Abstract
The title dinuclear platinum compound, [Pt2Cl4(C22H16N4)(C2H6S)2], with a long bridging bipyridyl-type ligand, is centrosymmetric and the PtII cation shows a slightly distorted square-planar coordination geometry. The Cl ligands are trans to each other, with a Cl—Pt—Cl angle of 178.83 (8)°. The pyridine ring forms a dihedral angle of 48.8 (2)° with the planar PtCl2SN unit. Within the molecule, the distance between Pt atoms is 20.262 (5) Å and the N⋯N separation between the terminal pyridyl rings is 16.23 (1)Å.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Barnett & Champness (2003 ▶); Costa et al. (2003 ▶); Han & Lee (2004 ▶); Hill et al. (1998 ▶); Huh et al. (2008 ▶) and references therein; Kinnunen et al. (2002 ▶); Leininger et al. (2000 ▶); Min et al. (2006 ▶); Kinnunen et al. (2002 ▶); Leininger et al. (2000 ▶); Min et al. (2006 ▶).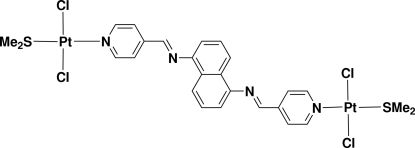
Experimental
Crystal data
[Pt2Cl4(C22H16N4)(C2H6S)2]
M r = 992.62
Triclinic,

a = 5.172 (2) Å
b = 7.2482 (11) Å
c = 20.728 (3) Å
α = 91.596 (12)°
β = 91.974 (19)°
γ = 97.804 (17)°
V = 769.0 (3) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 9.59 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.44 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Siemens P4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.115, T max = 0.383
3026 measured reflections
2696 independent reflections
2447 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.042
3 standard reflections every 97 reflections intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.036
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.05
2696 reflections
172 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.73 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.96 e Å−3
Data collection: XSCANS (Siemens, 1995 ▶); cell refinement: XSCANS; data reduction: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL; program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808024914/gk2157sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808024914/gk2157Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Pt1—N1 | 2.057 (6) |
| Pt1—S1 | 2.285 (2) |
| Pt1—Cl2 | 2.301 (2) |
| Pt1—Cl1 | 2.303 (2) |
| N1—Pt1—S1 | 175.98 (18) |
| N1—Pt1—Cl2 | 88.55 (19) |
| S1—Pt1—Cl2 | 95.31 (8) |
| N1—Pt1—Cl1 | 90.40 (19) |
| S1—Pt1—Cl1 | 85.74 (8) |
| Cl2—Pt1—Cl1 | 178.83 (8) |
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The N-donor linking (exo N-donor bidentate) ligands such as pyrazine, 4,4'-bipyridine, 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethylene, and 1,2-bis(4-pyridyl)ethane are widely used for the synthesis of discrete dinuclear, polynuclear, and coordination network compounds (Leininger et al., 2000; Kinnunen et al., 2002; Costa et al., 2003; Barnett & Champness, 2003). We also reported dinuclear discrete rods, tetranuclear rectangles, and one-dimensional coordination networks of Cp*Rh(III) compounds by employing such ligands, where Cp* is 1,2,3,4,5-pentamethylcyclopentadiene (Han & Lee, 2004). Recently, we reported several novel long bipyridyl-type linking ligands including ligand L and their coordination polymers of several transition metals (Min et al., 2006; Huh et al., 2008). As a continuation of our research, we decided to use ligand L to prepare novel platinum polynuclear or coordination network compounds. The layer diffusion (dichloromethane–benzene) of [Pt(SMe2)2Cl2] with an equimolar amount L with dichloromethane and benzene as solvents gave an unexpected dinuclear [Pt2L(SMe2)2Cl4] compound. Moreover, the reaction involving 2 equiv of L also gave the same product. The molecular structure of the title compound is shown Fig. 1. The complex molecule is centrosymmetric with the PtII ion exhibiting a slightly distorted square-planar coordination geometry. Each Pt atom is coordinated by two trans chloro ligands, one sulfur atom of SMe2, and pyridine N atom of ligand L. The PtCl2SN core is essentially planar with the highest displacement of 0.012 (2) Å for the Pt atom. Within the molecule, the distance between Pt atoms is 20.262 (5) Å, and the N···N separation between the terminal pyridyl rings of 16.23 (1) Å is somewhat longer than that of the free ligand (16.0 Å; Min et al., 2006).
Experimental
A dichloromethane solution (7 ml) of L (40 mg, 0.136 mmol) was layered onto the top of a benzene solution (7 ml) of Pt(SMe2)2Cl2 (50 mg, 0.130 mmol) (Hill et al., 1998). Yellow crystals of [Pt2L(SMe2)2Cl4] formed in 5 days (53 mg, 0.053 mmol, 39%). The title compound is insoluble in common organic solvents. Anal. Calcd for C26H28N4S2Cl2Pt2 (Mr = 992.62): C 31.46; H 2.84; N, 5.65; S 6.46. Found: C 31.32; H 2.87; N 6.03; S 6.65. IR (KBr, ν, cm-1): 1620 (s), 1590 (s), 1402 (s), 1378 (m), 1308 (s), 1197 (m), 1036 (m), 983 (m), 811 (m), 659 (m).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93-96 Å and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H)=1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. H atoms are omitted for clarity. Unlabeled atoms are related to labeled atoms by the symmetry operation i = -x + 1, -y + 1, -z + 1.
Crystal data
| [Pt2Cl4(C22H16N4)(C2H6S1)2] | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 992.62 | F000 = 468 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 2.143 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.172 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 21 reflections |
| b = 7.2482 (11) Å | θ = 4.7–12.5º |
| c = 20.728 (3) Å | µ = 9.59 mm−1 |
| α = 91.596 (12)º | T = 293 (2) K |
| β = 91.974 (19)º | Block, yellow |
| γ = 97.804 (17)º | 0.44 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 769.0 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Siemens P4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.042 |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | θmax = 25.1º |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmin = 2.0º |
| T = 293(2) K | h = −6→0 |
| ω scans | k = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan(North et al., 1968) | l = −24→24 |
| Tmin = 0.115, Tmax = 0.383 | 3 standard reflections |
| 3026 measured reflections | every 97 reflections |
| 2696 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
| 2447 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0492P)2 + 1.8521P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2696 reflections | Δρmax = 0.73 e Å−3 |
| 172 parameters | Δρmin = −0.96 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pt1 | −0.76885 (6) | 0.00003 (4) | 0.835419 (14) | 0.05066 (13) | |
| Cl2 | −0.8555 (5) | −0.2416 (3) | 0.76008 (12) | 0.0684 (5) | |
| Cl1 | −0.6804 (6) | 0.2461 (3) | 0.90917 (11) | 0.0783 (7) | |
| S1 | −1.0252 (5) | −0.1418 (3) | 0.91231 (11) | 0.0646 (5) | |
| N1 | −0.5382 (12) | 0.1450 (8) | 0.7698 (3) | 0.0477 (13) | |
| N2 | 0.1135 (13) | 0.4034 (9) | 0.6076 (3) | 0.0539 (15) | |
| C1 | −0.3549 (16) | 0.0685 (10) | 0.7380 (4) | 0.0536 (18) | |
| H1 | −0.3308 | −0.0536 | 0.7461 | 0.064* | |
| C2 | −0.2008 (16) | 0.1659 (11) | 0.6934 (4) | 0.0545 (18) | |
| H2 | −0.0744 | 0.1100 | 0.6723 | 0.065* | |
| C3 | −0.2373 (16) | 0.3491 (11) | 0.6804 (3) | 0.0515 (17) | |
| C4 | −0.4212 (15) | 0.4285 (10) | 0.7142 (4) | 0.0509 (17) | |
| H4 | −0.4454 | 0.5514 | 0.7075 | 0.061* | |
| C5 | −0.5705 (15) | 0.3241 (11) | 0.7584 (4) | 0.0505 (16) | |
| H5 | −0.6954 | 0.3784 | 0.7807 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | −0.0727 (15) | 0.4623 (11) | 0.6348 (3) | 0.0508 (17) | |
| H6 | −0.1095 | 0.5813 | 0.6260 | 0.061* | |
| C7 | 0.2847 (15) | 0.5245 (11) | 0.5700 (4) | 0.0515 (17) | |
| C8 | 0.3580 (18) | 0.7091 (12) | 0.5875 (4) | 0.060 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.2830 | 0.7612 | 0.6226 | 0.072* | |
| C9 | 0.5474 (18) | 0.8204 (12) | 0.5523 (4) | 0.063 (2) | |
| H9 | 0.5932 | 0.9456 | 0.5641 | 0.076* | |
| C10 | 0.3377 (16) | 0.2520 (11) | 0.4981 (4) | 0.0577 (19) | |
| H10 | 0.2125 | 0.1766 | 0.5201 | 0.069* | |
| C11 | 0.4057 (15) | 0.4428 (11) | 0.5180 (3) | 0.0491 (16) | |
| C12 | −1.208 (3) | −0.3570 (17) | 0.8815 (7) | 0.104 (4) | |
| H12A | −1.3382 | −0.3308 | 0.8502 | 0.156* | |
| H12B | −1.2914 | −0.4229 | 0.9164 | 0.156* | |
| H12C | −1.0920 | −0.4321 | 0.8615 | 0.156* | |
| C13 | −0.803 (2) | −0.2317 (17) | 0.9678 (5) | 0.089 (3) | |
| H13A | −0.6900 | −0.1301 | 0.9888 | 0.134* | |
| H13B | −0.7003 | −0.3103 | 0.9447 | 0.134* | |
| H13C | −0.9001 | −0.3027 | 0.9996 | 0.134* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pt1 | 0.0554 (2) | 0.04379 (18) | 0.05348 (19) | 0.00442 (12) | 0.01683 (13) | 0.00739 (12) |
| Cl2 | 0.0754 (14) | 0.0514 (10) | 0.0776 (13) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0253 (11) | −0.0063 (9) |
| Cl1 | 0.1031 (18) | 0.0645 (13) | 0.0607 (12) | −0.0161 (12) | 0.0249 (12) | −0.0036 (10) |
| S1 | 0.0712 (14) | 0.0539 (11) | 0.0696 (13) | 0.0034 (10) | 0.0301 (11) | 0.0115 (9) |
| N1 | 0.043 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.003 (3) | 0.008 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| N2 | 0.051 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.047 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.013 (3) | 0.012 (3) |
| C1 | 0.056 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.063 (4) | 0.004 (3) | 0.020 (4) | 0.012 (3) |
| C2 | 0.052 (4) | 0.058 (4) | 0.057 (4) | 0.016 (3) | 0.017 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C3 | 0.058 (5) | 0.057 (4) | 0.039 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.009 (3) |
| C4 | 0.052 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.055 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.016 (3) |
| C5 | 0.047 (4) | 0.058 (4) | 0.048 (4) | 0.006 (3) | 0.014 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C6 | 0.048 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.011 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
| C7 | 0.052 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.047 (4) | 0.012 (3) | 0.016 (3) | 0.017 (3) |
| C8 | 0.068 (5) | 0.061 (5) | 0.054 (4) | 0.013 (4) | 0.022 (4) | 0.013 (4) |
| C9 | 0.071 (6) | 0.056 (5) | 0.062 (5) | 0.005 (4) | 0.018 (4) | 0.014 (4) |
| C10 | 0.058 (5) | 0.055 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.004 (4) | 0.017 (4) | 0.012 (4) |
| C11 | 0.051 (4) | 0.055 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.010 (3) | 0.011 (3) | 0.016 (3) |
| C12 | 0.107 (9) | 0.083 (7) | 0.112 (9) | −0.034 (7) | 0.030 (8) | 0.018 (7) |
| C13 | 0.104 (9) | 0.101 (8) | 0.066 (6) | 0.016 (7) | 0.022 (6) | 0.026 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Pt1—N1 | 2.057 (6) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| Pt1—S1 | 2.285 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| Pt1—Cl2 | 2.301 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.376 (12) |
| Pt1—Cl1 | 2.303 (2) | C7—C11 | 1.420 (11) |
| S1—C13 | 1.795 (12) | C8—C9 | 1.418 (12) |
| S1—C12 | 1.799 (12) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.344 (10) | C9—C10i | 1.347 (12) |
| N1—C5 | 1.357 (10) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C6 | 1.250 (10) | C10—C9i | 1.347 (12) |
| N2—C7 | 1.427 (9) | C10—C11 | 1.426 (11) |
| C1—C2 | 1.386 (11) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—C11i | 1.435 (14) |
| C2—C3 | 1.398 (11) | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (11) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C6 | 1.484 (10) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (10) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| N1—Pt1—S1 | 175.98 (18) | N2—C6—H6 | 118.8 |
| N1—Pt1—Cl2 | 88.55 (19) | C3—C6—H6 | 118.8 |
| S1—Pt1—Cl2 | 95.31 (8) | C8—C7—C11 | 120.0 (7) |
| N1—Pt1—Cl1 | 90.40 (19) | C8—C7—N2 | 122.0 (7) |
| S1—Pt1—Cl1 | 85.74 (8) | C11—C7—N2 | 117.5 (7) |
| Cl2—Pt1—Cl1 | 178.83 (8) | C7—C8—C9 | 120.2 (8) |
| C13—S1—C12 | 99.7 (7) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| C13—S1—Pt1 | 105.2 (4) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| C12—S1—Pt1 | 111.4 (4) | C10i—C9—C8 | 121.2 (8) |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.8 (6) | C10i—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C1—N1—Pt1 | 122.1 (5) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.4 |
| C5—N1—Pt1 | 119.1 (5) | C9i—C10—C11 | 120.8 (7) |
| C6—N2—C7 | 120.3 (7) | C9i—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.1 (7) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 119.0 | C7—C11—C10 | 122.2 (7) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.0 | C7—C11—C11i | 119.2 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.4 (7) | C10—C11—C11i | 118.5 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | S1—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 | S1—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.4 (7) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C6 | 119.7 (7) | S1—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C6 | 121.8 (7) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (7) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | S1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | S1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 121.6 (7) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 119.2 | S1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.2 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| N2—C6—C3 | 122.4 (7) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2157).
References
- Barnett, S. A. & Champness, N. R. (2003). Coord. Chem. Rev.246, 145–168.
- Costa, P. M. F. J., Mora, M., Calhorda, M. J., Felix, V., Ferreira, P., Drew, M. G. B. & Wadepohl, H. (2003). J. Organomet. Chem.687, 57–68.
- Han, W. S. & Lee, S. W. (2004). Dalton Trans. pp. 1656–1663. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hill, G. S., Irwin, M. J., Levy, C. J., Rendina, L. M. & Puddephatt, R. J. (1998). Inorg. Synth.32, 149–153.
- Huh, S. H., Yun, H. J. & Lee, S. W. (2008). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 361, 2101–2108 .
- Kinnunen, T.-J. J., Haukka, M., Pesonen, E. & Pakkanen, T. A. (2002). J. Organomet. Chem.655, 31–38.
- Leininger, S., Olenyuk, B. & Stang, P. J. (2000). Chem. Rev.100, 853–908. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Min, D., Cho, B.-Y. & Lee, S. W. (2006). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 359, 577–584.
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1995). XSCANS User’s Manual Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808024914/gk2157sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808024914/gk2157Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



