Abstract
The title complex, [Ni4(C12H15NO4)4]·4H2O, has crystallographic fourfold inversion symmetry, with each NiII ion coordinated in a slightly distorted square-pyramidal coordination environment and forming an Ni4O4 cubane-like core. In the crystal structure, intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds connect complex and water molecules to form a three-dimensional network. The O atom of one of the unique hydroxymethyl groups is disordered over two sites, with the ratio of occupancies being approximately 0.79:0.21.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Dong, Li, Xu & Wang (2007 ▶); Dong, Li, Xu, Cui & Wang (2007 ▶); Koikawa et al. (2005 ▶); Mishtu et al. (2002 ▶); Nihei et al. (2003 ▶).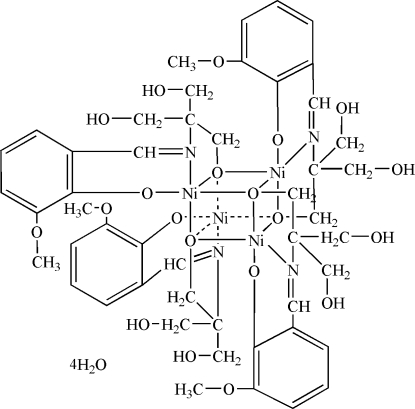
Experimental
Crystal data
[Ni4(C12H15NO4)4]·4H2O
M r = 1319.90
Tetragonal,
a = 18.754 (2) Å
c = 15.4395 (15) Å
V = 5430.3 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.45 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.30 × 0.29 × 0.28 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.670, T max = 0.686
11110 measured reflections
2399 independent reflections
1840 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.066
wR(F 2) = 0.194
S = 1.08
2399 reflections
186 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.70 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Siemens, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Siemens, 1996 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808009872/lh2612sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808009872/lh2612Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Ni1—O1 | 1.912 (4) |
| Ni1—O3 | 1.941 (4) |
| Ni1—N1 | 1.949 (6) |
| Ni1—O3i | 1.970 (4) |
| Ni1—O3ii | 2.565 (5) |
| O1—Ni1—O3 | 172.2 (2) |
| O1—Ni1—N1 | 94.3 (2) |
| O3—Ni1—N1 | 84.1 (2) |
| O1—Ni1—O3i | 94.57 (19) |
| O3—Ni1—O3i | 88.47 (19) |
| N1—Ni1—O3i | 166.1 (2) |
| O1—Ni1—O3ii | 94.23 (17) |
| O3—Ni1—O3ii | 79.80 (17) |
| N1—Ni1—O3ii | 117.2 (2) |
| O3i—Ni1—O3ii | 72.63 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 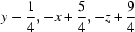 ; (ii)
; (ii) 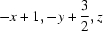 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5⋯N1 | 0.82 | 2.58 | 2.988 (9) | 112 |
| O4—H4⋯O6iii | 0.82 | 1.94 | 2.714 (8) | 157 |
| O4′—H4′⋯O6iii | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.68 (3) | 148 |
| O6—H6A⋯O1iv | 0.85 | 1.95 | 2.803 (7) | 180 |
| O6—H6B⋯O4v | 0.85 | 2.04 | 2.892 (9) | 180 |
Symmetry codes: (iii) 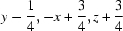 ; (iv)
; (iv) 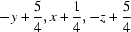 ; (v)
; (v) 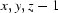 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant No. Y2004B02) for a research grant.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The chemistry of transition metal ion complexes of hydroxy (aryl-OH and alkyl-OH) rich molecules containing imine/amine group is important in the biomimetic studies of metalloproteins (Mishtu et al., 2002). Polynuclear metal complexes with tridentate ligand containing hydroxyl groups as terminal coordinating atoms have been reported and have attracted much attention (Nihei et al., 2003).
A few structurally characterized multinuclear complexes containing Schiff base ligands has been reported( e.g. Dong, Li, Xu & Wang (2007); Dong, Li, Xu, Cui & Wang (2007); Nihei et al., 2003). Herein, we report the synthesis and crystal structure of a novel tetranickel(II) complex with a tridentate Schiff base ligand derived from the condensation of o-vanillin and trihydroxymethylaminomethane.
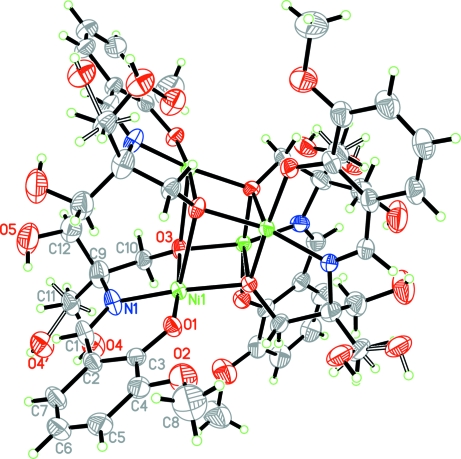
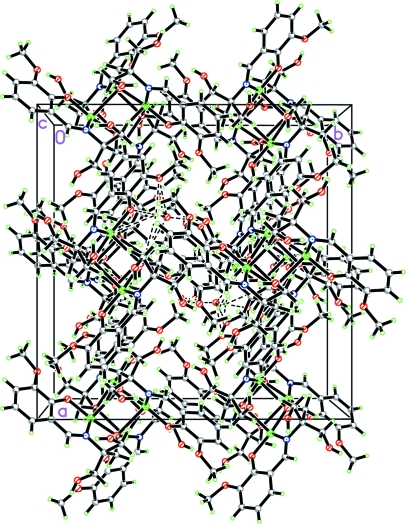
The title compound contains a tetranuclear cubane core based on an approximately cubic array of alternating nickel and oxygen atoms (Fig.1). Each NiII ion is in a distorted square-pyramidal coordination environment with one nitrogen and two oxygen atoms from one Schiff base ligand and two oxygen atoms from the symmetry related units of the cubane core. The Ni atom deviates from the basal plane (formed by O1, N1, O3 and O3i, symmetry code (i) y - 7/4, -x + 3/4, -z + 7/4) by 0.1299 (33) Å, with a significantly longer Ni—Oapical bond distance (Table 1). In the molecular structure, the Ni—Ni distances (3.472 (4) Å, 3.182 (3) Å) are longer than some reported values (Koikawa et al., 2005). In addition, there are four H2O solvent molecules, which are involved in intermolecular O-H···O hydrogen bonds (Fig. 2, Table 2) which stabilize the crystal atructure along with van der Waals forces.
Experimental
Trihydroxymethylaminomethane(1 mmol, 121.14 mg) was dissolved in hot methanol (10 ml) and added successively to a methanol solution(3 ml) of o-vanillin (1 mmol, 152.15 mg). The mixture was then stirred at 323 K for 2 h. Subsequently, an aqueous solution(2 ml) of nickel chlorate hexahydrate(1 mmol, 237.66 mg) was added dropwise and stirred for another 5 h. The solution was held at room temperature for ten days, whereupon green blocky crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained.
Refinement
Difference Fourier maps revealed that one of the hydroxymethyl group is distorted over two sites. The subsequent refinement of their occupancies gave the value of 0.791 (3) and 0.209 (3), respectively. All the H atoms were placed in geometrically calculated positions (C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å) and allowed to ride on their respective parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme. The water solvent molecules are not shown. Open bonds indicate disordered atoms and only the assymetric unit is labelled.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines. The disorder is not shown.
Crystal data
| [Ni4(C12H15NO4)4]·4H2O | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 1319.90 | F000 = 2752 |
| Tetragonal, I41/a | Dx = 1.614 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -I 4ad | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 18.754 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 3768 reflections |
| b = 18.754 (2) Å | θ = 2.2–25.2º |
| c = 15.4395 (15) Å | µ = 1.45 mm−1 |
| α = 90º | T = 298 (2) K |
| β = 90º | Block, green |
| γ = 90º | 0.30 × 0.29 × 0.28 mm |
| V = 5430.3 (10) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2399 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1840 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.034 |
| T = 298(2) K | θmax = 25.0º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 1.7º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.670, Tmax = 0.686 | k = −22→15 |
| 11110 measured reflections | l = −9→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.066 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.194 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0801P)2 + 60.7787P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2399 reflections | Δρmax = 1.23 e Å−3 |
| 186 parameters | Δρmin = −0.70 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Ni1 | 0.40964 (4) | 0.72996 (4) | 1.05945 (5) | 0.0374 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.3971 (4) | 0.6819 (3) | 0.9486 (4) | 0.0575 (16) | |
| O1 | 0.3327 (2) | 0.7952 (2) | 1.0412 (3) | 0.0480 (11) | |
| O2 | 0.2316 (3) | 0.8868 (4) | 1.0480 (5) | 0.097 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.4952 (2) | 0.6720 (2) | 1.0675 (3) | 0.0435 (10) | |
| O4 | 0.3704 (5) | 0.5372 (4) | 0.9346 (5) | 0.079 (2) | 0.791 (10) |
| H4 | 0.3533 | 0.5023 | 0.9103 | 0.119* | 0.791 (10) |
| O4' | 0.3587 (16) | 0.5547 (15) | 0.836 (2) | 0.079 (2) | 0.209 (10) |
| H4' | 0.3562 | 0.5134 | 0.8190 | 0.119* | 0.209 (10) |
| O5 | 0.4819 (5) | 0.6865 (5) | 0.7848 (5) | 0.120 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.4383 | 0.6853 | 0.7893 | 0.181* | |
| O6 | 0.3380 (3) | 0.6042 (3) | 0.0986 (4) | 0.0729 (16) | |
| H6A | 0.3733 | 0.5978 | 0.1322 | 0.088* | |
| H6B | 0.3472 | 0.5846 | 0.0503 | 0.088* | |
| C1 | 0.3427 (4) | 0.6889 (4) | 0.9010 (5) | 0.061 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.3392 | 0.6586 | 0.8535 | 0.073* | |
| C2 | 0.2852 (4) | 0.7394 (4) | 0.9132 (5) | 0.0529 (18) | |
| C3 | 0.2839 (3) | 0.7900 (4) | 0.9815 (4) | 0.0476 (16) | |
| C4 | 0.2269 (4) | 0.8386 (5) | 0.9823 (5) | 0.067 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.1712 (5) | 0.8344 (6) | 0.9218 (6) | 0.078 (3) | |
| H5A | 0.1334 | 0.8664 | 0.9245 | 0.094* | |
| C6 | 0.1727 (5) | 0.7834 (6) | 0.8595 (6) | 0.078 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.1354 | 0.7800 | 0.8201 | 0.094* | |
| C7 | 0.2279 (4) | 0.7377 (5) | 0.8544 (6) | 0.068 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.2281 | 0.7038 | 0.8104 | 0.081* | |
| C8 | 0.1829 (7) | 0.9466 (7) | 1.0493 (9) | 0.130 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.1797 | 0.9668 | 0.9923 | 0.195* | |
| H8B | 0.2001 | 0.9820 | 1.0891 | 0.195* | |
| H8C | 0.1366 | 0.9306 | 1.0675 | 0.195* | |
| C9 | 0.4572 (5) | 0.6290 (5) | 0.9262 (6) | 0.075 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.4932 (4) | 0.6144 (4) | 1.0099 (4) | 0.0523 (17) | |
| H10A | 0.4691 | 0.5749 | 1.0380 | 0.063* | |
| H10B | 0.5418 | 0.5995 | 0.9981 | 0.063* | |
| C11 | 0.4273 (5) | 0.5654 (5) | 0.8832 (6) | 0.073 (2) | |
| H11A | 0.4096 | 0.5781 | 0.8262 | 0.088* | 0.791 (10) |
| H11B | 0.4642 | 0.5296 | 0.8762 | 0.088* | 0.791 (10) |
| H11C | 0.4635 | 0.5509 | 0.8420 | 0.088* | 0.209 (10) |
| H11D | 0.4276 | 0.5290 | 0.9279 | 0.088* | 0.209 (10) |
| C12 | 0.5136 (5) | 0.6631 (6) | 0.8640 (6) | 0.085 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.5359 | 0.7033 | 0.8927 | 0.101* | |
| H12B | 0.5504 | 0.6283 | 0.8514 | 0.101* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ni1 | 0.0427 (5) | 0.0358 (5) | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0002 (3) | −0.0072 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| N1 | 0.080 (4) | 0.046 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.015 (3) | −0.022 (3) | −0.009 (3) |
| O1 | 0.045 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.043 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.009 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| O2 | 0.070 (4) | 0.125 (6) | 0.095 (5) | 0.048 (4) | −0.010 (4) | −0.019 (4) |
| O3 | 0.056 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.008 (2) | −0.0013 (19) |
| O4 | 0.094 (6) | 0.059 (4) | 0.086 (5) | 0.007 (4) | −0.005 (5) | −0.030 (4) |
| O4' | 0.094 (6) | 0.059 (4) | 0.086 (5) | 0.007 (4) | −0.005 (5) | −0.030 (4) |
| O5 | 0.111 (6) | 0.189 (8) | 0.061 (4) | 0.038 (6) | 0.005 (4) | 0.011 (5) |
| O6 | 0.053 (3) | 0.096 (4) | 0.070 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.011 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C1 | 0.079 (5) | 0.056 (4) | 0.048 (4) | 0.006 (4) | −0.022 (4) | −0.007 (3) |
| C2 | 0.055 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.045 (4) | −0.010 (3) | −0.013 (3) | 0.007 (3) |
| C3 | 0.039 (4) | 0.059 (4) | 0.044 (4) | −0.001 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.014 (3) |
| C4 | 0.049 (4) | 0.093 (6) | 0.058 (5) | 0.010 (4) | −0.001 (4) | 0.002 (5) |
| C5 | 0.050 (5) | 0.110 (8) | 0.075 (6) | 0.014 (5) | −0.004 (4) | 0.010 (6) |
| C6 | 0.060 (5) | 0.106 (7) | 0.069 (6) | −0.008 (5) | −0.018 (4) | 0.007 (5) |
| C7 | 0.064 (5) | 0.081 (6) | 0.058 (5) | −0.011 (4) | −0.025 (4) | 0.005 (4) |
| C8 | 0.105 (9) | 0.148 (12) | 0.137 (12) | 0.064 (9) | −0.013 (8) | −0.026 (9) |
| C9 | 0.088 (6) | 0.076 (6) | 0.061 (5) | 0.035 (5) | −0.005 (5) | −0.016 (4) |
| C10 | 0.054 (4) | 0.060 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.010 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.013 (3) |
| C11 | 0.081 (6) | 0.076 (6) | 0.061 (5) | 0.016 (5) | −0.007 (5) | −0.031 (5) |
| C12 | 0.085 (7) | 0.104 (8) | 0.065 (6) | 0.024 (6) | 0.001 (5) | −0.002 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Ni1—O1 | 1.912 (4) | C2—C7 | 1.408 (10) |
| Ni1—O3 | 1.941 (4) | C2—C3 | 1.419 (10) |
| Ni1—N1 | 1.949 (6) | C3—C4 | 1.405 (11) |
| Ni1—O3i | 1.970 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.403 (12) |
| Ni1—O3ii | 2.565 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.357 (13) |
| N1—C1 | 1.265 (9) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C9 | 1.541 (10) | C6—C7 | 1.345 (13) |
| O1—C3 | 1.303 (8) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C4 | 1.362 (11) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C8 | 1.446 (12) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| O3—C10 | 1.400 (8) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| O3—Ni1iii | 1.970 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| O4—C11 | 1.430 (12) | C9—C11 | 1.475 (13) |
| O4—H4 | 0.8200 | C9—C10 | 1.484 (11) |
| O4—H11D | 1.0883 | C9—C12 | 1.565 (14) |
| O4'—C11 | 1.49 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| O4'—H4' | 0.8200 | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| O5—C12 | 1.429 (12) | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| O5—H5 | 0.8200 | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| O6—H6A | 0.8500 | C11—H11C | 0.9698 |
| O6—H6B | 0.8499 | C11—H11D | 0.9699 |
| C1—C2 | 1.447 (11) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| O1—Ni1—O3 | 172.2 (2) | O2—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| O1—Ni1—N1 | 94.3 (2) | O2—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O3—Ni1—N1 | 84.1 (2) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O1—Ni1—O3i | 94.57 (19) | O2—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O3—Ni1—O3i | 88.47 (19) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N1—Ni1—O3i | 166.1 (2) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O1—Ni1—O3ii | 94.23 (17) | C11—C9—C10 | 114.6 (8) |
| O3—Ni1—O3ii | 79.80 (17) | C11—C9—N1 | 110.2 (8) |
| N1—Ni1—O3ii | 117.2 (2) | C10—C9—N1 | 104.9 (6) |
| O3i—Ni1—O3ii | 72.63 (17) | C11—C9—C12 | 108.1 (8) |
| C1—N1—C9 | 121.7 (6) | C10—C9—C12 | 107.5 (8) |
| C1—N1—Ni1 | 124.1 (6) | N1—C9—C12 | 111.6 (7) |
| C9—N1—Ni1 | 114.0 (5) | O3—C10—C9 | 115.0 (6) |
| C3—O1—Ni1 | 125.9 (4) | O3—C10—H10A | 108.5 |
| C4—O2—C8 | 119.0 (8) | C9—C10—H10A | 108.5 |
| C10—O3—Ni1 | 111.7 (4) | O3—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| C10—O3—Ni1iii | 121.9 (4) | C9—C10—H10B | 108.5 |
| Ni1—O3—Ni1iii | 108.9 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.5 |
| C11—O4—H4 | 109.5 | O4—C11—C9 | 109.4 (7) |
| H4—O4—H11D | 103.2 | O4—C11—O4' | 65.0 (13) |
| C11—O4'—H4' | 109.5 | C9—C11—O4' | 130.9 (13) |
| C12—O5—H5 | 109.5 | O4—C11—H11A | 109.8 |
| H6A—O6—H6B | 108.4 | C9—C11—H11A | 109.8 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 126.4 (7) | O4'—C11—H11A | 45.3 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 116.8 | O4—C11—H11B | 109.8 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 116.8 | C9—C11—H11B | 109.8 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 118.8 (7) | O4'—C11—H11B | 117.9 |
| C7—C2—C1 | 118.0 (7) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 123.1 (6) | O4—C11—H11C | 141.6 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 118.7 (7) | C9—C11—H11C | 104.8 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 124.4 (6) | O4'—C11—H11C | 104.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 116.9 (7) | H11A—C11—H11C | 73.3 |
| O2—C4—C5 | 125.6 (8) | O4—C11—H11D | 49.5 |
| O2—C4—C3 | 112.8 (7) | C9—C11—H11D | 104.3 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.6 (9) | O4'—C11—H11D | 104.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.7 (9) | H11A—C11—H11D | 145.1 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.1 | H11B—C11—H11D | 65.7 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.1 | H11C—C11—H11D | 105.4 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.5 (8) | O5—C12—C9 | 111.7 (8) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.8 | O5—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 | C9—C12—H12A | 109.3 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 122.3 (9) | O5—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 118.9 | C9—C12—H12B | 109.3 |
| C2—C7—H7 | 118.9 | H12A—C12—H12B | 107.9 |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 176.2 (7) |
Symmetry codes: (i) y−1/4, −x+5/4, −z+9/4; (ii) −x+1, −y+3/2, z; (iii) −y+5/4, x+1/4, −z+9/4.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5···N1 | 0.82 | 2.58 | 2.988 (9) | 112 |
| O4—H4···O6iv | 0.82 | 1.94 | 2.714 (8) | 157 |
| O4'—H4'···O6iv | 0.82 | 1.96 | 2.68 (3) | 148 |
| O6—H6A···O1v | 0.85 | 1.95 | 2.803 (7) | 180 |
| O6—H6B···O4vi | 0.85 | 2.04 | 2.892 (9) | 180 |
Symmetry codes: (iv) y−1/4, −x+3/4, z+3/4; (v) −y+5/4, x+1/4, −z+5/4; (vi) x, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2612).
References
- Dong, J.-F., Li, L.-Z., Xu, T., Cui, H. & Wang, D.-Q. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m1501–m1502.
- Dong, J.-F., Li, L.-Z., Xu, H.-Y. & Wang, D.-Q. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m2300.
- Koikawa, M., Ohba, M. & Tokii, T. (2005). Polyhedron, 24, 2257–2262.
- Mishtu, D., Chebrolu, P. R., Pauli, K. S. & Kari, R. (2002). Inorg. Chem. Commun.5, 380–383.
- Nihei, M., Hoshino, N., Ito, T. & Oshio, H. (2003). Polyhedron, 22, 2359–2362.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1996). SMART and SAINT Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808009872/lh2612sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808009872/lh2612Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report