Abstract
In the title compound, C17H17N3O2, a derivative of 4-aminoantipyrine, the structure displays a trans configuration with respect to the imine C=N double bond. The pyrazoline ring is essentially planar and makes a dihedral angle of 55.80 (1)° with the phenyl ring.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Ali et al. (2002 ▶); Allen et al. (1987 ▶); Carlton et al. (1995 ▶); Coolen et al. (1999 ▶); Cukurovali et al. (2002 ▶); Greisen & Andreasen (1976 ▶); Jiang et al. (2000 ▶); Liang et al. (2002 ▶); Tarafder et al. (2002 ▶).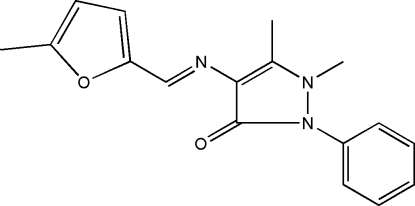
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H17N3O2
M r = 295.34
Monoclinic,

a = 11.811 (7) Å
b = 9.997 (6) Å
c = 14.116 (9) Å
β = 110.963 (9)°
V = 1556.4 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.40 × 0.40 × 0.40 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000 ▶) T min = 0.967, T max = 0.967
5012 measured reflections
2670 independent reflections
1904 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.097
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.066
wR(F 2) = 0.154
S = 1.07
2670 reflections
203 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2000 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015419/bq2080sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015419/bq2080Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful for the support of a special research grant (No. 05jk136) of the Education Department of Shaanxi Province.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In recent years, the role of antipyrine and antipyridine derivatives in biological processes have become a topic of study (Carlton et al., 1995; Coolen et al., 1999; Jiang et al., 2000). Antipyrine is an antipyretic drug that is still being used to measure the total hepatic oxidase activity. The properties of antipyrine make it a suitable marker for oxidative stress (Greisen & Andereasen, 1976). Schiff base ligands have demonstrated significant biological activities and new examples are being tested for their antitumor, antimicrobial and antiviral activities (Tarafder et al., 2002; Cukurovali et al., 2002; Ali et al., 2002). These properties stimulated our interest in this field. Crystals of the title compound, (I), were obtained as a new antipyrine Schiff base compound.
The perspective view of the structure and a packing diagram of (I) are illustrated in Fig.1 and 2, respectively. All the bond lengths and angles are in normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987) and comparable to those observed in a similar antipyrine Schiff base (Liang et al., 2002). As seen from Fig. 1, the pyrazoline ring is essentially planar. Atom O2 deviates from the pyrazoline mean plane by -0.117 (5) Å, whereas atoms C10 and C11 by 0.115 (7) and 0.582 (7) Å, on the same side. The dihedral angle between the pyrazoline ring and the C12—C17 phenyl ring is 55.80 (1) °. The furan ring and the pyrazoline ring are approximately coplanar with the dihedral angle between them of 4.79 (2) °. As expected, the molecular structure adopts a trans configuration about the C6═N1 bond.
Experimental
A mixture of 5-methyl-2-furaldehyd (0.1 mmol, 11.0 mg) and 4-aminoantipyrine (0.1 mmol, 20.3 mg) was dissolved in 10 ml methanol, and stirred for about 30 min at room temperature to give a clear yellow solution. After keeping this solution in air for 7 d, yellow block crystals were formed at the bottom of vessel by slowly evaporating the solvent.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with C—H distances in the range 0.93–0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq or 1.5Ueq(C/O)
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound in 30% probability ellipsoids. H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
The molecular packing of (I) viewed along the b-axis.
Crystal data
| C17H17N3O2 | F000 = 624 |
| Mr = 295.34 | Dx = 1.260 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3656 reflections |
| a = 11.811 (7) Å | θ = 2.6–27.1º |
| b = 9.997 (6) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 14.116 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 110.963 (9)º | Block, yellow |
| V = 1556.4 (16) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.40 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 2670 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1904 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.097 |
| T = 296 K | θmax = 25.0º |
| φ and ω scans | θmin = 1.9º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 2000) | h = −4→14 |
| Tmin = 0.967, Tmax = 0.967 | k = −11→9 |
| 5012 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.066 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0438P)2 + 0.5447P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.154 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.07 | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 2670 reflections | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
| 203 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.048 (4) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.46426 (15) | −0.0177 (2) | 0.11946 (13) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.10583 (17) | 0.3027 (2) | 0.15207 (15) | 0.0696 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.23169 (19) | 0.0950 (2) | 0.05296 (15) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| N2 | −0.07371 (19) | 0.1894 (2) | −0.08553 (15) | 0.0486 (6) | |
| N3 | −0.05032 (19) | 0.2766 (3) | −0.00250 (16) | 0.0519 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.1172 (2) | 0.1547 (3) | 0.01786 (18) | 0.0433 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.5813 (2) | −0.0571 (3) | 0.1754 (2) | 0.0488 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.0317 (2) | 0.1251 (3) | −0.07436 (18) | 0.0449 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.0408 (3) | 0.0357 (3) | −0.15564 (19) | 0.0576 (8) | |
| H4A | 0.0415 | 0.0887 | −0.2121 | 0.086* | |
| H4B | −0.0275 | −0.0238 | −0.1773 | 0.086* | |
| H4C | 0.1143 | −0.0154 | −0.1299 | 0.086* | |
| C6 | 0.3099 (2) | 0.1276 (3) | 0.1398 (2) | 0.0547 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.2884 | 0.1906 | 0.1788 | 0.066* | |
| C9 | 0.0665 (2) | 0.2508 (3) | 0.0669 (2) | 0.0486 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.6170 (3) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.2668 (2) | 0.0621 (9) | |
| H7 | 0.6913 | −0.0110 | 0.3191 | 0.075* | |
| C12 | −0.1484 (3) | 0.3267 (3) | 0.02341 (19) | 0.0511 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.4294 (2) | 0.0702 (3) | 0.1788 (2) | 0.0525 (8) | |
| C13 | −0.2464 (3) | 0.2472 (4) | 0.0175 (2) | 0.0605 (9) | |
| H10 | −0.2509 | 0.1595 | −0.0054 | 0.073* | |
| C3 | 0.5208 (3) | 0.0835 (4) | 0.2690 (2) | 0.0704 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.5206 | 0.1371 | 0.3227 | 0.084* | |
| C15 | −0.3310 (4) | 0.4306 (5) | 0.0795 (3) | 0.0885 (14) | |
| H12 | −0.3929 | 0.4662 | 0.0978 | 0.106* | |
| C17 | −0.1411 (3) | 0.4580 (4) | 0.0576 (2) | 0.0673 (9) | |
| H13 | −0.0750 | 0.5113 | 0.0615 | 0.081* | |
| C5 | 0.6407 (3) | −0.1481 (4) | 0.1252 (2) | 0.0652 (9) | |
| H14A | 0.7193 | −0.1726 | 0.1722 | 0.098* | |
| H14B | 0.6492 | −0.1038 | 0.0678 | 0.098* | |
| H14C | 0.5921 | −0.2270 | 0.1029 | 0.098* | |
| C11 | −0.1602 (3) | 0.2351 (4) | −0.1828 (2) | 0.0852 (13) | |
| H15A | −0.1321 | 0.3176 | −0.2015 | 0.128* | |
| H15B | −0.2378 | 0.2492 | −0.1769 | 0.128* | |
| H15C | −0.1675 | 0.1688 | −0.2338 | 0.128* | |
| C14 | −0.3378 (3) | 0.2996 (5) | 0.0461 (2) | 0.0763 (11) | |
| H16 | −0.4039 | 0.2468 | 0.0429 | 0.092* | |
| C16 | −0.2332 (4) | 0.5077 (4) | 0.0854 (3) | 0.0879 (13) | |
| H17 | −0.2288 | 0.5953 | 0.1086 | 0.105* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0387 (11) | 0.0633 (14) | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0038 (10) | 0.0134 (8) | −0.0004 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0511 (13) | 0.0848 (17) | 0.0624 (13) | 0.0078 (12) | 0.0077 (10) | −0.0311 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0359 (13) | 0.0542 (16) | 0.0473 (12) | −0.0030 (11) | 0.0159 (10) | −0.0022 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0550 (16) | 0.0423 (12) | 0.0061 (12) | 0.0099 (10) | −0.0064 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0401 (13) | 0.0561 (16) | 0.0545 (13) | 0.0049 (12) | 0.0106 (10) | −0.0120 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0361 (15) | 0.0492 (18) | 0.0442 (14) | −0.0031 (13) | 0.0139 (11) | −0.0025 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0309 (15) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0583 (16) | 0.0012 (13) | 0.0153 (12) | 0.0114 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0445 (16) | 0.0485 (18) | 0.0441 (14) | −0.0002 (14) | 0.0186 (12) | 0.0029 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0570 (19) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0473 (15) | 0.0056 (17) | 0.0167 (13) | −0.0030 (15) |
| C6 | 0.0446 (17) | 0.065 (2) | 0.0531 (16) | 0.0048 (15) | 0.0158 (13) | −0.0141 (15) |
| C9 | 0.0405 (16) | 0.0509 (18) | 0.0517 (15) | 0.0003 (14) | 0.0130 (12) | −0.0094 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0388 (16) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0631 (18) | −0.0015 (17) | 0.0039 (13) | −0.0026 (17) |
| C12 | 0.0445 (17) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0485 (15) | 0.0101 (15) | 0.0083 (12) | 0.0002 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0373 (16) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0562 (16) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0146 (13) | −0.0091 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0462 (18) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0596 (17) | 0.0060 (17) | 0.0080 (14) | −0.0076 (16) |
| C3 | 0.0514 (19) | 0.086 (3) | 0.0624 (18) | 0.0040 (19) | 0.0064 (15) | −0.0222 (18) |
| C15 | 0.060 (2) | 0.128 (4) | 0.076 (2) | 0.039 (3) | 0.0220 (18) | −0.011 (2) |
| C17 | 0.068 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0100 (18) | 0.0231 (17) | −0.0030 (17) |
| C5 | 0.0510 (18) | 0.081 (3) | 0.0661 (18) | 0.0154 (18) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0138 (18) |
| C11 | 0.084 (2) | 0.101 (3) | 0.0503 (17) | 0.032 (2) | −0.0009 (17) | −0.0012 (19) |
| C14 | 0.0406 (19) | 0.113 (4) | 0.069 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.0120 (15) | −0.005 (2) |
| C16 | 0.097 (3) | 0.075 (3) | 0.090 (3) | 0.035 (3) | 0.030 (2) | −0.009 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C4 | 1.375 (3) | C2—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C1 | 1.382 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.382 (4) |
| O2—C9 | 1.237 (3) | C12—C17 | 1.390 (4) |
| N1—C6 | 1.285 (3) | C4—C3 | 1.349 (4) |
| N1—C7 | 1.397 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.383 (5) |
| N2—C8 | 1.359 (3) | C13—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N2—N3 | 1.407 (3) | C3—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C11 | 1.461 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.366 (6) |
| N3—C9 | 1.401 (3) | C15—C14 | 1.384 (6) |
| N3—C12 | 1.424 (4) | C15—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.364 (3) | C17—C16 | 1.375 (5) |
| C7—C9 | 1.435 (4) | C17—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.337 (4) | C5—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C5 | 1.475 (4) | C5—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C10 | 1.488 (4) | C5—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C10—H4A | 0.9600 | C11—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C10—H4B | 0.9600 | C11—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C10—H4C | 0.9600 | C11—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C4 | 1.438 (4) | C14—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C6—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.414 (4) | ||
| C4—O1—C1 | 106.9 (2) | C17—C12—N3 | 117.8 (3) |
| C6—N1—C7 | 120.3 (2) | C3—C4—O1 | 109.0 (3) |
| C8—N2—N3 | 107.33 (19) | C3—C4—C6 | 131.8 (3) |
| C8—N2—C11 | 124.1 (2) | O1—C4—C6 | 119.2 (2) |
| N3—N2—C11 | 116.8 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 119.3 (3) |
| C9—N3—N2 | 108.6 (2) | C12—C13—H10 | 120.4 |
| C9—N3—C12 | 124.9 (2) | C14—C13—H10 | 120.4 |
| N2—N3—C12 | 119.8 (2) | C4—C3—C2 | 107.5 (3) |
| C8—C7—N1 | 122.5 (2) | C4—C3—H11 | 126.3 |
| C8—C7—C9 | 108.2 (2) | C2—C3—H11 | 126.3 |
| N1—C7—C9 | 129.3 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 120.0 (4) |
| C2—C1—O1 | 109.5 (3) | C16—C15—H12 | 120.0 |
| C2—C1—C5 | 133.7 (3) | C14—C15—H12 | 120.0 |
| O1—C1—C5 | 116.8 (2) | C16—C17—C12 | 118.9 (4) |
| N2—C8—C7 | 110.0 (2) | C16—C17—H13 | 120.5 |
| N2—C8—C10 | 120.7 (2) | C12—C17—H13 | 120.5 |
| C7—C8—C10 | 129.3 (3) | C1—C5—H14A | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H4A | 109.5 | C1—C5—H14B | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H4B | 109.5 | H14A—C5—H14B | 109.5 |
| H4A—C10—H4B | 109.5 | C1—C5—H14C | 109.5 |
| C8—C10—H4C | 109.5 | H14A—C5—H14C | 109.5 |
| H4A—C10—H4C | 109.5 | H14B—C5—H14C | 109.5 |
| H4B—C10—H4C | 109.5 | N2—C11—H15A | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—C4 | 122.4 (3) | N2—C11—H15B | 109.5 |
| N1—C6—H5 | 118.8 | H15A—C11—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C6—H5 | 118.8 | N2—C11—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C9—N3 | 122.4 (3) | H15A—C11—H15C | 109.5 |
| O2—C9—C7 | 132.3 (2) | H15B—C11—H15C | 109.5 |
| N3—C9—C7 | 105.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 120.1 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 107.2 (3) | C13—C14—H16 | 120.0 |
| C1—C2—H7 | 126.4 | C15—C14—H16 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—H7 | 126.4 | C15—C16—C17 | 121.1 (4) |
| C13—C12—C17 | 120.7 (3) | C15—C16—H17 | 119.5 |
| C13—C12—N3 | 121.6 (3) | C17—C16—H17 | 119.5 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2080).
References
- Ali, M. A., Mirza, A. H., Butcher, R. J., Tarafder, M. T. H., Keat, T. B. & Ali, A. M. (2002). J. Inorg. Biochem.92, 141–148. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2000). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Carlton, L. D., Schmith, V. D. & Brouwer, K. L. R. (1995). Prostaglandins, 50, 341–347. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Coolen, S. A. J., Everaerts, F. M. & Huf, F. A. (1999). J. Chromatogr. B, 732, 103–113. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cukurovali, A., Yilmaz, I., Özmen, H. & Ahmedzade, M. (2002). Transition Met. Chem.27, 171–176.
- Greisen, G. & Andreasen, P. B. (1976). Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.38, 49–58. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S. X., Bayón, J. E., Ferre, I., Mao, X. Z. & González-Gallego, J. (2000). Vet. Parasitology, 88, 177–186. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liang, H., Yu, Q. & Hu, R.-X. (2002). Transition Met. Chem.27, 454–457.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2000). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tarafder, M. T. H., Jin, K. T., Crouse, K. A., Ali, A. M., Yamin, B. M. & Fun, H. K. (2002). Polyhedron, 21, 2547–2554.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015419/bq2080sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015419/bq2080Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




