Abstract
In the title chalcone derivative, C13H8Cl2OS, the prop-2-en-1-one unit and the thiophene and 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings are each essentially planar. The interplanar angle between the thiophene and 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings is 19.87 (6)°. Weak intramolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl interactions involving the prop-2-en-1-one unit generate an S(5)S(5) ring motif. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into head-to-tail zigzag chains along the a axis and adjacent chains are cross-linked. These cross-linked chains are arranged into sheets parallel to the ab plane. The crystal structure is stabilized by weak C—H⋯O, C—H⋯Cl and C—H⋯π interactions. A π–π interaction was also observed with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.6845 (6) Å.
Related literature
For details of hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For related structures, see, for example: Fun et al. (2008a
▶,b
▶). For background on the applications of substituted chalcones, see, for example: Agrinskaya et al. (1999 ▶); Chopra et al. (2007 ▶); Goto et al. (1991 ▶); Gu et al. (2008a
▶,b
▶,c
▶); Patil et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶,c
▶); Sarojini et al. (2006 ▶); Wang et al. (2004 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H8Cl2OS
M r = 283.16
Monoclinic,
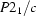
a = 9.5701 (4) Å
b = 13.9544 (6) Å
c = 10.4748 (4) Å
β = 118.735 (3)°
V = 1226.59 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.68 mm−1
T = 100.0 (1) K
0.58 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.695, T max = 0.919
41878 measured reflections
4435 independent reflections
3831 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.031
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.082
S = 1.06
4435 reflections
162 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808026524/ww2127sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808026524/ww2127Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.4512 (17) | 175 |
| C7—H7A⋯Cl1 | 0.93 | 2.68 | 3.0573 (11) | 105 |
| C7—H7A⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 2.8116 (17) | 101 |
| C10—H10A⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 3.33 | 3.8233 (13) | 115 |
| C12—H12A⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.87 | 3.6907 (13) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  . Cg1 is the centroid of the S1/C1–C4 ring.
. Cg1 is the centroid of the S1/C1–C4 ring.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India under grant No. SR/S2/LOP-17/2006. IAR and HKF thank Universiti Sains Malaysia and the Malaysian Government for the FRGS research grant No. 203/PFIZIK/671064. SC thanks Prince of Songkla University for generous support. The authors also thank Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Golden Goose grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811012.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In the last decades, the second-order nonlinear optical properties of chalcone derivatives have been widely investigated due to their possible applications in a variety of optoelectronic and photonic applications (Agrinskaya et al., 1999; Goto et al., 1991; Patil et al., 2007a, b, c; Sarojini et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2004). These derivatives also exhibit the optical limiting property which is a requirement of protecting the human eye or artificial optical sensor from damaging high-energy lasers (Gu et al., 2008a, b, c). In our continuing systematic study on chalcone derivatives, we report here the structure of the title compound.
In the structure of the title chalcone derivative (Fig. 1), bond lengths and angles are in normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987) and comparable to those in related structures (Fun et al., 2008a, b). The prop-2-en-1-one unit (O1/C5–C7), the thiophene ring and the 2,4-dichlorophenyl ring are individually essentially planar, with maximum deviations of 0.003 (1), 0.024 (1), -0.007 (1)Å for atom C4, C7 and C11, respectively. The total molecule is slightly twisted as indicated by the dihedral angles between the least-squares plane through the prop-2-en-1-one unit with the thiophene and 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings being 7.89 (7)° and 22.45 (7)°, and that between the thiophene and 2,4-dichlorophenyl rings being 19.87 (6)°.
In the structure, both weak intramolecular C7—H7A···O1 and C7—H7A···Cl1 interactions (Table 1) generate S(5) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995). In the crystal structure (Fig. 2) the molecules are linked in head-to-tail zigzag chains along the a-axis by weak C—H···Cl interactions and the adjacent chains were cross-linked by weak C—H···O interactions. These cross-linked chains are arranged into sheets parallel to the ab plane. The crystal is stabilized by weak C—H···O, C—H···Cl and C—H···π interactions (Table 1), π···π interaction was also observed with the Cg2···Cg2 distance of 3.6845 (6)Å (symmetry code: -x,1 - y, 1 - z); Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of S1/C1–C4 and C8–C13 rings.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by the condensation of 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde (0.01 mol, 1.75 g) with 2-acetylthiophene (0.01 mol, 1.07 ml) in methanol (60 ml) in the presence of a catalytic amount of sodium hydroxide solution (5 ml, 30%). After stirring (6 h), the contents of the flask were poured into ice-cold water (500 ml) and left to stand for 5 h. The resulting crude solid was filtered and dried. Needle colorless single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-Ray structure determination were grown by slow evaporation of the methanol solution at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions with d(C—H) = 0.93Å, Uiso=1.2Ueq(C) for vinylic and aromatic H atoms. The highest residual electron density peak is located at 0.70Å from C10 and the deepest hole is located at 0.51Å from S1.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of (I), showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atomic numbering. Weak intramolecular C—H···O and C—H···Cl interactions are drawn as dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of (I), viewed along the c axis showing the cross-linked chains approximately along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C13H8Cl2OS | F000 = 576 |
| Mr = 283.16 | Dx = 1.533 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4435 reflections |
| a = 9.5701 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–32.5º |
| b = 13.9544 (6) Å | µ = 0.68 mm−1 |
| c = 10.4748 (4) Å | T = 100.0 (1) K |
| β = 118.735 (3)º | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1226.59 (9) Å3 | 0.58 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX2 CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4435 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3831 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.031 |
| Detector resolution: 8.33 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 32.5º |
| T = 100.0(1) K | θmin = 2.4º |
| ω scans | h = −14→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.695, Tmax = 0.919 | l = −15→15 |
| 41878 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.082 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0403P)2 + 0.4876P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4435 reflections | Δρmax = 0.60 e Å−3 |
| 162 parameters | Δρmin = −0.28 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Experimental. The low-temperature data was collected with the Oxford Cyrosystem Cobra low-temperature attachment. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | −0.05796 (3) | 0.558919 (18) | 0.18442 (3) | 0.01990 (7) | |
| Cl2 | −0.34903 (3) | 0.43921 (2) | 0.48214 (3) | 0.02181 (7) | |
| S1 | 0.55248 (3) | 0.18039 (2) | 0.20853 (3) | 0.02097 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.30678 (11) | 0.32994 (6) | 0.13125 (9) | 0.02122 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.64865 (14) | 0.08866 (9) | 0.32542 (13) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| H1A | 0.7245 | 0.0504 | 0.3162 | 0.042 (5)* | |
| C2 | 0.60409 (14) | 0.07946 (9) | 0.43128 (13) | 0.0222 (2) | |
| H2A | 0.6448 | 0.0331 | 0.5039 | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C3 | 0.48923 (13) | 0.14851 (8) | 0.41751 (12) | 0.01776 (19) | |
| H3A | 0.4462 | 0.1531 | 0.4802 | 0.025 (4)* | |
| C4 | 0.44866 (12) | 0.20851 (7) | 0.29930 (11) | 0.01483 (17) | |
| C5 | 0.32870 (12) | 0.28469 (7) | 0.24030 (11) | 0.01551 (18) | |
| C6 | 0.23178 (13) | 0.30140 (8) | 0.31373 (11) | 0.01662 (18) | |
| H6A | 0.2532 | 0.2670 | 0.3972 | 0.033 (4)* | |
| C7 | 0.11366 (13) | 0.36566 (7) | 0.26054 (12) | 0.01658 (18) | |
| H7A | 0.0995 | 0.4012 | 0.1800 | 0.022 (4)* | |
| C8 | 0.00490 (12) | 0.38454 (7) | 0.31897 (11) | 0.01508 (17) | |
| C9 | −0.01998 (13) | 0.31711 (8) | 0.40561 (12) | 0.01814 (19) | |
| H9A | 0.0373 | 0.2601 | 0.4292 | 0.032 (4)* | |
| C10 | −0.12712 (13) | 0.33288 (8) | 0.45700 (12) | 0.01822 (19) | |
| H10A | −0.1418 | 0.2872 | 0.5141 | 0.030 (4)* | |
| C11 | −0.21239 (12) | 0.41837 (8) | 0.42150 (12) | 0.01651 (18) | |
| C12 | −0.19070 (12) | 0.48797 (7) | 0.33822 (11) | 0.01626 (18) | |
| H12A | −0.2472 | 0.5453 | 0.3164 | 0.023 (4)* | |
| C13 | −0.08277 (12) | 0.47006 (7) | 0.28828 (11) | 0.01535 (18) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.02152 (13) | 0.01786 (12) | 0.02316 (13) | 0.00278 (8) | 0.01301 (10) | 0.00674 (9) |
| Cl2 | 0.02120 (13) | 0.02533 (13) | 0.02547 (14) | 0.00247 (9) | 0.01647 (11) | 0.00112 (10) |
| S1 | 0.02269 (14) | 0.02431 (14) | 0.02117 (13) | 0.00481 (10) | 0.01474 (11) | 0.00138 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0269 (4) | 0.0218 (4) | 0.0201 (4) | 0.0047 (3) | 0.0155 (3) | 0.0046 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0255 (5) | 0.0248 (5) | 0.0084 (4) | 0.0113 (4) | 0.0015 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0049 (4) | 0.0092 (4) | 0.0019 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0195 (5) | 0.0187 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0100 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0159 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0096 (4) | −0.0013 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0152 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | −0.0004 (3) | 0.0093 (4) | −0.0019 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0191 (5) | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0159 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0107 (4) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0191 (4) | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0178 (4) | 0.0001 (3) | 0.0114 (4) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0147 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0005 (3) | 0.0084 (4) | −0.0001 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0211 (5) | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0216 (5) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0127 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0215 (5) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0005 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0016 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0187 (4) | 0.0170 (4) | 0.0000 (3) | 0.0097 (4) | −0.0015 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | 0.0018 (3) | 0.0081 (4) | 0.0006 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0158 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | −0.0003 (3) | 0.0075 (3) | 0.0016 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C13 | 1.7396 (10) | C6—C7 | 1.3367 (15) |
| Cl2—C11 | 1.7310 (11) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| S1—C1 | 1.7033 (12) | C7—C8 | 1.4629 (14) |
| S1—C4 | 1.7186 (10) | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| O1—C5 | 1.2317 (13) | C8—C13 | 1.4042 (14) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3720 (17) | C8—C9 | 1.4048 (15) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9425 | C9—C10 | 1.3858 (16) |
| C2—C3 | 1.4160 (16) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.3912 (15) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3865 (15) | C10—H10A | 0.9301 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9302 | C11—C12 | 1.3862 (15) |
| C4—C5 | 1.4656 (14) | C12—C13 | 1.3866 (15) |
| C5—C6 | 1.4806 (14) | C12—H12A | 0.9299 |
| C1—S1—C4 | 91.72 (6) | C6—C7—H7A | 117.4 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 112.39 (9) | C8—C7—H7A | 117.4 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 125.7 | C13—C8—C9 | 116.67 (9) |
| S1—C1—H1A | 121.9 | C13—C8—C7 | 121.62 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.43 (11) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.69 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 123.8 | C10—C9—C8 | 122.10 (10) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 123.8 | C10—C9—H9A | 119.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 111.85 (10) | C8—C9—H9A | 118.9 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 124.1 | C9—C10—C11 | 118.74 (10) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 124.1 | C9—C10—H10A | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 129.85 (9) | C11—C10—H10A | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—S1 | 111.60 (8) | C12—C11—C10 | 121.53 (10) |
| C5—C4—S1 | 118.44 (8) | C12—C11—Cl2 | 118.77 (8) |
| O1—C5—C4 | 120.84 (9) | C10—C11—Cl2 | 119.70 (8) |
| O1—C5—C6 | 122.07 (10) | C11—C12—C13 | 118.37 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 117.04 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 120.8 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.30 (10) | C13—C12—H12A | 120.8 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.9 | C12—C13—C8 | 122.57 (9) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.8 | C12—C13—Cl1 | 117.25 (8) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 125.15 (10) | C8—C13—Cl1 | 120.18 (8) |
| C4—S1—C1—C2 | −0.23 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −21.13 (17) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.06 (14) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.92 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.42 (15) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −177.58 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 175.55 (11) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.07 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—S1 | −0.59 (12) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.93 (17) |
| C1—S1—C4—C3 | 0.47 (9) | C9—C10—C11—Cl2 | 179.10 (9) |
| C1—S1—C4—C5 | −176.16 (9) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.99 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—O1 | −178.54 (11) | Cl2—C11—C12—C13 | −179.04 (8) |
| S1—C4—C5—O1 | −2.62 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.07 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.06 (16) | C11—C12—C13—Cl1 | −179.86 (8) |
| S1—C4—C5—C6 | 174.85 (7) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −0.86 (15) |
| O1—C5—C6—C7 | 1.53 (16) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 177.65 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −175.91 (10) | C9—C8—C13—Cl1 | 178.93 (8) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 176.55 (10) | C7—C8—C13—Cl1 | −2.57 (14) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | 160.45 (11) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.4512 (17) | 175 |
| C7—H7A···Cl1 | 0.93 | 2.68 | 3.0573 (11) | 105 |
| C7—H7A···O1 | 0.93 | 2.48 | 2.8116 (17) | 101 |
| C10—H10A···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 3.33 | 3.8233 (13) | 115 |
| C12—H12A···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.87 | 3.6907 (13) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y, z; (iii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WW2127).
References
- Agrinskaya, N. V., Lukoshkin, V. A., Kudryavtsev, V. V., Nosova, G. I., Solovskaya, N. A. & Yakimanski, A. V. (1999). Phys. Solid State 41, 1914–1917.
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl 34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chopra, D., Mohan, T. P., Vishalakshi, B. & Guru Row, T. N. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o704–o710. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Chantrapromma, S., Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008b). Acta Cryst. E64, o1720–o1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fun, H.-K., Jebas, S. R., Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008a). Acta Cryst. E64, o1510–o1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y., Hayashi, A., Kimura, Y. & Nakayama, M. (1991). J. Cryst. Growth 108, 688–698.
- Gu, B., Ji, W. & Huang, X.-Q. (2008a). Appl. Optics 47, 1187–1192. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gu, B., Ji, W., Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008b). J. Appl. Phys 103, 103511-1–103511-6.
- Gu, B., Ji, W., Patil, P. S., Dharmaprakash, S. M. & Wang, H. T. (2008c). Appl. Phys. Lett 92, 091118-1–091118-3.
- Patil, P. S., Dharmaprakash, S. M., Ramakrishna, K., Fun, H.-K., Sai Santosh Kumar, R. & Rao, D. N. (2007a). J. Cryst. Growth 303, 520–524.
- Patil, P. S., Fun, H.-K., Chantrapromma, S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o2497–o2498.
- Patil, P. S., Teh, J. B.-J., Fun, H.-K., Razak, I. A. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2007c). Acta Cryst. E63, o2122–o2123.
- Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Ashalatha, B. V., Indira, J. & Lobo, K. G. (2006). J. Cryst. Growth 295, 54–59.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Lu, C.-R. & Zhang, D.-C. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o696–o698. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808026524/ww2127sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808026524/ww2127Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




