Abstract
In the title compound, C10H19N3 2+·2Br−, the plane of the three butyl C atoms nearest to the pyridine ring is almost perpendicular to the ring [dihedral angle = 84.80 (2)°]. The N atom of the ammonium group is displaced by 1.150 (8) Å from the plane of these three C atoms. The iminium N atom lies on the opposite side of this plane. The crystal structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the N and Br atoms, as well as by intermolecular C—H⋯Br interactions.
Related literature
For the synthesis of (S)-1-bromo-3-methylbutan-2-amine hydrobromide, see: Xu et al. (2006 ▶). For related literature, see: Luo et al. (2006 ▶).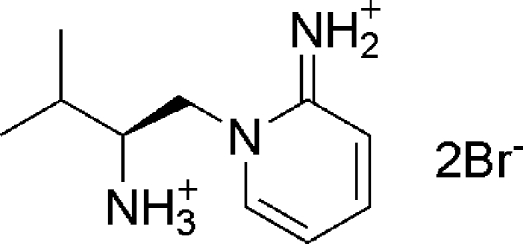
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H19N3 2+·2Br−
M r = 341.10
Monoclinic,
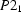
a = 5.9311 (11) Å
b = 12.456 (2) Å
c = 9.6807 (18) Å
β = 99.733 (3)°
V = 704.9 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 5.73 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.45 × 0.34 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.381, T max = 1.000 (expected range = 0.119–0.313)
4117 measured reflections
2307 independent reflections
2054 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.038
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 0.99
2307 reflections
147 parameters
3 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.91 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.71 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 696 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.06 (2)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012154/cs2071sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012154/cs2071Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2B⋯Br2 | 0.84 (7) | 2.55 (7) | 3.368 (7) | 167 (8) |
| N2—H2A⋯Br1i | 0.84 (8) | 2.53 (8) | 3.357 (6) | 168 (10) |
| N3—H3C⋯Br2ii | 0.89 | 2.50 | 3.369 (5) | 166 |
| N3—H3B⋯Br1 | 0.89 | 2.46 | 3.238 (5) | 147 |
| N3—H3A⋯Br2iii | 0.89 | 2.43 | 3.281 (5) | 160 |
| C3—H3⋯Br1iv | 0.93 | 3.02 | 3.892 (8) | 157 |
| C4—H4⋯Br1v | 0.93 | 2.91 | 3.748 (8) | 150 |
| C6—H6A⋯Br1vi | 0.97 | 2.96 | 3.528 (7) | 119 |
| C5—H5⋯Br2ii | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.721 (7) | 162 |
| C8—H8⋯Br2 | 0.98 | 2.93 | 3.793 (7) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 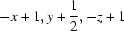 ; (ii)
; (ii) 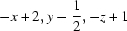 ; (iii)
; (iii) 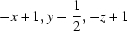 ; (iv)
; (iv) 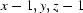 ; (v)
; (v) 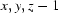 ; (vi)
; (vi) 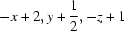 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
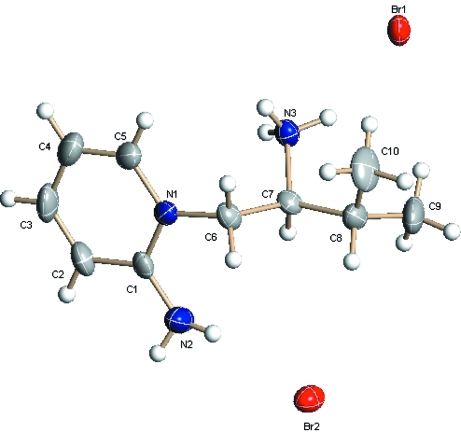
Ionic liquids, specially functional ionic liquids, have received growing attention recently due to their tuneable features for various chemical tasks. (S. Luo, et al., 2006). The title compound, readily synthesized from commercially available L-valine and 2-aminopyridine, might have potential utilities in some specific chemical tasks, when it is converted into a kind of functional ionic liquid by neutralization with sodium hydroxide. The structure of (S)-1-(2-ammonio-3-methylbutyl)pyridin-2(1H)-iminium dibromide is shown in Fig. 1.
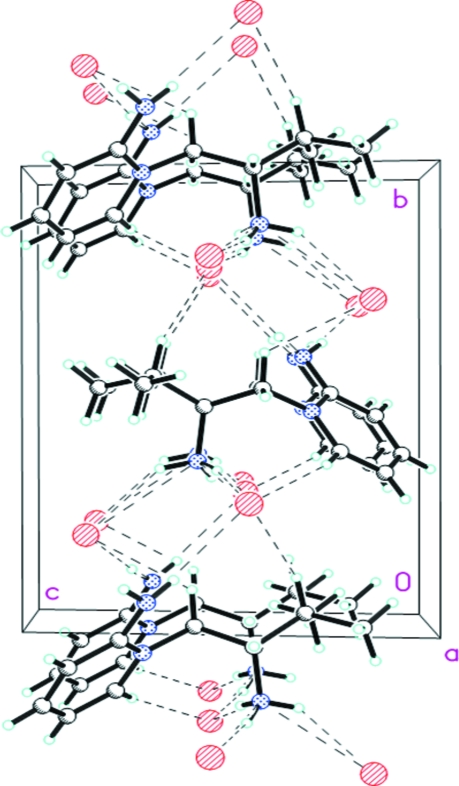
The crystal is built of doubly protonated cations and bromide anions. The protonation of the amines is appropriate like in the scheme, for the C1—N2 bond distance reveals its double bond property. The dihedral angle between the plane of three alkyl carbons C6/C7/C8 and the pyridine ring is 84.80 (2) °, which means the two planes are approximately perpendicular to one another. The atom N3 of the ammonium group bonded to the alkyl chain is displaced from the plane of three carbons C6/C7/C8 by 1.150 (8) Å. The iminium N2 lies on the opposite side of this plane. The crystal structure is stablized by hydrogen-bonds between the atoms N and Br as well as by intermolecular C—H—Br interactions. The molecular packing of the title compound showing H-bridge interactions between cationic-anionic groups is shown in Fig. 2.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by treating 2-aminopyridine (0.94 g,10 mmol) with (S)-1-bromo-3-methylbutan-2-amine hydrobromide (2.47 g,10 mmol) in MeCN (30 ml) under stirring at 353 K for 24 h (yield 81%). The compound (S)-1-bromo-3-methylbutan-2-amine hydrobromide was obtained from commercially available L-valine by reduction with NaBH4 and subsequent bromination with PBr3 (Xu et al., 2006). Suitable crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution at room temperature.
Refinement
All carbon-bonded H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93 Å (aromatic), C—H = 0.98 Å (sp), C—H = 0.93 Å (sp2), C—H = 0.96 Å(sp3) and refined using a riding model, with Uiso(H)=1.2eq(C). N-bound H atoms were located in a difference map and refined with an N—H distance restraint of 0.86 (3) Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound with the atomic labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The molecular packing of the title compound showing H-bridge interactions between cationic-anionic groups.
Crystal data
| C10H19N32+·2Br– | F000 = 340 |
| Mr = 341.10 | Dx = 1.607 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.9311 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 1818 reflections |
| b = 12.456 (2) Å | θ = 5.4–53.4º |
| c = 9.6807 (18) Å | µ = 5.73 mm−1 |
| β = 99.733 (3)º | T = 293 (2) K |
| V = 704.9 (2) Å3 | Prismatic, colorless |
| Z = 2 | 0.45 × 0.34 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2307 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2054 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.038 |
| T = 293(2) K | θmax = 27.0º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 2.1º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.381, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −12→15 |
| 4117 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0533P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 0.99 | Δρmax = 0.91 e Å−3 |
| 2307 reflections | Δρmin = −0.71 e Å−3 |
| 147 parameters | Extinction correction: none |
| 3 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 696 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.06 (2) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 1.02019 (11) | 0.21057 (4) | 0.84434 (6) | 0.03666 (18) | |
| Br2 | 0.61945 (10) | 0.78903 (5) | 0.54550 (7) | 0.03742 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.7631 (8) | 0.4733 (4) | 0.2958 (5) | 0.0269 (11) | |
| N2 | 0.4665 (11) | 0.5923 (5) | 0.3096 (7) | 0.0398 (14) | |
| N3 | 0.9054 (9) | 0.3672 (4) | 0.5746 (5) | 0.0291 (11) | |
| H3A | 0.7799 | 0.3302 | 0.5406 | 0.044* | |
| H3B | 0.9481 | 0.3518 | 0.6651 | 0.044* | |
| H3C | 1.0172 | 0.3496 | 0.5280 | 0.044* | |
| C1 | 0.5506 (11) | 0.5110 (5) | 0.2454 (6) | 0.0295 (14) | |
| C2 | 0.4223 (13) | 0.4609 (6) | 0.1291 (7) | 0.0404 (17) | |
| H2 | 0.2766 | 0.4863 | 0.0937 | 0.048* | |
| C3 | 0.5050 (15) | 0.3772 (7) | 0.0677 (7) | 0.052 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.4149 | 0.3427 | −0.0072 | 0.062* | |
| C4 | 0.7331 (15) | 0.3408 (7) | 0.1176 (8) | 0.052 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.7975 | 0.2856 | 0.0725 | 0.062* | |
| C5 | 0.8497 (13) | 0.3880 (6) | 0.2301 (7) | 0.0378 (16) | |
| H5 | 0.9953 | 0.3628 | 0.2661 | 0.045* | |
| C6 | 0.9101 (11) | 0.5224 (6) | 0.4176 (7) | 0.0314 (14) | |
| H6A | 0.8922 | 0.5998 | 0.4119 | 0.038* | |
| H6B | 1.0686 | 0.5060 | 0.4131 | 0.038* | |
| C7 | 0.8569 (10) | 0.4843 (5) | 0.5581 (6) | 0.0274 (13) | |
| H7 | 0.6928 | 0.4945 | 0.5567 | 0.033* | |
| C8 | 0.9855 (11) | 0.5495 (6) | 0.6818 (7) | 0.0369 (16) | |
| H8 | 0.9549 | 0.6256 | 0.6605 | 0.044* | |
| C9 | 0.8975 (15) | 0.5251 (8) | 0.8154 (7) | 0.057 (2) | |
| H9A | 0.9414 | 0.4535 | 0.8456 | 0.086* | |
| H9B | 0.7338 | 0.5309 | 0.7994 | 0.086* | |
| H9C | 0.9614 | 0.5753 | 0.8867 | 0.086* | |
| C10 | 1.2447 (12) | 0.5333 (8) | 0.6994 (8) | 0.057 (2) | |
| H10A | 1.3194 | 0.5787 | 0.7734 | 0.086* | |
| H10B | 1.2962 | 0.5514 | 0.6135 | 0.086* | |
| H10C | 1.2809 | 0.4596 | 0.7224 | 0.086* | |
| H2A | 0.355 (12) | 0.623 (8) | 0.260 (9) | 0.09 (4)* | |
| H2B | 0.525 (13) | 0.636 (6) | 0.371 (7) | 0.06 (3)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0508 (4) | 0.0348 (4) | 0.0231 (3) | −0.0033 (3) | 0.0026 (3) | −0.0009 (3) |
| Br2 | 0.0309 (3) | 0.0355 (4) | 0.0448 (4) | 0.0023 (3) | 0.0033 (3) | −0.0065 (3) |
| N1 | 0.033 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.007 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| N2 | 0.040 (4) | 0.035 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.006 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| N3 | 0.032 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.026 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C1 | 0.041 (4) | 0.028 (4) | 0.018 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C2 | 0.042 (4) | 0.051 (5) | 0.025 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.005 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C3 | 0.074 (5) | 0.054 (5) | 0.025 (4) | −0.011 (4) | −0.002 (4) | −0.012 (4) |
| C4 | 0.077 (6) | 0.049 (5) | 0.032 (4) | 0.006 (4) | 0.014 (4) | −0.010 (3) |
| C5 | 0.051 (4) | 0.038 (4) | 0.026 (4) | 0.009 (3) | 0.012 (3) | 0.003 (3) |
| C6 | 0.031 (3) | 0.032 (4) | 0.028 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.001 (3) |
| C7 | 0.021 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.029 (3) | 0.001 (2) | −0.001 (2) | 0.003 (3) |
| C8 | 0.046 (4) | 0.030 (4) | 0.031 (4) | 0.002 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.006 (3) |
| C9 | 0.066 (5) | 0.077 (6) | 0.025 (4) | 0.014 (5) | −0.003 (4) | −0.015 (4) |
| C10 | 0.035 (4) | 0.088 (7) | 0.043 (5) | −0.016 (4) | −0.008 (3) | −0.014 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—H3B | 2.4578 | C4—C5 | 1.325 (10) |
| Br2—H2B | 2.55 (7) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.356 (8) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.380 (8) | C6—C7 | 1.523 (9) |
| N1—C6 | 1.476 (8) | C6—H6A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C1 | 1.329 (9) | C6—H6B | 0.9700 |
| N2—H2A | 0.84 (8) | C7—C8 | 1.538 (9) |
| N2—H2B | 0.84 (7) | C7—H7 | 0.9800 |
| N3—C7 | 1.490 (8) | C8—C9 | 1.506 (11) |
| N3—H3A | 0.8900 | C8—C10 | 1.531 (10) |
| N3—H3B | 0.8900 | C8—H8 | 0.9800 |
| N3—H3C | 0.8900 | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.396 (9) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.334 (11) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.431 (11) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 119.8 (6) | C7—C6—H6A | 108.8 |
| C1—N1—C6 | 122.1 (5) | N1—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| C5—N1—C6 | 118.2 (5) | C7—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| C1—N2—H2A | 114 (7) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.7 |
| C1—N2—H2B | 133 (6) | N3—C7—C6 | 109.6 (5) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 107 (9) | N3—C7—C8 | 111.9 (5) |
| C7—N3—H3A | 109.5 | C6—C7—C8 | 112.3 (6) |
| C7—N3—H3B | 109.5 | N3—C7—H7 | 107.6 |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 109.5 | C6—C7—H7 | 107.6 |
| C7—N3—H3C | 109.5 | C8—C7—H7 | 107.6 |
| H3A—N3—H3C | 109.5 | C9—C8—C10 | 111.4 (6) |
| H3B—N3—H3C | 109.5 | C9—C8—C7 | 111.3 (6) |
| N2—C1—N1 | 119.7 (6) | C10—C8—C7 | 111.9 (6) |
| N2—C1—C2 | 121.4 (7) | C9—C8—H8 | 107.3 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 118.8 (7) | C10—C8—H8 | 107.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 121.2 (7) | C7—C8—H8 | 107.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.4 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.4 | C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.7 (7) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.2 | C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.2 | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 117.9 (7) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 121.0 | C8—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 121.0 | C8—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—N1 | 122.5 (7) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.7 | C8—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 118.7 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C7 | 113.7 (5) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H6A | 108.8 | ||
| C5—N1—C1—N2 | 179.3 (6) | C6—N1—C5—C4 | −178.0 (7) |
| C6—N1—C1—N2 | −2.4 (9) | C1—N1—C6—C7 | 82.3 (7) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 1.2 (8) | C5—N1—C6—C7 | −99.4 (7) |
| C6—N1—C1—C2 | 179.5 (6) | N1—C6—C7—N3 | 64.0 (7) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | −177.9 (7) | N1—C6—C7—C8 | −170.9 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 0.2 (10) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | −67.1 (7) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.8 (11) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 169.2 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 4.2 (11) | N3—C7—C8—C10 | 58.3 (8) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −3.0 (11) | C6—C7—C8—C10 | −65.5 (8) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.3 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2B···Br2 | 0.84 (7) | 2.55 (7) | 3.368 (7) | 167 (8) |
| N2—H2A···Br1i | 0.84 (8) | 2.53 (8) | 3.357 (6) | 168 (10) |
| N3—H3C···Br2ii | 0.89 | 2.50 | 3.369 (5) | 166 |
| N3—H3B···Br1 | 0.89 | 2.46 | 3.238 (5) | 147 |
| N3—H3A···Br2iii | 0.89 | 2.43 | 3.281 (5) | 160 |
| C3—H3···Br1iv | 0.93 | 3.02 | 3.892 (8) | 157 |
| C4—H4···Br1v | 0.93 | 2.91 | 3.748 (8) | 150 |
| C6—H6A···Br1vi | 0.97 | 2.96 | 3.528 (7) | 119 |
| C5—H5···Br2ii | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.721 (7) | 162 |
| C8—H8···Br2 | 0.98 | 2.93 | 3.793 (7) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1; (iii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1; (iv) x−1, y, z−1; (v) x, y, z−1; (vi) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CS2071).
References
- Bruker (2000). SAINT-Plus Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2001). SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Luo, S., Mi, X., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Xu, H. & Cheng, J. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.45, 3093–3097. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xu, D. Q., Luo, S. P., Yue, H. D., Wang, L. P., Liu, Y. K. & Xu, Z. Y. (2006). Synlett, 16, 2569–2572.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012154/cs2071sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012154/cs2071Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report