Abstract
The title compound, C15H8O5, also known as nordamnacanthal, was isolated from the Malaysian Morinda citrifolia L. The 20 non-H atoms are coplanar. The structure is stabilized by intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and intermolecular O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming bilayers of molecular tapes with alternating stacking directions along the a axis.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Chan-Blanco et al. (2006 ▶); Ismail (1998 ▶); Ohsawa & Ohba (1993 ▶); Singh et al. (1984 ▶); Whistler (1985 ▶); Wijnsma & Verpoorte (1986 ▶); Zhu et al. (2008 ▶).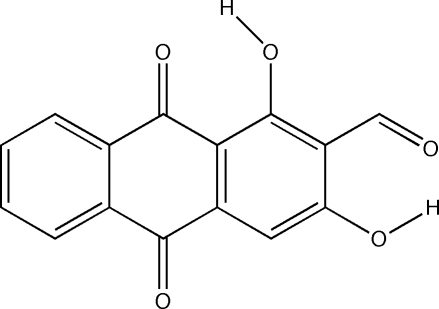
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H8O5
M r = 268.21
Monoclinic,
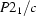
a = 10.547 (2) Å
b = 5.669 (1) Å
c = 20.231 (3) Å
β = 110.62 (4)°
V = 1132.1 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.60 × 0.39 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
14030 measured reflections
2298 independent reflections
1554 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.150
S = 1.06
2296 reflections
181 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Data collection: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶) and COLLECT (Nonius, 1999 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO and COLLECT; data reduction: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and publCIF (Westrip, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808004169/bg2162sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808004169/bg2162Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O2 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.590 (3) | 148 |
| O1—H1⋯O5 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.577 (2) | 146 |
| O1—H1⋯O5i | 0.82 | 2.34 | 2.933 (2) | 130 |
| C4—H4⋯O4ii | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.358 (2) | 166 |
| C10—H10⋯O2iii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.312 (3) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 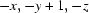 ; (ii)
; (ii) 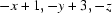 ; (iii)
; (iii) 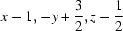 .
.
Acknowledgments
KA thanks the Universiti Teknologi MARA and the Ministry of Science and Technology for financial support, and the Institut de Chimie des Substances Naturelles for research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
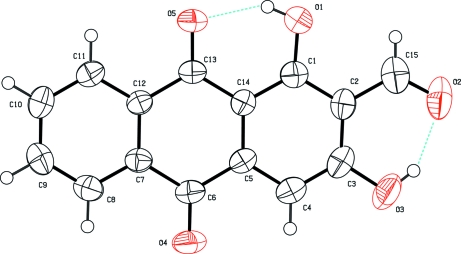
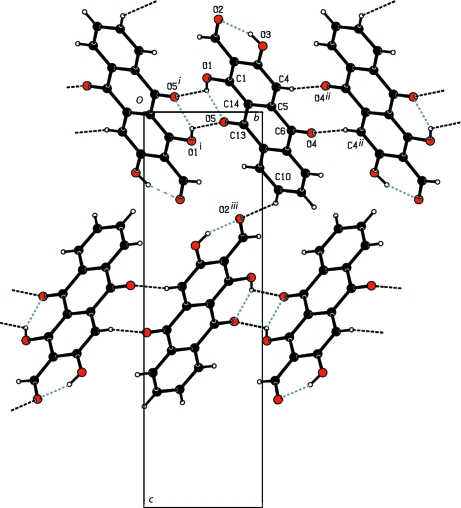
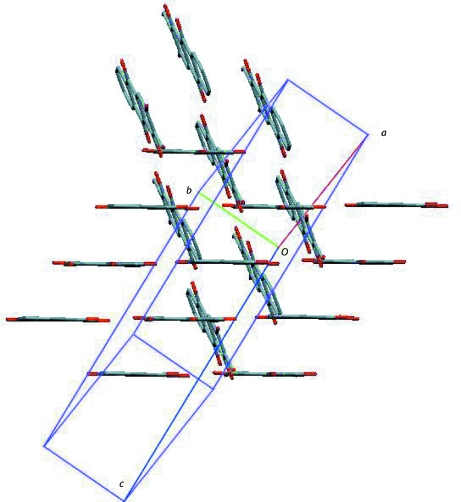
Morinda citrifolia Linn. (Noni), has been one of the most used traditional folk medicinal plants in Polynesia for over 2000 years (Whistler,1985). It has been reported to have a broad range of therapeutic and nutritional properties (Chan-Blanco et al.,2006) including antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, antitumor, analgesic, hypotensive, anti-inflammatory and immune enhancing effects (Singh et al., 1984). Nordamnacanthal, damnacanthal and morindone (Ismail, 1998; Wijnsma & Verpoorte, 1986) have been isolated from the Malaysian Morinda citrifolia Linn. The crystal structure of damnacanthal having been reported by Ohsawa & Ohba (1993), we present in this communication the crystal structure of nordamnacanthal (I). (Fig. 1) shows its molecular structure. The C—C bond lengths in the anthraquinone ring range from 1.377 (3) Å to 1.484 (3) Å, the carbonyl bond distances from 1.220 (2) Å to 1.237 (2) Å and the two hydroxyl bond distances are 1.326 (2) Å and 1.349 (2) Å; all are comparable to those observed in similar structures (Ohsawa & Ohba, 1993; Zhu et al., 2008). All 20 non-H atoms of (I) are essentially coplanar, their mean deviation from the least-squares molecular plane being 0.028 Å and the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings being 1.27 (10)°. The molecule features two intramolecular O—H···O hydrogen bonds, with O3···O2 distance of 2.590 (3) Å and O1···O5 distance of 2.577 (2) Å. Additionally, atom O1 is also engaged into an intermolecular hydrogen bond with atom O5, viz. O1—H1···O5i [symmetry code:(i) -x, 1 - y, -z] leading to the formation of a coplanar centrosymmetric dimer via the key {H—O1—C1—C14—C13—O5}2 synthon, R22(12). Adjacent dimers extend through synthon R22(10) of weak C4—H4···O4ii [symmetry code:(ii) 1 - x, 3 - y, -z] hydrogen bond to form molecular tapes running parallel to the [120] and [120] directions (Fig. 2). The dihedral angle between the two molecular tape orientations is 66.03° and an additional weak C10—H10···O4iii [symmetry code:(ii) -1 + x, 3/2 - y, -1/2 + z] hydrogen bond links the tapes along the c axis. The tapes are stacked along the a axis, forming two kinds of layers in which molecules related by an inversion center stack with an interplanar spacing of 3.255 (4) Å and a centroid offset of ca 3.5 Å (Fig. 3).
Experimental
Morinda citrifolia used in this study was collected from kg. Tanjung Keramat, Langkap, Perak. The roots were harvested, washed, chopped into small pieces and then dried at room temperature for one week. The dried sample was then ground to small size using grinder. The ground roots (1.5 kg) were soaked at room temperature in dichloromethane for 48 h. The solvent was then removed by filtration and fresh solvent added to the plant material. The extraction was repeated three times. The combined filtrate was evaporated under reduced pressure to give brown coloured residue (35.6 g). The crude extract was fractionated using Medium Pressure Liquid Chromatography (MPLC) system fitted with Buchi Pump Module C-601. The sample (10 g) was introduced dry after being pre-absorbed onto acid-washed silica gel (10 g) in two portions. The column (150 mm x 40 mm) was packed with 90 g acid-washed silica gel (Merck 7734) and eluted gradiently with petroleum ether, chloroform and chloroform enriched with increasing percentages of methanol (1%, 2% and 5%). Seven combined fractions were collected based on thin layer chromatography (TLC) pattern (labeled A, B, C, D, E, F, and G).
Nordamnacanthal (1.65 g) were isolated from fraction A after column chromatography. The fraction was re-chromatographed using small column (400 mm x 20 mm) packed with 2% acid-washed silica gel (Merck 9385) eluted gradiently with petroleum ether and chloroform. The first orange band eluted out from the column was collected in small vials and inspected using analytical TLC developed in PE:CHCl3 (4:6) showing a single spot of a purified compound. Recrystallization from hot CHCl3 gave bright orange crystals.
Refinement
All H atoms were located in difference maps but then were treated as riding in geometrically positions, with O—H = 0.82 Å, and C—H = 0.93 Å (sp2) and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(carrier).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Perspective view of the title compound with the atom numbering; displacement ellipsoids are at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular O—H···O interactions are shown as dotted lines.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure showing non-parallel molecular slabs forming herringbone pattern along a. (Intra-)Inter-molecular hydrogen bonds are indicated by (dotted) dashed lines. Symmetry codes: as in Table 1.
Fig. 3.
The crystal packing showing the two orientations taken by the stacking of molecular tapes. Note the offset between successive layers.
Crystal data
| C15H8O5 | F000 = 552 |
| Mr = 268.21 | Dx = 1.574 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71070 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 10451 reflections |
| a = 10.547 (2) Å | θ = 0.4–26.4º |
| b = 5.669 (1) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| c = 20.231 (3) Å | T = 293 (2) K |
| β = 110.62 (4)º | Prism, orange |
| V = 1132.1 (5) Å3 | 0.60 × 0.39 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 1554 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.029 |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmax = 26.4º |
| T = 293(2) K | θmin = 2.1º |
| φ and ω scans | h = 0→13 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −7→0 |
| 14030 measured reflections | l = −25→22 |
| 2298 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.150 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0705P)2 + 0.3487P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2296 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 181 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections (2298) except two reflections with Delta(F2)/e.s.d. greater than 9 (2296). The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O4 | 0.32777 (16) | 1.4401 (3) | −0.05914 (8) | 0.0669 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.02849 (14) | 0.7077 (2) | −0.03142 (7) | 0.0531 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.22406 (15) | 0.5649 (2) | 0.07880 (7) | 0.0525 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.1487 | 0.5610 | 0.0479 | 0.063* | |
| O3 | 0.62014 (15) | 1.0321 (3) | 0.15870 (9) | 0.0746 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.6408 | 0.9283 | 0.1889 | 0.090* | |
| O2 | 0.58762 (18) | 0.6610 (3) | 0.22568 (9) | 0.0811 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.2604 (2) | 1.2727 (3) | −0.05264 (10) | 0.0437 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.12238 (19) | 1.2323 (3) | −0.10446 (9) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.04523 (18) | 1.0390 (3) | −0.09796 (9) | 0.0364 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.09986 (19) | 0.8728 (3) | −0.03790 (10) | 0.0388 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.23549 (18) | 0.9106 (3) | 0.01290 (10) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.31419 (18) | 1.1053 (3) | 0.00715 (10) | 0.0396 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.4429 (2) | 1.1451 (4) | 0.05601 (11) | 0.0493 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.4935 | 1.2742 | 0.0513 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.4949 (2) | 0.9898 (4) | 0.11180 (11) | 0.0521 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.4211 (2) | 0.7925 (4) | 0.11979 (10) | 0.0461 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.2905 (2) | 0.7533 (3) | 0.06963 (10) | 0.0425 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.4762 (3) | 0.6333 (4) | 0.17886 (13) | 0.0652 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.4247 | 0.5031 | 0.1817 | 0.078* | |
| C11 | −0.0846 (2) | 1.0056 (4) | −0.14710 (10) | 0.0446 (5) | |
| H11 | −0.1359 | 0.8766 | −0.1430 | 0.054* | |
| C10 | −0.1371 (2) | 1.1638 (4) | −0.20178 (10) | 0.0509 (5) | |
| H10 | −0.2239 | 1.1414 | −0.2346 | 0.061* | |
| C9 | −0.0613 (2) | 1.3547 (4) | −0.20791 (11) | 0.0539 (6) | |
| H9 | −0.0975 | 1.4613 | −0.2447 | 0.065* | |
| C8 | 0.0679 (2) | 1.3894 (4) | −0.15996 (10) | 0.0486 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.1185 | 1.5183 | −0.1648 | 0.058* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O4 | 0.0621 (10) | 0.0626 (10) | 0.0708 (11) | −0.0288 (8) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0066 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0512 (9) | 0.0466 (8) | 0.0591 (9) | −0.0150 (7) | 0.0163 (7) | 0.0068 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0511 (9) | 0.0471 (8) | 0.0565 (9) | −0.0020 (7) | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0087 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0866 (12) | 0.0726 (11) | −0.0075 (8) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0060 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0657 (11) | 0.0934 (13) | 0.0606 (11) | 0.0183 (10) | −0.0071 (9) | 0.0054 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0411 (11) | 0.0474 (11) | −0.0107 (9) | 0.0201 (9) | −0.0052 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0434 (11) | 0.0367 (10) | 0.0381 (10) | −0.0049 (8) | 0.0167 (9) | −0.0044 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0367 (10) | 0.0360 (10) | 0.0374 (10) | −0.0028 (8) | 0.0142 (8) | −0.0048 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0355 (10) | 0.0421 (11) | −0.0054 (8) | 0.0187 (9) | −0.0036 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0370 (10) | 0.0388 (10) | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0138 (8) | −0.0027 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0359 (10) | 0.0413 (10) | 0.0426 (11) | −0.0048 (8) | 0.0152 (8) | −0.0075 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0496 (12) | 0.0536 (13) | −0.0085 (9) | 0.0176 (10) | −0.0075 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0386 (11) | 0.0605 (13) | 0.0511 (13) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0081 (10) | −0.0113 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0427 (11) | 0.0504 (12) | 0.0423 (11) | 0.0075 (9) | 0.0112 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0432 (11) | 0.0404 (11) | 0.0474 (11) | 0.0016 (8) | 0.0202 (9) | −0.0033 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0664 (15) | 0.0655 (15) | 0.0561 (14) | 0.0136 (12) | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0028 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0413 (11) | 0.0467 (11) | 0.0457 (11) | −0.0068 (9) | 0.0149 (9) | −0.0065 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0433 (11) | 0.0603 (13) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0075 (9) | −0.0059 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0634 (14) | 0.0528 (13) | 0.0422 (12) | 0.0073 (11) | 0.0146 (11) | 0.0072 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0578 (13) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0471 (12) | −0.0066 (9) | 0.0209 (11) | 0.0014 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O4—C6 | 1.220 (2) | C14—C5 | 1.410 (3) |
| O5—C13 | 1.237 (2) | C5—C4 | 1.388 (3) |
| O1—C1 | 1.326 (2) | C4—C3 | 1.383 (3) |
| O1—H1 | 0.8200 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| O3—C3 | 1.349 (3) | C3—C2 | 1.404 (3) |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C2—C1 | 1.411 (3) |
| O2—C15 | 1.233 (3) | C2—C15 | 1.446 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.482 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C5 | 1.484 (3) | C11—C10 | 1.380 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.389 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C12 | 1.399 (2) | C10—C9 | 1.377 (3) |
| C12—C11 | 1.393 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C13 | 1.484 (3) | C9—C8 | 1.380 (3) |
| C13—C14 | 1.454 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C14—C1 | 1.407 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—O1—H1 | 109.5 | O3—C3—C2 | 120.4 (2) |
| C3—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C4—C3—C2 | 121.61 (18) |
| O4—C6—C7 | 120.56 (18) | C3—C2—C1 | 118.88 (18) |
| O4—C6—C5 | 121.01 (18) | C3—C2—C15 | 121.0 (2) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 118.43 (16) | C1—C2—C15 | 120.1 (2) |
| C8—C7—C12 | 119.32 (18) | O1—C1—C14 | 122.54 (18) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.77 (17) | O1—C1—C2 | 117.17 (18) |
| C12—C7—C6 | 120.91 (17) | C14—C1—C2 | 120.29 (18) |
| C11—C12—C7 | 119.84 (17) | O2—C15—C2 | 123.5 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.92 (16) | O2—C15—H15 | 118.2 |
| C7—C12—C13 | 120.23 (16) | C2—C15—H15 | 118.2 |
| O5—C13—C14 | 121.38 (17) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.01 (19) |
| O5—C13—C12 | 119.46 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 119.15 (16) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 |
| C1—C14—C5 | 118.53 (17) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.08 (19) |
| C1—C14—C13 | 120.26 (17) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C5—C14—C13 | 121.21 (17) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—C14 | 121.66 (18) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 118.30 (17) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 |
| C14—C5—C6 | 120.04 (17) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.03 (19) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.12 (19) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.9 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 118.0 (2) | ||
| O4—C6—C7—C8 | −1.6 (3) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −179.58 (18) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 178.31 (17) | C5—C4—C3—O3 | −179.91 (17) |
| O4—C6—C7—C12 | 179.08 (18) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | 0.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | −1.0 (3) | O3—C3—C2—C1 | −179.82 (18) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.3 (3) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −0.3 (3) |
| C6—C7—C12—C11 | 179.58 (17) | O3—C3—C2—C15 | 1.2 (3) |
| C8—C7—C12—C13 | −178.19 (17) | C4—C3—C2—C15 | −179.25 (19) |
| C6—C7—C12—C13 | 1.1 (3) | C5—C14—C1—O1 | −179.51 (17) |
| C11—C12—C13—O5 | −1.1 (3) | C13—C14—C1—O1 | 1.1 (3) |
| C7—C12—C13—O5 | 177.34 (17) | C5—C14—C1—C2 | 0.7 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −179.93 (16) | C13—C14—C1—C2 | −178.70 (17) |
| C7—C12—C13—C14 | −1.5 (3) | C3—C2—C1—O1 | 179.83 (17) |
| O5—C13—C14—C1 | 2.3 (3) | C15—C2—C1—O1 | −1.2 (3) |
| C12—C13—C14—C1 | −178.89 (16) | C3—C2—C1—C14 | −0.3 (3) |
| O5—C13—C14—C5 | −177.04 (18) | C15—C2—C1—C14 | 178.65 (18) |
| C12—C13—C14—C5 | 1.8 (3) | C3—C2—C15—O2 | 1.2 (4) |
| C1—C14—C5—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C1—C2—C15—O2 | −177.7 (2) |
| C13—C14—C5—C4 | 178.95 (17) | C7—C12—C11—C10 | −0.4 (3) |
| C1—C14—C5—C6 | 178.98 (16) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | 178.07 (17) |
| C13—C14—C5—C6 | −1.7 (3) | C12—C11—C10—C9 | 0.0 (3) |
| O4—C6—C5—C4 | 0.6 (3) | C11—C10—C9—C8 | 0.4 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5—C4 | −179.34 (17) | C10—C9—C8—C7 | −0.5 (3) |
| O4—C6—C5—C14 | −178.84 (19) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.2 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5—C14 | 1.3 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −179.14 (18) |
| C14—C5—C4—C3 | −0.2 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O2 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.590 (3) | 148 |
| O1—H1···O5 | 0.82 | 1.86 | 2.577 (2) | 146 |
| O1—H1···O5i | 0.82 | 2.34 | 2.933 (2) | 130 |
| C4—H4···O4ii | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.358 (2) | 166 |
| C10—H10···O2iii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.312 (3) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x+1, −y+3, −z; (iii) x−1, −y+3/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BG2162).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Chan-Blanco, Y., Vaillant, F., Perez, A. M., Reynes, M., Brillonet, J. M. & Brat, P. (2006). J. Food Compos. Anal.19, 645–654.
- Ismail, N. H. (1998). PhD thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst.39, 453–457.
- Nonius. (1999). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Ohsawa, Y. & Ohba, S. (1993). Acta Cryst. C49, 2149–2151.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y., Ikahihifo, T., Pamive, M. & Slatter, C. (1984). J. Ethnopharmacol.12, 305–325. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Westrip, S. P. (2008). publCIF. In preparation.
- Whistler, W. A. (1985). J. Ethnopharmacol.13, 239–280. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wijnsma, R. & Verpoorte, R. (1986). Anthraquinones Rubiaceae in Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products, edited by W. Herz, H. Griesebach, G. W. Kirby & C. H. Tamn, pp. 79–149. New York: Springer-Verlag.
- Zhu, L.-C., Zhao, Z.-G. & Yu, S.-J. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808004169/bg2162sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808004169/bg2162Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report