Abstract
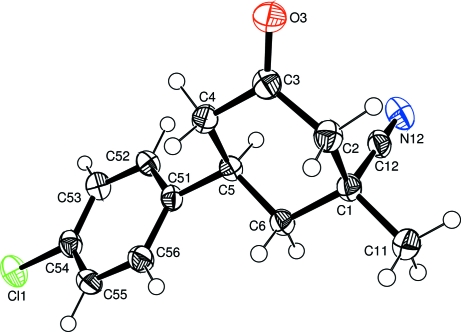
In the title molecule, C14H14ClNO, the cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation. The cyano group and the methyl group have axial and equatorial orientations, respectively. The benzene ring has an equatorial orientation. A C—H⋯π interaction involving the benzene ring is found in the crystal structure.
Related literature
Subramanyam et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶) and Thiruvalluvar et al. (2007 ▶) have reported the crystal structures of substituted cyclohexane derivatives, in which the cyclohexane rings are in a chair conformation.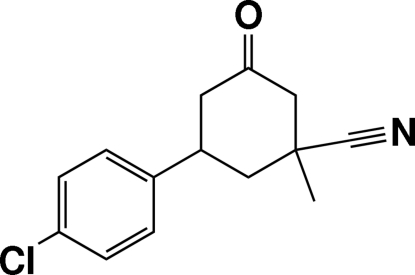
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H14ClNO
M r = 247.71
Monoclinic,
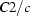
a = 23.3358 (6) Å
b = 6.0031 (2) Å
c = 20.8948 (6) Å
β = 122.386 (2)°
V = 2471.81 (14) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 160 (1) K
0.28 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (Blessing, 1995 ▶) T min = 0.877, T max = 0.956
28232 measured reflections
2822 independent reflections
2211 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.058
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.107
S = 1.05
2822 reflections
154 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.32 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO-SMN (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO-SMN and SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012816/ww2118sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012816/ww2118Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4B⋯Cgi | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.5333 (18) | 157 |
Symmetry code: (i) 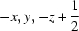 . Cg is the centroid of the benzene ring.
. Cg is the centroid of the benzene ring.
Acknowledgments
AT thanks the UGC, India, for the award of a Minor Research Project [file No. MRP-2355/06 (UGC-SERO), link No. 2355, 10/01/2007].
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Subramanyam et al. (2007a,b) and Thiruvalluvar et al. (2007) have reported the crystal structures of substituted cyclohexane derivatives, in which the cyclohexane rings are in chair conformation. The molecular structure of the title compound, with atomic numbering scheme, is shown in Fig. 1. The cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation. The cyano group and the methyl group at position 1 have axial and equatorial orientations respectively. The benzene ring at position 5 has an equatorial orientation. A C4—H4B···π(-x, y, 1/2 - z) interaction involving the benzene ring is found in the structure. No classical hydrogen bonds are found in the crystal structure.
Experimental
A mixture of 5–4'-chlorophenyl-3-methylcyclohex-2-enone (6.40 g, 0.02 mol), potassium cyanide (2.60 g, 0.04 mol), ammonium chloride (1.59 g, 0.03 mol), dimethyl formamide (50 ml) and water (2 ml) was heated with stirring for 16–18 h at 353 K. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and poured into water. The product was extracted with CH2Cl2 (3x10 ml) and the organic layer was dried, evaporated and purified by column chromatography (hexane-EtOAc, 4.5:1 v/v). The yield of the isolated product was 4.30 g (87%).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.95 Å for Csp2, 0.98 Å for methyl C, 0.99 Å for methylene C and 1.00 Å for methine C; Uiso(H) = xUeq(carrier atom), where x = 1.5 for methyl and 1.2 for all other C atoms
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom-numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms are represented by spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C14H14ClNO | F000 = 1040 |
| Mr = 247.71 | Dx = 1.331 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Melting point: 358 K |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 23.3358 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 31960 reflections |
| b = 6.0031 (2) Å | θ = 2.0–27.5º |
| c = 20.8948 (6) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| β = 122.386 (2)º | T = 160 (1) K |
| V = 2471.81 (14) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.28 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD area-detector diffractometer | 2822 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Nonius FR590 sealed tube generator | 2211 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: horizontally mounted graphite crystal | Rint = 0.058 |
| Detector resolution: 9 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5º |
| T = 160(1) K | θmin = 2.1º |
| φ and ω scans with κ offsets | h = −30→29 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(Blessing, 1995) | k = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.877, Tmax = 0.956 | l = −27→27 |
| 28232 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.107 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0525P)2 + 1.7764P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2822 reflections | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 154 parameters | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Experimental. Cooling Device: Oxford Cryosystems Cryostream 700 Crystal mount: glued on a glass fibre Mosaicity (°.): 0.793 (2) Frames collected: 394 Seconds exposure per frame: 16 Degrees rotation per frame: 1.6 Crystal-Detector distance (mm): 30.0 |
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | −0.25175 (2) | 0.41436 (8) | 0.08818 (3) | 0.0406 (2) | |
| O3 | 0.15529 (6) | 1.0355 (2) | 0.24871 (7) | 0.0401 (4) | |
| N12 | 0.08284 (8) | 0.8728 (3) | 0.02081 (8) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.12125 (8) | 0.5713 (3) | 0.12750 (9) | 0.0257 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.16797 (8) | 0.6816 (3) | 0.20566 (9) | 0.0296 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.13140 (8) | 0.8524 (3) | 0.22416 (9) | 0.0290 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.06351 (8) | 0.7819 (3) | 0.21034 (9) | 0.0292 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.01764 (7) | 0.6715 (3) | 0.13228 (8) | 0.0241 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.05647 (8) | 0.4842 (3) | 0.12188 (9) | 0.0264 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.15935 (9) | 0.3848 (3) | 0.11531 (10) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.10064 (8) | 0.7426 (3) | 0.06780 (9) | 0.0277 (5) | |
| C51 | −0.04910 (7) | 0.6001 (3) | 0.12231 (8) | 0.0239 (4) | |
| C52 | −0.10261 (8) | 0.7514 (3) | 0.09191 (8) | 0.0270 (5) | |
| C53 | −0.16454 (8) | 0.6975 (3) | 0.08277 (9) | 0.0293 (5) | |
| C54 | −0.17302 (8) | 0.4867 (3) | 0.10337 (9) | 0.0289 (5) | |
| C55 | −0.12083 (9) | 0.3334 (3) | 0.13444 (10) | 0.0322 (5) | |
| C56 | −0.05897 (8) | 0.3916 (3) | 0.14389 (10) | 0.0304 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.18685 | 0.56475 | 0.24527 | 0.0355* | |
| H2B | 0.20638 | 0.75446 | 0.20642 | 0.0355* | |
| H4A | 0.04006 | 0.91413 | 0.21396 | 0.0350* | |
| H4B | 0.07101 | 0.67576 | 0.25040 | 0.0350* | |
| H5 | 0.00699 | 0.78708 | 0.09293 | 0.0289* | |
| H6A | 0.02664 | 0.41375 | 0.07173 | 0.0316* | |
| H6B | 0.06906 | 0.36910 | 0.16120 | 0.0316* | |
| H11A | 0.17294 | 0.27012 | 0.15427 | 0.0524* | |
| H11B | 0.19981 | 0.44642 | 0.11878 | 0.0524* | |
| H11C | 0.12964 | 0.31858 | 0.06508 | 0.0524* | |
| H52 | −0.09668 | 0.89480 | 0.07705 | 0.0325* | |
| H53 | −0.20035 | 0.80334 | 0.06276 | 0.0353* | |
| H55 | −0.12702 | 0.19013 | 0.14917 | 0.0386* | |
| H56 | −0.02282 | 0.28695 | 0.16550 | 0.0365* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0277 (2) | 0.0501 (3) | 0.0477 (3) | −0.0075 (2) | 0.0227 (2) | 0.0017 (2) |
| O3 | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0447 (7) | −0.0129 (6) | 0.0243 (6) | −0.0142 (6) |
| N12 | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0456 (9) | 0.0359 (8) | −0.0065 (7) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0043 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0237 (8) | 0.0280 (8) | 0.0280 (8) | −0.0011 (6) | 0.0156 (7) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0279 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0131 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0287 (8) | 0.0343 (9) | 0.0220 (7) | −0.0040 (7) | 0.0122 (7) | −0.0022 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0316 (9) | 0.0297 (8) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0184 (7) | −0.0036 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0249 (8) | 0.0253 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0019 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0257 (8) | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0287 (8) | −0.0037 (6) | 0.0165 (7) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0339 (9) | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0438 (10) | 0.0003 (7) | 0.0255 (8) | −0.0037 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0248 (8) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0284 (8) | −0.0071 (7) | 0.0169 (7) | −0.0056 (7) |
| C51 | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0215 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0136 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C52 | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0285 (8) | 0.0254 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C53 | 0.0242 (8) | 0.0352 (9) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0117 (7) | 0.0038 (7) |
| C54 | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0365 (9) | 0.0276 (8) | −0.0071 (7) | 0.0147 (7) | −0.0036 (7) |
| C55 | 0.0348 (9) | 0.0265 (8) | 0.0423 (10) | −0.0033 (7) | 0.0254 (8) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C56 | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0047 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C54 | 1.744 (2) | C54—C55 | 1.380 (3) |
| O3—C3 | 1.215 (2) | C55—C56 | 1.393 (3) |
| N12—C12 | 1.145 (2) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.545 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C6 | 1.544 (3) | C4—H4A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C11 | 1.533 (3) | C4—H4B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C12 | 1.484 (2) | C5—H5 | 1.0000 |
| C2—C3 | 1.511 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.511 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| C4—C5 | 1.541 (2) | C11—H11A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.531 (3) | C11—H11B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C51 | 1.518 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9800 |
| C51—C52 | 1.392 (3) | C52—H52 | 0.9500 |
| C51—C56 | 1.391 (3) | C53—H53 | 0.9500 |
| C52—C53 | 1.391 (3) | C55—H55 | 0.9500 |
| C53—C54 | 1.385 (3) | C56—H56 | 0.9500 |
| Cl1···N12i | 3.335 (2) | H4B···C51ii | 3.0000 |
| Cl1···C12i | 3.397 (2) | H4B···C52ii | 3.0000 |
| Cl1···H2Aii | 3.0900 | H4B···C53ii | 2.9600 |
| O3···H6Biii | 2.7300 | H4B···C54ii | 2.9200 |
| O3···H11Aiii | 2.6300 | H4B···C55ii | 2.8900 |
| O3···H55iv | 2.7100 | H4B···C56ii | 2.9200 |
| N12···Cl1v | 3.335 (2) | H5···N12 | 2.9200 |
| N12···H5 | 2.9200 | H5···C12 | 2.5200 |
| N12···H6Avi | 2.8200 | H5···H52 | 2.3500 |
| N12···H52vii | 2.6300 | H6A···C56 | 3.0800 |
| N12···H11Ciii | 2.8500 | H6A···H11C | 2.5500 |
| C4···C12 | 3.527 (3) | H6A···N12vi | 2.8200 |
| C12···C4 | 3.527 (3) | H6A···C12vi | 2.9900 |
| C12···Cl1v | 3.397 (2) | H6B···O3ix | 2.7300 |
| C6···H56 | 2.7300 | H6B···C56 | 2.8100 |
| C12···H5 | 2.5200 | H6B···H11A | 2.5700 |
| C12···H6Avi | 2.9900 | H6B···H56 | 2.2500 |
| C51···H4Bii | 3.0000 | H11A···O3ix | 2.6300 |
| C52···H4A | 3.0700 | H11A···H2A | 2.4900 |
| C52···H55iii | 3.0700 | H11A···H6B | 2.5700 |
| C52···H4Bii | 3.0000 | H11B···H2B | 2.5500 |
| C52···H11Cvi | 3.0200 | H11C···N12ix | 2.8500 |
| C53···H4Bii | 2.9600 | H11C···H6A | 2.5500 |
| C53···H53viii | 2.9900 | H11C···C52vi | 3.0200 |
| C54···H4Bii | 2.9200 | H52···C55iii | 3.0700 |
| C55···H52ix | 3.0700 | H52···H5 | 2.3500 |
| C55···H4Bii | 2.8900 | H52···N12vii | 2.6300 |
| C56···H6A | 3.0800 | H53···C53viii | 2.9900 |
| C56···H6B | 2.8100 | H53···H53viii | 2.4800 |
| C56···H4Bii | 2.9200 | H55···C52ix | 3.0700 |
| H2A···H11A | 2.4900 | H55···O3x | 2.7100 |
| H2A···Cl1ii | 3.0900 | H56···C6 | 2.7300 |
| H2B···H11B | 2.5500 | H56···H4Aix | 2.5700 |
| H4A···C52 | 3.0700 | H56···H6B | 2.2500 |
| H4A···H56iii | 2.5700 | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 109.48 (15) | C3—C2—H2B | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C11 | 110.17 (15) | H2A—C2—H2B | 108.00 |
| C2—C1—C12 | 108.61 (15) | C3—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| C6—C1—C11 | 111.80 (15) | C3—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| C6—C1—C12 | 107.91 (15) | C5—C4—H4A | 109.00 |
| C11—C1—C12 | 108.79 (15) | C5—C4—H4B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.70 (16) | H4A—C4—H4B | 108.00 |
| O3—C3—C2 | 121.85 (19) | C4—C5—H5 | 107.00 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 122.09 (18) | C6—C5—H5 | 107.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.05 (15) | C51—C5—H5 | 107.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 112.68 (15) | C1—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 109.74 (14) | C1—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C51 | 110.28 (14) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.00 |
| C6—C5—C51 | 114.51 (15) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 111.74 (15) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.00 |
| N12—C12—C1 | 178.0 (2) | C1—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| C5—C51—C52 | 118.81 (16) | C1—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| C5—C51—C56 | 123.05 (16) | C1—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| C52—C51—C56 | 118.12 (18) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| C51—C52—C53 | 121.54 (17) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| C52—C53—C54 | 118.75 (18) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| Cl1—C54—C53 | 118.89 (15) | C51—C52—H52 | 119.00 |
| Cl1—C54—C55 | 119.86 (15) | C53—C52—H52 | 119.00 |
| C53—C54—C55 | 121.2 (2) | C52—C53—H53 | 121.00 |
| C54—C55—C56 | 119.07 (17) | C54—C53—H53 | 121.00 |
| C51—C56—C55 | 121.26 (18) | C54—C55—H55 | 120.00 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.00 | C56—C55—H55 | 120.00 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.00 | C51—C56—H56 | 119.00 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.00 | C55—C56—H56 | 119.00 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −51.31 (19) | C4—C5—C51—C52 | 88.61 (17) |
| C11—C1—C2—C3 | −174.65 (16) | C4—C5—C51—C56 | −89.75 (19) |
| C12—C1—C2—C3 | 66.3 (2) | C6—C5—C51—C52 | −147.05 (14) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 58.91 (17) | C6—C5—C51—C56 | 34.6 (2) |
| C11—C1—C6—C5 | −178.71 (13) | C5—C51—C52—C53 | −178.71 (14) |
| C12—C1—C6—C5 | −59.12 (17) | C56—C51—C52—C53 | −0.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—O3 | −133.05 (17) | C5—C51—C56—C55 | 179.36 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 47.0 (2) | C52—C51—C56—C55 | 1.0 (2) |
| O3—C3—C4—C5 | 132.96 (17) | C51—C52—C53—C54 | −1.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −47.1 (2) | C52—C53—C54—Cl1 | −177.24 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 51.79 (19) | C52—C53—C54—C55 | 1.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C51 | 178.83 (14) | Cl1—C54—C55—C56 | 177.93 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −59.17 (18) | C53—C54—C55—C56 | −1.1 (3) |
| C51—C5—C6—C1 | 176.20 (12) | C54—C55—C56—C51 | −0.3 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, y−1/2, z; (ii) −x, y, −z+1/2; (iii) x, y+1, z; (iv) −x, y+1, −z+1/2; (v) x+1/2, y+1/2, z; (vi) −x, −y+1, −z; (vii) −x, −y+2, −z; (viii) −x−1/2, −y+3/2, −z; (ix) x, y−1, z; (x) −x, y−1, −z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4B···Cgii | 0.99 | 2.60 | 3.5333 (18) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, y, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WW2118).
References
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Nonius (2000). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Subramanyam, M., Thiruvalluvar, A., Mohan, R. T. S. & Kamatchi, S. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o2717.
- Subramanyam, M., Thiruvalluvar, A., Sabapathy Mohan, R. T. & Kamatchi, S. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o2715–o2716.
- Thiruvalluvar, A., Subramanyam, M., Mohan, R. T. S., Kamatchi, S. & Murugavel, K. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2780.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012816/ww2118sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808012816/ww2118Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report