 (4) | C28—H28 | 0.9303 |
| C24—C25 | 1.383 (3) | C29—H29 | 0.9296 |
| C24—C29 | 1.381 (4) | ||
| Cl16···C26i | 3.629 (3) | H2B···H6A | 2.4989 |
| Cl16···H6Bii | 3.1028 | H2B···H15 | 2.5367 |
| Cl16···H20iii | 2.9831 | H3A···C18 | 2.4914 |
| O8···H2A | 2.4862 | H3A···C19 | 2.7733 |
| O8···H15 | 2.7200 | H3B···H5A | 2.3453 |
| O8···H5Aiv | 2.8746 | H3B···H17 | 2.4164 |
| O8···H17iv | 2.8583 | H3B···C10x | 3.0203 |
| O8···H21v | 2.6767 | H3B···C15x | 3.0457 |
| O9···H6B | 2.5606 | H5A···H3B | 2.3453 |
| O9···H11 | 2.5312 | H5A···H17 | 2.4216 |
| N1···N4 | 2.865 (3) | H5A···O8x | 2.8746 |
| N4···N1 | 2.865 (3) | H5B···C24 | 2.5009 |
| N4···H19 | 2.7600 | H5B···C29 | 2.7426 |
| N4···H29 | 2.7616 | H5B···H12ix | 2.2977 |
| C2···C15 | 3.421 (4) | H6A···C10 | 2.9100 |
| C3···C19 | 3.341 (4) | H6A···H2B | 2.4989 |
| C5···C29 | 3.326 (4) | H6A···C20vii | 3.0905 |
| C6···C11 | 3.588 (4) | H6A···H20vii | 2.5882 |
| C11···C6 | 3.588 (4) | H6B···O9 | 2.5606 |
| C15···C2 | 3.421 (4) | H6B···Cl16ix | 3.1028 |
| C19···C29 | 3.428 (4) | H6B···H22xi | 2.5247 |
| C19···C3 | 3.341 (4) | H11···O9 | 2.5312 |
| C26···Cl16vi | 3.629 (3) | H11···C27ii | 2.9834 |
| C29···C19 | 3.428 (4) | H12···H5Bii | 2.2977 |
| C29···C5 | 3.326 (4) | H14···C26vii | 3.0673 |
| C2···H15 | 3.0460 | H14···C27vii | 3.0150 |
| C10···H2B | 3.0749 | H15···O8 | 2.7200 |
| C10···H6A | 2.9100 | H15···C2 | 3.0460 |
| C10···H3Biv | 3.0203 | H15···H2B | 2.5367 |
| C15···H3Biv | 3.0457 | H17···H3B | 2.4164 |
| C15···H2B | 2.8738 | H17···H5A | 2.4216 |
| C18···H3A | 2.4914 | H17···H23 | 2.3276 |
| C19···H29 | 3.0851 | H17···H25 | 2.3258 |
| C19···H3A | 2.7733 | H17···O8x | 2.8583 |
| C20···H6Avii | 3.0905 | H19···N4 | 2.7600 |
| C21···H2Av | 3.0936 | H19···C29 | 3.0375 |
| C23···H27viii | 3.0998 | H19···H29 | 2.4822 |
| C24···H5B | 2.5009 | H20···H6Avii | 2.5882 |
| C26···H14vii | 3.0673 | H20···Cl16xii | 2.9831 |
| C27···H14vii | 3.0150 | H21···O8v | 2.6767 |
| C27···H11ix | 2.9834 | H22···H6Bxiii | 2.5247 |
| C29···H5B | 2.7426 | H23···H17 | 2.3276 |
| C29···H19 | 3.0375 | H25···H17 | 2.3258 |
| H2A···O8 | 2.4862 | H27···C23xiv | 3.0998 |
| H2A···C21v | 3.0936 | H29···N4 | 2.7616 |
| H2B···C10 | 3.0749 | H29···C19 | 3.0851 |
| H2B···C15 | 2.8738 | H29···H19 | 2.4822 |
| O8—S7—O9 | 119.92 (12) | C3—C2—H2B | 109.79 |
| O8—S7—N1 | 106.87 (11) | H2A—C2—H2B | 108.30 |
| O8—S7—C10 | 108.10 (13) | N4—C3—H3A | 109.44 |
| O9—S7—N1 | 107.06 (11) | N4—C3—H3B | 109.43 |
| O9—S7—C10 | 107.89 (12) | C2—C3—H3A | 109.43 |
| N1—S7—C10 | 106.23 (11) | C2—C3—H3B | 109.45 |
| S7—N1—C2 | 117.23 (16) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.00 |
| S7—N1—C6 | 116.13 (16) | N4—C5—H5A | 109.60 |
| C2—N1—C6 | 110.86 (18) | N4—C5—H5B | 109.59 |
| C3—N4—C5 | 107.52 (18) | C6—C5—H5A | 109.59 |
| C3—N4—C17 | 110.91 (18) | C6—C5—H5B | 109.52 |
| C5—N4—C17 | 110.54 (17) | H5A—C5—H5B | 108.06 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 109.3 (2) | N1—C6—H6A | 109.82 |
| N4—C3—C2 | 111.0 (2) | N1—C6—H6B | 109.82 |
| N4—C5—C6 | 110.4 (2) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.84 |
| N1—C6—C5 | 109.2 (2) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.84 |
| S7—C10—C11 | 119.87 (19) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.34 |
| S7—C10—C15 | 120.1 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.23 |
| C11—C10—C15 | 120.0 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.31 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.5 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.84 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.4 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.79 |
| Cl16—C13—C12 | 120.2 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.52 |
| Cl16—C13—C14 | 119.3 (2) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.37 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 120.5 (3) | C10—C15—H15 | 119.73 |
| C13—C14—C15 | 119.1 (2) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.73 |
| C10—C15—C14 | 120.5 (3) | N4—C17—H17 | 107.75 |
| N4—C17—C18 | 110.71 (18) | C18—C17—H17 | 107.76 |
| N4—C17—C24 | 111.52 (17) | C24—C17—H17 | 107.73 |
| C18—C17—C24 | 111.19 (18) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.61 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 121.5 (2) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.51 |
| C17—C18—C23 | 120.3 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.01 |
| C19—C18—C23 | 118.3 (2) | C21—C20—H20 | 119.98 |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.9 (3) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.20 |
| C19—C20—C21 | 120.0 (3) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.20 |
| C20—C21—C22 | 119.6 (3) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.68 |
| C21—C22—C23 | 120.7 (3) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.65 |
| C18—C23—C22 | 120.6 (3) | C18—C23—H23 | 119.71 |
| C17—C24—C25 | 119.4 (2) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.74 |
| C17—C24—C29 | 122.4 (2) | C24—C25—H25 | 119.78 |
| C25—C24—C29 | 118.2 (2) | C26—C25—H25 | 119.83 |
| C24—C25—C26 | 120.4 (2) | C25—C26—H26 | 119.51 |
| C25—C26—C27 | 121.0 (3) | C27—C26—H26 | 119.53 |
| C26—C27—C28 | 119.5 (3) | C26—C27—H27 | 120.19 |
| C27—C28—C29 | 120.2 (3) | C28—C27—H27 | 120.26 |
| C24—C29—C28 | 120.7 (3) | C27—C28—H28 | 119.90 |
| N1—C2—H2A | 109.75 | C29—C28—H28 | 119.94 |
| N1—C2—H2B | 109.78 | C24—C29—H29 | 119.65 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.89 | C28—C29—H29 | 119.65 |
| O8—S7—N1—C2 | −42.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (4) |
| O9—S7—N1—C2 | −171.75 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (4) |
| C10—S7—N1—C2 | 73.2 (2) | C11—C12—C13—Cl16 | 179.6 (2) |
| O8—S7—N1—C6 | −176.37 (16) | Cl16—C13—C14—C15 | 179.9 (2) |
| O9—S7—N1—C6 | 53.96 (19) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (4) |
| C10—S7—N1—C6 | −61.13 (19) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.5 (4) |
| O9—S7—C10—C11 | −13.5 (2) | N4—C17—C18—C19 | −48.4 (3) |
| N1—S7—C10—C11 | 101.0 (2) | C24—C17—C18—C23 | −104.7 (3) |
| O8—S7—C10—C15 | 37.7 (2) | N4—C17—C24—C25 | −135.1 (2) |
| O9—S7—C10—C15 | 168.8 (2) | N4—C17—C24—C29 | 45.2 (3) |
| N1—S7—C10—C15 | −76.7 (2) | C18—C17—C24—C25 | 100.8 (2) |
| O8—S7—C10—C11 | −144.6 (2) | C18—C17—C24—C29 | −78.9 (3) |
| S7—N1—C2—C3 | 166.58 (18) | N4—C17—C18—C23 | 130.7 (2) |
| C6—N1—C2—C3 | −56.9 (3) | C24—C17—C18—C19 | 76.1 (3) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | 57.6 (2) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | 0.6 (4) |
| S7—N1—C6—C5 | −165.36 (15) | C17—C18—C23—C22 | −178.6 (3) |
| C3—N4—C5—C6 | 61.4 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 178.2 (3) |
| C17—N4—C3—C2 | 178.14 (18) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | −0.9 (4) |
| C5—N4—C3—C2 | −60.9 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.7 (5) |
| C3—N4—C17—C24 | 177.36 (17) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.1 (5) |
| C17—N4—C5—C6 | −177.4 (2) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −0.2 (5) |
| C3—N4—C17—C18 | −58.3 (2) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | 0.0 (5) |
| C5—N4—C17—C18 | −177.4 (2) | C17—C24—C25—C26 | −179.4 (2) |
| C5—N4—C17—C24 | 58.2 (2) | C25—C24—C29—C28 | 0.7 (4) |
| N1—C2—C3—N4 | 59.0 (3) | C29—C24—C25—C26 | 0.3 (4) |
| N4—C5—C6—N1 | −60.3 (3) | C17—C24—C29—C28 | −179.5 (2) |
| S7—C10—C11—C12 | −177.6 (2) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | −1.0 (4) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (4) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 0.5 (4) |
| S7—C10—C15—C14 | 177.0 (2) | C26—C27—C28—C29 | 0.6 (4) |
| C11—C10—C15—C14 | −0.6 (4) | C27—C28—C29—C24 | −1.2 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (v) −x, −y, −z+1; (vi) x, y−1, z; (vii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (viii) x−1, y, z; (ix) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (x) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (xi) x, −y−1/2, z−1/2; (xii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (xiii) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2; (xiv) x+1, y, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2A···O8 | 0.97 | 2.49 | 2.890 (3) | 105 |
| C6—H6B···O9 | 0.97 | 2.56 | 2.965 (3) | 105 |
| C11—H11···O9 | 0.93 | 2.53 | 2.905 (3) | 104 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG2365).
References
- Bassindale, A. (1984). The Third Dimension in Organic Chemistry, ch. 1, p. 11. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
- Berkheij, M., van der Sluis, L., Sewing, C., den Boer, D. J., Terpstra, J. W., Heimstra, H., Bakker, W. I. I., van den Hoogen Band, A. & van Maarseveen, J. H. (2005). Tetrahedron, 46, 2369–2371.
- Campbell, H., Cline, W., Evans, M., Lloyd, J. & Peck, A. W. (1973). Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol.6, 170–176. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc.97, 1354–1358.
- Dinsmore, C. J. & Beshore, D. C. (2002). Tetrahedron, 58, 3297–3312.
- Humle, C. & Cherrier, M. P. (1999). Tetrahedron Lett.40, 5295–5299.
- Johnson, C. K. (1976). ORTEPII Report ORNL-5138. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Katzung, B. G. (1995). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 6th ed. San Francisco: University of California.
- MacScience (2002). XPRESS MacScience Co. Ltd, Yokohama, Japan.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067888/hg2365sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807067888/hg2365Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report