Abstract
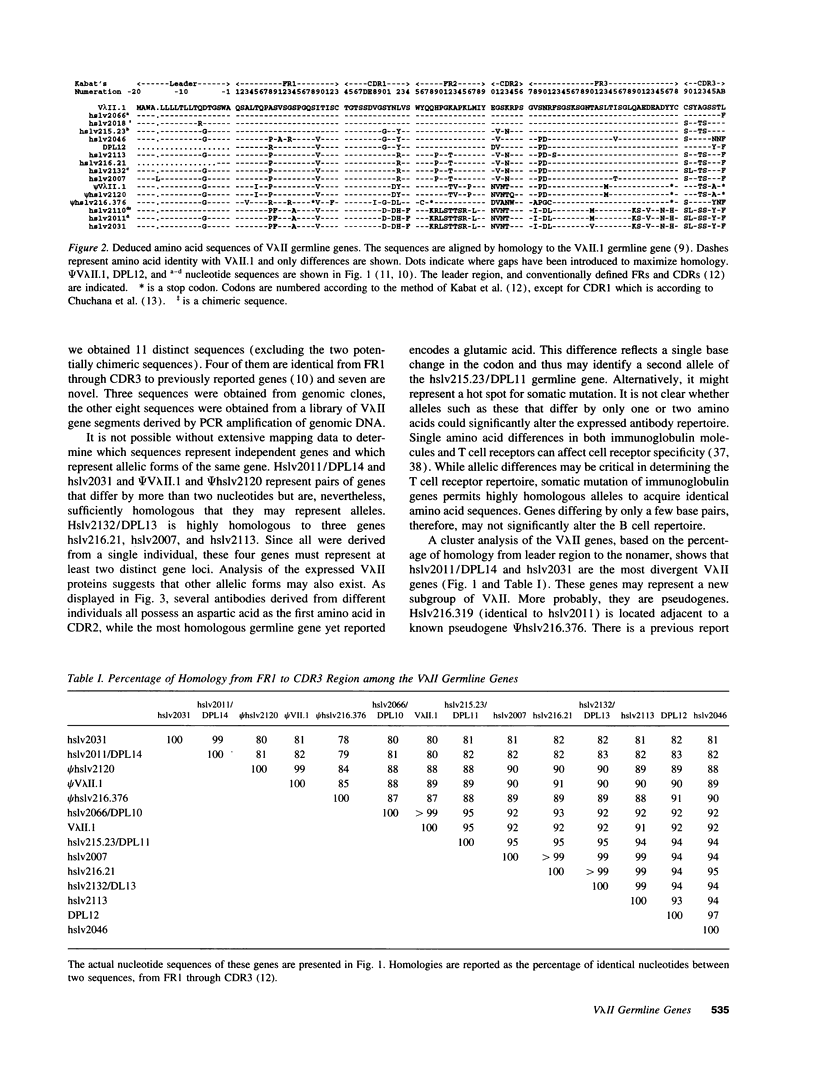
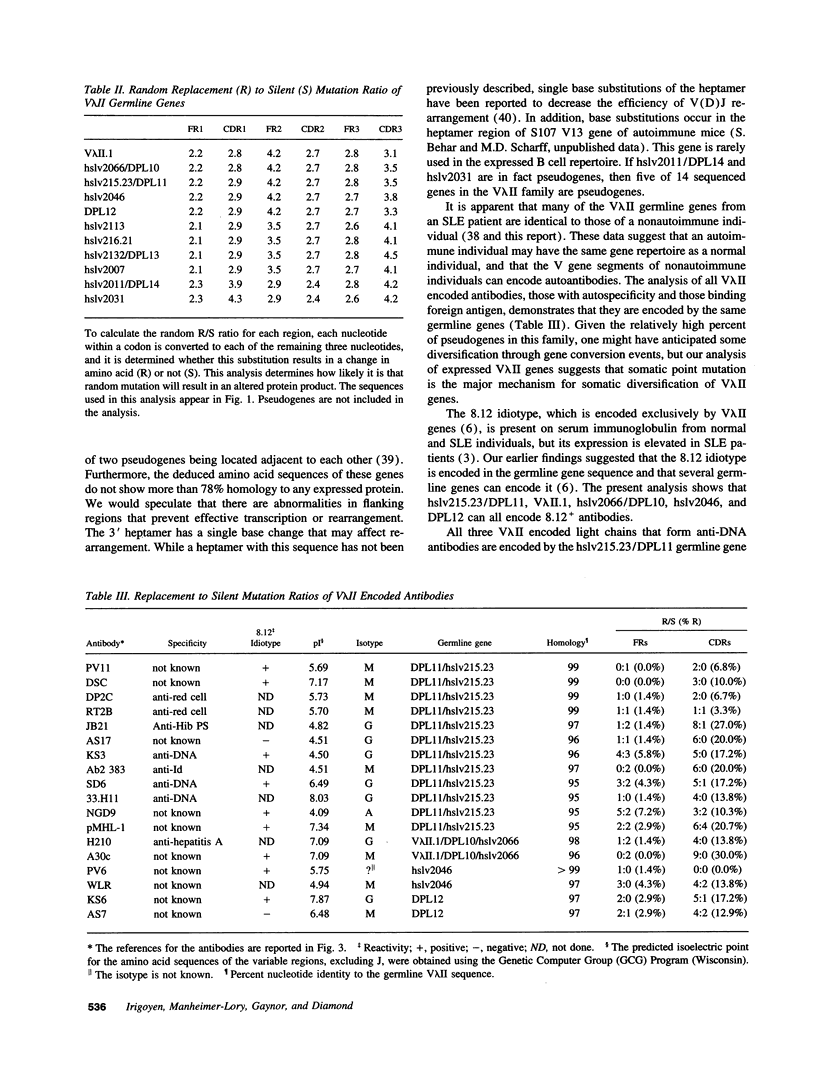
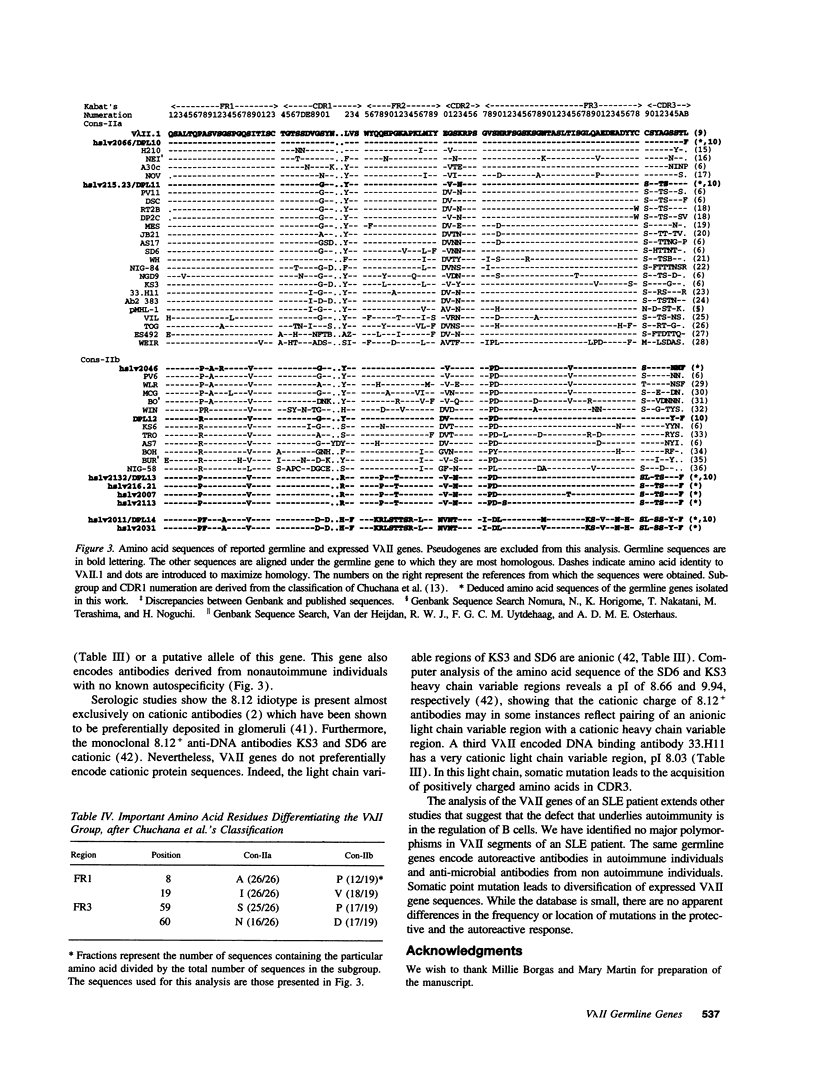
The 8.12 idiotype characterizes a subpopulation of anti-DNA antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The idiotype is present on lambda light chains and has previously been shown to be exclusively encoded by V lambda II light chains. RFLP analysis of the V lambda II gene family has shown the family to consist of 10 to 15 members. Thus far, the sequences of seven V lambda II germline genes are reported in the literature with one of these a pseudogene. To identify the V lambda II genes that encode 8.12 positive antibodies and to further characterize the V lambda II family, germline V lambda II clones were derived from a patient with SLE. Two libraries were constructed: a genomic DNA library and a library of PCR-derived V lambda II gene products obtained using a conserved V lambda II leader region primer and a primer for the nonamer region 3' of the coding sequence. We now describe seven new germline genes, two of which are pseudogenes. Comparison of V lambda II germline genes to sequences of 8.12 positive light chains produced by EBV-transformed B cell lines show that all 8.12 positive light chains are encoded by a limited number of highly homologous members of the V lambda II family. 8.12 negative V lambda II encoded light chains also derive from a limited number of V lambda II genes, suggesting that only a subset of the apparently available V lambda II genes are commonly expressed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adderson E. E., Shackelford P. G., Insel R. A., Quinn A., Wilson P. M., Carroll W. L. Immunoglobulin light chain variable region gene sequences for human antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide are dominated by a limited number of V kappa and V lambda segments and VJ combinations. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):729–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI115649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockly F., Alexandre D., Chuchana P., Huck S., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. First nucleotide sequence of a human immunoglobulin variable lambda gene belonging to subgroup II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3976–3976. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C. J., Spellerberg M. B., Smith G. A., Carter S. J., Hamblin T. J., Stevenson F. K. Autoanti-red cell antibodies synthesized by patients with infectious mononucleosis utilize the VH4-21 gene segment. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):1051–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. L., Chiu Y. Y., Humphrey R. L., Poljak R. J. Amino acid sequence of the human myeloma lambda chain Win. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 20;537(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuchana P., Blancher A., Brockly F., Alexandre D., Lefranc G., Lefranc M. P. Definition of the human immunoglobulin variable lambda (IGLV) gene subgroups. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1317–1325. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Combriato G., Klobeck H. G. V lambda and J lambda-C lambda gene segments of the human immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus are separated by 14 kb and rearrange by a deletion mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jun;21(6):1513–1522. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Katz J. B., Paul E., Aranow C., Lustgarten D., Scharff M. D. The role of somatic mutation in the pathogenic anti-DNA response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:731–757. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond B., Scharff M. D. Somatic mutation of the T15 heavy chain gives rise to an antibody with autoantibody specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5841–5844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Deutsch H. F. Primary structure of the Mcg lambda chain. Biochemistry. 1974 Sep 24;13(20):4102–4114. doi: 10.1021/bi00717a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver F. A., Hilschmann N. The primary structure of a monoclonal human lambda-type immunoglobulin L-chain of subgroup II (Bence-Jones protein NEI). Eur J Biochem. 1972 Mar 15;26(1):10–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawinowicz M. A., Merlini G., Birken S., Osserman E. F., Kabat E. A. Amino acid sequence of the FV region of a human monoclonal IgM (NOV) with specificity for the capsular polysaccharide of the group B meningococcus and of Escherichia coli K1, which cross-reacts with polynucleotides and with denatured DNA. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 1;147(3):915–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H. Characteristics of pathogenic subpopulations of antibodies to DNA. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):747–752. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Lieber M. R., Mizuuchi K., Gellert M. V(D)J recombination: a functional definition of the joining signals. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. J., Putnam F. W. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. V. Amino acid sequence of a human IgA lambda light chain (Bur). J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9006–9016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabusch J. R., Deutsch H. F. Primary structure of a human lambda-chain (Weir) of the Mcg type. Mol Immunol. 1982 Jul;19(7):901–906. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jukes T. H., King J. L. Evolutionary nucleotide replacements in DNA. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):605–606. doi: 10.1038/281605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer C. R., Patton H. M., Jr, McGuire B. S., Jr, Garver F. A. The V region sequence of lambda Bence-Jones protein Wh: evidence for separate germ-line sets within lambda-subgroups. J Immunol. 1980 Jan;124(1):301–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler H., Rudofsky S., Kluskens L. The primary structure of a human lambda II chain. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):415–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küppers R., Fischer U., Rajewsky K., Gause A. Immunoglobulin heavy and light chain gene sequences of a human CD5 positive immunocytoma and sequences of four novel VHIII germline genes. Immunol Lett. 1992 Sep;34(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(92)90027-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. P., Parry N., Peakman T. C., Crowe J. S. Rescue and expression of human immunoglobulin genes to generate functional human monoclonal antibodies. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas. 1992 Jul;3(3):146–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh A., Halpern A., Perkins D., Lazo A., Halpern R., Diamond B. A monoclonal antibody to a cross-reactive idiotype on cationic human anti-DNA antibodies expressing lambda light chains: a new reagent to identify a potentially differential pathogenic subset. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 1;138(1):123–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh A., Preud'Homme J. L., Solomon A., Diamond B. Preferential expression of the systemic lupus erythematosus-associated idiotype 8.12 in sera containing monoclonal immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3730–3733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Ikenaka T. Primary structure of cryo Bence-Jones protein (Tog) from the urine of a patient with IgD myeloma. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jul;16(7):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Diamond B. Characterization of two human anti-DNA antibodies bearing the pathogenic idiotype 8.12. Autoimmunity. 1993;16(1):13–21. doi: 10.3109/08916939309010643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Iliev A. A., Livneh A., Diamond B. The anti-DNA-associated idiotype 8.12 is encoded by the V lambda II gene family and maps to the vicinity of L chain CDR1. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3588–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Livneh A., Manheimer-Lory A. J., Diamond B. Characterization of the human Ig V lambda II gene family and analysis of V lambda II and C lambda polymorphism in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2771–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Manheimer-Lory A., Livneh A., Solomon A., Aranow C., Ghossein C., Shefner R., Offen D., Pillinger M., Diamond B. Pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies in SLE: idiotypic families and genetic origins. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):295–313. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponstingl H., Hilschmann N. Vollständige Aminosäuresequenz einer lambda-Kette der Subgruppe II (Bence-Jones-Protein VIL). Die Evolution als Ursache der Antikörper-Spezifität. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1969 Sep;350(9):1148–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posnett D. N. Allelic variations of human TCR V gene products. Immunol Today. 1990 Oct;11(10):368–373. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90143-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz R., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstrukur eines monoklonalen IgA-Immunoglobulins (IgA Tro.), I. Die Aminosäuresequenz der L-Kette, lambda-Typ, Subgruppe II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Aug;356(8):1333–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayasu T., Takahashi N., Shinoda T., Okuyama T., Tomioka H. Comparative studies on the structure of the light chains of human immunoglobulins. III. Amino acid sequence of a lambda type Bence Jones euglobulin. J Biochem. 1981 Feb;89(2):421–436. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonoike H., Kametani F., Hoshi A., Shinoda T., Isobe T. Amino acid sequence of an amyloidogenic Bence Jones protein in myeloma-associated systemic amyloidosis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80757-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tveteraas T., Sletten K., Westermark P. The amino acid sequence of a carbohydrate-containing immunoglobulin-light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):183–190. doi: 10.1042/bj2320183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasicek T. J., Leder P. Structure and expression of the human immunoglobulin lambda genes. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):609–620. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikler M., Putnam F. W. Amino acid sequence of human lambda chains. 3. Tryptic peptides, chymotryptic peptides, and sequence of protein Bo. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4488–4507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Winter G. Cloning and sequencing of human immunoglobulin V lambda gene segments. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1456–1461. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler T. H., Fehr H., Kalden J. R. Analysis of immunoglobulin variable region genes from human IgG anti-DNA hybridomas. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1719–1728. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu D., Kim H. S., Deutsch H. F. Variable-region sequences of five human lambda-chain proteins reacting with an idiotypic antibody to the MCG Bence-Jones protein. Mol Immunol. 1983 Oct;20(10):1107–1116. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



