Abstract
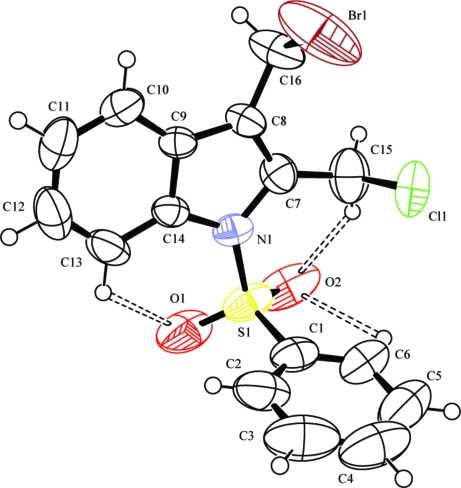
In the title compound, C16H13BrClNO2S, the indole mean plane forms a dihedral angle of 73.59 (19)° with the phenyl ring. The molecular structure is stabilized by weak intramolecular C—H⋯O interactions. The Br atom is disordered over two positions with site occupancy factors of 0.7 and 0.3.
Related literature
For related crystal structures, see: Chakkaravarthi et al. (2007 ▶, 2008 ▶). For the biological activities of indole derivatives, see: Chai et al. (2006 ▶); Nieto et al. (2005 ▶); Olgen & Coban (2003 ▶).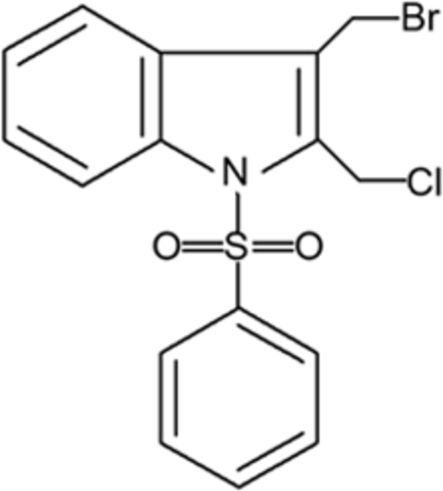
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H13BrClNO2S
M r = 398.69
Monoclinic,
a = 11.8501 (9) Å
b = 16.3525 (13) Å
c = 8.5793 (6) Å
β = 108.766 (3)°
V = 1574.1 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.92 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.16 × 0.14 × 0.14 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.559, T max = 0.665
14367 measured reflections
2770 independent reflections
1822 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.045
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.066
wR(F 2) = 0.231
S = 1.06
2770 reflections
209 parameters
12 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.92 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: APEX2; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808007678/bt2689sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808007678/bt2689Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6—H6⋯O2 | 0.93 | 2.51 | 2.877 (9) | 104 |
| C13—H13⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.31 | 2.873 (10) | 118 |
| C15—H15B⋯O2 | 0.97 | 2.17 | 2.939 (10) | 136 |
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Sophisticated Analytical Instrument Facility, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, for the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In continuation of our studies of indole derivatives, which are known to exhibit anti-oxidant activity (Olgen & Coban, 2003), antihepatitis B virus activities (Chai et al., 2006) and antibacterial (Nieto et al., 2005) activities, we report the crystal structure of the title compound (I).
The geometric parameters of the molecule of (I) (Fig. 1) agree well with the reported structures (Chakkaravarthi et al., 2007, 2008). The indole mean plane forms a dihedral angle of 73.59 (19)° with the phenyl ring. The N1—S1—C1 plane is almost orthogonal to indole ring (dihedral angle 82.30 (22)°) and makes 76.93 (22)° with the phenyl ring. The indole mean plane and C8—C16—BR1 plane are nearly orthogonal to each other forming a dihedral angle of 82.23 (0.29)°.
The sum of bond angles around N1 (359.99°) shows that N1 is sp2-hybridized. The torsion angles O1—S1—N1—C14 and O2—S1—N1—C7 [17.8 (6)° and -33.4 (6)°, respectively] indicate the syn conformation of the sulfonyl moiety. The molecular structure is stabilized by weak intramolecular C—H···O interactions.
Experimental
1-(Phenylsulfonyl)-3-(bromomethyl)-2-methylindole (0.5 g, 1.37 mmol) was dissolved in dry ccl4(10 ml) and then powdered N-chloro succinimide was added. To this, azobisisobutyronitrle (50 mg) was also added and then refluxed for 2 h on a waterbath. After the reaction was completed, succinimide was floated on the surface of the reaction mixture. It was then filtered off and washed with CCl4 (3 ml). The solvent was removed carefully under vacuo. The crude product was recrystallized from CCl4. Yield:76 percentage.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using riding model with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic C—H and C—H = 0.97 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for CH2. The Br atom is disordered over two positions with the occupancies of 0.709 (16) and 0.291 (16), respectively. The distances C1—C2, C2—C3, C3—C4, C4—C5, C10—C11 and C11—C12 were restrained to 1.395 (1) Å, the distances C16—BR1 and C16—Br1A were restrained to 1.91 (10) Å and the distance CL1—C15 was restrained to 1.76 (5) Å. The anisotropic thermal parameters of C15, C16, BR1, BR1A, CL1 atoms were restrained with DELU in the final cycles of the refinement (Sheldrick, 2008).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atomic labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms. Only major parts of the disordered atoms are drawn. Intramolecular H-bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C16H13BrClNO2S | F000 = 800 |
| Mr = 398.69 | Dx = 1.682 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4037 reflections |
| a = 11.8501 (9) Å | θ = 2.5–25.0º |
| b = 16.3525 (13) Å | µ = 2.92 mm−1 |
| c = 8.5793 (6) Å | T = 295 (2) K |
| β = 108.766 (3)º | Block, colourless |
| V = 1574.1 (2) Å3 | 0.16 × 0.14 × 0.14 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer | 2770 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1822 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.045 |
| T = 295(2) K | θmax = 25.0º |
| ω and φ scans | θmin = 2.2º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −14→13 |
| Tmin = 0.559, Tmax = 0.665 | k = −19→19 |
| 14367 measured reflections | l = −10→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.066 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.231 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.127P)2 + 1.9456P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2770 reflections | Δρmax = 0.42 e Å−3 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmin = −0.91 e Å−3 |
| 12 restraints | Extinction correction: none |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.90925 (16) | −0.10531 (12) | 0.5085 (3) | 0.0872 (6) | |
| Br1 | 0.8135 (6) | 0.1043 (5) | 0.3205 (5) | 0.1572 (16) | 0.709 (16) |
| Br1A | 0.7901 (4) | 0.1251 (3) | 0.3139 (9) | 0.093 (2) | 0.291 (16) |
| S1 | 0.70049 (14) | −0.13649 (11) | 0.8192 (2) | 0.0743 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.6340 (5) | −0.1191 (4) | 0.9258 (8) | 0.114 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.6743 (5) | −0.2077 (3) | 0.7212 (8) | 0.109 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.6795 (4) | −0.0573 (3) | 0.6922 (5) | 0.0539 (11) | |
| C1 | 0.8512 (6) | −0.1369 (4) | 0.9320 (7) | 0.0655 (17) | |
| C2 | 0.8952 (7) | −0.0826 (5) | 1.0604 (8) | 0.097 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.8449 | −0.0449 | 1.0854 | 0.117* | |
| C3 | 1.0161 (8) | −0.0849 (8) | 1.1523 (11) | 0.127 (4) | |
| H3 | 1.0474 | −0.0485 | 1.2387 | 0.153* | |
| C4 | 1.0885 (9) | −0.1418 (7) | 1.1133 (13) | 0.122 (4) | |
| H4 | 1.1688 | −0.1441 | 1.1753 | 0.147* | |
| C5 | 1.0442 (8) | −0.1951 (6) | 0.9845 (13) | 0.113 (3) | |
| H5 | 1.0947 | −0.2325 | 0.9590 | 0.135* | |
| C6 | 0.9256 (7) | −0.1932 (5) | 0.8934 (10) | 0.086 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.8953 | −0.2295 | 0.8065 | 0.103* | |
| C7 | 0.7000 (5) | −0.0556 (3) | 0.5384 (7) | 0.0574 (14) | |
| C8 | 0.6681 (5) | 0.0197 (3) | 0.4715 (6) | 0.0535 (14) | |
| C9 | 0.6288 (5) | 0.0680 (3) | 0.5809 (5) | 0.0463 (12) | |
| C10 | 0.5887 (6) | 0.1477 (4) | 0.5707 (7) | 0.0622 (15) | |
| H10 | 0.5837 | 0.1796 | 0.4790 | 0.075* | |
| C11 | 0.5563 (6) | 0.1790 (4) | 0.6984 (8) | 0.078 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.5295 | 0.2327 | 0.6939 | 0.094* | |
| C12 | 0.5633 (7) | 0.1313 (5) | 0.8332 (9) | 0.083 (2) | |
| H12 | 0.5406 | 0.1537 | 0.9182 | 0.099* | |
| C13 | 0.6026 (6) | 0.0519 (5) | 0.8471 (6) | 0.0687 (18) | |
| H13 | 0.6064 | 0.0203 | 0.9388 | 0.082* | |
| C14 | 0.6365 (4) | 0.0206 (3) | 0.7184 (6) | 0.0468 (12) | |
| C15 | 0.7557 (4) | −0.1232 (4) | 0.4743 (11) | 0.086 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.7151 | −0.1294 | 0.3572 | 0.103* | |
| H15B | 0.7464 | −0.1739 | 0.5278 | 0.103* | |
| C16 | 0.6722 (5) | 0.0443 (4) | 0.3064 (7) | 0.084 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.6030 | 0.0777 | 0.2520 | 0.101* | 0.709 (16) |
| H16B | 0.6686 | −0.0042 | 0.2400 | 0.101* | 0.709 (16) |
| H16C | 0.6052 | 0.0802 | 0.2560 | 0.101* | 0.291 (16) |
| H16D | 0.6645 | −0.0033 | 0.2363 | 0.101* | 0.291 (16) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0663 (11) | 0.0872 (13) | 0.1176 (15) | 0.0181 (9) | 0.0429 (10) | −0.0109 (10) |
| Br1 | 0.235 (3) | 0.159 (3) | 0.106 (2) | −0.112 (2) | 0.095 (2) | −0.0245 (15) |
| Br1A | 0.063 (4) | 0.105 (3) | 0.098 (3) | −0.014 (2) | 0.008 (2) | 0.041 (3) |
| S1 | 0.0540 (9) | 0.0688 (11) | 0.0926 (12) | −0.0071 (8) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0402 (9) |
| O1 | 0.082 (3) | 0.142 (5) | 0.130 (5) | 0.015 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.087 (4) |
| O2 | 0.087 (3) | 0.059 (3) | 0.144 (5) | −0.029 (3) | −0.016 (3) | 0.035 (3) |
| N1 | 0.057 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.052 (2) | 0.000 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.013 (2) |
| C1 | 0.061 (4) | 0.067 (4) | 0.065 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.028 (3) |
| C2 | 0.100 (6) | 0.123 (7) | 0.058 (4) | −0.002 (5) | 0.010 (4) | 0.011 (4) |
| C3 | 0.123 (8) | 0.145 (10) | 0.079 (6) | −0.039 (8) | −0.016 (6) | 0.010 (6) |
| C4 | 0.077 (6) | 0.138 (9) | 0.121 (8) | −0.020 (6) | −0.010 (6) | 0.051 (7) |
| C5 | 0.076 (6) | 0.116 (7) | 0.139 (8) | 0.024 (5) | 0.025 (6) | 0.041 (7) |
| C6 | 0.072 (5) | 0.077 (5) | 0.096 (5) | 0.011 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.019 (4) |
| C7 | 0.064 (4) | 0.051 (3) | 0.059 (3) | −0.005 (3) | 0.023 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C8 | 0.070 (4) | 0.053 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.020 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C9 | 0.047 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.034 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.005 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C10 | 0.066 (4) | 0.050 (3) | 0.061 (3) | 0.006 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.005 (3) |
| C11 | 0.066 (4) | 0.066 (4) | 0.095 (5) | 0.014 (3) | 0.014 (4) | −0.021 (4) |
| C12 | 0.071 (4) | 0.106 (6) | 0.073 (4) | 0.003 (4) | 0.028 (4) | −0.036 (4) |
| C13 | 0.062 (4) | 0.104 (5) | 0.037 (3) | −0.001 (4) | 0.013 (3) | −0.002 (3) |
| C14 | 0.043 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.038 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C15 | 0.079 (3) | 0.074 (5) | 0.110 (6) | −0.007 (4) | 0.039 (4) | −0.026 (4) |
| C16 | 0.134 (5) | 0.073 (4) | 0.051 (3) | −0.026 (4) | 0.038 (4) | 0.001 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C15 | 1.772 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.359 (8) |
| Br1—C16 | 1.9114 (11) | C7—C15 | 1.481 (9) |
| Br1A—C16 | 1.9084 (11) | C8—C9 | 1.415 (8) |
| S1—O2 | 1.411 (6) | C8—C16 | 1.489 (7) |
| S1—O1 | 1.415 (6) | C9—C10 | 1.381 (8) |
| S1—N1 | 1.659 (4) | C9—C14 | 1.390 (7) |
| S1—C1 | 1.737 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.371 (7) |
| N1—C14 | 1.417 (7) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.417 (7) | C11—C12 | 1.375 (8) |
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (8) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (10) | C12—C13 | 1.372 (10) |
| C2—C3 | 1.396 (8) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.387 (8) |
| C3—C4 | 1.379 (9) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.371 (9) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (12) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—H16C | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C16—H16D | 0.9700 |
| O2—S1—O1 | 119.3 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.6 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 107.2 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.3 (6) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 105.7 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 108.5 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| O1—S1—C1 | 109.1 (4) | C13—C12—C11 | 122.5 (6) |
| N1—S1—C1 | 106.2 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 118.8 |
| C14—N1—C7 | 108.0 (4) | C11—C12—H12 | 118.8 |
| C14—N1—S1 | 125.7 (4) | C12—C13—C14 | 117.1 (6) |
| C7—N1—S1 | 126.3 (4) | C12—C13—H13 | 121.4 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.8 (7) | C14—C13—H13 | 121.4 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 119.9 (6) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.9 (5) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 119.3 (5) | C13—C14—N1 | 131.9 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.3 (8) | C9—C14—N1 | 107.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C7—C15—Cl1 | 111.8 (4) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.4 | C7—C15—H15A | 109.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.1 (9) | Cl1—C15—H15A | 109.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C7—C15—H15B | 109.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 | Cl1—C15—H15B | 109.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.2 (9) | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C8—C16—Br1A | 113.8 (4) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.4 | C8—C16—Br1 | 112.0 (4) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.1 (9) | C8—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | Br1A—C16—H16A | 97.1 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | Br1—C16—H16A | 109.2 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.5 (8) | C8—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 | Br1A—C16—H16B | 118.6 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 | Br1—C16—H16B | 109.2 |
| C8—C7—N1 | 107.6 (5) | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.9 |
| C8—C7—C15 | 128.1 (6) | C8—C16—H16C | 108.4 |
| N1—C7—C15 | 124.2 (6) | Br1A—C16—H16C | 94.7 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 109.4 (5) | Br1—C16—H16C | 107.0 |
| C7—C8—C16 | 123.8 (6) | H16B—C16—H16C | 111.0 |
| C9—C8—C16 | 126.7 (5) | C8—C16—H16D | 110.3 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 120.5 (5) | Br1A—C16—H16D | 119.9 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 131.7 (5) | Br1—C16—H16D | 110.9 |
| C14—C9—C8 | 107.8 (5) | H16A—C16—H16D | 104.9 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 118.7 (5) | H16C—C16—H16D | 108.0 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.6 | ||
| O2—S1—N1—C14 | 146.0 (5) | C15—C7—C8—C16 | 7.1 (9) |
| O1—S1—N1—C14 | 17.8 (6) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.3 (6) |
| C1—S1—N1—C14 | −98.1 (5) | C16—C8—C9—C10 | −2.1 (10) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | −33.4 (6) | C7—C8—C9—C14 | −0.3 (6) |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | −161.6 (5) | C16—C8—C9—C14 | 178.3 (5) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | 82.5 (5) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.2 (8) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | −167.5 (6) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.8 (6) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −36.0 (6) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.4 (10) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | 77.6 (6) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.3 (11) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | 11.3 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.4 (10) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 142.8 (5) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.9 (8) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | −103.7 (5) | C12—C13—C14—N1 | −179.4 (6) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (11) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.9 (8) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.6 (7) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −179.4 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (15) | C10—C9—C14—N1 | 179.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (17) | C8—C9—C14—N1 | −0.6 (6) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.0 (16) | C7—N1—C14—C13 | 179.9 (6) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.3 (13) | S1—N1—C14—C13 | 0.4 (8) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (11) | C7—N1—C14—C9 | 1.3 (6) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.5 (6) | S1—N1—C14—C9 | −178.2 (4) |
| C14—N1—C7—C8 | −1.5 (6) | C8—C7—C15—Cl1 | 76.0 (8) |
| S1—N1—C7—C8 | 178.0 (4) | N1—C7—C15—Cl1 | −98.7 (7) |
| C14—N1—C7—C15 | 174.1 (5) | C7—C8—C16—Br1A | −112.1 (6) |
| S1—N1—C7—C15 | −6.4 (8) | C9—C8—C16—Br1A | 69.5 (8) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | 1.1 (6) | C7—C8—C16—Br1 | −98.2 (7) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | −174.3 (5) | C9—C8—C16—Br1 | 83.4 (8) |
| N1—C7—C8—C16 | −177.5 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···O2 | 0.93 | 2.51 | 2.877 (9) | 104 |
| C13—H13···O1 | 0.93 | 2.31 | 2.873 (10) | 118 |
| C15—H15B···O2 | 0.97 | 2.17 | 2.939 (10) | 136 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT2689).
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chai, H., Zhao, C. & Gong, P. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem.14, 911–917. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chakkaravarthi, G., Dhayalan, V., Mohanakrishnan, A. K. & Manivannan, V. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Chakkaravarthi, G., Ramesh, N., Mohanakrishnan, A. K. & Manivannan, V. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3564.
- Nieto, M. J., Alovero, F. L., Manzo, R. H. & Mazzieri, M. R. (2005). Eur. J. Med. Chem.40, 361–369. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Olgen, S. & Coban, T. (2003). Biol. Pharm. Bull.26, 736–738. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808007678/bt2689sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808007678/bt2689Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report