Abstract
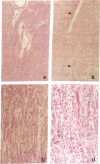
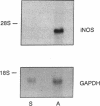
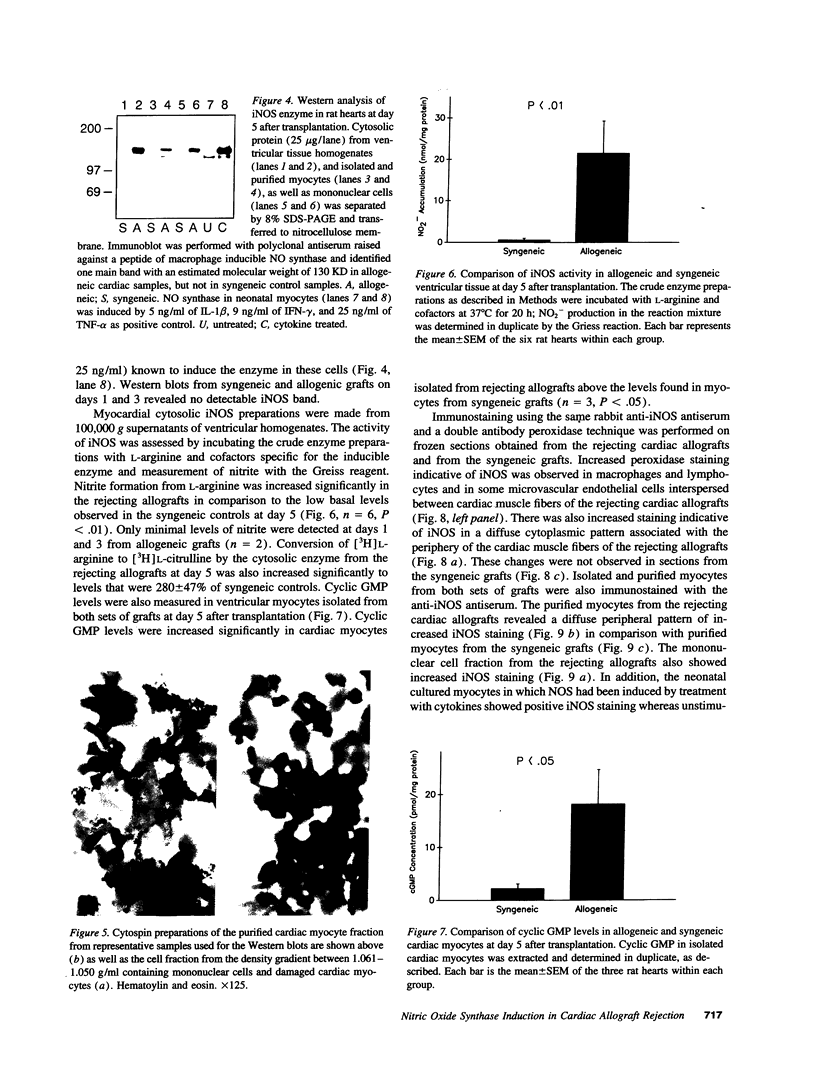
Cardiac transplantation, effective therapy for end-stage heart failure, is frequently complicated by allograft rejection, the mechanisms of which remain incompletely understood. Nitric oxide (NO), a vasodilator which is cytotoxic and negatively inotropic, can be produced in large amounts by an inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in response to cytokines. To investigate whether iNOS is induced during cardiac allograft rejection, hearts from Lewis or Wistar-Furth rats were transplanted into Lewis recipients. At day 5, allogeneic grafts manifested reduced contractility and histologic evidence of rejection (inflammatory infiltrate, edema, necrosis of myocytes). The mRNA for iNOS and iNOS protein were detected in ventricular homogenates and in isolated cardiac myocytes from rejecting allogeneic grafts but not in tissue and myocytes from syngeneic control grafts. Immunocytochemistry showed increased iNOS staining in infiltrating macrophages and in microvascular endothelial cells and cardiac muscle fibers and also in isolated purified cardiac myocytes from the rejecting allografts. Using a myocardial cytosolic iNOS preparation, nitrite formation from L-arginine and [3H] citrulline formation from [3H]L-arginine were increased significantly in the rejecting allogeneic grafts (P < 0.01). Myocardial cyclic GMP was also increased significantly (P < 0.05). The data indicate myocardial iNOS mRNA, protein and enzyme activity are induced in infiltrating macrophages and cardiac myocytes of the rejecting allogeneic grafts. Synthesis of NO by iNOS may contribute to myocyte necrosis and ventricular failure during cardiac allograft rejection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amezcua J. L., Palmer R. M., de Souza B. M., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthesized from L-arginine regulates vascular tone in the coronary circulation of the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1119–1124. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand J. L., Kelly R. A., Marsden P. A., Smith T. W., Michel T. Control of cardiac muscle cell function by an endogenous nitric oxide signaling system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):347–351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balligand J. L., Ungureanu D., Kelly R. A., Kobzik L., Pimental D., Michel T., Smith T. W. Abnormal contractile function due to induction of nitric oxide synthesis in rat cardiac myocytes follows exposure to activated macrophage-conditioned medium. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2314–2319. doi: 10.1172/JCI116461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham M. E. Cardiac transplant atherosclerosis. Transplant Proc. 1987 Aug;19(4 Suppl 5):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady A. J., Poole-Wilson P. A., Harding S. E., Warren J. B. Nitric oxide production within cardiac myocytes reduces their contractility in endotoxemia. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 2):H1963–H1966. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.263.6.H1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady A. J., Warren J. B., Poole-Wilson P. A., Williams T. J., Harding S. E. Nitric oxide attenuates cardiac myocyte contraction. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 2):H176–H182. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.1.H176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Xie Q. W., Calaycay J., Mumford R. A., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Nathan C. Calmodulin is a subunit of nitric oxide synthase from macrophages. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):599–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Pellat C., Henry Y. Generation of EPR-detectable nitrosyl-iron complexes in tumor target cells cocultured with activated macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10162–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Wietzerbin J., Hibbs J. B., Jr Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor induce the L-arginine-dependent cytotoxic effector mechanism in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1587–1592. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid H., Larson D. M., Springhorn J. P., Attawia M. A., Nayak R. C., Smith T. W., Kelly R. A. Role of epicardial mesothelial cells in the modification of phenotype and function of adult rat ventricular myocytes in primary coculture. Circ Res. 1992 Jul;71(1):40–50. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel M. S., Oddis C. V., Jacob T. D., Watkins S. C., Hattler B. G., Simmons R. L. Negative inotropic effects of cytokines on the heart mediated by nitric oxide. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):387–389. doi: 10.1126/science.1631560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman R. A., Langrehr J. M., Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Simmons R. L. Alloantigen-induced activation of rat splenocytes is regulated by the oxidative metabolism of L-arginine. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2220–2226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Darley-Usmar V. M., Wilson M. T., Moncada S. Production of hydroxyl radicals from the simultaneous generation of superoxide and nitric oxide. Biochem J. 1992 Jan 15;281(Pt 2):419–424. doi: 10.1042/bj2810419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ialenti A., Ianaro A., Moncada S., Di Rosa M. Modulation of acute inflammation by endogenous nitric oxide. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90526-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelm M., Schrader J. Control of coronary vascular tone by nitric oxide. Circ Res. 1990 Jun;66(6):1561–1575. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.6.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Belloni P. Endothelial cell production of nitrogen oxides in response to interferon gamma in combination with tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, or endotoxin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):772–776. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Kolb-Bachofen V., Berschick B., Burkart V., Kolb H. Activated macrophages kill pancreatic syngeneic islet cells via arginine-dependent nitric oxide generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Mar 29;175(3):752–758. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91630-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr EPR demonstration of iron-nitrosyl complex formation by cytotoxic activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster J. R., Jr, Langrehr J. M., Bergonia H. A., Murase N., Simmons R. L., Hoffman R. A. EPR detection of heme and nonheme iron-containing protein nitrosylation by nitric oxide during rejection of rat heart allograft. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10994–10998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langrehr J. M., Hoffman R. A., Billiar T. R., Lee K. K., Schraut W. H., Simmons R. L. Nitric oxide synthesis in the in vivo allograft response: a possible regulatory mechanism. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):335–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langrehr J. M., Murase N., Markus P. M., Cai X., Neuhaus P., Schraut W., Simmons R. L., Hoffman R. A. Nitric oxide production in host-versus-graft and graft-versus-host reactions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):679–683. doi: 10.1172/JCI115911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Severn A., Millott S., Schmidt J., Salter M., Moncada S. A possible novel pathway of regulation by murine T helper type-2 (Th2) cells of a Th1 cell activity via the modulation of the induction of nitric oxide synthase on macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2489–2494. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S. The 1991 Ulf von Euler Lecture. The L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Jul;145(3):201–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Hevel J. M., Marletta M. A., Ward P. A. Tissue injury caused by deposition of immune complexes is L-arginine dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6338–6342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Lindsey E. S. Improved technique of heart transplantation in rats. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1969 Feb;57(2):225–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osbakken M., Ivanics T., Zhang D., Mitra R., Blum H. Isolated cardiomyocytes in conjunction with NMR spectroscopy techniques to study metabolism and ion flux. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15340–15347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Bridge L., Foxwell N. A., Moncada S. The role of nitric oxide in endothelial cell damage and its inhibition by glucocorticoids. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):11–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Vodovotz Y., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., Nathan C. F. Role of nitric oxide in antagonistic effects of transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-1 beta on the beating rate of cultured cardiac myocytes. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1921–1930. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1282674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Nava E., Moncada S. Induction and potential biological relevance of a Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthase in the myocardium. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):575–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R., Smith J. A., Lewis M. J., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthase in cultured endocardial cells of the pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):21–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Nathan C. F. Nitric oxide. A macrophage product responsible for cytostasis and respiratory inhibition in tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1543–1555. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson A. W., Phillips R. S., Severn A., Moncada S., Liew F. Y. The role of TH1 and TH2 cells in a rodent malaria infection. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1931–1934. doi: 10.1126/science.8100366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberg B. A., Robinson T. F. Oxygen requirements, morphology, cell coat and membrane permeability of calcium-tolerant myocytes from hearts of adult rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;216(2):231–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00233618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. J., Lovett M., Wong-Lee J., Moeller F., Kitamura M., Goralski T. J., Billingham M. E., Starnes V. A., Clayberger C. Cytokine gene expression in rejecting cardiac allografts. Transplantation. 1992 Aug;54(2):326–332. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199208000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q. W., Cho H. J., Calaycay J., Mumford R. A., Swiderek K. M., Lee T. D., Ding A., Troso T., Nathan C. Cloning and characterization of inducible nitric oxide synthase from mouse macrophages. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):225–228. doi: 10.1126/science.1373522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X., Cai B., Sciacca R. R., Cannon P. J. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages by oxidized low-density lipoproteins. Circ Res. 1994 Feb;74(2):318–328. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Belder A. J., Radomski M. W., Why H. J., Richardson P. J., Bucknall C. A., Salas E., Martin J. F., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthase activities in human myocardium. Lancet. 1993 Jan 9;341(8837):84–85. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92559-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]