Abstract
The title crystal structure (systematic name: N-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-aminium chloride), C10H16N+·Cl−, was orginally determined by Simon, Bocskei & Torok [Acta Pharm. Hung. (1992). 62, 225–230] and Yao, Kan & Wang [Huaxue Shijie (1999). 40, 568–570] at room temperature but no atomic coordinates are available for these determinations. The molecule has interest with respect to biological activity. In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds form one-dimensional chains.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Cho (1990 ▶); Cho & Melega (2002 ▶); Davis & Swalwell (1994 ▶); O’Neil et al. (2001 ▶); Simon et al. (1992 ▶); Yao et al. (1999 ▶); Yu et al. (2003 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H16N+·Cl−
M r = 185.69
Monoclinic,
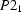
a = 7.1022 (11) Å
b = 7.2949 (11) Å
c = 10.8121 (17) Å
β = 97.293 (4)°
V = 555.64 (15) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.30 mm−1
T = 90 (2) K
0.28 × 0.14 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.922, T max = 0.971
5892 measured reflections
2720 independent reflections
2379 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.117
S = 1.05
2720 reflections
174 parameters
1 restraint
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1235 Freidel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.00 (10)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: CrystalMaker (Palmer, 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011550/lh2608sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011550/lh2608Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1D⋯Cl1i | 0.93 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 3.069 (2) | 179 (4) |
| N1—H1E⋯Cl1ii | 0.90 (3) | 2.22 (3) | 3.116 (2) | 176 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 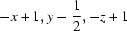 ; (ii)
; (ii) 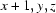 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Geospatial–Intelligence Agency (HM1582-05-1-2024) and the National Science Foundation (CHE-0604527). PMH expresses his gratitude to the Syracuse University and STEM Fellowship programs.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The compound, (+)-methamphetamine hydrochloride has been reinvestigated in this study by single-crystal x-ray diffraction to provide a complete determination of the atomic coordinates and lattice dimensions at 90 (2) K. Earlier structural studies on this compound by Simon et al. (1992) and by Yanhong et al. (1999) were performed at or near room temperature and did not include atomic coordinates. The determination of crystallographic data at cryogenic temperatures improves the precision of the atomic coordinates and also provides insight into temperature-induced lattice changes. This information is important in the complete understanding of the molecular solid and is particularly useful for validation of first-principles solid-state modeling.
The compound studied is a synthetic sympathomimetic drug and is specified as a controlled substance by the United States Federal government (O'Neil et al., 2001). The substance is a strong stimulant that affects the central nervous system (CNS) and contributes cardiactoxicity (Yu et al., 2003). The use of methamphetamine has increased substantially and is becoming a problem nation wide with its use increasing across all age groups (Cho & Melega, 2002). The compound has a more potent effect on the CNS than structurally similar amphetamine due to its increased penetration of the CNS (Davis & Swalwell,1994). The potency of methamphetamine is also dependent upon its chirality, as its dextrorotatory enantiomer exhibits an effect roughly fives times greater than that provided by the levorotatory enantiomer (Cho, 1990). The stimulant effects of methamphetamine can be compared to the effects brought on by the use of cocaine, however, the duration of the effects can be much greater for the methamphetamine than for cocaine (Cho, 1990).
The (+)-methamphetamine hydrochloride form of methamphetamine has become the primary form used (Cho & Melega, 2002). This highlights the importance of complete characterization of the substance. Knowledge of the solid-state Crystal Structure of this compound is imperative for its identification and detection via various spectroscopic methods, such as solid-state NMR and terahertz. The unit-cell dimensions determined by this study are slightly smaller than those published by Simon et al., (1992) leading to a reduction in the unit cell volume of approximately 2.4% from the previously calculated value. Overall the basic structural parameters, such as the space group, P21, are in agreement with earlier work (Simon et al., 1992).
Experimental
The material for this work was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and was used without any further purification.
Refinement
H atoms were located in a difference map and refined freely.
Figures
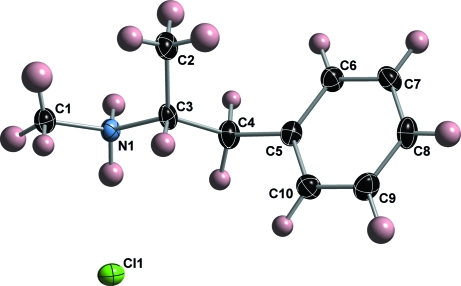
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom numbering scheme and thermal ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level.
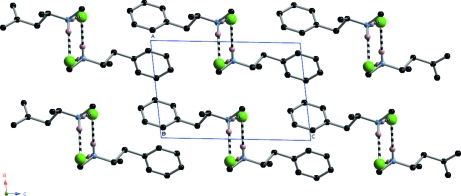
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound viewed in the ac plane, showing hydrogen bonds as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
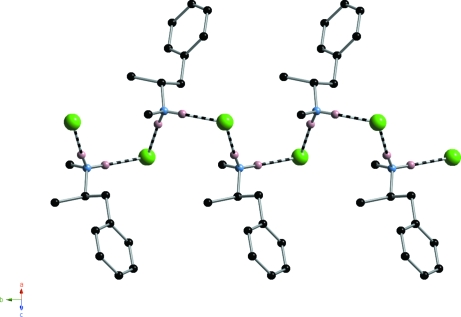
Fig. 3.
The crystal packing of the title compound, showing hydrogen bonds as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C10H16N+·Cl– | F000 = 200 |
| Mr = 185.69 | Dx = 1.110 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 964 reflections |
| a = 7.1022 (11) Å | θ = 2.9–22.5º |
| b = 7.2949 (11) Å | µ = 0.30 mm−1 |
| c = 10.8121 (17) Å | T = 90 (2) K |
| β = 97.293 (4)º | Block, colorless |
| V = 555.64 (15) Å3 | 0.28 × 0.14 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2720 independent reflections |
| Monochromator: graphite | 2379 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 512 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.047 |
| T = 90(2) K | θmax = 28.2º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 1.9º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.922, Tmax = 0.971 | k = −9→9 |
| 5892 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | All H-atom parameters refined |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0575P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 2720 reflections | Δρmin = −0.46 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Extinction correction: none |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1235 Freidel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.00 (10) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R– factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.23185 (8) | 0.78305 (9) | 0.55574 (6) | 0.02213 (16) | |
| N1 | 0.8031 (3) | 0.6811 (3) | 0.5363 (2) | 0.0172 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.6896 (4) | 0.7867 (6) | 0.4357 (2) | 0.0224 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.7510 (5) | 0.8922 (5) | 0.7083 (3) | 0.0256 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.7409 (4) | 0.6944 (4) | 0.6644 (3) | 0.0187 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.8700 (4) | 0.5637 (4) | 0.7481 (3) | 0.0236 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.8089 (4) | 0.5381 (4) | 0.8763 (2) | 0.0202 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.8940 (4) | 0.6384 (4) | 0.9782 (3) | 0.0228 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.8402 (4) | 0.6117 (4) | 1.0956 (3) | 0.0249 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.7005 (4) | 0.4842 (4) | 1.1138 (3) | 0.0262 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.6134 (4) | 0.3862 (4) | 1.0127 (3) | 0.0281 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.6678 (4) | 0.4130 (4) | 0.8947 (3) | 0.0248 (6) | |
| H1A | 0.718 (5) | 0.908 (6) | 0.446 (3) | 0.039 (10)* | |
| H1D | 0.791 (4) | 0.560 (5) | 0.509 (3) | 0.024 (8)* | |
| H1B | 0.558 (4) | 0.754 (4) | 0.436 (2) | 0.018 (7)* | |
| H1E | 0.925 (4) | 0.717 (4) | 0.541 (3) | 0.020 (8)* | |
| H1C | 0.733 (4) | 0.747 (5) | 0.356 (3) | 0.027 (9)* | |
| H2A | 0.650 (5) | 0.967 (5) | 0.659 (3) | 0.026 (9)* | |
| H2B | 0.880 (5) | 0.945 (5) | 0.718 (3) | 0.030 (10)* | |
| H2C | 0.724 (5) | 0.895 (5) | 0.791 (3) | 0.034 (9)* | |
| H3A | 0.622 (5) | 0.651 (5) | 0.654 (3) | 0.023 (8)* | |
| H4A | 0.863 (4) | 0.446 (4) | 0.701 (3) | 0.017 (7)* | |
| H4B | 0.996 (4) | 0.626 (4) | 0.757 (3) | 0.013 (7)* | |
| H6 | 0.980 (4) | 0.725 (4) | 0.965 (3) | 0.017 (7)* | |
| H7 | 0.900 (4) | 0.680 (4) | 1.164 (3) | 0.021 (7)* | |
| H8 | 0.681 (5) | 0.457 (5) | 1.193 (3) | 0.027 (9)* | |
| H9 | 0.521 (4) | 0.278 (7) | 1.025 (3) | 0.030 (7)* | |
| H10 | 0.611 (4) | 0.337 (4) | 0.827 (3) | 0.017 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0193 (3) | 0.0208 (3) | 0.0275 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | 0.0077 (2) | 0.0022 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0186 (11) | 0.0200 (12) | 0.0139 (10) | −0.0016 (9) | 0.0064 (8) | 0.0003 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0263 (12) | 0.0248 (12) | 0.0166 (11) | −0.0002 (17) | 0.0055 (9) | 0.0004 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0345 (17) | 0.0268 (15) | 0.0167 (14) | 0.0038 (13) | 0.0082 (12) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0191 (13) | 0.0265 (14) | 0.0114 (12) | −0.0008 (11) | 0.0052 (10) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0268 (14) | 0.0282 (16) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0038 (12) | 0.0076 (11) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0193 (12) | 0.0226 (13) | 0.0192 (13) | 0.0032 (10) | 0.0049 (10) | 0.0024 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0222 (13) | 0.0260 (14) | 0.0205 (13) | −0.0036 (12) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0266 (14) | 0.0293 (15) | 0.0184 (13) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0016 (11) | −0.0043 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0280 (14) | 0.0352 (16) | 0.0172 (13) | 0.0045 (12) | 0.0094 (11) | 0.0061 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0267 (15) | 0.0294 (16) | 0.0292 (15) | −0.0050 (12) | 0.0070 (12) | 0.0057 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0254 (14) | 0.0270 (14) | 0.0222 (13) | −0.0025 (11) | 0.0034 (11) | −0.0017 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C1 | 1.485 (4) | C4—H4A | 1.00 (3) |
| N1—C3 | 1.510 (3) | C4—H4B | 1.00 (3) |
| N1—H1D | 0.93 (3) | C5—C10 | 1.388 (4) |
| N1—H1E | 0.90 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.395 (4) |
| C1—H1A | 0.91 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.386 (4) |
| C1—H1B | 0.97 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.90 (3) |
| C1—H1C | 0.99 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.392 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.518 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.95 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 1.00 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.384 (4) |
| C2—H2B | 0.99 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.90 (3) |
| C2—H2C | 0.94 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.393 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.536 (4) | C9—H9 | 1.05 (4) |
| C3—H3A | 0.89 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.96 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.515 (4) | ||
| C1—N1—C3 | 116.4 (2) | C5—C4—C3 | 113.4 (2) |
| C1—N1—H1D | 104 (2) | C5—C4—H4A | 111.2 (18) |
| C3—N1—H1D | 109 (2) | C3—C4—H4A | 104.2 (17) |
| C1—N1—H1E | 108.9 (19) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.2 (17) |
| C3—N1—H1E | 108.5 (19) | C3—C4—H4B | 103.6 (16) |
| H1D—N1—H1E | 110 (3) | H4A—C4—H4B | 115 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 109 (2) | C10—C5—C6 | 118.7 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1B | 107.8 (17) | C10—C5—C4 | 120.5 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 116 (3) | C6—C5—C4 | 120.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1C | 106.5 (18) | C7—C6—C5 | 120.5 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 108 (3) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.9 (19) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 110 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 118.5 (19) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110 (2) | C6—C7—C8 | 120.5 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 114 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.6 (19) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 116 (3) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.8 (19) |
| C3—C2—H2C | 108 (2) | C9—C8—C7 | 119.3 (3) |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 106 (3) | C9—C8—H8 | 122 (2) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 101 (3) | C7—C8—H8 | 119 (2) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 109.9 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 120.2 (3) |
| N1—C3—C4 | 106.2 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.9 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 113.9 (3) | C10—C9—H9 | 118.3 (17) |
| N1—C3—H3A | 104 (2) | C5—C10—C9 | 120.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 113 (2) | C5—C10—H10 | 120.6 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 118.4 (18) |
| C1—N1—C3—C2 | −60.4 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—C3—C4 | 176.0 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.1 (4) |
| N1—C3—C4—C5 | −171.5 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.1 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 67.5 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.2 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C10 | 82.9 (3) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −0.8 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −97.6 (3) | C4—C5—C10—C9 | 178.8 (3) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.8 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | −0.2 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1D···Cl1i | 0.93 (4) | 2.14 (4) | 3.069 (2) | 179 (4) |
| N1—H1E···Cl1ii | 0.90 (3) | 2.22 (3) | 3.116 (2) | 176 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2608).
References
- Bruker (2002). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cho, A. K. (1990). Science, 249, 631–634. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cho, A. K. & Melega, W. P. (2002). J. Addict. Dis.21, 21–34. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Davis, G. G. & Swalwell, C. I. (1994). J. Forensic Sci.39, 1481–1485. [PubMed]
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- O’Neil, M. J., Smith, A., Heckelman, P. E. & Budavari, S. (2001). Editors. The Merck Index, 13th ed., entry 5975. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck & Co.
- Palmer, D. (2006). CrystalMaker CrystalMaker Software Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Simon, K., Bocskei, Z. & Torok, Z. (1992). Acta Pharm. Hung.62, 225–230. [PubMed]
- Yao, Y., Kan, Y. & Wang, S. (1999). Huaxue Shijie, 40, 568–570.
- Yu, Q., Larson, D. F. & Watson, R. R. (2003). Life Sci.73, 129–140. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011550/lh2608sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011550/lh2608Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report