Abstract
In vivo, epithelial cells which line the intestine are intimately associated with lymphocytes, termed intraepithelial lymphocytes. Previous studies have demonstrated that intraepithelial lymphocytes are present in the uninflamed mucosa, and become especially prominent in various human enteropathies including coeliac disease, tropical sprue, dermatitis herpetiformis, and giardiasis. Using the intestinal crypt cell line T84, and a previously well-defined human mucosa-derived lymphocyte (MDL) line with phenotypic features similar to (but not specific for) intraepithelial lymphocytes, we describe a co-culture model to study the functional sequellae of MDL-T84 cell interactions in vitro. A co-culture method was defined which permitted reconstitution of the paracellular spaces of physiologically confluent epithelial monolayers with MDL. Such co-cultures thus mimicked the correct geometry of intraepithelial lymphocytes-epithelial cell interactions. The presence of physiologically positioned MDL brought about specific and dramatic effects on intestinal epithelial monolayer function. In a dose-dependent fashion, the presence of MDL significantly attenuated barrier function (expressed as a decrease in monolayer resistance), decreased epithelial electrogenic Cl- secretion, and modulated epithelial-neutrophil interactions. Such effects were not reproduced in monolayers similarly reconstituted with inert polystyrene beads equivalent in size to MDL. These MDL-elicited effects on epithelial function specifically required direct MDL apposition to the epithelial basolateral membrane. Furthermore, this specific form of MDL-epithelial basolateral contact released soluble factors which were able to confer the MDL-reconstituted phenotype on virgin epithelial monolayers in the absence of MDL. We have previously shown that many aspects of the MDL converted epithelial phenotype described here can be induced by IFN-gamma. While IFN-gamma, a cytokine produced by many lymphocytes including intraepithelial lymphocytes, was detectable in conditioned supernatants from co-cultures, it existed at concentrations insufficient to fully explain the physiologic effects observed here.
Full text
PDF


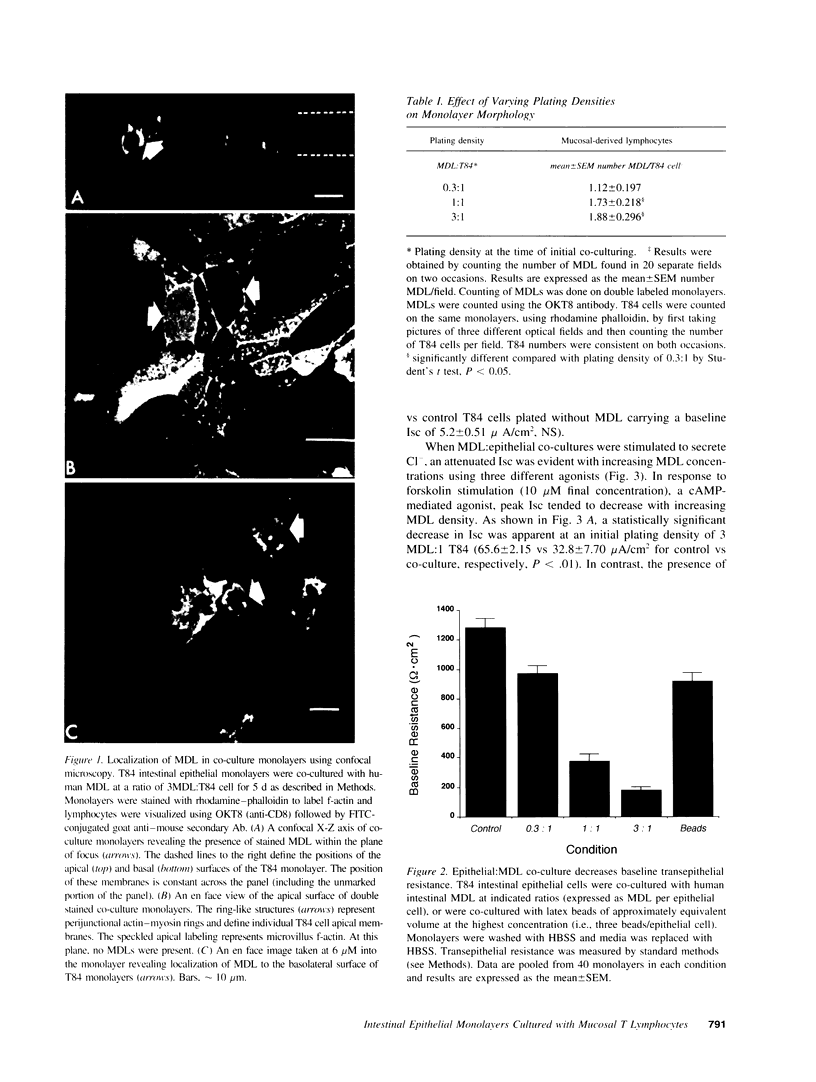
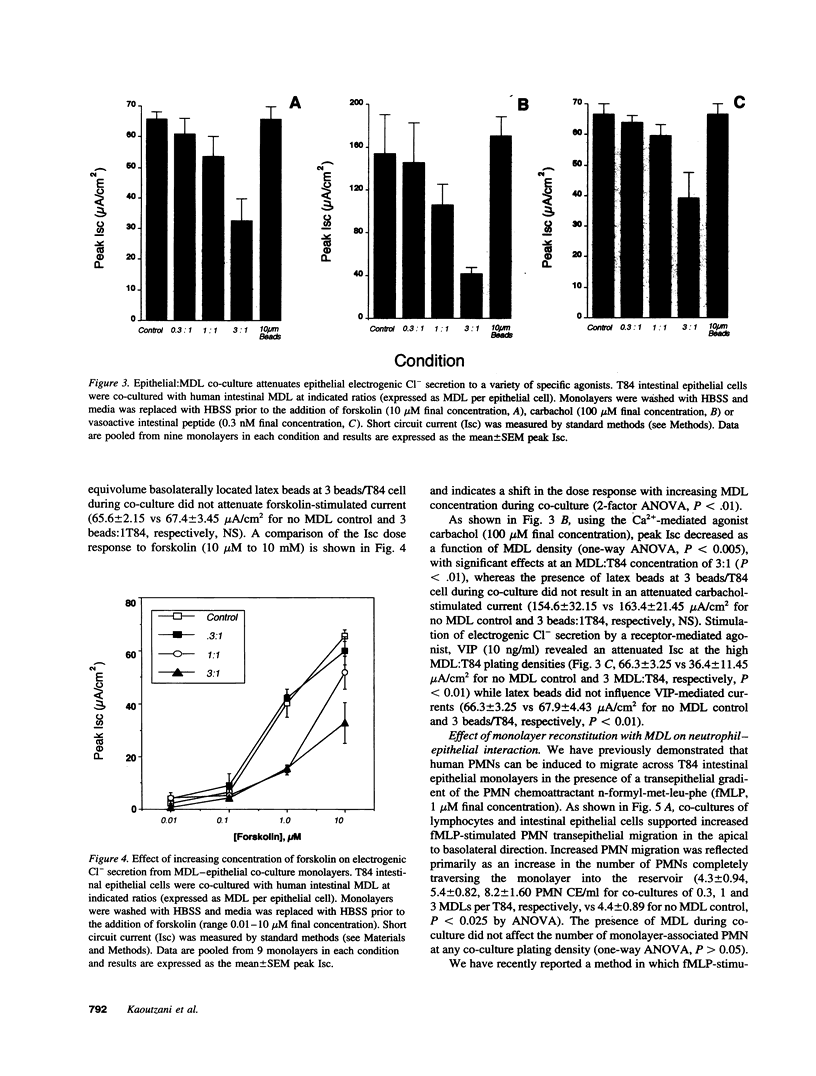
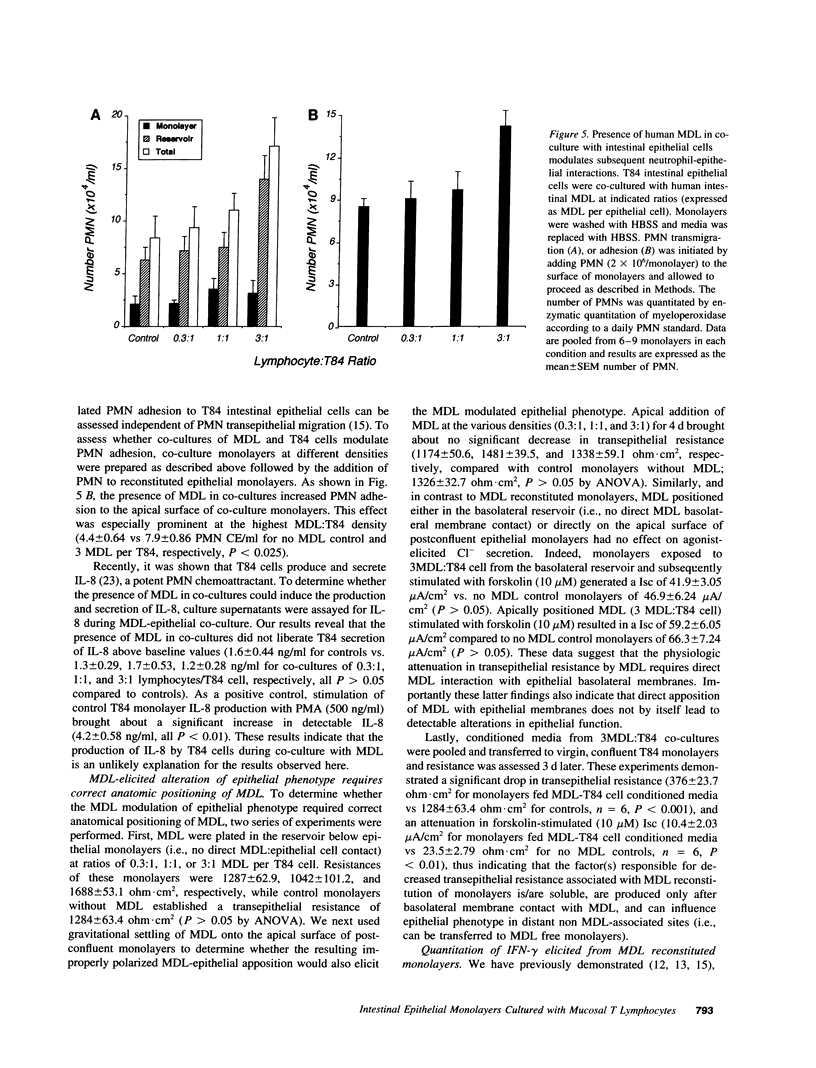
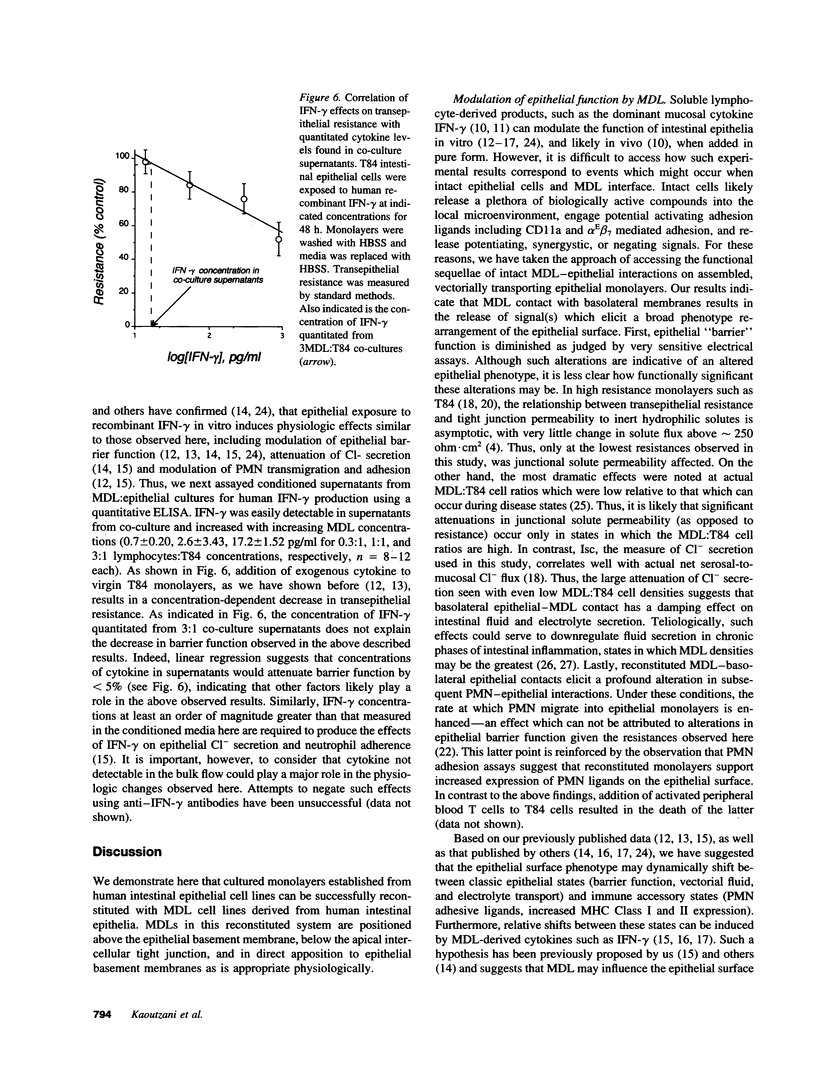


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. B., Planchon S. M., Roche J. K. IFN-gamma modulation of epithelial barrier function. Time course, reversibility, and site of cytokine binding. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2356–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepek K. L., Parker C. M., Madara J. L., Brenner M. B. Integrin alpha E beta 7 mediates adhesion of T lymphocytes to epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3459–3470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerf-Bensussan N., Bègue B., Gagnon J., Meo T. The human intraepithelial lymphocyte marker HML-1 is an integrin consisting of a beta 7 subunit associated with a distinctive alpha chain. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):273–277. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgan S. P., Parkos C. A., Delp C., Arnaout M. A., Madara J. L. Neutrophil migration across cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers is modulated by epithelial exposure to IFN-gamma in a highly polarized fashion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;120(3):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.3.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Madara J. L. Established intestinal cell lines as model systems for electrolyte transport studies. Methods Enzymol. 1990;192:354–389. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)92082-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Fryklund J., Larsson H. Gamma-interferon-mediated down-regulation of electrolyte secretion by intestinal epithelial cells: a local immune mechanism? Scand J Immunol. 1989 Oct;30(4):499–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarry A., Cerf-Bensussan N., Brousse N., Selz F., Guy-Grand D. Subsets of CD3+ (T cell receptor alpha/beta or gamma/delta) and CD3- lymphocytes isolated from normal human gut epithelium display phenotypical features different from their counterparts in peripheral blood. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1097–1103. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Functional and structural aspects of the epithelial lymphocyte, with implications for coeliac disease and tropical sprue. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;114:55–75. doi: 10.3109/00365528509093768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromichalis J., Brueton M. J., McNeish A. S., Anderson C. M. Evaluation of the intraepithelial lymphocyte count in the jejunum in childhood enteropathies. Gut. 1976 Aug;17(8):600–603. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.8.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Shlien R. Evidence for function of Ia molecules on gut epithelial cells in man. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1471–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash S., Stafford J., Madara J. L. Effects of polymorphonuclear leukocyte transmigration on the barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1104–1113. doi: 10.1172/JCI113167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. M., Cepek K. L., Russell G. J., Shaw S. K., Posnett D. N., Schwarting R., Brenner M. B. A family of beta 7 integrins on human mucosal lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Delp C., Arnaout M. A., Madara J. L. Neutrophil migration across a cultured intestinal epithelium. Dependence on a CD11b/CD18-mediated event and enhanced efficiency in physiological direction. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1605–1612. doi: 10.1172/JCI115473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. D., Rice S. J., France N. E., Walker-Smith J. A. Small intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte levels in cow's milk protein intolerance. Gut. 1979 Jun;20(6):509–512. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.6.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiding M., Nordström I., Kilander A., Andersson G., Hanson L. A., Holmgren J., Czerkinsky C. Intestinal immune responses in humans. Oral cholera vaccination induces strong intestinal antibody responses and interferon-gamma production and evokes local immunological memory. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):143–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI115270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M., Matthews J., Hecht G., Delp C., Madara J. L. Stabilization of F-actin prevents cAMP-elicited Cl- secretion in T84 cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):1903–1909. doi: 10.1172/JCI115215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolpen A. H., Guinan E. C., Fiers W., Pober J. S. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon act singly and in combination to reorganize human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Pathol. 1986 Apr;123(1):16–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Fujihashi K., Beagley K. W., McGhee J. R., Kiyono H. Cytokine synthesis by intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Both gamma/delta T cell receptor-positive and alpha/beta T cell receptor-positive T cells in the G1 phase of cell cycle produce IFN-gamma and IL-5. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 1;150(1):106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




