Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title complex, [Cu(C2H8N2)2(H2O)2](C8H8NO2)2·2H2O, contains one anion, one half-cation and one water molecule. The CuII atom in the [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ cation (en is ethylenediamine) lies on an inversion centre. The four N atoms of the en ligands in the equatorial plane around the CuII atom form a slightly distorted square-planar arrangement, while the slightly distorted Jahn–Teller octahedral coordination is completed by two water O atoms in axial positions. In the crystal structure, intra- and intermolecular N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For general background, see: Hathaway & Hodgson (1973 ▶); Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶); Janiak (2000 ▶); Jeffrey (1997 ▶). For similar structures, see: Jašková et al. (2007 ▶); Miminoshvili et al. (2005 ▶); Carballo et al. (2005 ▶); Segla et al. (2000 ▶); Liu et al. (2004 ▶); Sharma et al. (2005 ▶); Anacona et al. (2002 ▶); Emsley et al. (1988 ▶, 1990 ▶); Li et al. (2005 ▶); Gonzalez-Alvarez et al. (2003 ▶); Lee et al. (2005 ▶); Mahadevan et al. (1986 ▶); Kovbasyuk et al. (1997 ▶); Harrison et al. (2007 ▶).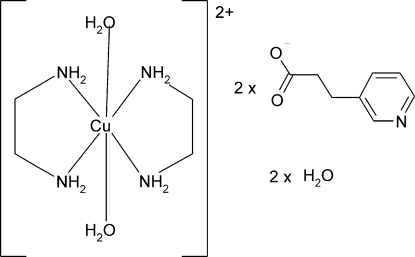
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(C2H8N2)2(H2O)2](C8H8NO2)2·2H2O
M r = 556.13
Triclinic,

a = 6.2620 (1) Å
b = 8.5660 (2) Å
c = 13.3550 (4) Å
α = 75.271 (1)°
β = 83.809 (1)°
γ = 70.863 (1)°
V = 654.30 (3) Å3
Z = 1
Ag Kα radiation
μ = 0.47 mm−1
T = 153 (2) K
0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: numerical (HABITUS; Herrendorf & Bärnighausen, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.808, T max = 0.915
15039 measured reflections
2989 independent reflections
2644 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.079
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.086
S = 1.07
2989 reflections
160 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: KappaCCD Software (Nonius, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SCALEPACK and DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: enCIFer (Allen et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808005400/hk2427sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808005400/hk2427Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O2i | 0.92 | 2.32 | 3.130 (3) | 147 |
| N1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.92 | 2.41 | 3.247 (2) | 152 |
| N1—H1B⋯O2W | 0.92 | 2.11 | 2.944 (3) | 151 |
| N2—H2A⋯O1ii | 0.92 | 2.29 | 3.150 (3) | 155 |
| N2—H2B⋯O1 | 0.92 | 2.12 | 3.019 (2) | 164 |
| O1W—H1W⋯O2i | 0.84 | 2.06 | 2.873 (3) | 164 |
| O1W—H2W⋯O1 | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.814 (2) | 164 |
| O2W—H3W⋯N3iii | 0.84 | 2.08 | 2.899 (3) | 163 |
| O2W—H4W⋯O2iv | 0.84 | 2.03 | 2.859 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of the Slovak Republic and the Slovak Academy of Sciences (grant Nos. 1/4454/07 and 1/0353/08).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
It is well known that copper(II) complexes having ethylenediamine (en) ligands show flexible coordination environment and adopt semi-coordation with tetragonal distortion. As part of our efforts to investigate metal(II) complexes based on pyridyl-carboxylic acids, we report herein the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
The asymmetric unit of (I), (Fig. 1), contains one anion, one half-cation and one water molecule. The CuII atom in the centrosymmetric [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ cation lies on the inversion centre. The four N atoms of the ethylenediamine ligands in the equatorial plane around the CuII atom form a slightly distorted square-planar arrangement, while the slightly distorted Jahn-Teller octahedral coordination is completed by the two O atoms of water molecules in the axial positions (Table 1 and Fig. 1).
The Cu—N1 [2.015 (2) Å] and Cu—N2 [2.022 (2) Å] bond lengths and N1—Cu—N2 [84.91 (7)°] bond angle agree with those found in other [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ complexes (Table 1). The Cu—O1W [2.503 (2) Å] bond is much longer than Cu—N bonds, as a result of the Jahn-Teller distortion. The Cu—OW bonds in other [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ complexes are in the range of 2.416 (3)–2.693 (9) Å (Table 1). The value of the T parameter (Hathaway & Hodgson, 1973), which indicates the degree of tetragonal distortion about the CuII atom, is 0.81 and it agrees with the reported values, in the range of 0.76–0.84, for other [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ complexes (Table 1).
In the crystal structure, the [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ coordination cations and 3-(3-pyridyl)propionate anions are linked by O—H···O and N—H···O hydrogen-bonds (Table 2, Fig. 2) in parallel to the a axis. The amine H atom is linked to both carboxylate O atoms of 3-(3-pyridyl)propionate by three-centered/bifurcated N—H···O hydrogen-bonds (Jeffrey, 1997) and both of them form the R12(4) ring motif (Bernstein et al., 1995). The similar R12(4) ring motifs with sulfonate or carboxylate groups are reported in[Cu(en)2(H2O)2](4-amino- naphthalene-1-sulfonate)2.2 H2O (Li et al., 2005)and [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]- (N-carboxyglycinate).H2O (Kovbasyuk et al., 1997).
The O—H···O hydrogen bonds between the coordinated water molecules and the carboxylate O atoms of 3-(3-pyridyl)propionate anions and N—H···O hydrogen bonds of amine H atoms form the R21(6) and R22(8) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995). These ring motifs are also reported for other [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]X2 complexes, while only the R22(8) ring motifs are present in [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]X2 complexes, [where X = 4-chlorobenzoate (Lee et al., 2005); X = 4-fluorobenzoate (Liu et al., 2004), X = isonicotinate (Segla et al., 2000) and X = 4-nitrobenzoate (Harrison et al., 2007)]. On the other hand, the R21(6) ring motifs are reported for [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]X2 complexes, [where X = naphthalene-2-sulfonate (Sharma et al., 2005) and X = 2,6-dimethoxynicotinate (Jašková et al., 2007)]. To the best of our knowledge, only [Cu(en)2(H2O)2](2-aminobenzoate)2 complex (Miminoshvili et al., 2005), exhibits both R21(6) and R22(8) ring motifs, in the crystal structure.
The additional N—H···O hydrogen bonds form further R21(6) ring motifs. Finally, two [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ cations and two 3-(3-pyridyl)propionate anions are joined through R42(8) ring motifs to form a layer parallel to the a axis. The layers of [Cu(en)2(H2O)2]2+ cations and 3-(3-pyridyl)- propionate anions are linked to form a three-dimensional network through uncoordinated water molecules by O—H···O and O—H···N hydrogen-bonds (Fig. 3).
The additional interactions between the 3-(3-pyridyl)propionate anions of (I) are the π-π stacking interactions (Janiak, 2000) between the two adjacent pyridine rings, (N3/C6—C10), with the centroid to centroid distances of Cg···Cgv = 3.66 Å [symmetry code: (v) -x,-y + 2,-z + 2]. The distance between parallel planes of the stacked pyridine rings is 3.33 Å.
Experimental
The violet [Cu(en)2(H2O)2](3-pypr)2.2H2O was formed in a methanolic solution of [Cu(3-pypr)2(H2O)2] (1.25 mmol) by adding ethylenediamine in the molar ratio of 1:2. The resulting solution was left to slowly evaporate at room temperature. In isolating the complex, it was necessary to add acetone to the concentrated solution. Well shaped violet crystals, suitable for X-ray structure analysis were collected after a few hours by filtration and finally dried in vacuo (yield; 90%). Anal. Calc. for C20H40N6O8; C, 43.20; H, 7.25; N, 15.11; Cu, 11.43. Found: C, 43.45; H, 7.47; N, 15.30; Cu, 11.21%. Selected IR data (cm-1): 1592 versus,br (νa(COO-) + ν(C?N)); 1392 versus (νs(COO-)); 605 s (δ(py), pyridine ring in-plane bending); 405 m (γ(py), pyridine ring out-of-plane bending). Electronic data (cm-1): 18 400 br.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with O—H = 0.84 Å (for H2O), N—H = 0.92 Å (for NH2) and C—H = 0.95 and 0.99 Å for aromatic and methylene H, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C,N,O), where x = 0.92 for O2W H and x = 1.2 for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of (I), showing the formation of R21(4), R12(6), R24(8) and R22(8) motifs [symmetry codes: (i) x + 1, y, z; (ii) -x, -y + 1, -z + 1].
Fig. 3.
A packing diagram of (I), showing hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking interactions, as dashed lines [symmetry codes: (iii) x + 1, y, z - 1; (iv) -x, -y + 2, -z + 1].
Crystal data
| [Cu(C2H8N2)2(H2O1)2](C8H8NO2)2·2H2O | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 556.13 | F000 = 295 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.411 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Ag Kα radiation λ = 0.56085 Å |
| a = 6.2620 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 2489 reflections |
| b = 8.5660 (2) Å | θ = 3.3–21.4º |
| c = 13.3550 (4) Å | µ = 0.47 mm−1 |
| α = 75.271 (1)º | T = 153 (2) K |
| β = 83.809 (1)º | Prism, violet |
| γ = 70.863 (1)º | 0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 654.30 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2989 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2644 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.079 |
| T = 153(2) K | θmax = 21.4º |
| ω and φ scans | θmin = 3.3º |
| Absorption correction: numerical(HABITUS; Herrendorf & Bärnighausen, 1997) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.808, Tmax = 0.915 | k = −11→11 |
| 15039 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.086 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0215P)2 + 0.3896P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.07 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2989 reflections | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 160 parameters | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes.Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane)2.3086 (0.0059) x + 8.2273 (0.0023) y - 0.2376 (0.0130) z = 6.3254 (0.0154)* 0.0032 (0.0016) N3* -0.0044 (0.0016) C6* 0.0010 (0.0017) C7* -0.0039 (0.0017) C8* 0.0003 (0.0018) C9* 0.0038 (0.0017) C103.3255 (0.0028) N3_$63.3331 (0.0028) C6_$63.3277 (0.0030) C7_$63.3326 (0.0031) C8_$63.3285 (0.0029) C9_$63.3249 (0.0030) C10_$6Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0032 |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.02500 (12) | |
| N1 | 0.5413 (3) | 0.7274 (2) | 0.48893 (14) | 0.0328 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.6147 | 0.7242 | 0.5459 | 0.039* | |
| H1B | 0.6270 | 0.7540 | 0.4306 | 0.039* | |
| N2 | 0.1813 (3) | 0.6372 (2) | 0.45504 (14) | 0.0307 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.1410 | 0.5969 | 0.4047 | 0.037* | |
| H2B | 0.0813 | 0.6297 | 0.5104 | 0.037* | |
| N3 | −0.0294 (4) | 0.8099 (3) | 1.12361 (17) | 0.0520 (6) | |
| O1 | −0.0720 (3) | 0.6040 (3) | 0.66095 (13) | 0.0493 (5) | |
| O2 | −0.4121 (3) | 0.7310 (2) | 0.71927 (15) | 0.0518 (5) | |
| O1W | 0.3984 (3) | 0.4843 (2) | 0.68797 (15) | 0.0515 (5) | |
| H1W | 0.4422 | 0.5531 | 0.7088 | 0.063* | |
| H2W | 0.2570 | 0.5084 | 0.6916 | 0.063* | |
| O2W | 0.6770 (4) | 0.9227 (3) | 0.29173 (16) | 0.0682 (6) | |
| H3W | 0.7363 | 0.8948 | 0.2368 | 0.063* | |
| H4W | 0.6086 | 1.0274 | 0.2809 | 0.063* | |
| C1 | 0.1767 (4) | 0.8158 (3) | 0.41381 (19) | 0.0399 (5) | |
| H1C | 0.0192 | 0.8928 | 0.4130 | 0.048* | |
| H1D | 0.2402 | 0.8312 | 0.3421 | 0.048* | |
| C2 | 0.3163 (4) | 0.8558 (3) | 0.4831 (2) | 0.0399 (5) | |
| H2C | 0.3294 | 0.9709 | 0.4542 | 0.048* | |
| H2D | 0.2442 | 0.8520 | 0.5530 | 0.048* | |
| C3 | −0.2033 (4) | 0.6638 (3) | 0.72904 (17) | 0.0339 (5) | |
| C4 | −0.1063 (4) | 0.6478 (3) | 0.83208 (19) | 0.0418 (5) | |
| H4A | −0.2050 | 0.6083 | 0.8890 | 0.050* | |
| H4B | 0.0448 | 0.5608 | 0.8387 | 0.050* | |
| C5 | −0.0846 (6) | 0.8114 (3) | 0.8436 (2) | 0.0575 (8) | |
| H5A | −0.2360 | 0.8978 | 0.8392 | 0.069* | |
| H5B | 0.0113 | 0.8527 | 0.7860 | 0.069* | |
| C6 | 0.0179 (4) | 0.7906 (3) | 0.94565 (19) | 0.0389 (5) | |
| C7 | −0.1118 (4) | 0.8301 (3) | 1.0313 (2) | 0.0458 (6) | |
| H7 | −0.2711 | 0.8749 | 1.0242 | 0.055* | |
| C8 | 0.1937 (5) | 0.7467 (3) | 1.1312 (2) | 0.0507 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.2567 | 0.7298 | 1.1962 | 0.061* | |
| C9 | 0.3376 (4) | 0.7045 (3) | 1.0513 (2) | 0.0460 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.4963 | 0.6603 | 1.0606 | 0.055* | |
| C10 | 0.2489 (4) | 0.7271 (3) | 0.95738 (19) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.3462 | 0.6992 | 0.9005 | 0.050* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu | 0.02142 (18) | 0.02502 (19) | 0.0296 (2) | −0.00597 (13) | −0.00336 (13) | −0.00873 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0370 (10) | 0.0319 (10) | 0.0332 (10) | −0.0132 (8) | −0.0058 (8) | −0.0086 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0292 (9) | −0.0082 (7) | −0.0023 (7) | −0.0121 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0777 (16) | 0.0397 (12) | 0.0397 (13) | −0.0190 (11) | 0.0090 (11) | −0.0145 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0421 (9) | 0.0819 (14) | 0.0342 (9) | −0.0235 (9) | 0.0035 (7) | −0.0280 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0620 (12) | 0.0555 (12) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0106 (8) | −0.0300 (9) |
| O1W | 0.0399 (9) | 0.0668 (12) | 0.0526 (11) | −0.0158 (8) | 0.0015 (8) | −0.0243 (9) |
| O2W | 0.0781 (14) | 0.0525 (12) | 0.0540 (13) | −0.0063 (10) | 0.0207 (11) | −0.0053 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0404 (13) | 0.0026 (9) | −0.0085 (10) | −0.0078 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0478 (13) | 0.0284 (11) | 0.0425 (14) | −0.0068 (10) | −0.0010 (10) | −0.0129 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0380 (12) | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0311 (12) | −0.0163 (9) | −0.0034 (9) | −0.0119 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0532 (14) | 0.0418 (13) | 0.0336 (13) | −0.0141 (11) | −0.0079 (10) | −0.0126 (10) |
| C5 | 0.089 (2) | 0.0386 (14) | 0.0508 (17) | −0.0225 (14) | −0.0349 (15) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0540 (14) | 0.0294 (11) | 0.0378 (13) | −0.0159 (10) | −0.0144 (11) | −0.0068 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0436 (13) | 0.0338 (12) | 0.0636 (18) | −0.0142 (10) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0137 (12) |
| C8 | 0.083 (2) | 0.0384 (14) | 0.0338 (14) | −0.0169 (13) | −0.0209 (13) | −0.0078 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0479 (14) | 0.0426 (14) | 0.0516 (16) | −0.0146 (11) | −0.0149 (12) | −0.0121 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0519 (14) | 0.0419 (13) | 0.0353 (13) | −0.0169 (11) | −0.0005 (10) | −0.0132 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu—O1Wi | 2.503 (2) | C1—C2 | 1.506 (3) |
| Cu—O1W | 2.503 (2) | C1—H1C | 0.9900 |
| Cu—N1i | 2.015 (2) | C1—H1D | 0.9900 |
| Cu—N1 | 2.015 (2) | C2—H2C | 0.9900 |
| Cu—N2i | 2.022 (2) | C2—H2D | 0.9900 |
| Cu—N2 | 2.022 (2) | C3—C4 | 1.521 (3) |
| O1—C3 | 1.251 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.498 (3) |
| O2—C3 | 1.250 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9900 |
| O1W—H1W | 0.84 | C4—H4B | 0.9900 |
| O1W—H2W | 0.84 | C5—C6 | 1.513 (3) |
| O2W—H3W | 0.84 | C5—H5A | 0.9900 |
| O2W—H4W | 0.84 | C5—H5B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C2 | 1.472 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.378 (4) |
| N1—H1A | 0.9200 | C6—C10 | 1.379 (3) |
| N1—H1B | 0.9200 | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C1 | 1.480 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.363 (4) |
| N2—H2A | 0.9200 | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2B | 0.9200 | C9—C10 | 1.370 (3) |
| N3—C8 | 1.327 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C7 | 1.337 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| O1Wi—Cu—O1W | 180.0 | H1C—C1—H1D | 108.5 |
| N1i—Cu—O1Wi | 88.72 (7) | N1—C2—C1 | 107.48 (18) |
| N1—Cu—O1Wi | 91.28 (7) | N1—C2—H2C | 110.2 |
| N2i—Cu—O1Wi | 93.19 (6) | C1—C2—H2C | 110.2 |
| N2—Cu—O1Wi | 86.81 (6) | N1—C2—H2D | 110.2 |
| N1i—Cu—O1W | 91.28 (7) | C1—C2—H2D | 110.2 |
| N1—Cu—O1W | 88.72 (7) | H2C—C2—H2D | 108.5 |
| N2i—Cu—O1W | 86.81 (6) | O2—C3—O1 | 124.1 (2) |
| N2—Cu—O1W | 93.19 (6) | O2—C3—C4 | 117.4 (2) |
| N1i—Cu—N1 | 180.00 (11) | O1—C3—C4 | 118.4 (2) |
| N1i—Cu—N2i | 84.91 (7) | C5—C4—C3 | 113.0 (2) |
| N1—Cu—N2i | 95.09 (7) | C5—C4—H4A | 109.0 |
| N1i—Cu—N2 | 95.09 (7) | C3—C4—H4A | 109.0 |
| N1—Cu—N2 | 84.91 (7) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.0 |
| N2i—Cu—N2 | 180.0 | C3—C4—H4B | 109.0 |
| C2—N1—Cu | 108.14 (13) | H4A—C4—H4B | 107.8 |
| C2—N1—H1A | 110.1 | C4—C5—C6 | 111.8 (2) |
| Cu—N1—H1A | 110.1 | C4—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| C2—N1—H1B | 110.1 | C6—C5—H5A | 109.2 |
| Cu—N1—H1B | 110.1 | C4—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 108.4 | C6—C5—H5B | 109.2 |
| C1—N2—Cu | 107.44 (13) | H5A—C5—H5B | 107.9 |
| C1—N2—H2A | 110.2 | C7—C6—C10 | 116.7 (2) |
| Cu—N2—H2A | 110.2 | C7—C6—C5 | 122.5 (2) |
| C1—N2—H2B | 110.2 | C10—C6—C5 | 120.8 (2) |
| Cu—N2—H2B | 110.2 | N3—C7—C6 | 124.6 (2) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 108.5 | N3—C7—H7 | 117.7 |
| C8—N3—C7 | 116.3 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 117.7 |
| Cu—O1W—H1W | 110.3 | N3—C8—C9 | 123.8 (2) |
| Cu—O1W—H2W | 104.9 | N3—C8—H8 | 118.1 |
| H1W—O1W—H2W | 111.9 | C9—C8—H8 | 118.1 |
| H3W—O2W—H4W | 111.2 | C8—C9—C10 | 118.7 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2 | 107.81 (18) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.7 |
| N2—C1—H1C | 110.1 | C10—C9—H9 | 120.7 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 110.1 | C9—C10—C6 | 119.8 (2) |
| N2—C1—H1D | 110.1 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—H1D | 110.1 | C6—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| N2i—Cu—N1—C2 | −165.34 (14) | O1—C3—C4—C5 | 104.8 (3) |
| N2—Cu—N1—C2 | 14.66 (14) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −178.5 (2) |
| O1Wi—Cu—N1—C2 | 101.34 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −96.9 (3) |
| O1W—Cu—N1—C2 | −78.66 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C10 | 81.8 (3) |
| N1i—Cu—N2—C1 | −165.31 (14) | C8—N3—C7—C6 | −0.2 (4) |
| N1—Cu—N2—C1 | 14.70 (14) | C10—C6—C7—N3 | −0.5 (4) |
| O1Wi—Cu—N2—C1 | −76.88 (14) | C5—C6—C7—N3 | 178.2 (2) |
| O1W—Cu—N2—C1 | 103.12 (14) | C7—N3—C8—C9 | 0.7 (4) |
| Cu—N2—C1—C2 | −40.8 (2) | N3—C8—C9—C10 | −0.4 (4) |
| Cu—N1—C2—C1 | −40.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C6 | −0.4 (4) |
| N2—C1—C2—N1 | 54.5 (2) | C7—C6—C10—C9 | 0.8 (3) |
| O2—C3—C4—C5 | −77.7 (3) | C5—C6—C10—C9 | −178.0 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O2ii | 0.92 | 2.32 | 3.130 (3) | 147 |
| N1—H1A···O1ii | 0.92 | 2.41 | 3.247 (2) | 152 |
| N1—H1B···O2W | 0.92 | 2.11 | 2.944 (3) | 151 |
| N2—H2A···O1iii | 0.92 | 2.29 | 3.150 (3) | 155 |
| N2—H2B···O1 | 0.92 | 2.12 | 3.019 (2) | 164 |
| O1W—H1W···O2ii | 0.84 | 2.06 | 2.873 (3) | 164 |
| O1W—H2W···O1 | 0.84 | 2.00 | 2.814 (2) | 164 |
| O2W—H3W···N3iv | 0.84 | 2.08 | 2.899 (3) | 163 |
| O2W—H4W···O2v | 0.84 | 2.03 | 2.859 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x+1, y, z−1; (v) −x, −y+2, −z+1.
Table 2 Comparative geometrical parameters (Å, °) and T parameter for selected trans-[Cu(en)2(H2O)2] X2 complexes
| X2 | Cu–N1 | Cu–N2 | Cu–OW | Ta | N1–Cu–N2 |
| (3-pypr)2.2H2O | 2.015 (2) | 2.022 (2) | 2.503 (2) | 0.81 | 84.91 (7) |
| (2,6-(MeO)2nic)2b | 2.018 (2) | 2.020 (2) | 2.467 (2) | 0.82 | 83.96 (8) |
| (4-O2Nbz)2c | 2.015 (2) | 2.027 (2) | 2.537 (2) | 0.80 | 84.92 (7) |
| (2-NH2bz)2d | 2.012 (4) | 2.020 (5) | 2.503 (4) | 0.81 | 84.52 (9) |
| (benz)2e | 2.009 (4) | 2.017 (4) | 2.653 (5) | 0.76 | 84.8 (2) |
| (isonic)2f | 2.021 (2) | 2.018 (2) | 2.598 (2) | 0.78 | 84.98 (6) |
| (4-Fbz)2g | 2.018 (4) | 2.021 (4) | 2.579 (4) | 0.78 | 85.0 (2) |
| (naphs)2h | 2.020 (2) | 2.018 (2) | 2.513 (1) | 0.80 | 84.63 (7) |
| (stz)2.2H2Oi | 2.042 (3) | 2.033 (3) | 2.484 (3) | 0.82 | 84.1 (1) |
| F2.4H2Oj | 2.019 (5) | 2.023 (5) | 2.571 (6) | 0.78 | 84.6 (2) |
| (NH2naphs)2.2H2Ok | 2.023 (2) | 2.012 (2) | 2.437 (2) | 0.83 | 84.30 (9) |
| (Clbtts)2l | 2.019 (4) | 2.049 (3) | 2.416 (3) | 0.84 | 84.2 (2) |
| (Cl-Fbz)2m | 2.009 (2) | 2.016 (2) | 2.618 (1) | 0.77 | 84.30 (6) |
| (BPh4)2.2DMSOn | 2.022 (10) | 2.055 (8) | 2.693 (9) | 0.76 | 84.9 (4) |
| (edcarb).2H2Oo | 1.996 (2) | 2.022 (2) | 2.556 (2) | 0.79 | 84.78 (7) |
(a) The value of the T parameter (T = RS/RL), indicating the degree of tetragonal distortion about the CuII atom (Hathaway & Hodgson, 1973); (b) Jašková et al. (2007) [2,6-(MeO)2nic is 2,6-dimethoxynicotinate]; (c) Harrison et al. (2007) [4-O2Nbz is 4-nitrobenzoate]; (d) Miminoshvili et al. (2005) [2-NH2bzc is 2-aminobenzoate]; (e) Carballo et al. (2005) [benz is benzilate]; (f) Segla et al. (2000) [isonic is isonicotinate]; (g) Liu et al. (2004) [4-Fbz is 4-fluorobenzoate]; (h) Sharma et al. (2005) [naphs is naphthalene-2-sulfonate]; (i) Anacona et al. (2002) [stz is sulfathiazole]; (j) Emsley et al. (1988; 1990); (k) Li et al. (2005) [NH2naphs is 4-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonate]; (l) Gonzalez-Alvarez et al. (2003) [Clbtts is N-2-(6-chlorobenzothiazole)toluenesulfonamide]; (m) Lee et al. (2005); (n) Mahadevan et al. (1986); (o) Kovbasyuk et al. (1997) [edcarb is ethylene-1,2-dicarbonate].
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2427).
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst.37, 335–338.
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Anacona, J. R., Ramos, N. & de Delgado, G. D. (2002). J. Coord. Chem.55, 901–908.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Carballo, R., Covelo, B., Garcia-Matinez, E. & Vazquez-Lopez, E. M. (2005). Appl. Organomet. Chem.19, 394–395.
- Emsley, J., Arif, M., Bates, P. A. & Hursthouse, M. B. (1988). Chem. Commun. pp. 1387–1388.
- Emsley, J., Arif, M., Bates, P. A. & Hursthouse, M. B. (1990). J. Mol. Struct.220, 1–12.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Gonzalez-Alvarez, M., Alzuet, G., Borras, J., Macias, B., Montejo-Bernardo, J. M. & Garcia-Granda, S. (2003). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.629, 239–243.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Slawin, A. M. Z., Sharma, R. P., Sharma, B. & Bhama, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m178–m180.
- Hathaway, B. J. & Hodgson, P. G. (1973). J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem.35, 4071–4081.
- Herrendorf, W. & Bärnighausen, H. (1997). HABITUS Universities of Giessen and Karlsruhe, Germany.
- Janiak, C. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 3885–3896.
- Jašková, J., Mikloš, D., Korabik, M., Jorík, V., Segla, P., Kaliňáková, B., Hudecová, D., Švorec, J., Fischer, A., Mrozinski, J., Lis, T. & Melník, M. (2007). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 360, 2711–2720.
- Jeffrey, G. A. (1997). An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding Oxford University Press.
- Kovbasyuk, L. A., Fritsky, I. O., Kokozay, V. N. & Iskenderov, T. S. (1997). Polyhedron, 16, 1723–1729.
- Lee, J.-C., Takahashi, H. & Matsui, Y. (2005). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct.220, 491–492.
- Li, M.-T., Wang, C.-G., Wu, Y. & Fu, X.-C. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, m1660–m1661.
- Liu, Z.-D., Tan, M.-Y. & Zhu, H.-L. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, m1081–m1083.
- Mahadevan, C., Rout, G. C., Seshasayee, M. & Sastry, S. (1986). J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res.16, 799–805.
- Miminoshvili, K. E., Sobolev, A. N., Miminoshvili, E. B., Beridze, L. A. & Kutelia, E. R. (2005). J. Struct. Chem.46, 560–565.
- Nonius (1997). Kappa-CCD Server Software Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Segla, P., Palicová, M., Koman, M., Mikloš, D. & Melník, M. (2000). Inorg. Chem. Commun.3, 120–125.
- Sharma, R. P., Sharma, R., Bala, R., Rychlewska, U. & Warzajtis, B. (2005). J. Mol. Struct.738, 291–298.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808005400/hk2427sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808005400/hk2427Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





