Abstract
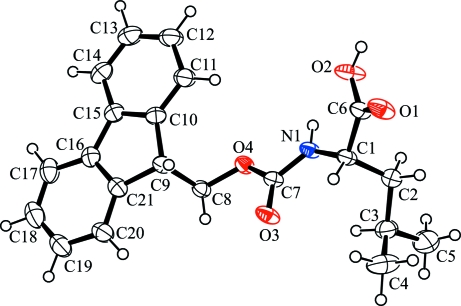
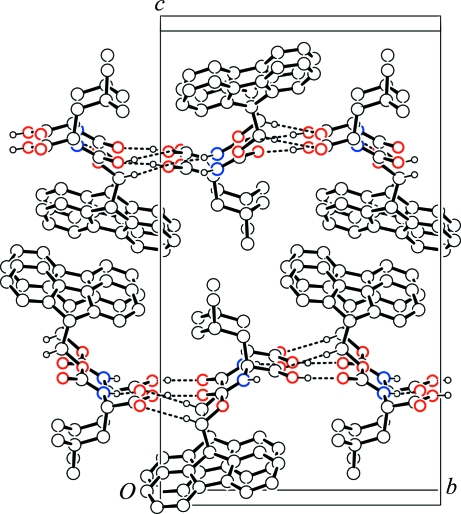
The title compound [systematic name: fluoren-9-yl N-(1-carboxy-3-methylbutyl)carbamate], C21H23NO4, exhibits torsion angles that vary from the typical values found in other Fmoc-protected amino acids, viz. the orientations of the fluorene and carboxyl groups [C—O—C—C = 93.8 (2) and N—C—C=O = −23.6 (2)°]. The crystal structure exhibits two intermolecular hydrogen bonds (O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O) that link the molecules into two-dimensional sheets parallel to the ab plane.
Related literature
For related literature on the structures of N-α-Fmoc-protected amino acids, see: Valle et al. (1984 ▶); Yamada et al. (2008 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H23NO4
M r = 353.40
Orthorhombic,
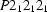
a = 5.4953 (1) Å
b = 14.2700 (3) Å
c = 24.3759 (6) Å
V = 1911.51 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.40 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Rigaku AFC-8 diffractometer with Saturn70 CCD detector
Absorption correction: none
40257 measured reflections
3207 independent reflections
2906 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.055
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.111
S = 1.09
3207 reflections
327 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: HKL-2000 (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: HKL-2000; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2004 (Burla et al., 2005 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808014372/fl2198sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808014372/fl2198Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2H⋯O3i | 0.85 (3) | 1.82 (3) | 2.6558 (17) | 167 (3) |
| N1—H1N⋯O1ii | 0.87 (3) | 2.24 (3) | 3.0751 (18) | 161 (2) |
| C8—H8A⋯O1iii | 0.90 (2) | 2.51 (2) | 3.392 (2) | 166 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 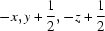 ; (ii)
; (ii) 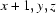 ; (iii)
; (iii) 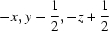 .
.
Acknowledgments
KY thanks the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, Culture, and Technology (MEXT) of Japan for funding this work [Young Scientists (B), 20750022].
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The fluoren-9-ylmethoxycarbonyl (Fmoc) group is currently one of the most frequently used protecting groups for peptide synthesis since rapid cleavages can be readily achieved under mild basic conditions with racemization-free results. Almost all the Fmoc-protected twenty-L-amino acids are commercially available. The crystal structures of N-α-Fmoc-protected-L-alanine monohydrate (II, Valle et al., 1984) and L-serine (III, Yamada et al., 2008) have been reported so far. In the present study, we have carried out the crystal structure analysis of N-α-Fmoc-L-leucine, (I).
The bond distances and bond angles of (I, Fig. 1) are consistent with the typical values of Fmoc-protected amino acids found in the other crystal structures. Some torsion angles, however, are found to be quite different. The torsion angle of O2—C6—C1—N1, for example, is -23.6 (2)°, which is in disagreement with the previous observations in the Fmoc-protected amino acids in which the corresponding angles are 150.6° and 175.8° for (II) (Valle et al., 1984) and (III) (Yamada et al., 2008), respectively. Another example is that the torsion angle of C6—C1—N1—C7 in (I) is found to be -134.51 (15)°, which is in reasonable agreement with that of (II), -151.6°, but is inconsistent with that found in (II), -65.6°. Each angle between the fluorene ring and the NC(δb O)O plane is found to be different among the three Fmoc-protected amino acids. The torsion angles C7—O4—C8—C9 and O4—C8—C9—C10 for the title compound, for instance, are 93.78 (16)° and 60.54 (17)°, respectively. On the other hand, the corresponding angles are -179.7° and -172.1°, and 121.9° and -68.2° for (II) and (III), respectively.
Crystals of (I) contain two intermolecular hydrogen bonds (Table 1), which are formed between the carboxyl (O2—H2H) and amide oxygens (O3), and between the amide (N1—H1N) and the carbonyl (O1). The molecules are linked by O2—H2H···O3 hydrogen bonds to form a chain structure along the b axis. The linkage is supported by an additional C—H···O interaction (C8—H8A···O1). The chains are joined together by the N1—H1N···O1 hydrogen bonds to form a sheet structure parallel to the ab plane. The Fmoc and i-butyl moieties are packed between the sheets (Fig. 2).
Experimental
A powdered sample (I) was obtained from Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. (Osaka, Japan) and was used for crystallization without further purifications. Colourless needle like crystals of (I) were slowly grown from a saturated dichloromethane solution.
Refinement
All H atoms were found in difference maps an refined with isotropic thermal parameters.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the molecular structure of (I), showing the atom labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of (I) viewed. The hydrogen atoms were omitted for clarity, except for those forming the hydrogen bonds. Broken lines indicate the hydrogen bonds.
Crystal data
| C21H23NO4 | F000 = 752 |
| Mr = 353.40 | Dx = 1.228 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 40402 reflections |
| a = 5.49530 (10) Å | θ = 2.2–30.0º |
| b = 14.2700 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 24.3759 (6) Å | T = 150 K |
| V = 1911.51 (7) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku AFC-8 diffractometer with Saturn70 CCD detector | 3207 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus rotating anode | 2906 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: confocal | Rint = 0.055 |
| Detector resolution: 28.5714 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 30.0º |
| T = 150 K | θmin = 2.2º |
| ω scans | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −20→20 |
| 40257 measured reflections | l = −34→34 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.111 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0687P)2 + 0.1717P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.09 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3207 reflections | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 327 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Experimental. All Friedel pairs were merged, and all f''s of containing atoms were set to zero. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.3755 (2) | 0.42665 (9) | 0.27853 (7) | 0.0421 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.0123 (2) | 0.47101 (9) | 0.26982 (7) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| H2H | −0.047 (5) | 0.526 (2) | 0.2667 (11) | 0.055 (7)* | |
| O3 | 0.1016 (2) | 0.15166 (8) | 0.23545 (6) | 0.0360 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.4680 (2) | 0.22208 (8) | 0.22403 (5) | 0.0306 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.1792 (2) | 0.29706 (9) | 0.26957 (6) | 0.0284 (3) | |
| H1N | 0.280 (5) | 0.3438 (18) | 0.2738 (9) | 0.044 (6)* | |
| C1 | −0.0651 (3) | 0.31083 (10) | 0.29096 (7) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| H1 | −0.171 (4) | 0.2659 (15) | 0.2718 (9) | 0.035 (5)* | |
| C2 | −0.0783 (4) | 0.29621 (13) | 0.35339 (8) | 0.0406 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.047 (5) | 0.3372 (19) | 0.3712 (10) | 0.048 (7)* | |
| H2B | −0.225 (6) | 0.322 (2) | 0.3692 (13) | 0.065 (8)* | |
| C3 | −0.0497 (4) | 0.19389 (13) | 0.37135 (8) | 0.0413 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.102 (5) | 0.1685 (18) | 0.3516 (10) | 0.048 (7)* | |
| C4 | −0.2695 (5) | 0.13470 (17) | 0.35502 (14) | 0.0601 (7) | |
| H4A | −0.312 (6) | 0.1369 (19) | 0.3131 (11) | 0.060 (8)* | |
| H4B | −0.387 (8) | 0.163 (3) | 0.3755 (15) | 0.088 (11)* | |
| H4C | −0.262 (6) | 0.065 (2) | 0.3677 (13) | 0.072 (9)* | |
| C5 | 0.0014 (9) | 0.18903 (19) | 0.43291 (10) | 0.0705 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.163 (8) | 0.227 (3) | 0.4437 (15) | 0.093 (12)* | |
| H5B | 0.017 (6) | 0.124 (2) | 0.4463 (11) | 0.060 (8)* | |
| H5C | −0.127 (7) | 0.223 (2) | 0.4509 (13) | 0.072 (9)* | |
| C6 | −0.1606 (3) | 0.40869 (10) | 0.27831 (7) | 0.0299 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.2373 (3) | 0.21843 (10) | 0.24241 (6) | 0.0261 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.5484 (3) | 0.14752 (11) | 0.18786 (6) | 0.0289 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.476 (5) | 0.0932 (16) | 0.1976 (9) | 0.034 (5)* | |
| H8B | 0.721 (5) | 0.1412 (15) | 0.1960 (9) | 0.034 (5)* | |
| C9 | 0.5153 (3) | 0.17588 (11) | 0.12778 (7) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.337 (5) | 0.1858 (16) | 0.1193 (9) | 0.043 (6)* | |
| C10 | 0.6613 (3) | 0.26233 (11) | 0.11325 (7) | 0.0308 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.6335 (4) | 0.35445 (12) | 0.13131 (8) | 0.0385 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.504 (5) | 0.3707 (16) | 0.1573 (9) | 0.035 (5)* | |
| C12 | 0.8001 (4) | 0.42145 (13) | 0.11327 (9) | 0.0456 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.783 (5) | 0.4852 (19) | 0.1253 (10) | 0.054 (7)* | |
| C13 | 0.9889 (4) | 0.39782 (15) | 0.07795 (8) | 0.0459 (5) | |
| H13 | 1.117 (5) | 0.4495 (19) | 0.0642 (11) | 0.057 (7)* | |
| C14 | 1.0166 (4) | 0.30626 (15) | 0.05954 (8) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| H14 | 1.148 (5) | 0.2884 (16) | 0.0338 (10) | 0.048 (6)* | |
| C15 | 0.8514 (3) | 0.23871 (12) | 0.07728 (7) | 0.0323 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.8333 (3) | 0.13832 (12) | 0.06424 (6) | 0.0329 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.9738 (4) | 0.08170 (16) | 0.03029 (8) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| H17 | 1.114 (5) | 0.1107 (17) | 0.0111 (10) | 0.048 (7)* | |
| C18 | 0.9091 (5) | −0.01199 (16) | 0.02442 (8) | 0.0505 (5) | |
| H18 | 1.003 (6) | −0.0545 (19) | 0.0001 (11) | 0.060 (7)* | |
| C19 | 0.7076 (5) | −0.04829 (14) | 0.05165 (8) | 0.0473 (5) | |
| H19 | 0.671 (5) | −0.1136 (19) | 0.0461 (10) | 0.053 (7)* | |
| C20 | 0.5670 (4) | 0.00808 (12) | 0.08599 (8) | 0.0392 (4) | |
| H20 | 0.423 (5) | −0.0159 (18) | 0.1060 (11) | 0.053 (7)* | |
| C21 | 0.6305 (3) | 0.10141 (11) | 0.09189 (6) | 0.0317 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0258 (5) | 0.0769 (9) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0034 (6) | −0.0057 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0258 (6) | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0910 (11) | −0.0004 (4) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0087 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0236 (5) | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0623 (7) | −0.0025 (4) | 0.0012 (5) | −0.0085 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0245 (5) | 0.0259 (5) | 0.0415 (6) | −0.0027 (4) | 0.0051 (5) | −0.0058 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0232 (6) | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0430 (7) | −0.0026 (5) | 0.0012 (5) | −0.0035 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0194 (6) | 0.0423 (8) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0036 (6) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0521 (11) | 0.0276 (7) | 0.0422 (8) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0104 (8) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0447 (10) | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0466 (9) | 0.0005 (8) | 0.0056 (8) | 0.0076 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0468 (13) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0911 (19) | −0.0093 (10) | 0.0005 (13) | 0.0225 (12) |
| C5 | 0.115 (3) | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0480 (11) | 0.0009 (17) | 0.0066 (16) | 0.0115 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0243 (7) | 0.0214 (6) | 0.0440 (8) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0012 (6) | −0.0026 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0204 (6) | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0002 (5) | −0.0014 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0270 (7) | 0.0235 (6) | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0249 (7) | 0.0254 (7) | 0.0370 (7) | −0.0001 (6) | −0.0018 (6) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C10 | 0.0282 (8) | 0.0287 (7) | 0.0353 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | −0.0020 (6) | 0.0030 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0407 (10) | 0.0293 (8) | 0.0455 (9) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0529 (12) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0537 (10) | −0.0085 (9) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0034 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0463 (11) | 0.0412 (10) | 0.0500 (10) | −0.0140 (9) | −0.0004 (9) | 0.0089 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0490 (10) | 0.0389 (8) | −0.0064 (8) | 0.0021 (7) | 0.0082 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0338 (7) | 0.0326 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0364 (8) | 0.0296 (6) | 0.0047 (7) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0523 (11) | 0.0360 (8) | 0.0134 (9) | −0.0003 (8) | −0.0033 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0625 (14) | 0.0489 (11) | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0206 (11) | −0.0069 (9) | −0.0108 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0671 (14) | 0.0341 (9) | 0.0406 (8) | 0.0092 (9) | −0.0122 (10) | −0.0079 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0299 (8) | 0.0395 (8) | −0.0001 (8) | −0.0082 (8) | −0.0026 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0298 (7) | 0.0324 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | −0.0060 (6) | −0.0021 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C6 | 1.208 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.97 (2) |
| O2—C6 | 1.318 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.514 (2) |
| O2—H2H | 0.85 (3) | C9—C21 | 1.515 (2) |
| O3—C7 | 1.2217 (18) | C9—H9 | 1.01 (3) |
| O4—C7 | 1.3460 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.395 (2) |
| O4—C8 | 1.4506 (18) | C10—C15 | 1.405 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.3413 (18) | C11—C12 | 1.395 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.453 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.98 (2) |
| N1—H1N | 0.87 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.390 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.523 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.96 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.538 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.390 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.98 (2) | C13—H13 | 1.07 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.532 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.393 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 1.00 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.99 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.96 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.471 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.527 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.391 (3) |
| C3—C5 | 1.528 (3) | C16—C21 | 1.405 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 1.03 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.391 (3) |
| C4—H4A | 1.05 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.99 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.91 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.391 (4) |
| C4—H4C | 1.04 (3) | C18—H18 | 0.99 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 1.08 (4) | C19—C20 | 1.395 (3) |
| C5—H5B | 0.98 (3) | C19—H19 | 0.96 (3) |
| C5—H5C | 0.96 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.384 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.530 (2) | C20—H20 | 0.99 (3) |
| C8—H8A | 0.90 (2) | ||
| C6—O2—H2H | 111.1 (19) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.5 (13) |
| C7—O4—C8 | 117.44 (12) | H8A—C8—H8B | 107 (2) |
| C7—N1—C1 | 120.66 (13) | C10—C9—C21 | 102.41 (13) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 123.1 (16) | C10—C9—C8 | 112.11 (13) |
| C1—N1—H1N | 116.1 (16) | C21—C9—C8 | 108.51 (13) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 111.69 (13) | C10—C9—H9 | 110.6 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 112.36 (15) | C21—C9—H9 | 112.6 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 107.96 (13) | C8—C9—H9 | 110.4 (13) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 106.7 (13) | C11—C10—C15 | 120.30 (16) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 107.3 (13) | C11—C10—C9 | 129.51 (16) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 110.7 (13) | C15—C10—C9 | 110.16 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 114.03 (14) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.34 (19) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 111.3 (15) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.5 (13) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 108.5 (14) | C12—C11—H11 | 121.1 (13) |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.2 (18) | C13—C12—C11 | 121.27 (19) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 112.6 (18) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.4 (17) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 100 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.3 (17) |
| C4—C3—C5 | 112.1 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.65 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 111.80 (19) | C14—C13—H13 | 118.2 (15) |
| C5—C3—C2 | 110.04 (18) | C12—C13—H13 | 121.1 (14) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 108.9 (14) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.62 (19) |
| C5—C3—H3 | 107.1 (14) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.8 (14) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 106.6 (15) | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 114.4 (17) | C14—C15—C10 | 120.82 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4B | 100 (2) | C14—C15—C16 | 130.61 (18) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 111 (3) | C10—C15—C16 | 108.56 (15) |
| C3—C4—H4C | 115 (2) | C17—C16—C21 | 120.53 (18) |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109 (2) | C17—C16—C15 | 131.08 (19) |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 107 (3) | C21—C16—C15 | 108.36 (15) |
| C3—C5—H5A | 112 (2) | C16—C17—C18 | 118.6 (2) |
| C3—C5—H5B | 112.7 (16) | C16—C17—H17 | 118.0 (14) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109 (3) | C18—C17—H17 | 123.4 (14) |
| C3—C5—H5C | 107 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.8 (2) |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 104 (3) | C17—C18—H18 | 121.1 (16) |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 112 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 118.0 (16) |
| O1—C6—O2 | 124.21 (15) | C18—C19—C20 | 120.84 (19) |
| O1—C6—C1 | 122.02 (15) | C18—C19—H19 | 117.2 (17) |
| O2—C6—C1 | 113.70 (14) | C20—C19—H19 | 121.9 (17) |
| O3—C7—N1 | 125.15 (15) | C21—C20—C19 | 118.5 (2) |
| O3—C7—O4 | 123.98 (14) | C21—C20—H20 | 118.9 (15) |
| N1—C7—O4 | 110.87 (13) | C19—C20—H20 | 122.6 (15) |
| O4—C8—C9 | 110.58 (13) | C20—C21—C16 | 120.73 (16) |
| O4—C8—H8A | 109.7 (14) | C20—C21—C9 | 129.00 (17) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 115.2 (14) | C16—C21—C9 | 110.22 (14) |
| O4—C8—H8B | 104.0 (13) | ||
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | −134.51 (15) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.3 (3) |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | 103.99 (16) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 178.99 (18) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −70.9 (2) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.7 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 165.48 (17) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −177.72 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −69.5 (3) | C11—C10—C15—C16 | −178.72 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C5 | 165.2 (2) | C9—C10—C15—C16 | 2.82 (18) |
| N1—C1—C6—O1 | 159.29 (17) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—O1 | −76.7 (2) | C10—C15—C16—C17 | 178.86 (18) |
| N1—C1—C6—O2 | −23.6 (2) | C14—C15—C16—C21 | −178.76 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6—O2 | 100.39 (19) | C10—C15—C16—C21 | 0.63 (18) |
| C1—N1—C7—O3 | −3.6 (2) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | −0.1 (3) |
| C1—N1—C7—O4 | 177.08 (13) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −178.11 (18) |
| C8—O4—C7—O3 | 8.3 (2) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.3 (3) |
| C8—O4—C7—N1 | −172.31 (13) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.7 (3) |
| C7—O4—C8—C9 | 93.78 (16) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | 0.8 (3) |
| O4—C8—C9—C10 | 60.54 (17) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | −0.5 (3) |
| O4—C8—C9—C21 | 172.91 (13) | C19—C20—C21—C9 | −177.57 (17) |
| C21—C9—C10—C11 | 176.89 (18) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | 0.2 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −67.0 (2) | C15—C16—C21—C20 | 178.61 (16) |
| C21—C9—C10—C15 | −4.84 (17) | C17—C16—C21—C9 | 177.72 (15) |
| C8—C9—C10—C15 | 111.28 (16) | C15—C16—C21—C9 | −3.83 (18) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | −0.7 (3) | C10—C9—C21—C20 | −177.46 (17) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 177.40 (17) | C8—C9—C21—C20 | 63.8 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.3 (3) | C10—C9—C21—C16 | 5.24 (17) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.1 (3) | C8—C9—C21—C16 | −113.45 (15) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.1 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2H···O3i | 0.85 (3) | 1.82 (3) | 2.6558 (17) | 167 (3) |
| N1—H1N···O1ii | 0.87 (3) | 2.24 (3) | 3.0751 (18) | 161 (2) |
| C8—H8A···O1iii | 0.90 (2) | 2.51 (2) | 3.392 (2) | 166 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FL2198).
References
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., De Caro, L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2005). J. Appl. Cryst.38, 381–388.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Valle, G., Bonora, G. M. & Toniolo, C. (1984). Can. J. Chem.62, 2661–2666.
- Yamada, K., Hashizume, D., Shimizu, T., Ohiki, S. & Yokoyama, S. (2008). J. Mol. Struct. In the press.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808014372/fl2198sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808014372/fl2198Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report