Abstract
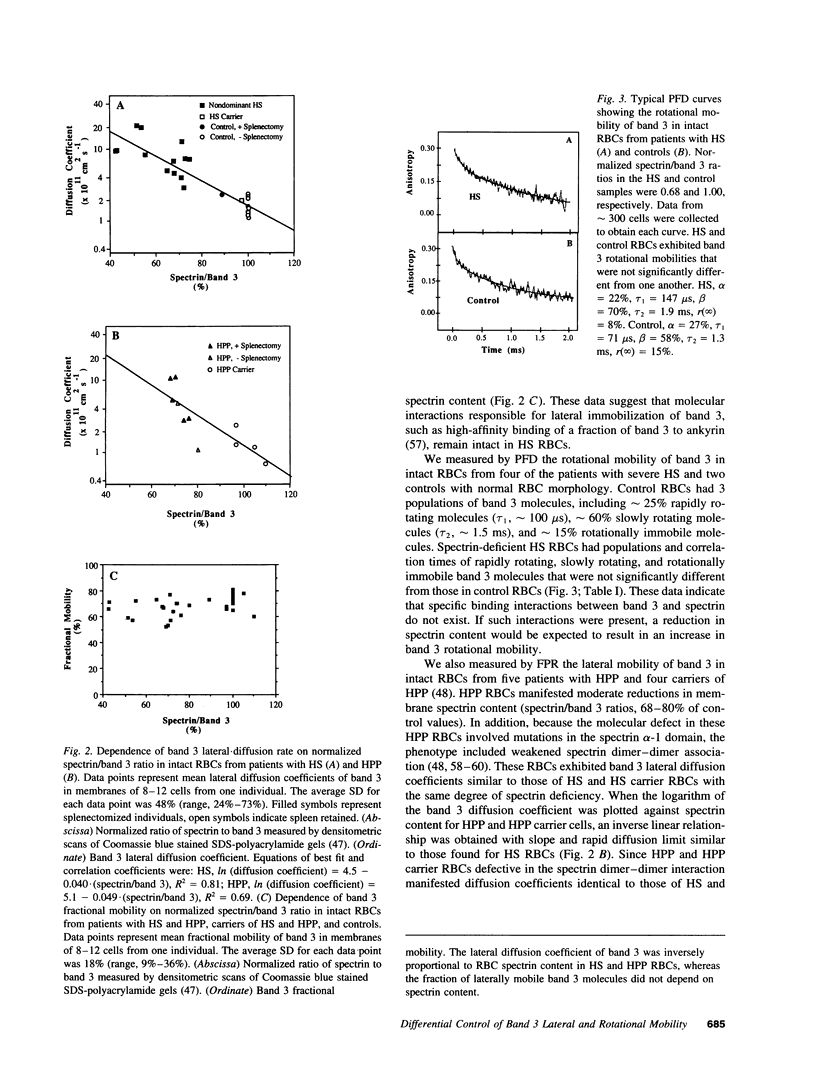
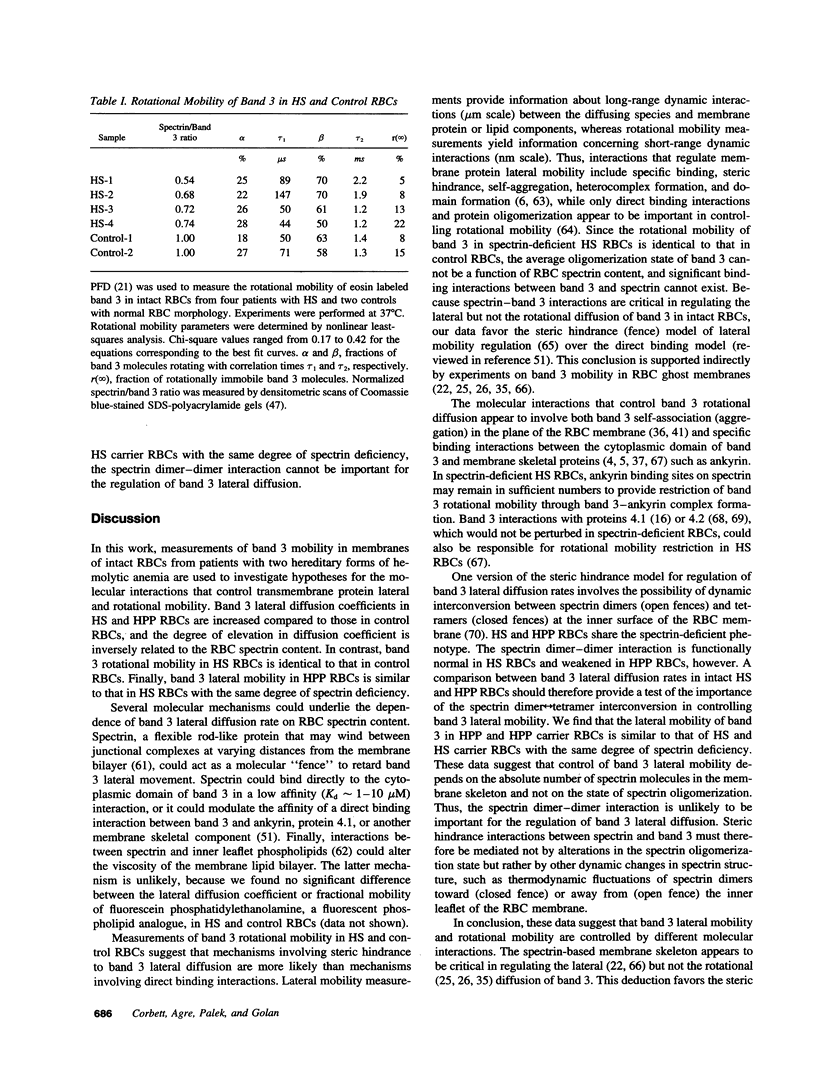
Measurements of integral membrane protein lateral mobility and rotational mobility have been separately used to investigate dynamic protein--protein and protein-lipid interactions that underlie plasma membrane structure and function. In model bilayer membranes, the mobilities of reconstituted proteins depend on the size of the diffusing molecule and the viscosity of the lipid bilayer. There are no direct tests, however, of the relationship between mechanisms that control protein lateral mobility and rotational mobility in intact biological membranes. We have measured the lateral and rotational mobility of band 3 in spectrin-deficient red blood cells from patients with hereditary spherocytosis and hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Our data suggest that band 3 lateral mobility is regulated by the spectrin content of the red cell membrane. In contrast, band 3 rotational mobility is unaffected by changes in spectrin content. Band 3 lateral mobility and rotational mobility must therefore be controlled by different molecular mechanisms.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Asimos A., Casella J. F., McMillan C. Inheritance pattern and clinical response to splenectomy as a reflection of erythrocyte spectrin deficiency in hereditary spherocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 18;315(25):1579–1583. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612183152504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Casella J. F., Zinkham W. H., McMillan C., Bennett V. Partial deficiency of erythrocyte spectrin in hereditary spherocytosis. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):380–383. doi: 10.1038/314380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Orringer E. P., Bennett V. Deficient red-cell spectrin in severe, recessively inherited spherocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 13;306(19):1155–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205133061906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alloisio N., Morlé L., Bachir D., Guetarni D., Colonna P., Delaunay J. Red cell membrane sialoglycoprotein beta in homozygous and heterozygous 4.1(-) hereditary elliptocytosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 11;816(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90392-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Lovrien R. E. Glycophorin is linked by band 4.1 protein to the human erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):655–658. doi: 10.1038/307655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. A., Marchesi V. T. Regulation of the association of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 with glycophorin by a polyphosphoinositide. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):295–298. doi: 10.1038/318295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin R. H., Chan S. S., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of cell surface components by time-resolved phosphorescence anisotropy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod D., Koppel D. E., Schlessinger J., Elson E., Webb W. W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):1055–1069. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85755-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The molecular basis for membrane - cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 1982;18(1):49–65. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1982.240180106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitbol M., Dempsey C., Watts A., Devaux P. F. Weak interaction of spectrin with phosphatidylcholine-phosphatidylserine multilayers: a 2H and 31P NMR study. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. The anion transport system of the red blood cell. The role of membrane protein evaluated by the use of 'probes'. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):239–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Che A., Cherry R. J., Bannister L. H., Dluzewski A. R. Aggregation of band 3 in hereditary ovalocytic red blood cell membranes. Electron microscopy and protein rotational diffusion studies. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jul;105(Pt 3):655–660. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.3.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Bürkli A., Busslinger M., Schneider G., Parish G. R. Rotational diffusion of band 3 proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):389–393. doi: 10.1038/263389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J. Rotational and lateral diffusion of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):289–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Harrison J. P., Cherry R. J. Cytoskeletal restraints of band 3 rotational mobility in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 19;981(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzer T. L., Palek J. Partial spectrin deficiency in hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):919–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzer T., Palek J., Lawler J., Liu S. C., Jarolim P., Lahav M., Prchal J. T., Wang W., Alter B. P., Schewitz G. Structural and functional heterogeneity of alpha spectrin mutations involving the spectrin heterodimer self-association site: relationships to hematologic expression of homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis and hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1990 Jun 1;75(11):2235–2244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett J. D., Golan D. E. Band 3 and glycophorin are progressively aggregated in density-fractionated sickle and normal red blood cells. Evidence from rotational and lateral mobility studies. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):208–217. doi: 10.1172/JCI116172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa F. F., Agre P., Watkins P. C., Winkelmann J. C., Tang T. K., John K. M., Lux S. E., Forget B. G. Linkage of dominant hereditary spherocytosis to the gene for the erythrocyte membrane-skeleton protein ankyrin. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 11;323(15):1046–1050. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010113231507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L. Membrane dynamics studied by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and photobleaching recovery. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1986;40:367–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan D. E., Alecio M. R., Veatch W. R., Rando R. R. Lateral mobility of phospholipid and cholesterol in the human erythrocyte membrane: effects of protein-lipid interactions. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 17;23(2):332–339. doi: 10.1021/bi00297a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan D. E., Brown C. S., Cianci C. M., Furlong S. T., Caulfield J. P. Schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni use lysophosphatidylcholine to lyse adherent human red blood cells and immobilize red cell membrane components. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):819–828. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golan D. E., Veatch W. Lateral mobility of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane studied by fluorescence photobleaching recovery: evidence for control by cytoskeletal interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2537–2541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K., Ishihara A., Inman R. Lateral diffusion of proteins in membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:163–175. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P., Garland P. B. Depolarization of fluorescence depletion. A microscopic method for measuring rotational diffusion of membrane proteins on the surface of a single cell. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppel D. E., Sheetz M. P., Schindler M. Matrix control of protein diffusion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren C., Cohen C. M. Associations of human erythrocyte band 4.2. Binding to ankyrin and to the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10212–10218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsgren C., Cohen C. M. Purification and properties of human erythrocyte band 4.2. Association with the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Derick L. H., Agre P., Palek J. Alteration of the erythrocyte membrane skeletal ultrastructure in hereditary spherocytosis, hereditary elliptocytosis, and pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Zhai S., Palek J., Golan D. E., Amato D., Hassan K., Nurse G. T., Babona D., Coetzer T., Jarolim P. Molecular defect of the band 3 protein in southeast Asian ovalocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 29;323(22):1530–1538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011293232205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low P. S. Structure and function of the cytoplasmic domain of band 3: center of erythrocyte membrane-peripheral protein interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 22;864(2):145–167. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matayoshi E. D., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of band 3 in erythrocyte membranes. 1. Comparison of ghosts and intact cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3527–3538. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Winardi R., Knowles D., Leung A., Parra M., George E., Conboy J., Chasis J. Molecular basis for membrane rigidity of hereditary ovalocytosis. A novel mechanism involving the cytoplasmic domain of band 3. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):686–692. doi: 10.1172/JCI115636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlebach T., Cherry R. J. Influence of cholesterol on the rotation and self-association of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 31;21(18):4225–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00261a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlebach T., Cherry R. J. Rotational diffusion and self-association of band 3 in reconstituted lipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 12;24(4):975–983. doi: 10.1021/bi00325a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Bron C., Girardet M., Cherry R. J. Band 3-glycophorin A association in erythrocyte membrane demonstrated by combining protein diffusion measurements with antibody-induced cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1887–1893. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cherry R. J. Anchorage of a band 3 population at the erythrocyte cytoplasmic membrane surface: protein rotational diffusion measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4702–4706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cherry R. J. Influence of temperature and cholesterol on the rotational diffusion of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3457–3465. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Gahmberg C. G., Cherry R. J. Rotational diffusion of band 3 proteins in membranes from En(a-) and neuraminidase-treated normal human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):636–642. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90467-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E., Cherry R. J. Dimeric association of band 3 in the erythrocyte membrane demonstrated by protein diffusion measurements. Nature. 1979 Feb 8;277(5696):493–494. doi: 10.1038/277493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E., Kessler M., Cherry R. J. Labeling of human erythrocyte membranes with eosin probes used for protein diffusion measurements: inhibition of anion transport and photo-oxidative inactivation of acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 19;550(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90219-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palek J., Liu S. C., Liu P. Y., Prchal J., Castleberry R. P. Altered assembly of spectrin in red cell membranes in hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1981 Jan;57(1):130–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack G. R., Anderson R. A., Leto T. L., Marchesi V. T. Interactions between protein 4.1 and band 3. An alternative binding site for an element of the membrane skeleton. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3676–3683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M. E., Chasis J. A., Mohandas N. Identification of a functional role for human erythrocyte sialoglycoproteins beta and gamma. Blood. 1987 Apr;69(4):1068–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Koppel D. E., Sheetz M. P. Modulation of membrane protein lateral mobility by polyphosphates and polyamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1457–1461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield A. E., Reardon D. M., Tanner M. J. Defective anion transport activity of the abnormal band 3 in hereditary ovalocytic red blood cells. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):836–838. doi: 10.1038/355836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Casaly J. 2,3-Diphosphoglycerate and ATP dissociate erythrocyte membrane skeletons. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9955–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Membrane skeletal dynamics: role in modulation of red cell deformability, mobility of transmembrane proteins, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Schindler M., Koppel D. E. Lateral mobility of integral membrane proteins is increased in spherocytic erythrocytes. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):510–511. doi: 10.1038/285510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Palek J. Modulation of lateral mobility of band 3 in the red cell membrane by oxidative cross-linking of spectrin. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):424–425. doi: 10.1038/297424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley L., Foley M., Anders R. F., Dluzewski A. R., Gratzer W. B., Jones G. L., Sawyer W. H. Rotational dynamics of the integral membrane protein, band 3, as a probe of the membrane events associated with Plasmodium falciparum infections of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 27;1025(2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90090-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley L., Nash G. B., Jones G. L., Sawyer W. H. Decreased rotational diffusion of band 3 in Melanesian ovalocytes from Papua, New Guinea. J Membr Biol. 1991 Apr;121(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF01870651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S., Merkle H., Kusumi A. Regulation of band 3 mobilities in erythrocyte ghost membranes by protein association and cytoskeletal meshwork. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7447–7452. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Ohnishi S. Restriction of the lateral motion of band 3 in the erythrocyte membrane by the cytoskeletal network: dependence on spectrin association state. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6133–6139. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt K., Cherry R. J. Both ankyrin and band 4.1 are required to restrict the rotational mobility of band 3 in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 31;1103(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90104-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T. M., Barisas B. G. Protein rotational motion in solution measured by polarized fluorescence depletion. Biophys J. 1986 Jul;50(1):41–53. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83437-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



