Abstract
In the cation of the title compound, C22H24N3O4 +·Cl−, an active ingredient of the anticancer drug also known as Tarceva, the quinazoline ring system is planar within 0.044 (3) Å. The dihedral angle formed by the mean planes of the two six-membered quinazoline rings is 3.2 (1)°. Both N-bound H atoms participate in N—H⋯Cl bonds, which link the ions into infinite chains running along the b axis. C—H⋯O interactions involving neighboring cations provide additional stabilization of these aggregates.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Herbst et al. (2005 ▶); Minna & Dowell (2005 ▶); Li et al. (2007 ▶); Xia (2005 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).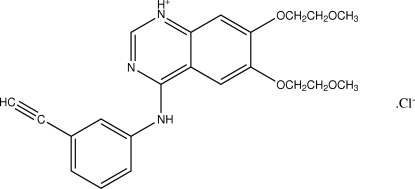
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H24N3O4 +·Cl−
M r = 429.89
Monoclinic,
a = 14.5351 (15) Å
b = 18.4863 (19) Å
c = 8.1222 (8) Å
β = 102.966 (2)°
V = 2126.8 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.21 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
24377 measured reflections
5001 independent reflections
3649 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.050
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.073
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.16
5001 reflections
275 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PARST (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011707/ya2075sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011707/ya2075Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯Cl1 | 0.86 | 2.46 | 3.277 (2) | 160 |
| N1—HN1⋯Cl1i | 0.86 | 2.23 | 3.066 (2) | 165 |
| C1—H1⋯O4i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.372 (3) | 167 |
Symmetry code: (i) 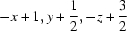 .
.
Acknowledgments
SS thanks the Vice Chancellor and the management of Kalasalingam University, Anand Nagar, Krishnankoil, for their support and encouragement.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Erlotinib hydrochloride, (I), also known under its tradename Tarceva, is a potent reversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor with single agent activity in patients with non-small lung cancer, pancreatic cancer and several other types of cancer (Herbst et al., 2005). It is the first drug to demonstrate an increase in survival in phase III trials in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (Minna & Dowell, 2005). It has recently been shown to be potent inhibitor of JAK2 V617F activity; JAK2 V617F is a mutant of tyrosine kinase JAK2 (Li et al., 2007). As no crystal structure of the title compound has yet been published, we have undertaken the single-crystal X-ray diffraction study and report here its results.
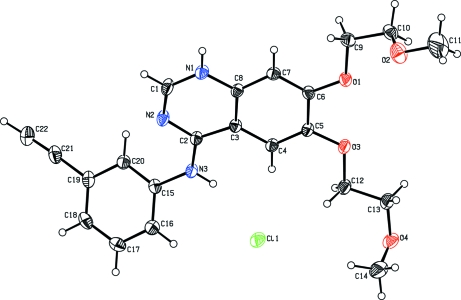
The X-ray study confirmed the molecular structure and atomic connectivity for (I), as illustrated in Fig. 1. The C21—C22 bond length [1.170 (4) Å] is consistent with its acetylenic character, as evidenced by literature value of 1.174 (11) Å (see Allen et al., 1987). The geometry of the quinazoline ring system is comparable to that in the reported related structure (Xia, 2005).
The bicyclic system is effectively planar with a maximum deviation of 0.044 (3) Å for the C1 atom. The dihedral angle formed by the mean planes of two six membered rings of quinazoline moiety is 3.2 (1)°. The benzene ring C15—C20 and its attached ethynyl group are coplanar with a maximum deviation -0.011 (3) Å for the C20 atom. The dihedral angle between this ring and quinazoline ring system is 34.4 (1)°. The short contacts H3···H4 (2.12 Å) and H7···H9A (2.14 Å) result in substantial widening of the C2—N3—C15 and C6—O1—C9 bond angles [127.4 (2)° and 117.1 (2)°, respectively].
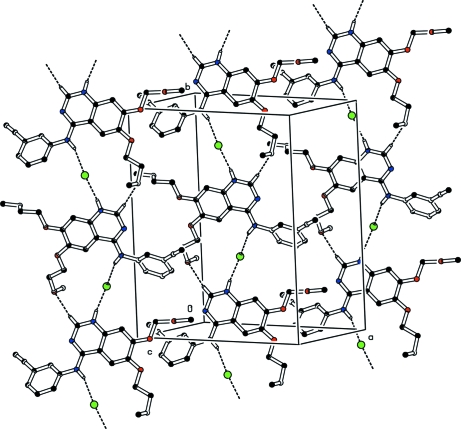
Both N-bound H atoms (HN1 and H3) participate in H-bonds with the Cl1 anion (Table 2). These bonds link cations and anions into the infinite chains running along the b axis of the crystal. The C1—H1···O4 interactions involving neighboring cations provide additional stabilization for these chains (Fig. 2).
Experimental
In order to obtain crystals suitable for X-ray study, commercially available erlotinib hydrochloride was dissolved in a methanol-water solution (90:10v/v); the solvents were then allowed to evaporate slowly.
Refinement
The acetylenic H22 atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically [C22—H22 0.95 (3) Å]; all other H atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H distances of 0.93–0.97 Å, N—H 0.86 Å and were included in the refinement in the riding motion approximation with Uiso= 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H and 1.2Ueq for all other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure and atom-numbering scheme for (I); displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and H atoms are shown as small spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
Molecular packing of (I) viewed along the c axis; H-bonds are shown as dashed lines; H atoms, not involved in H-bonds, have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C22H24N3O4+·Cl– | F000 = 904 |
| Mr = 429.89 | Dx = 1.343 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 9448 reflections |
| a = 14.5351 (15) Å | θ = 2.2–23.4º |
| b = 18.4863 (19) Å | µ = 0.21 mm−1 |
| c = 8.1222 (8) Å | T = 293 (2) K |
| β = 102.966 (2)º | Block, colourless |
| V = 2126.8 (4) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.22 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX area-detector diffractometer | 3649 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.050 |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmax = 28.0º |
| T = 293(2) K | θmin = 1.8º |
| ω scans | h = −18→19 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −24→24 |
| 24377 measured reflections | l = −10→10 |
| 5001 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.073 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0551P)2 + 0.7563P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.16 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 5001 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 275 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.50200 (5) | 0.34427 (3) | 0.62635 (9) | 0.0469 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.27725 (11) | 0.61695 (9) | 0.9544 (2) | 0.0395 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.10485 (14) | 0.70220 (13) | 0.9170 (3) | 0.0648 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.29876 (12) | 0.48732 (9) | 0.8521 (2) | 0.0417 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.20059 (13) | 0.31485 (10) | 0.6875 (3) | 0.0514 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.57019 (14) | 0.69146 (10) | 0.8273 (3) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| HN1 | 0.5603 | 0.7355 | 0.8527 | 0.047* | |
| N2 | 0.67238 (14) | 0.60941 (11) | 0.7423 (3) | 0.0408 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.63506 (13) | 0.48880 (10) | 0.7058 (3) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.5945 | 0.4550 | 0.7065 | 0.042* | |
| C1 | 0.64787 (18) | 0.67467 (13) | 0.7780 (4) | 0.0435 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.6887 | 0.7123 | 0.7678 | 0.052* | |
| C2 | 0.61060 (16) | 0.55508 (12) | 0.7464 (3) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.52182 (16) | 0.56803 (12) | 0.7918 (3) | 0.0310 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.45169 (16) | 0.51536 (12) | 0.7961 (3) | 0.0321 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.4604 | 0.4681 | 0.7637 | 0.039* | |
| C5 | 0.37123 (16) | 0.53333 (13) | 0.8474 (3) | 0.0324 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.35795 (16) | 0.60529 (13) | 0.9019 (3) | 0.0326 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.42426 (17) | 0.65734 (12) | 0.8963 (3) | 0.0346 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.4158 | 0.7044 | 0.9305 | 0.042* | |
| C8 | 0.50471 (16) | 0.63882 (12) | 0.8385 (3) | 0.0320 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.26703 (18) | 0.68616 (14) | 1.0300 (4) | 0.0417 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.2742 | 0.7248 | 0.9530 | 0.050* | |
| H9B | 0.3151 | 0.6919 | 1.1333 | 0.050* | |
| C10 | 0.17127 (19) | 0.68926 (15) | 1.0675 (4) | 0.0448 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.1574 | 0.6439 | 1.1166 | 0.054* | |
| H10B | 0.1689 | 0.7277 | 1.1478 | 0.054* | |
| C11 | 0.0123 (3) | 0.7093 (3) | 0.9450 (7) | 0.1109 (16) | |
| H11A | −0.0314 | 0.7178 | 0.8392 | 0.166* | |
| H11B | 0.0106 | 0.7492 | 1.0197 | 0.166* | |
| H11C | −0.0047 | 0.6656 | 0.9949 | 0.166* | |
| C12 | 0.30023 (17) | 0.41876 (13) | 0.7695 (4) | 0.0422 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.3512 | 0.3889 | 0.8318 | 0.051* | |
| H12B | 0.3093 | 0.4256 | 0.6558 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | 0.2062 (2) | 0.38355 (15) | 0.7650 (4) | 0.0510 (7) | |
| H13A | 0.1974 | 0.3784 | 0.8793 | 0.061* | |
| H13B | 0.1560 | 0.4142 | 0.7029 | 0.061* | |
| C14 | 0.1801 (3) | 0.3188 (2) | 0.5094 (5) | 0.0765 (11) | |
| H14A | 0.1774 | 0.2709 | 0.4631 | 0.115* | |
| H14B | 0.2286 | 0.3460 | 0.4740 | 0.115* | |
| H14C | 0.1203 | 0.3423 | 0.4699 | 0.115* | |
| C15 | 0.72087 (16) | 0.46773 (12) | 0.6616 (3) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.71529 (18) | 0.41268 (14) | 0.5436 (3) | 0.0396 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.6575 | 0.3912 | 0.4968 | 0.048* | |
| C17 | 0.7960 (2) | 0.38986 (16) | 0.4959 (4) | 0.0474 (7) | |
| H17 | 0.7922 | 0.3529 | 0.4169 | 0.057* | |
| C18 | 0.88191 (19) | 0.42120 (15) | 0.5641 (4) | 0.0473 (7) | |
| H18 | 0.9356 | 0.4060 | 0.5296 | 0.057* | |
| C19 | 0.88874 (17) | 0.47541 (13) | 0.6842 (3) | 0.0395 (6) | |
| C20 | 0.80763 (17) | 0.49842 (13) | 0.7347 (3) | 0.0371 (6) | |
| H20 | 0.8118 | 0.5341 | 0.8168 | 0.045* | |
| C21 | 0.9793 (2) | 0.50773 (16) | 0.7563 (4) | 0.0490 (7) | |
| C22 | 1.0541 (2) | 0.5325 (2) | 0.8100 (5) | 0.0653 (9) | |
| H22 | 1.115 (2) | 0.5534 (16) | 0.849 (4) | 0.063 (9)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0508 (4) | 0.0276 (3) | 0.0642 (5) | −0.0062 (3) | 0.0173 (3) | −0.0023 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0339 (9) | 0.0328 (9) | 0.0559 (11) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0190 (8) | −0.0044 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0438 (12) | 0.0814 (16) | 0.0696 (15) | 0.0176 (11) | 0.0135 (10) | 0.0081 (12) |
| O3 | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0315 (9) | 0.0628 (12) | −0.0071 (7) | 0.0207 (9) | −0.0071 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0525 (12) | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0694 (14) | −0.0093 (9) | 0.0145 (10) | −0.0046 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0223 (10) | 0.0611 (14) | −0.0008 (9) | 0.0158 (10) | −0.0023 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0270 (11) | 0.0661 (15) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0036 (10) |
| N3 | 0.0276 (10) | 0.0264 (10) | 0.0527 (13) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0009 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0330 (14) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0715 (19) | −0.0040 (11) | 0.0184 (13) | 0.0048 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0279 (12) | 0.0266 (12) | 0.0412 (14) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0083 (10) | 0.0030 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0280 (12) | 0.0289 (12) | 0.0361 (13) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0073 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0424 (14) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0091 (10) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0299 (12) | 0.0299 (12) | 0.0377 (13) | −0.0032 (10) | 0.0080 (10) | 0.0028 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0297 (12) | 0.0329 (13) | 0.0361 (13) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0095 (10) | 0.0009 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0361 (13) | 0.0237 (11) | 0.0447 (14) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0107 (11) | −0.0030 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0299 (12) | 0.0263 (12) | 0.0394 (13) | −0.0007 (9) | 0.0068 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0431 (15) | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0490 (16) | 0.0055 (12) | 0.0147 (12) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0493 (16) | 0.0390 (15) | 0.0512 (16) | 0.0085 (12) | 0.0221 (13) | 0.0014 (13) |
| C11 | 0.045 (2) | 0.152 (4) | 0.135 (4) | 0.034 (2) | 0.019 (2) | −0.013 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0350 (14) | 0.0305 (13) | 0.0636 (18) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0162 (12) | −0.0027 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0448 (16) | 0.0404 (15) | 0.073 (2) | −0.0095 (12) | 0.0240 (15) | −0.0085 (14) |
| C14 | 0.093 (3) | 0.066 (2) | 0.077 (3) | −0.032 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0167 (19) |
| C15 | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0260 (12) | 0.0403 (14) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0125 (11) | 0.0077 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0385 (14) | 0.0353 (14) | 0.0443 (15) | 0.0027 (11) | 0.0079 (11) | 0.0015 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0542 (17) | 0.0441 (16) | 0.0466 (16) | 0.0070 (13) | 0.0167 (13) | −0.0070 (13) |
| C18 | 0.0421 (16) | 0.0517 (17) | 0.0538 (17) | 0.0127 (13) | 0.0230 (13) | 0.0022 (14) |
| C19 | 0.0330 (13) | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0533 (17) | 0.0038 (11) | 0.0158 (12) | 0.0107 (12) |
| C20 | 0.0346 (13) | 0.0285 (12) | 0.0496 (16) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0123 (11) | −0.0001 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0387 (16) | 0.0495 (17) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0052 (13) | 0.0237 (14) | 0.0062 (14) |
| C22 | 0.0416 (19) | 0.077 (2) | 0.082 (2) | −0.0098 (17) | 0.0233 (17) | −0.0084 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C6 | 1.352 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9700 |
| O1—C9 | 1.441 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| O2—C10 | 1.397 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| O2—C11 | 1.419 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| O3—C5 | 1.361 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| O3—C12 | 1.436 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| O4—C13 | 1.412 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.507 (3) |
| O4—C14 | 1.412 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| N1—C1 | 1.317 (3) | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C8 | 1.378 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| N1—HN1 | 0.8600 | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| N2—C1 | 1.309 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C2 | 1.353 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| N3—C2 | 1.337 (3) | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| N3—C15 | 1.427 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.388 (3) |
| N3—H3 | 0.8600 | C15—C20 | 1.389 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.382 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.440 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C8 | 1.400 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.375 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.416 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.368 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.386 (4) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.429 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.399 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.370 (3) | C19—C21 | 1.444 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.397 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C21—C22 | 1.170 (4) |
| C9—C10 | 1.491 (3) | C22—H22 | 0.95 (3) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9700 | ||
| C6—O1—C9 | 117.09 (19) | H10A—C10—H10B | 108.3 |
| C10—O2—C11 | 111.7 (3) | O2—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C5—O3—C12 | 116.48 (18) | O2—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C13—O4—C14 | 112.8 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C8 | 120.4 (2) | O2—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—HN1 | 119.8 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—HN1 | 119.8 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C1—N2—C2 | 117.6 (2) | O3—C12—C13 | 106.5 (2) |
| C2—N3—C15 | 127.4 (2) | O3—C12—H12A | 110.4 |
| C2—N3—H3 | 116.3 | C13—C12—H12A | 110.4 |
| C15—N3—H3 | 116.3 | O3—C12—H12B | 110.4 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 125.4 (2) | C13—C12—H12B | 110.4 |
| N2—C1—H1 | 117.3 | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.6 |
| N1—C1—H1 | 117.3 | O4—C13—C12 | 111.1 (2) |
| N3—C2—N2 | 117.4 (2) | O4—C13—H13A | 109.4 |
| N3—C2—C3 | 121.2 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.4 |
| N2—C2—C3 | 121.4 (2) | O4—C13—H13B | 109.4 |
| C8—C3—C4 | 117.6 (2) | C12—C13—H13B | 109.4 |
| C8—C3—C2 | 116.7 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 125.7 (2) | O4—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.7 (2) | O4—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | O4—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O3—C5—C4 | 125.2 (2) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O3—C5—C6 | 114.5 (2) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.3 (2) | C16—C15—C20 | 120.1 (2) |
| O1—C6—C7 | 124.4 (2) | C16—C15—N3 | 117.1 (2) |
| O1—C6—C5 | 115.7 (2) | C20—C15—N3 | 122.8 (2) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.9 (2) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.2 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.4 | C18—C17—C16 | 120.6 (3) |
| N1—C8—C7 | 119.4 (2) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.7 |
| N1—C8—C3 | 118.3 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.7 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 122.2 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.2 (2) |
| O1—C9—C10 | 108.1 (2) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| O1—C9—H9A | 110.1 | C19—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C10—C9—H9A | 110.1 | C18—C19—C20 | 119.6 (2) |
| O1—C9—H9B | 110.1 | C18—C19—C21 | 120.0 (2) |
| C10—C9—H9B | 110.1 | C20—C19—C21 | 120.4 (2) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 108.4 | C15—C20—C19 | 119.6 (2) |
| O2—C10—C9 | 108.7 (2) | C15—C20—H20 | 120.2 |
| O2—C10—H10A | 109.9 | C19—C20—H20 | 120.2 |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.9 | C22—C21—C19 | 177.3 (3) |
| O2—C10—H10B | 109.9 | C21—C22—H22 | 178 (2) |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.9 | ||
| C2—N2—C1—N1 | 4.2 (4) | C1—N1—C8—C3 | −1.7 (4) |
| C8—N1—C1—N2 | −2.7 (4) | C6—C7—C8—N1 | 177.9 (2) |
| C15—N3—C2—N2 | 1.5 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | −2.4 (4) |
| C15—N3—C2—C3 | −178.7 (2) | C4—C3—C8—N1 | −177.0 (2) |
| C1—N2—C2—N3 | 178.4 (2) | C2—C3—C8—N1 | 4.1 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2—C3 | −1.3 (4) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | 3.4 (4) |
| N3—C2—C3—C8 | 177.5 (2) | C2—C3—C8—C7 | −175.5 (2) |
| N2—C2—C3—C8 | −2.7 (3) | C6—O1—C9—C10 | 176.3 (2) |
| N3—C2—C3—C4 | −1.2 (4) | C11—O2—C10—C9 | −177.2 (3) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | 178.5 (2) | O1—C9—C10—O2 | −76.9 (3) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | −1.2 (3) | C5—O3—C12—C13 | −170.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 177.5 (2) | C14—O4—C13—C12 | −79.6 (3) |
| C12—O3—C5—C4 | −11.3 (3) | O3—C12—C13—O4 | −179.3 (2) |
| C12—O3—C5—C6 | 168.7 (2) | C2—N3—C15—C16 | −146.2 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—O3 | 178.3 (2) | C2—N3—C15—C20 | 35.6 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.7 (4) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −1.7 (4) |
| C9—O1—C6—C7 | −8.6 (3) | N3—C15—C16—C17 | −179.9 (2) |
| C9—O1—C6—C5 | 172.4 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.1 (4) |
| O3—C5—C6—O1 | 1.8 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.1 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—O1 | −178.3 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.5 (4) |
| O3—C5—C6—C7 | −177.3 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C21 | 179.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 2.7 (4) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 2.4 (4) |
| O1—C6—C7—C8 | −179.6 (2) | N3—C15—C20—C19 | −179.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.6 (4) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | −1.3 (4) |
| C1—N1—C8—C7 | 177.9 (2) | C21—C19—C20—C15 | 178.7 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···Cl1 | 0.86 | 2.46 | 3.277 (2) | 160 |
| N1—HN1···Cl1i | 0.86 | 2.23 | 3.066 (2) | 165 |
| C1—H1···O4i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.372 (3) | 167 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: YA2075).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–S19.
- Bruker (2001). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Herbst, R. S., Prager, D., Hermann, R., Fehrenbacher, L., Johnson, B. E., Sandler, A., Kris, M. G., Tran, H. T., Klein, P., Li, X., Ramies, D., Johnson, D. H. & Miller, V. A. (2005). J. Clin. Oncol.23, 5892–5899. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Li, Z., Xu, M., Xing, S., Ho, W. T., Ishii, T., Li, Q., Fu, X. & Zhao, Z. J. (2007). J. Biol. Chem.282, 3428–3432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Minna, J. D. & Dowell, J. (2005). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. pp. S14–S15. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst.28, 659.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Xia, M. (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o3380–o3382.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011707/ya2075sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011707/ya2075Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report