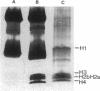
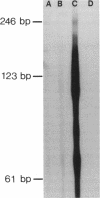
Abstract
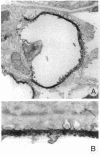
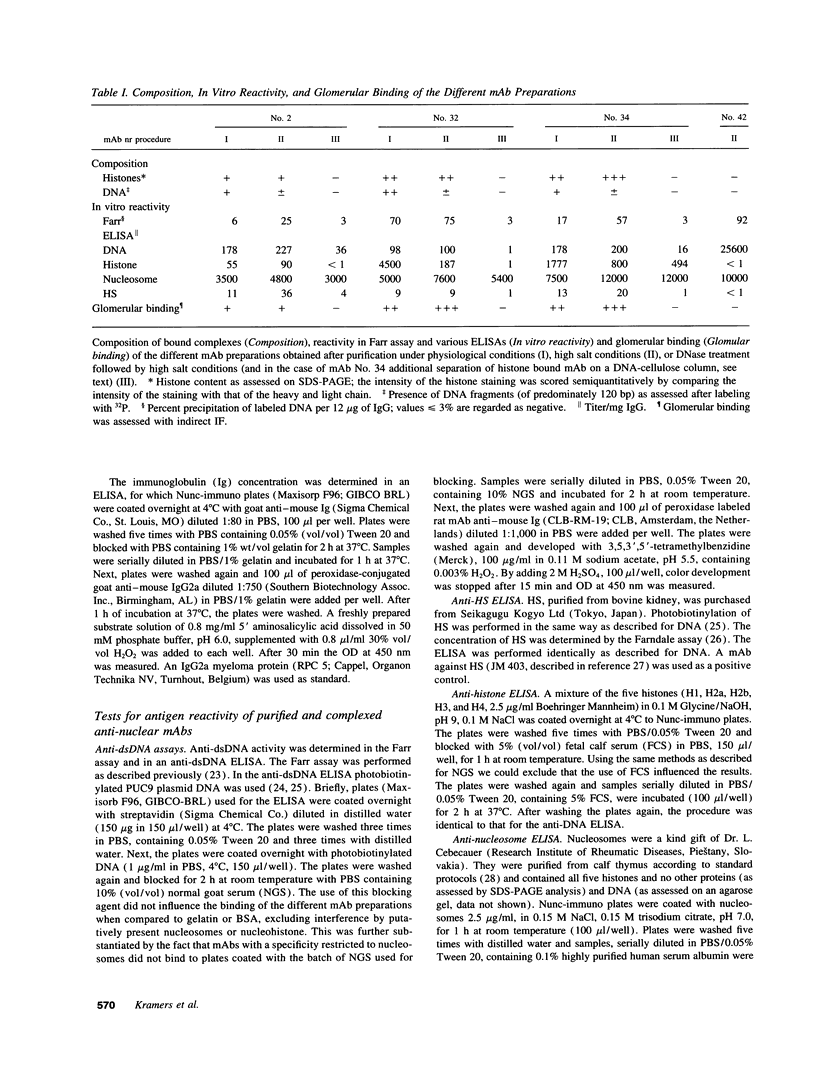
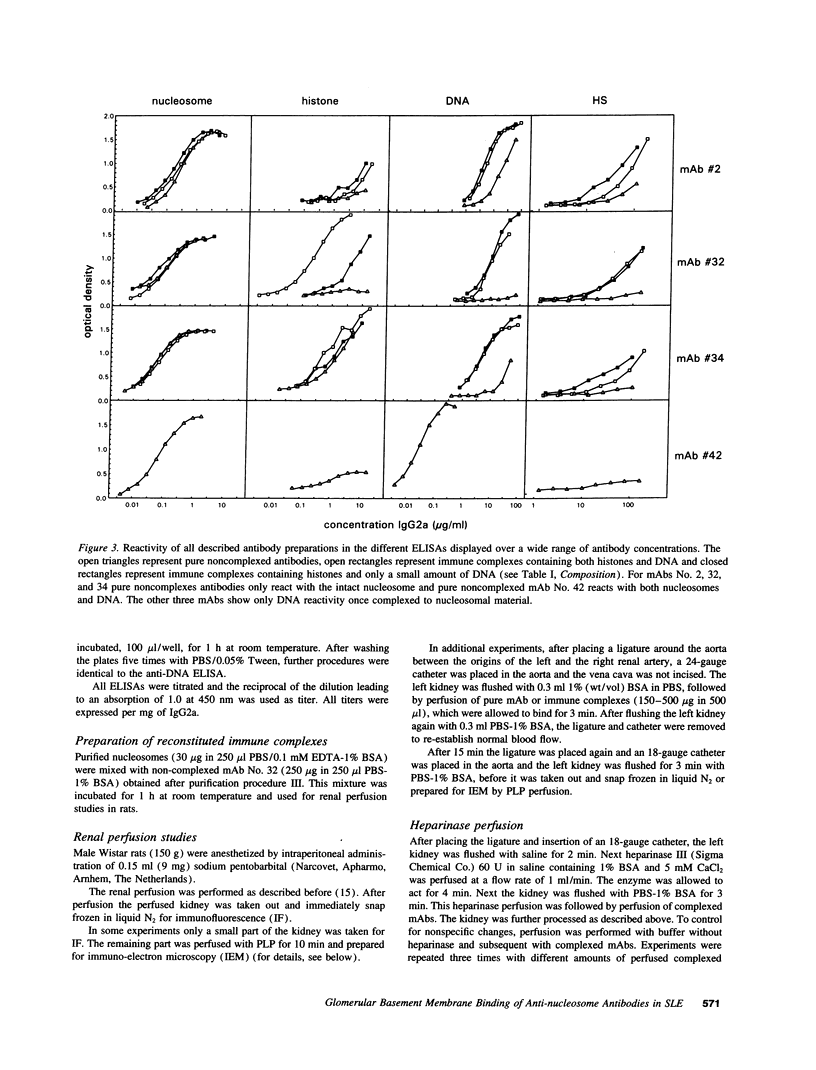
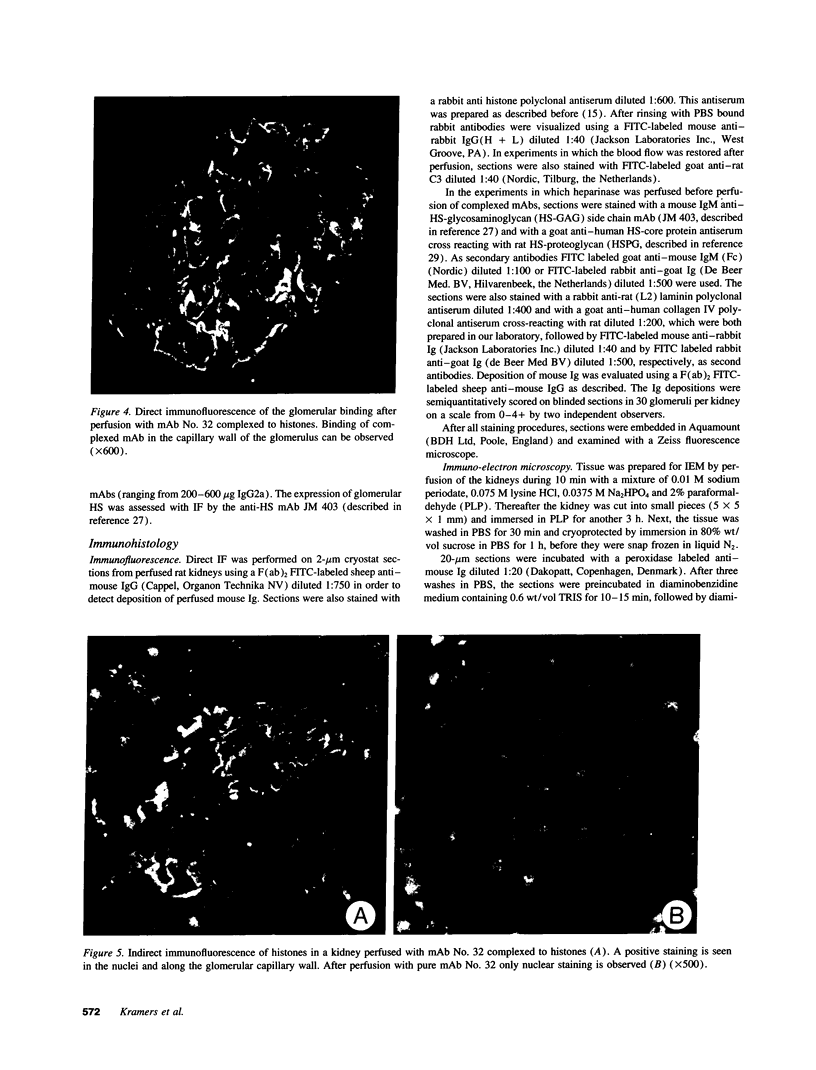
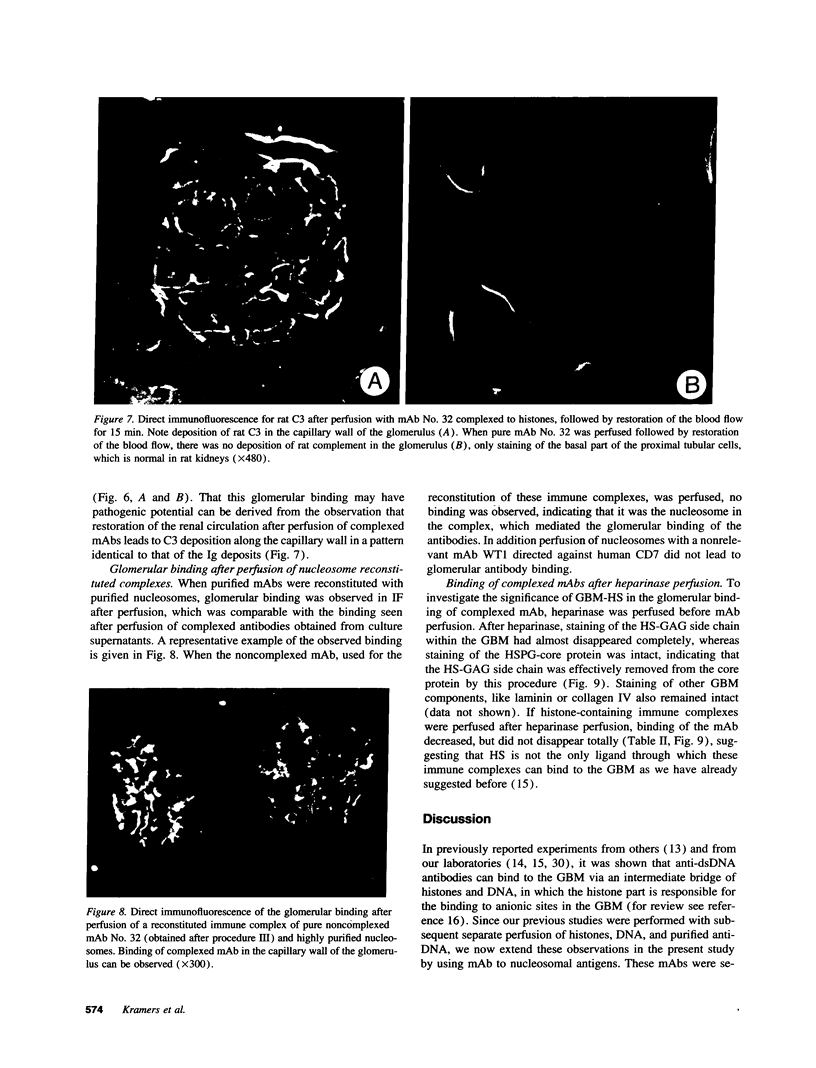
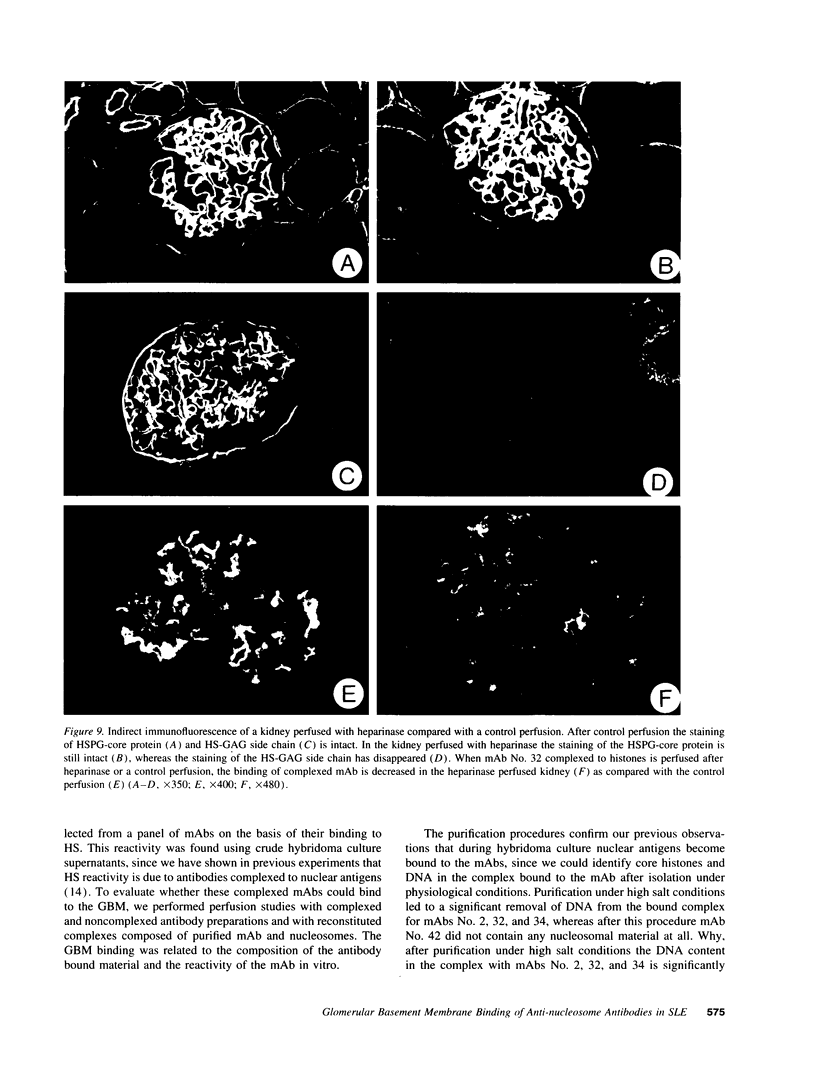
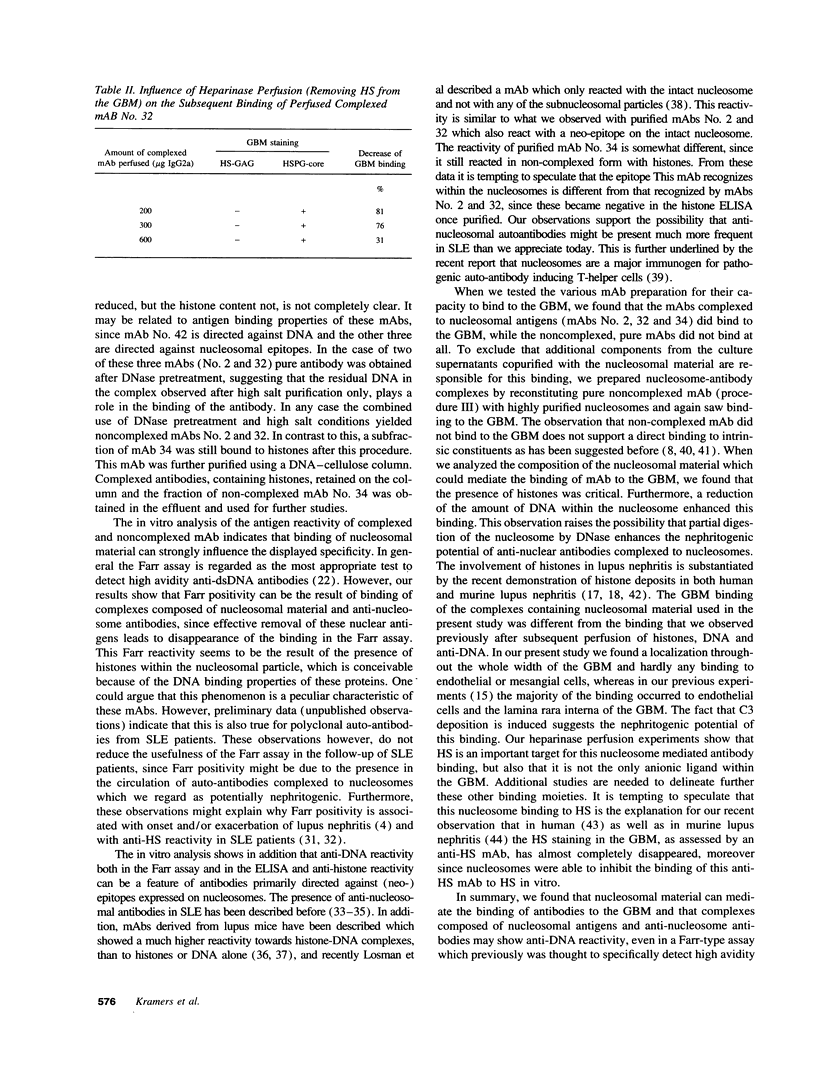
Histones can mediate the binding of DNA and anti-DNA to the glomerular basement membrane (GBM). In ELISA histone/DNA/anti-DNA complexes are able to bind to heparan sulfate (HS), an intrinsic constituent of the GBM. We questioned whether histone containing immune complexes are able to bind to the GBM, and if so, whether the ligand in the GBM is HS. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) complexed to nucleosomal antigens and noncomplexed mAbs were isolated from culture supernatants of four IgG anti-nuclear mAbs. All noncomplexed mAbs showed strong anti-nucleosome reactivity in ELISA. One of them showed in addition anti-DNA reactivity in noncomplexed form. The other three mAbs only showed anti-DNA reactivity when they were complexed to nucleosomal antigens. After renal perfusion a fine granular binding of complexed mAbs to the glomerular capillary wall and activation of complement was observed in immunofluorescence, whereas noncomplexed mAbs did not bind. Immuno-electron microscopy showed binding of complexes to the whole width of the GBM. When HS in the GBM was removed by renal heparinase perfusion the binding of complexed mAb decreased, but did not disappear completely. We conclude that anti-nucleosome mAbs, which do not bind DNA, become DNA reactive once complexed to nucleosomal antigens. These complexed mAbs can bind to the GBM. The binding ligand in the GBM is partly, but not solely, HS. Binding to the GBM of immune complexes containing nucleosomal material might be an important event in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brinkman K., Termaat R. M., de Jong J., van den Brink H. G., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Cross-reactive binding patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA are often caused by DNA/anti-DNA immune complexes. Res Immunol. 1989 Jun-Aug;140(5-6):595–612. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Anti-DNA antibodies and lupus nephritis: the complexity of crossreactivity. Immunol Today. 1990 Jul;11(7):232–234. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90095-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L., Balderas R. S., Theofilopoulos A. N. Genesis and evolution of antichromatin autoantibodies in murine lupus implicates T-dependent immunization with self antigen. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1687–1696. doi: 10.1172/JCI116378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Rubin R. L. Drug-induced anti-histone autoantibodies display two patterns of reactivity with substructures of chromatin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):680–690. doi: 10.1172/JCI115353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Burdick G. Clearance and organ localization of small DNA anti-DNA immune complexes in mice. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):1816–1822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Jarusiripipat P., Burdick G. A new ELISA for the detection of double-stranded DNA antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Aug 28;132(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90402-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Mannik M. Clearance of circulating DNA-anti-DNA immune complexes in mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1210–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farndale R. W., Sayers C. A., Barrett A. J. A direct spectrophotometric microassay for sulfated glycosaminoglycans in cartilage cultures. Connect Tissue Res. 1982;9(4):247–248. doi: 10.3109/03008208209160269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylkema M. N., Huygen H., Kramers C., vd Wal T. J., de Jong J., van Bruggen M. C., Swaak A. J., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Clinical evaluation of a modified ELISA, using photobiotinylated DNA, for the detection of anti-DNA antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1994 Mar 29;170(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(94)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Viard J. P., Allenet B., Anin M. F., Slama F. B., Vandekerckhove J., Primo J., Markovits J., Jacob F., Bach J. F. A monoclonal anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody binds to a 94-kDa cell-surface protein on various cell types via nucleosomes or a DNA-histone complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4669–4673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalunian K. C., Panosian-Sahakian N., Ebling F. M., Cohen A. H., Louie J. S., Kaine J., Hahn B. H. Idiotypic characteristics of immunoglobulins associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Studies of antibodies deposited in glomeruli of humans. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;32(5):513–522. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Systemic lupus erythematosus: prototype of immune complex nephritis in man. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):169s–179s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., LaPointe J. W., Lorch Y. Preparation of nucleosomes and chromatin. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:3–14. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramers C., Termaat R. M., ter Borg E. J., van Bruggen M. C., Kallenberg C. G., Berden J. H. Higher anti-heparan sulphate reactivity during systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) disease exacerbations with renal manifestations; a long term prospective analysis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jul;93(1):34–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb06493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramers K., Hylkema M., Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., Smeenk R., Berden J. Histones in lupus nephritis. Exp Nephrol. 1993 Jul-Aug;1(4):224–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losman J. A., Fasy T. M., Novick K. E., Massa M., Monestier M. Nucleosome-specific antibody from an autoimmune MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mouse. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Apr;36(4):552–560. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losman M. J., Fasy T. M., Novick K. E., Monestier M. Monoclonal autoantibodies to subnucleosomes from a MRL/Mp(-)+/+ mouse. Oligoclonality of the antibody response and recognition of a determinant composed of histones H2A, H2B, and DNA. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1561–1569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaio M. P., Carlson J., Cataldo J., Ucci A., Migliorini P., Pankewycz O. Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan C., Adams S., Stanik V., Datta S. K. Nucleosome: a major immunogen for pathogenic autoantibody-inducing T cells of lupus. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1367–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Brezis M., Rosenmann E., Eilat D. Anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to renal antigens and induce kidney dysfunction in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3076–3082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumore P. M., Steinman C. R. Endogenous circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence as multimeric complexes bound to histone. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):69–74. doi: 10.1172/JCI114716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T. M., Stöckl F. W., Weber R., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S. R., Vogt A. Histones have high affinity for the glomerular basement membrane. Relevance for immune complex formation in lupus nephritis. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1879–1894. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedeke T., Stoeckl F., Muller S., Sugisaki Y., Batsford S., Woitas R., Vogt A. Glomerular immune deposits in murine lupus models may contain histones. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeenk R. J., Brinkman K., van den Brink H. G., Westgeest A. A. Reaction patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3786–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöckl F., Muller S., Batsford S., Schmiedeke T., Waldherr R., Andrassy K., Sugisaki Y., Nakabayashi K., Nagasawa T., Rodriguez-Iturbe B. A role for histones and ubiquitin in lupus nephritis? Clin Nephrol. 1994 Jan;41(1):10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):226–235. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. P., Kujala G., Edberg J. C., Foreman P., Davis J. S., 4th, Wright E. The kinetics of clearance of human antibody/dsDNA immune complexes from rabbit circulation. Effects of dsDNA size, rheumatoid factor, and reduction and alkylation of the antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3785–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Assmann K. J., Dijkman H. B., van Gompel F., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-DNA antibodies can bind to the glomerulus via two distinct mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1992 Dec;42(6):1363–1371. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Assmann K. J., van Son J. P., Dijkman H. B., Koene R. A., Berden J. H. Antigen-specificity of antibodies bound to glomeruli of mice with systemic lupus erythematosus-like syndromes. Lab Invest. 1993 Feb;68(2):164–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., Nossent J. C., Swaak A. J., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Anti-heparan sulphate reactivity in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with renal or non-renal manifestations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):268–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termaat R. M., Brinkman K., van Gompel F., van den Heuvel L. P., Veerkamp J. H., Smeenk R. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate is mediated via bound DNA/histone complexes. J Autoimmun. 1990 Oct;3(5):531–545. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Totoritis M. C., Tan E. M., McNally E. M., Rubin R. L. Association of antibody to histone complex H2A-H2B with symptomatic procainamide-induced lupus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1431–1436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Faiferman I., Koffler D. Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antinative DNA antibody with glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):90–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Borg E. J., Horst G., Hummel E. J., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):634–643. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Berden J. H. A monoclonal antibody against GBM heparan sulfate induces an acute selective proteinuria in rats. Kidney Int. 1992 Jan;41(1):115–123. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Born J., van den Heuvel L. P., Bakker M. A., Veerkamp J. H., Assmann K. J., Weening J. J., Berden J. H. Distribution of GBM heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein and side chains in human glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 1993 Feb;43(2):454–463. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel L. P., van den Born J., van de Velden T. J., Veerkamp J. H., Monnens L. A., Schroder C. H., Berden J. H. Isolation and partial characterization of heparan sulphate proteoglycan from the human glomerular basement membrane. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):457–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2640457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]