Abstract
In the title compound, C12H11N5O2, the molecule adopts an E configuration, with the benzene and pyrazine rings located on opposite sides of the N=C double bond. The face-to-face separations of 3.413 (14) and 3.430 (8) Å, respectively between parallel benzene rings and between pyrazine rings indicate the existence of π–π stacking between adjacent molecules. The crystal structure also contains N—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For general background, see: Okabe et al. (1993 ▶); Hu et al. (2001 ▶); Chen et al. (2007 ▶). For a related structure, see: Shan et al. (2008 ▶).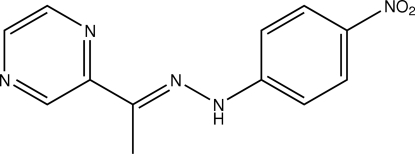
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H11N5O2
M r = 257.26
Monoclinic,
a = 8.0101 (6) Å
b = 12.5154 (11) Å
c = 12.1506 (12) Å
β = 98.564 (2)°
V = 1204.51 (18) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.40 × 0.38 × 0.26 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID IP diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
11633 measured reflections
2747 independent reflections
1446 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.149
S = 1.08
2747 reflections
174 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: PROCESS-AUTO (Rigaku, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: PROCESS-AUTO; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Rigaku, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR92 (Altomare et al., 1993 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017479/sg2248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017479/sg2248Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2N⋯N5i | 0.91 | 2.30 | 3.185 (2) | 164 |
| C11—H11⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.300 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 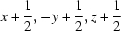 ; (ii)
; (ii) 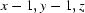 .
.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (No. M203027).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Hydrazone and its derivatives have attracted much attention because of their potential application in biology (Okabe et al., 1993; Hu et al., 2001). As part of an ongoing investigation into anti-cancer compounds (Chen et al., 2007), the title compound has recently been prepared in our laboratory and its crystal structure is presented here.
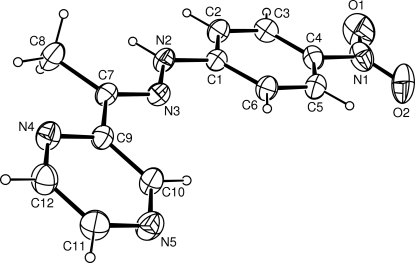
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The molecule adopts an E-configuration, with the benzene and pyrazine rings located on the opposite positions of the N3=C7 double bond, similar to that found in a related structure, (E)-2-Furyl methyl ketone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (Shan et al., 2008). The pyrazine plane is twisted with respect to the benzene ring by a smaller dihedral angle of 14.25 (10)°.
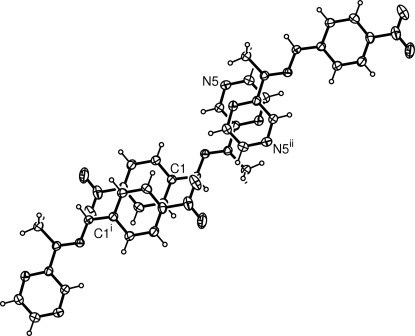
The partially overlapped arrangement is observed between parallel benzene rings and between parallel pyrazine rings (Fig. 2), face-to-face separations of 3.413 (14) [for benzene rings] and 3.430 (8) Å [for pyrazine rings] are significantly shorter than van der Waals thickness of the aromatic ring (3.70 Å), and indicate the existence of π-π stacking between the adjacent molecules. Intermolecular N—H···N and weak C—H···O hydrogen bondings are present in the crystal structure (Table 1).
Experimental
4-Nitrophenylhydrazine (0.31 g, 2 mmol) was dissolved in ethanol (10 ml), then H2SO4 solution (98%, 0.5 ml) was added slowly to the ethanol solution with stirring. The solution was heated at about 333 K for several minutes until the solution cleared. An ethanol solution (5 ml) of acetylpyrazine (0.24 g, 2 mmol) was dropped slowly into the above solution with continuous stirring, and the mixture solution was kept at about 333 K for 0.5 h. When the solution had cooled to room temperature, yellow microcrystals appeared. They were separated and washed with cold water three times to get the product 0.40 g. Single crystals of the title compound were obtained by recrystallization from an absolute ethanol solution.
Refinement
Methyl H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.96 Å and torsion angle was refined to fit the electron density, Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C). Imino H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined as riding in its as-found relative position, Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). Aromatic H atoms were placed in calculated positions with C—H = 0.93 and refined in riding mode with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with 30% probability displacement ellipsoids (arbitrary spheres for H atoms), dashed line indicates hydrogen bonding.
Fig. 2.
A diagram showing π-π stacking [symmetry codes: (i) 2 - x,1 - y,1 - z; (ii) 1 - x,-y,1 - z].
Crystal data
| C12H11N5O2 | F000 = 536 |
| Mr = 257.26 | Dx = 1.419 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 498 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71069 Å |
| a = 8.0101 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 4236 reflections |
| b = 12.5154 (11) Å | θ = 3.2–25.0º |
| c = 12.1506 (12) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 98.564 (2)º | T = 295 (2) K |
| V = 1204.51 (18) Å3 | Prism, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.38 × 0.26 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID IP diffractometer | 2747 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1446 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| Detector resolution: 10.00 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.4º |
| T = 295(2) K | θmin = 3.0º |
| ω scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −16→16 |
| 11633 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0615P)2 + 0.2787P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.149 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.09 | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 2747 reflections | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.024 (3) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.9003 (3) | 0.68785 (16) | 0.3418 (2) | 0.0684 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.6332 (2) | 0.36085 (12) | 0.57394 (13) | 0.0448 (4) | |
| H2N | 0.6470 | 0.3652 | 0.6496 | 0.054* | |
| N3 | 0.5365 (2) | 0.28334 (12) | 0.51838 (13) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| N4 | 0.3197 (2) | 0.04376 (14) | 0.55830 (14) | 0.0518 (5) | |
| N5 | 0.2175 (2) | 0.07812 (15) | 0.33069 (14) | 0.0571 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.9806 (3) | 0.75846 (16) | 0.3955 (2) | 0.1041 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.8729 (3) | 0.68826 (16) | 0.2397 (2) | 0.1012 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.6976 (2) | 0.43994 (15) | 0.51344 (16) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.7855 (3) | 0.52394 (16) | 0.57162 (17) | 0.0490 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.7989 | 0.5251 | 0.6490 | 0.059* | |
| C3 | 0.8519 (3) | 0.60439 (16) | 0.51558 (18) | 0.0521 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.9109 | 0.6601 | 0.5544 | 0.062* | |
| C4 | 0.8306 (3) | 0.60198 (15) | 0.40117 (18) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.7461 (3) | 0.51920 (17) | 0.34168 (17) | 0.0513 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.7339 | 0.5187 | 0.2644 | 0.062* | |
| C6 | 0.6803 (3) | 0.43744 (17) | 0.39758 (16) | 0.0482 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.6246 | 0.3809 | 0.3583 | 0.058* | |
| C7 | 0.4778 (2) | 0.20837 (14) | 0.57459 (15) | 0.0408 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.5120 (3) | 0.19727 (18) | 0.69835 (17) | 0.0593 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.6317 | 0.1939 | 0.7222 | 0.089* | |
| H8B | 0.4602 | 0.1331 | 0.7202 | 0.089* | |
| H8C | 0.4663 | 0.2578 | 0.7322 | 0.089* | |
| C9 | 0.3700 (2) | 0.13023 (15) | 0.50718 (15) | 0.0408 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.3179 (3) | 0.14575 (16) | 0.39353 (16) | 0.0496 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.3553 | 0.2063 | 0.3602 | 0.059* | |
| C11 | 0.1699 (3) | −0.00860 (18) | 0.38283 (19) | 0.0569 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.1002 | −0.0587 | 0.3424 | 0.068* | |
| C12 | 0.2214 (3) | −0.02519 (17) | 0.49398 (19) | 0.0554 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.1865 | −0.0871 | 0.5263 | 0.067* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0742 (15) | 0.0486 (11) | 0.0895 (17) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0352 (12) | 0.0135 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0566 (11) | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0341 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0005 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0478 (10) | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0397 (9) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | −0.0009 (7) |
| N4 | 0.0623 (12) | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0465 (10) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0044 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0678 (13) | 0.0578 (11) | 0.0435 (10) | −0.0075 (9) | 0.0012 (9) | −0.0042 (9) |
| O1 | 0.1140 (18) | 0.0645 (12) | 0.137 (2) | −0.0350 (12) | 0.0270 (15) | 0.0119 (13) |
| O2 | 0.146 (2) | 0.0841 (14) | 0.0860 (15) | −0.0086 (13) | 0.0569 (14) | 0.0232 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0454 (11) | 0.0388 (10) | 0.0393 (10) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0064 (8) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0588 (13) | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0419 (11) | −0.0015 (10) | 0.0050 (9) | −0.0038 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0542 (13) | 0.0412 (11) | 0.0609 (14) | −0.0029 (9) | 0.0087 (10) | −0.0062 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0517 (12) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0577 (13) | 0.0055 (9) | 0.0198 (10) | 0.0075 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0610 (14) | 0.0527 (12) | 0.0414 (11) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0117 (10) | 0.0022 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0569 (13) | 0.0471 (11) | 0.0411 (11) | −0.0013 (10) | 0.0088 (9) | −0.0023 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0381 (10) | 0.0370 (10) | 0.0050 (8) | 0.0046 (8) | 0.0027 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0780 (17) | 0.0573 (13) | 0.0396 (12) | −0.0086 (12) | −0.0009 (11) | 0.0065 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0459 (11) | 0.0391 (10) | 0.0379 (10) | 0.0036 (8) | 0.0079 (8) | 0.0035 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0605 (14) | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0394 (11) | −0.0045 (10) | 0.0060 (10) | 0.0024 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0619 (15) | 0.0520 (13) | 0.0561 (13) | −0.0091 (11) | 0.0064 (11) | −0.0063 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0634 (14) | 0.0473 (12) | 0.0568 (13) | −0.0107 (10) | 0.0127 (11) | 0.0019 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—O1 | 1.223 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N1—O2 | 1.226 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.381 (3) |
| N1—C4 | 1.452 (3) | C5—C6 | 1.376 (3) |
| N2—N3 | 1.357 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C1 | 1.378 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2N | 0.9106 | C7—C9 | 1.470 (3) |
| N3—C7 | 1.290 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.494 (3) |
| N4—C12 | 1.339 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| N4—C9 | 1.339 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| N5—C10 | 1.328 (3) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| N5—C11 | 1.340 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.395 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.394 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.368 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.367 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (3) | ||
| O1—N1—O2 | 122.5 (2) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.6 (2) |
| O1—N1—C4 | 118.7 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.2 |
| O2—N1—C4 | 118.8 (2) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.2 |
| N3—N2—C1 | 118.65 (15) | N3—C7—C9 | 114.78 (16) |
| N3—N2—H2N | 121.3 | N3—C7—C8 | 125.00 (18) |
| C1—N2—H2N | 119.8 | C9—C7—C8 | 120.23 (17) |
| C7—N3—N2 | 118.88 (16) | C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| C12—N4—C9 | 116.19 (18) | C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C10—N5—C11 | 115.78 (18) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—C6 | 122.25 (18) | C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 118.10 (17) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.64 (19) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.42 (19) | N4—C9—C10 | 120.35 (18) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | N4—C9—C7 | 118.11 (16) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C10—C9—C7 | 121.53 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.2 (2) | N5—C10—C9 | 123.13 (19) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 | N5—C10—H10 | 118.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C9—C10—H10 | 118.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.53 (19) | N5—C11—C12 | 121.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—N1 | 119.1 (2) | N5—C11—H11 | 119.2 |
| C5—C4—N1 | 119.3 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.2 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.56 (19) | N4—C12—C11 | 122.9 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | N4—C12—H12 | 118.6 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | C11—C12—H12 | 118.6 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2N···N5i | 0.91 | 2.30 | 3.185 (2) | 164 |
| C11—H11···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.300 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SG2248).
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst.26, 343–350.
- Chen, Z.-Y., Wu, G.-Q., Jiang, F.-X., Tian, Y.-L. & Shan, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1919–o1920.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Hu, W., Sun, N. & Yang, Z. (2001). Chem. J. Chin. Univ.22, 2014–2017.
- Okabe, N., Nakamura, T. & Fukuda, H. (1993). Acta Cryst. C49, 1678–1680.
- Rigaku. (1998). PROCESS-AUTO Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku. (2002). CrystalStructure Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Shan, S., Tian, Y.-L., Wang, S.-H., Wang, W.-L. & Xu, Y.-L. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017479/sg2248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017479/sg2248Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report