Abstract
The title compound, C7H15N3P+·BF4 − or [PTA-Me][BF4], is the N-methylated derivative of the well known water-soluble aminophosphine 1,3,5-triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA). The asymmetric unit consists of a cage-like cation [PTA-Me]+ and a disordered tetrafluoroborate anion; two F atoms are disordered equally over two sites. A network of weak intermolecular C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds results in a three-dimensional supramolecular assembly.
Related literature
For general background, see: Kirillov et al. (2007 ▶); Smoleński & Pombeiro (2008 ▶). For a comprehensive review of PTA chemistry, see: Phillips et al. (2004 ▶). For the synthesis of PTA and [PTA-Me]I, see: Daigle et al. (1974 ▶); Daigle (1998 ▶). For related organic structures, see: Jogun et al. (1978 ▶); Forward et al. (1996 ▶); Otto et al. (2005 ▶); Kirillov et al. (2008 ▶). For related metal–organic structures, see: Kovacs et al. (2004 ▶); Smoleński et al. (2003 ▶); Pruchnik et al. (1999 ▶).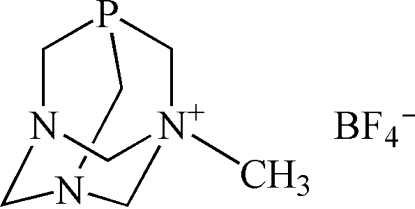
Experimental
Crystal data
C7H15N3P+·BF4 −
M r = 259.00
Orthorhombic,
a = 11.994 (2) Å
b = 11.6933 (18) Å
c = 15.569 (2) Å
V = 2183.5 (6) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.28 mm−1
T = 150 (2) K
0.16 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.956, T max = 0.972
10402 measured reflections
1948 independent reflections
1391 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.061
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.045
wR(F 2) = 0.121
S = 1.05
1948 reflections
164 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808003401/hb2695sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808003401/hb2695Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2A⋯F2i | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.438 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5A⋯F4ii | 0.99 | 2.35 | 3.314 (3) | 166 |
| C6—H6B⋯F4 | 0.99 | 2.46 | 3.364 (3) | 152 |
| C11—H11B⋯F2iii | 0.98 | 2.43 | 3.350 (4) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 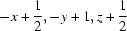 ; (ii)
; (ii) 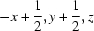 ; (iii)
; (iii) 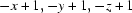 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) and its POCI 2010 programme (FEDER funded).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Being interested in the coordination chemistry of aminophosphine 1,3,5-triaza-7-phospha-adamantane (PTA) and related ligands (Kirillov et al., 2007; Smoleński & Pombeiro, 2008), we have prepared compound (I) from the analogous salt, [PTA-Me]I (Daigle et al., 1974; Daigle, 1998), to determine the coordination behaviour of the [PTA-Me]+ species in the absence of iodide ions.
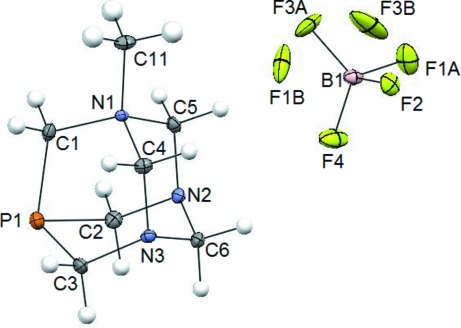
Compound (I) crystallizes in an orthorhombic crystal system and its unit cell is composed of a cage-like N-methylated [PTA-Me]+ cation whose positive charge is balanced by a disordered tetrafluoroborate anion (Fig. 1). The title compound appears to be isostructural to the related salt (Jogun et al., 1978) that possesses the same anion but the P-methylated [PTA-Me]+ cation. The geometrical parameters for (I) are comparable to those of other compounds with N-methylated PTA cores, either free (Kirillov et al., 2008; Otto et al., 2005; Forward et al., 1996) or coordinated to the metal centres (Kovacs et al., 2004; Smoleński et al., 2003; Pruchnik et al., 1999).
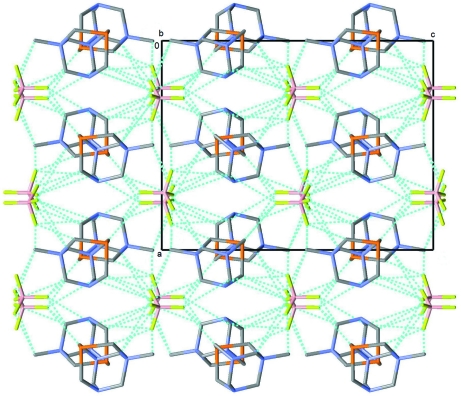
In (I), the [PTA-Me]+ units are disposed relatively close to the [BF4]- anions, thus allowing their extensive assembling via weak intermolecular C—H···F hydrogen bonds [mean C···F separation = 3.366 (3) Å], resulting in the formation of a three-dimensional supramolecular framework (Table 1, Fig. 2).
Experimental
An aqueous solution (25 ml) of [PTA-Me]I (1.00 mmol, 300 mg) and a methanolic (25 ml) solution of Tl[BF4] (1.00 mmol, 300 mg) were combined at ambient temperature [Caution: Thallium compounds are highly toxic and thus must be handled with extreme caution]. The resulting white suspension was stirred for 15 min and then filtered off, giving a white powder of thallium iodide that was discarded. The colourless filtrate was evaporated in vacuo, resulting in a white solid. It was recrystallized from MeOH to furnish colourless plates of (I) in ca 80% yield (after isolation by filtration and drying in vacuo).
[PTA-Me][BF4] is very soluble in middle-range polar solvents like Me2CO, CHCl3 and CH2Cl2, less soluble in H2O, MeOH, EtOH and DMSO, and insoluble in C6H6, and Et2O. FT–IR (KBr pellet), cm-1: 2965 w, 2908 w, 1461 s, 1407 s, 1347 w, 1313 s, 1292 s, 1249 s, 1120 s, 1094 s br, 1023 s, 983 s, 920 s, 899 s, 815 s, 769 s, 748 m, 732 m, 687 w, 635 w, 557 s, 534 w and 440 w. 1H NMR (300 MHz, D2O, 25°C, Me4Si): 4.86 and 4.75 (J(HAHB) = 11.4 Hz, 4H, NCHAHBN+), 4.52 and 4.36 (J(HAHB) = 13.8 Hz, 2H, NCHAHBN), 4.25 (d, 2J (H—P) = 6.8 Hz, 2H, PCH2N+), 3.88 and 3.75 (J(HAHB) = 15.3 Hz, 3J(HA—P) = 15.3 Hz, 3J(HB—P) = 8.7 Hz, 4H, PCHAHBN), 2.66 (s, 3H, N+CH3). 31P{1H} NMR (121.4 MHz, D2O, 25°C, 85% H3PO4): -85.7 (s).
Refinement
All the hydrogen atoms were inserted in calculated positions (C—H = 0.98–0.99 Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(methyl C). Atoms F1 and F3 are disordered over two sites with equal occupancies.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 20% probability level. H atoms are represented as spheres of arbitrary radius. The disordered F1 and F3 atoms are shown over their two positions.
Fig. 2.
Partial representation (view along the b axis) of the crystal packing diagram of (I) showing the generation of the three-dimensional supramolecular assembly via C—H···F hydrogen bonds and C···F short contacts (blue dotted lines). Hydrogen atoms and disordered F1B and F3B atoms are omitted for clarity. C, grey; N, blue; P, orange; F, light green; B, pink.
Crystal data
| C7H15N3P+·BF4– | F000 = 1072 |
| Mr = 259.00 | Dx = 1.576 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 1323 reflections |
| a = 11.994 (2) Å | θ = 3.4–25.2º |
| b = 11.6933 (18) Å | µ = 0.28 mm−1 |
| c = 15.569 (2) Å | T = 150 (2) K |
| V = 2183.5 (6) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.16 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer | 1948 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1391 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.061 |
| T = 150(2) K | θmax = 25.3º |
| ω scans | θmin = 2.6º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.956, Tmax = 0.972 | k = −14→13 |
| 10402 measured reflections | l = −18→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.121 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0512P)2 + 1.8936P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1948 reflections | Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.5509 (2) | 0.7943 (2) | 0.68018 (19) | 0.0248 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.5329 | 0.8736 | 0.6627 | 0.030* | |
| H1B | 0.6303 | 0.7806 | 0.6663 | 0.030* | |
| C2 | 0.3782 (2) | 0.7850 (2) | 0.79565 (18) | 0.0245 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.3505 | 0.7667 | 0.8539 | 0.029* | |
| H2B | 0.3533 | 0.8635 | 0.7815 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 0.5459 (2) | 0.6251 (2) | 0.80269 (18) | 0.0253 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.6251 | 0.6043 | 0.7937 | 0.030* | |
| H3B | 0.5247 | 0.5997 | 0.8611 | 0.030* | |
| C4 | 0.5074 (2) | 0.5884 (2) | 0.65244 (18) | 0.0219 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.4671 | 0.5360 | 0.6133 | 0.026* | |
| H4B | 0.5883 | 0.5749 | 0.6448 | 0.026* | |
| C5 | 0.3552 (2) | 0.7325 (2) | 0.64672 (18) | 0.0211 (6) | |
| H5A | 0.3364 | 0.8136 | 0.6357 | 0.025* | |
| H5B | 0.3100 | 0.6848 | 0.6074 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.3583 (2) | 0.5857 (2) | 0.75217 (18) | 0.0216 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.3384 | 0.5678 | 0.8124 | 0.026* | |
| H6B | 0.3146 | 0.5344 | 0.7145 | 0.026* | |
| C11 | 0.5016 (3) | 0.7311 (3) | 0.53413 (18) | 0.0295 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.4557 | 0.6780 | 0.5006 | 0.044* | |
| H11B | 0.5806 | 0.7173 | 0.5217 | 0.044* | |
| H11C | 0.4824 | 0.8099 | 0.5187 | 0.044* | |
| B1 | 0.2262 (3) | 0.4814 (3) | 0.4904 (2) | 0.0266 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.48031 (17) | 0.71288 (17) | 0.62773 (13) | 0.0146 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.32749 (18) | 0.70450 (19) | 0.73373 (14) | 0.0199 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.47713 (18) | 0.56276 (18) | 0.73947 (14) | 0.0190 (5) | |
| F1A | 0.1098 (3) | 0.5043 (4) | 0.4732 (3) | 0.0580 (13) | 0.59 |
| F2 | 0.23739 (16) | 0.37060 (14) | 0.46049 (11) | 0.0376 (5) | |
| F3A | 0.2858 (5) | 0.5568 (4) | 0.4471 (3) | 0.0634 (14) | 0.59 |
| F4 | 0.2252 (2) | 0.48727 (18) | 0.57697 (12) | 0.0627 (7) | |
| P1 | 0.53278 (7) | 0.78233 (7) | 0.79717 (5) | 0.0275 (2) | |
| F1B | 0.3444 (5) | 0.5214 (6) | 0.4871 (5) | 0.071 (2) | 0.41 |
| F3B | 0.1703 (10) | 0.5502 (6) | 0.4431 (5) | 0.096 (3) | 0.41 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0204 (14) | 0.0198 (15) | 0.0343 (18) | −0.0049 (12) | −0.0006 (13) | 0.0022 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0265 (15) | 0.0223 (15) | 0.0246 (16) | 0.0008 (12) | 0.0046 (13) | −0.0034 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0204 (15) | 0.0314 (16) | 0.0240 (16) | −0.0016 (12) | −0.0053 (13) | 0.0056 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0266 (15) | 0.0158 (14) | 0.0233 (17) | 0.0058 (12) | 0.0027 (12) | 0.0003 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0187 (14) | 0.0220 (15) | 0.0225 (16) | 0.0024 (11) | −0.0058 (12) | 0.0006 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0184 (14) | 0.0244 (16) | 0.0219 (15) | −0.0034 (12) | 0.0007 (12) | 0.0028 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0391 (17) | 0.0301 (17) | 0.0193 (17) | 0.0029 (14) | 0.0054 (13) | 0.0036 (13) |
| B1 | 0.039 (2) | 0.0219 (18) | 0.0187 (19) | 0.0019 (16) | 0.0014 (15) | −0.0018 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0174 (11) | 0.0138 (11) | 0.0126 (12) | −0.0002 (9) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0028 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0176 (11) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0203 (12) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0008 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0215 (12) | 0.0179 (12) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0010 (10) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0039 (9) |
| F1A | 0.039 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.091 (4) | 0.0133 (19) | −0.020 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| F2 | 0.0468 (12) | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0393 (12) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0028 (9) | −0.0112 (8) |
| F3A | 0.085 (4) | 0.045 (3) | 0.060 (3) | −0.027 (3) | 0.034 (3) | 0.009 (2) |
| F4 | 0.120 (2) | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0273 (12) | −0.0117 (13) | −0.0007 (12) | −0.0048 (9) |
| P1 | 0.0306 (4) | 0.0273 (4) | 0.0244 (5) | −0.0070 (3) | −0.0052 (3) | −0.0014 (3) |
| F1B | 0.044 (4) | 0.075 (5) | 0.094 (6) | −0.032 (3) | 0.031 (4) | −0.057 (4) |
| F3B | 0.165 (10) | 0.047 (5) | 0.075 (6) | 0.046 (6) | −0.072 (6) | −0.005 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.514 (3) | C5—N1 | 1.547 (3) |
| C1—P1 | 1.840 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9900 | C5—H5B | 0.9900 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9900 | C6—N3 | 1.463 (3) |
| C2—N2 | 1.479 (3) | C6—N2 | 1.466 (3) |
| C2—P1 | 1.854 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9900 | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9900 | C11—N1 | 1.495 (3) |
| C3—N3 | 1.477 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C3—P1 | 1.847 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9900 | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9900 | B1—F3B | 1.281 (7) |
| C4—N3 | 1.434 (3) | B1—F3A | 1.319 (5) |
| C4—N1 | 1.540 (3) | B1—F4 | 1.350 (4) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9900 | B1—F2 | 1.383 (4) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9900 | B1—F1A | 1.447 (5) |
| C5—N2 | 1.433 (4) | B1—F1B | 1.493 (7) |
| N1—C1—P1 | 114.83 (18) | N1—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 108.6 | N1—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| P1—C1—H1A | 108.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—H1B | 108.6 | N1—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| P1—C1—H1B | 108.6 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 107.5 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| N2—C2—P1 | 114.14 (18) | F3B—B1—F3A | 64.6 (6) |
| N2—C2—H2A | 108.7 | F3B—B1—F4 | 122.5 (5) |
| P1—C2—H2A | 108.7 | F3A—B1—F4 | 118.7 (4) |
| N2—C2—H2B | 108.7 | F3B—B1—F2 | 116.5 (4) |
| P1—C2—H2B | 108.7 | F3A—B1—F2 | 113.7 (3) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 107.6 | F4—B1—F2 | 112.6 (3) |
| N3—C3—P1 | 114.38 (18) | F3B—B1—F1A | 43.2 (5) |
| N3—C3—H3A | 108.7 | F3A—B1—F1A | 107.7 (4) |
| P1—C3—H3A | 108.7 | F4—B1—F1A | 99.6 (3) |
| N3—C3—H3B | 108.7 | F2—B1—F1A | 101.8 (3) |
| P1—C3—H3B | 108.7 | F3B—B1—F1B | 106.3 (7) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.6 | F3A—B1—F1B | 42.2 (3) |
| N3—C4—N1 | 112.3 (2) | F4—B1—F1B | 91.5 (4) |
| N3—C4—H4A | 109.1 | F2—B1—F1B | 101.0 (3) |
| N1—C4—H4A | 109.1 | F1A—B1—F1B | 148.4 (5) |
| N3—C4—H4B | 109.1 | C11—N1—C1 | 109.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—H4B | 109.1 | C11—N1—C4 | 110.0 (2) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.9 | C1—N1—C4 | 110.0 (2) |
| N2—C5—N1 | 111.8 (2) | C11—N1—C5 | 109.3 (2) |
| N2—C5—H5A | 109.2 | C1—N1—C5 | 110.3 (2) |
| N1—C5—H5A | 109.2 | C4—N1—C5 | 107.28 (19) |
| N2—C5—H5B | 109.2 | C5—N2—C6 | 110.1 (2) |
| N1—C5—H5B | 109.2 | C5—N2—C2 | 112.1 (2) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 | C6—N2—C2 | 111.8 (2) |
| N3—C6—N2 | 113.1 (2) | C4—N3—C6 | 109.6 (2) |
| N3—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C4—N3—C3 | 112.6 (2) |
| N2—C6—H6A | 109.0 | C6—N3—C3 | 111.3 (2) |
| N3—C6—H6B | 109.0 | C1—P1—C3 | 96.42 (13) |
| N2—C6—H6B | 109.0 | C1—P1—C2 | 95.98 (13) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 107.8 | C3—P1—C2 | 95.91 (13) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2A···F2i | 0.99 | 2.54 | 3.438 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5A···F4ii | 0.99 | 2.35 | 3.314 (3) | 166 |
| C6—H6B···F4 | 0.99 | 2.46 | 3.364 (3) | 152 |
| C11—H11B···F2iii | 0.98 | 2.43 | 3.350 (4) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, −y+1, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB2695).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Bruker (2004). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Daigle, D. J. (1998). Inorg. Synth.32, 40–45.
- Daigle, D. J., Pepperman, A. B. Jr & Vail, S. L. (1974). J. Heterocycl. Chem.11, 407–408.
- Forward, J. M., Staples, R. J. & Fackler, J. P. Jr (1996). Z. Kristallogr.211, 131–132.
- Jogun, K. H., Stezowski, J. J., Fluck, E. & Weissgraeber, H.-J. (1978). Z. Naturforsch. Teil B, 33, 1257–1262.
- Kirillov, A. M., Smoleński, P., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2007). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 2686–2692.
- Kirillov, A. M., Smoleński, P., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o496–o497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, J., Joó, F., Benyei, A. C. & Laurenczy, G. (2004). Dalton Trans. pp. 2336–2340. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst.39, 453–457.
- Otto, S., Ionescu, A. & Roodt, A. (2005). J. Organomet. Chem.690, 4337–4342.
- Phillips, A. D., Gonsalvi, L., Romerosa, A., Vizza, F. & Peruzzini, M. (2004). Coord. Chem. Rev.248, 955–993.
- Pruchnik, F. P., Smoleński, P., Galdecka, E. & Galdecki, Z. (1999). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 293, 110–114.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smoleński, P. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2008). Dalton Trans. pp. 87–91. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smoleński, P., Pruchnik, F. P., Ciunik, Z. & Lis, T. (2003). Inorg. Chem.42, 3318–3222. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808003401/hb2695sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808003401/hb2695Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report