Abstract
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C20H16ClN5, the dihedral angle between the pyrazole ring and the phenyl ring is 54.7 (1)° and that between the pyrazole ring and the chloro-substituted phenyl ring is 72.4 (1)°. The methyl H atoms are disordered over two positions with site occupancy factors of ca 0.7 and 0.3. One amino H is disordered equally over two positions. In the crystal structure, the molecules are linked via intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonding.
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H16ClN5
M r = 361.83
Orthorhombic,

a = 10.4700 (11) Å
b = 14.0482 (15) Å
c = 25.409 (3) Å
V = 3737.3 (7) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.22 mm−1
T = 294 (2) K
0.49 × 0.48 × 0.45 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.901, T max = 0.908
32456 measured reflections
4661 independent reflections
3055 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.118
S = 1.03
4661 reflections
237 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011562/nc2101sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011562/nc2101Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H1N3⋯N4i | 0.86 | 2.41 | 3.159 (2) | 146 |
| N3—H2N3⋯N2ii | 0.86 | 2.53 | 3.325 (2) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20772025), the Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (No. 2008HASTIT006) and the Department of Education of Henan Province (No. 2008 A150013).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The structure determination was undertaken as a part of a project on the synthesis of new pyrazole derivatives. In the title compound the dihedral angle between the pyrazole ring and the non-substituted phenyl ring which is directly connected to the pyrazole ring is 54.7 (1)° and that between the pyrazole ring and the chloro-substituted phenyl ring is 72.4 (1)°. The dihedral angle between the non-substituted and the chloro-substituted phenyl ring amount to 69.7 (1)° (Fig. 1).
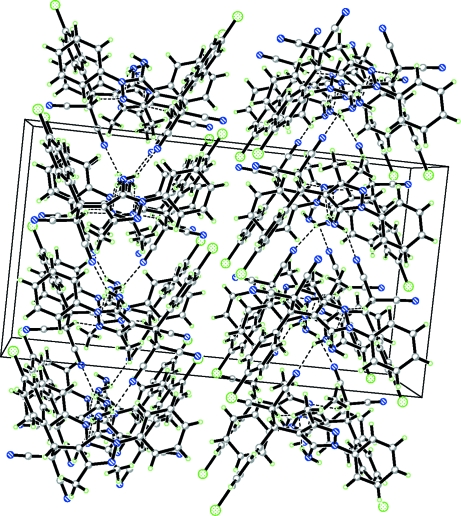
In the crystal structure the molecules are connected via intermolecular N—H···N hydrogen bonding between the amino group at N3 and the N atoms N2 and N4 (Fig. 2 and Table 1).
Experimental
To 1 ml of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate ([bmim][BF4]), 4-chloroaldehyde (1 mmol), malononitrile (1 mmol) and 5-amino-3-methyl-1-phenylpyrazole (1 mmol) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h and afterwards extracted five times with 2 ml of diethylether. The ether extracts were combined and concentrated. The obtained residue was recrystallized with 95% ethanol to give the product in a yield of 95% as white solid. Single crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of the solvent from a petroleum ether-ethyl ether (1:1 v/v) solution.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions (methyl H atoms are disordered in two orientations) and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H distances of 0.93 - 0.98 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) (1.5 for methyl H atoms). The N-H H atoms were located in difference map, their bond lengths were set to ideal values and afterwards they were refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). One of the N-H H atoms is disordered and was refined using a split model.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, with labelling displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. The disordering of the H atoms is not shown for clarity.
Fig. 2.
Crystal structure of the title compound with view along the a-axis. Intermolecular N—H···N hydrogen bonding is shown as dashed lines and the disordering of the H atoms is not shown for clarity.
Crystal data
| C20H16ClN5 | Dx = 1.286 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 361.83 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Cell parameters from 8329 reflections |
| a = 10.4700 (11) Å | θ = 2.5–25.8º |
| b = 14.0482 (15) Å | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| c = 25.409 (3) Å | T = 294 (2) K |
| V = 3737.3 (7) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.49 × 0.48 × 0.45 mm |
| F000 = 1504 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4661 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3055 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| T = 294(2) K | θmax = 28.4º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 2.5º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 1997) | h = −14→13 |
| Tmin = 0.901, Tmax = 0.909 | k = −18→18 |
| 32456 measured reflections | l = −33→33 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0404P)2 + 1.3457P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.118 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.03 | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 4661 reflections | Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3 |
| 237 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0012 (3) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes)are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are takeninto account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, anglesand torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are onlyused when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic)treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR andgoodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are basedon F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression ofF2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and isnot relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors basedon F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 0.34596 (7) | 1.04230 (4) | 0.53076 (2) | 0.0837 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.27144 (14) | 0.71251 (10) | 0.78626 (5) | 0.0509 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.17726 (15) | 0.64522 (12) | 0.77803 (6) | 0.0605 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.43568 (16) | 0.79533 (11) | 0.74011 (5) | 0.0623 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.4155 (2) | 0.44105 (12) | 0.68772 (7) | 0.0751 (5) | |
| N5 | 0.52582 (19) | 0.58634 (13) | 0.54493 (7) | 0.0748 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.18531 (16) | 0.62494 (13) | 0.72710 (6) | 0.0512 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.28333 (15) | 0.67629 (11) | 0.70228 (5) | 0.0414 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.33723 (15) | 0.73171 (11) | 0.74145 (6) | 0.0429 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.0940 (2) | 0.55545 (17) | 0.70288 (8) | 0.0772 (7) | |
| H4A | 0.0613 | 0.5811 | 0.6706 | 0.116* | 0.73 |
| H4B | 0.0245 | 0.5440 | 0.7267 | 0.116* | 0.73 |
| H4C | 0.1376 | 0.4967 | 0.6958 | 0.116* | 0.73 |
| H4D | 0.0876 | 0.5001 | 0.7249 | 0.116* | 0.27 |
| H4E | 0.1244 | 0.5372 | 0.6687 | 0.116* | 0.27 |
| H4F | 0.0114 | 0.5845 | 0.6996 | 0.116* | 0.27 |
| C5 | 0.29537 (17) | 0.74496 (15) | 0.83845 (6) | 0.0579 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.2963 (2) | 0.84064 (18) | 0.84956 (9) | 0.0847 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.2812 | 0.8854 | 0.8233 | 0.102* | |
| C7 | 0.3206 (3) | 0.8691 (3) | 0.90156 (14) | 0.1220 (14) | |
| H7 | 0.3232 | 0.9335 | 0.9099 | 0.146* | |
| C8 | 0.3407 (3) | 0.8023 (4) | 0.94005 (12) | 0.1401 (18) | |
| H8 | 0.3567 | 0.8218 | 0.9744 | 0.168* | |
| C9 | 0.3375 (3) | 0.7080 (3) | 0.92837 (10) | 0.1239 (13) | |
| H9 | 0.3504 | 0.6632 | 0.9548 | 0.149* | |
| C10 | 0.3151 (2) | 0.6782 (2) | 0.87746 (8) | 0.0846 (7) | |
| H10 | 0.3133 | 0.6136 | 0.8695 | 0.102* | |
| C11 | 0.33508 (15) | 0.76013 (11) | 0.61584 (5) | 0.0415 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.22572 (17) | 0.79784 (13) | 0.59298 (6) | 0.0516 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.1491 | 0.7647 | 0.5956 | 0.062* | |
| C13 | 0.2283 (2) | 0.88387 (14) | 0.56630 (6) | 0.0588 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.1545 | 0.9082 | 0.5510 | 0.071* | |
| C14 | 0.3417 (2) | 0.93244 (12) | 0.56298 (6) | 0.0550 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.45228 (19) | 0.89664 (13) | 0.58425 (7) | 0.0569 (5) | |
| H15 | 0.5287 | 0.9299 | 0.5811 | 0.068* | |
| C16 | 0.44836 (17) | 0.81010 (12) | 0.61058 (6) | 0.0510 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.5230 | 0.7853 | 0.6249 | 0.061* | |
| C17 | 0.32395 (14) | 0.66623 (11) | 0.64546 (5) | 0.0401 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.2568 | 0.6296 | 0.6278 | 0.048* | |
| C18 | 0.44800 (16) | 0.60557 (11) | 0.64192 (6) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| H18 | 0.5153 | 0.6391 | 0.6613 | 0.053* | |
| C19 | 0.42937 (18) | 0.51193 (13) | 0.66700 (6) | 0.0525 (4) | |
| C20 | 0.49158 (17) | 0.59315 (12) | 0.58707 (7) | 0.0511 (4) | |
| H1N3 | 0.4639 | 0.8173 | 0.7695 | 0.061* | |
| H2N3 | 0.5027 | 0.7693 | 0.7270 | 0.061* | 0.50 |
| H3N3 | 0.4647 | 0.8134 | 0.7101 | 0.061* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.1235 (5) | 0.0600 (3) | 0.0677 (3) | 0.0238 (3) | 0.0273 (3) | 0.0234 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0586 (9) | 0.0588 (8) | 0.0354 (7) | −0.0138 (7) | 0.0064 (6) | −0.0075 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0636 (9) | 0.0760 (11) | 0.0418 (8) | −0.0252 (8) | 0.0098 (7) | −0.0067 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0761 (11) | 0.0659 (9) | 0.0448 (8) | −0.0308 (8) | 0.0096 (7) | −0.0120 (7) |
| N4 | 0.1013 (14) | 0.0569 (10) | 0.0669 (11) | 0.0076 (9) | −0.0131 (10) | 0.0121 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0918 (13) | 0.0807 (12) | 0.0518 (9) | 0.0059 (10) | 0.0158 (9) | −0.0074 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0587 (10) | 0.0405 (8) | −0.0137 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0033 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0474 (8) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0338 (7) | −0.0020 (7) | 0.0003 (6) | −0.0009 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0505 (9) | 0.0416 (8) | 0.0365 (7) | −0.0045 (7) | 0.0040 (6) | −0.0021 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0765 (14) | 0.0976 (16) | 0.0575 (11) | −0.0416 (12) | 0.0044 (10) | −0.0101 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0810 (13) | 0.0384 (8) | −0.0124 (9) | 0.0110 (7) | −0.0155 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0862 (16) | 0.0897 (16) | 0.0782 (14) | −0.0306 (13) | 0.0300 (12) | −0.0365 (12) |
| C7 | 0.102 (2) | 0.157 (3) | 0.107 (2) | −0.063 (2) | 0.0500 (18) | −0.088 (2) |
| C8 | 0.091 (2) | 0.268 (5) | 0.0613 (17) | −0.046 (3) | 0.0176 (15) | −0.071 (3) |
| C9 | 0.112 (2) | 0.220 (4) | 0.0398 (12) | 0.002 (3) | 0.0031 (13) | −0.0061 (18) |
| C10 | 0.0911 (17) | 0.120 (2) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0025 (15) | 0.0073 (10) | −0.0001 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0507 (9) | 0.0458 (8) | 0.0281 (7) | 0.0033 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0513 (10) | 0.0586 (10) | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0051 (8) | −0.0033 (7) | 0.0022 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0670 (12) | 0.0632 (11) | 0.0461 (9) | 0.0200 (10) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0052 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0803 (13) | 0.0494 (9) | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0139 (9) | 0.0115 (8) | 0.0056 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0649 (11) | 0.0555 (10) | 0.0503 (10) | −0.0040 (9) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0076 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0514 (10) | 0.0555 (10) | 0.0462 (9) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0083 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0450 (8) | 0.0438 (8) | 0.0315 (7) | −0.0024 (7) | −0.0039 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0516 (9) | 0.0471 (9) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0018 (7) | −0.0056 (6) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0623 (11) | 0.0530 (10) | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0088 (8) | −0.0079 (8) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0560 (10) | 0.0515 (10) | 0.0457 (9) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0001 (8) | −0.0027 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C14 | 1.7477 (17) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C3 | 1.3577 (19) | C7—C8 | 1.371 (5) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3819 (19) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.424 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.359 (5) |
| N2—C1 | 1.328 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C3 | 1.365 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.379 (3) |
| N3—H1N3 | 0.8602 | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N3—H2N3 | 0.8587 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N3—H3N3 | 0.8595 | C11—C16 | 1.385 (2) |
| N4—C19 | 1.136 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.389 (2) |
| N5—C20 | 1.133 (2) | C11—C17 | 1.523 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.404 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.386 (2) |
| C1—C4 | 1.499 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.372 (3) |
| C2—C17 | 1.5117 (19) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.373 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9600 | C15—C16 | 1.388 (2) |
| C4—H4C | 0.9600 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4D | 0.9600 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4E | 0.9600 | C17—C18 | 1.556 (2) |
| C4—H4F | 0.9600 | C17—H17 | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.373 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.475 (2) |
| C5—C10 | 1.380 (3) | C18—C20 | 1.477 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.404 (4) | C18—H18 | 0.9800 |
| C3—N1—N2 | 111.78 (12) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.9 |
| C3—N1—C5 | 128.89 (14) | C8—C7—C6 | 120.3 (3) |
| N2—N1—C5 | 119.03 (13) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| C1—N2—N1 | 104.41 (13) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.8 |
| C3—N3—H1N3 | 118.2 | C9—C8—C7 | 120.5 (3) |
| C3—N3—H2N3 | 110.3 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| H1N3—N3—H2N3 | 102.1 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| C3—N3—H3N3 | 118.9 | C8—C9—C10 | 120.3 (3) |
| H1N3—N3—H3N3 | 122.9 | C8—C9—H9 | 119.8 |
| H2N3—N3—H3N3 | 59.4 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.8 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 111.96 (14) | C9—C10—C5 | 119.6 (3) |
| N2—C1—C4 | 119.96 (16) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C2—C1—C4 | 128.07 (15) | C5—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 105.31 (13) | C16—C11—C12 | 118.19 (15) |
| C3—C2—C17 | 128.66 (14) | C16—C11—C17 | 123.53 (14) |
| C1—C2—C17 | 125.92 (14) | C12—C11—C17 | 118.29 (14) |
| N1—C3—N3 | 122.28 (14) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.41 (17) |
| N1—C3—C2 | 106.52 (13) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.3 |
| N3—C3—C2 | 131.19 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.3 |
| C1—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C14—C13—C12 | 118.72 (17) |
| C1—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| C1—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.56 (16) |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C13—C14—Cl1 | 119.35 (15) |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C15—C14—Cl1 | 119.09 (16) |
| C1—C4—H4D | 109.5 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.04 (18) |
| H4A—C4—H4D | 141.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| H4B—C4—H4D | 56.3 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| H4C—C4—H4D | 56.3 | C11—C16—C15 | 121.05 (16) |
| C1—C4—H4E | 109.5 | C11—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4E | 56.3 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.5 |
| H4B—C4—H4E | 141.1 | C2—C17—C11 | 114.36 (12) |
| H4C—C4—H4E | 56.3 | C2—C17—C18 | 109.95 (12) |
| H4D—C4—H4E | 109.5 | C11—C17—C18 | 112.45 (12) |
| C1—C4—H4F | 109.5 | C2—C17—H17 | 106.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4F | 56.3 | C11—C17—H17 | 106.5 |
| H4B—C4—H4F | 56.3 | C18—C17—H17 | 106.5 |
| H4C—C4—H4F | 141.1 | C19—C18—C20 | 110.08 (14) |
| H4D—C4—H4F | 109.5 | C19—C18—C17 | 110.68 (14) |
| H4E—C4—H4F | 109.5 | C20—C18—C17 | 112.15 (13) |
| C6—C5—C10 | 121.1 (2) | C19—C18—H18 | 107.9 |
| C6—C5—N1 | 120.4 (2) | C20—C18—H18 | 107.9 |
| C10—C5—N1 | 118.53 (19) | C17—C18—H18 | 107.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.2 (3) | N4—C19—C18 | 177.99 (18) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.9 | N5—C20—C18 | 178.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H1N3···N4i | 0.86 | 2.41 | 3.159 (2) | 146 |
| N3—H2N3···N2ii | 0.86 | 2.53 | 3.325 (2) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x+1/2, y, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NC2101).
References
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011562/nc2101sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011562/nc2101Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report