Abstract
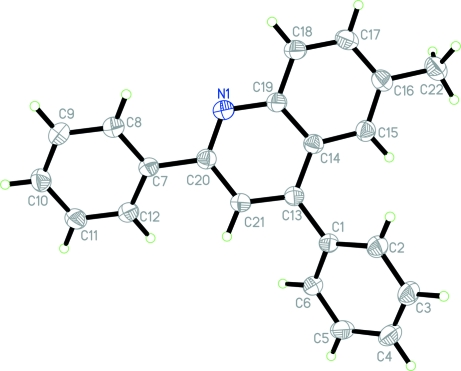
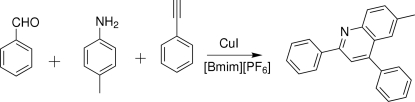
The molecules of the title compound, C22H17N, are linked by weak interactions, among which the most prominent are C—H⋯π interactions. The dihedral angles between the phenyl rings and the quinoline ring system are 43.3 (3) and 21.4 (3)°. The title product resulted from a three-component reaction of benzaldehyde, 1-ethynylbenzene and p-toluidine via C—H activation of 1-ethynylbenzene catalyzed by CuI in the ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶); Park & Alper (2005 ▶); Shi et al. (2004 ▶); Skraup (1880 ▶). 
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H17N
M r = 295.37
Orthorhombic,
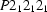
a = 7.766 (1) Å
b = 9.851 (1) Å
c = 20.756 (2) Å
V = 1588.0 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.07 mm−1
T = 294 (2) K
0.41 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.971, T max = 0.979
8562 measured reflections
1720 independent reflections
1302 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.051
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.120
S = 1.04
1720 reflections
210 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SMART; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015651/fb2095sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015651/fb2095Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C14–C19 rings, respectively .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6—H6⋯Cg3i | 0.93 | 2.75 | 3.551 (3) | 145 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg2i | 0.93 | 2.92 | 3.726 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry code: (i) 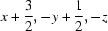 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the State Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, for funding this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Quinolines and their derivatives are very important in medical chemistry because of their extensive occurrence in natural products. Also, quinolines possess a wide spectrum of biological activities. The classic method of quinoline synthesis is Skraup's procedure (Skraup, 1880). The synthesis of the title compound follows a study of transition-metal catalyzed multi-component reactions which is a powerful synthetic tool to access complex structures from simple precursors by a one-pot procedure (Shi et al., 2004; Park & Alper, 2005).
In the title compound, all the bond lengths are normal (Allen et al., 1987). The angle between both phenyl rings in the structure is 34.6 (3) °. The dihedral angle between the phenyl ring C1—C6 and the ring C14—C21/N1 is 43.3 (3) °. The dihedral angle between the C7—C12 phenyl ring and the C14—C21/N1 ring is 21.4 (3) °.
Experimental
The p-toluidine (1.5 mmol) and benzaldehyde(1.5 mmol) were taken along with a catalytic quantity of CuI (0.45 mmol) in ionic liquid 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate (5 ml) (Scheme 2). The resulting mixture was stirred at 298 K for 15 minutes. At this stage 1-ethynylbenzene (1 mmol) was quickly poured into the reaction mixture and the temperature was raised to 404 K, kept at this temperature for 6 hours, then cooled to room temperature. The product was extracted from the reaction mixture by addition of diethyl ether. (It was possible to recover ionic liquid layer and to use it again without any pretreatment.) The combined organic layer was concentrated and the desired product was isolated by silica gel column chromatography(petrol/EtOAc, 20:1). Colourless sheet crystals were recrystallized from the deuterated chloroform CDCl3 by evaporation in the course of several days. Their average size was 2.5-3 mm.
Refinement
Though all the H atoms could be located in the difference electron-density maps, they were placed into the idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms. The constrained distances: C—H = 0.93 or 0.96 Å for the aryl or the methyl hydrogens, respectively. The hydrogens' isotropic displacement parameters : Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C) for aryl or methyl hydrogens, respectively. In the absence of significant anomalous scattering effects 1413 Friedel pairs have been merged.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure with the atom-numbering scheme. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The formation of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C22H17N | F000 = 624 |
| Mr = 295.37 | Dx = 1.235 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P2ac2ab | Cell parameters from 803 reflections |
| a = 7.766 (1) Å | θ = 2.3–24.5º |
| b = 9.851 (1) Å | µ = 0.07 mm−1 |
| c = 20.756 (2) Å | T = 294 (2) K |
| V = 1588.0 (3) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.41 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1720 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1302 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.052 |
| T = 294(2) K | θmax = 25.5º |
| ω scans | θmin = 2.0º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −8→9 |
| Tmin = 0.971, Tmax = 0.979 | k = −11→11 |
| 8562 measured reflections | l = −25→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.120 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0684P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1720 reflections | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 210 parameters | Δρmin = −0.14 e Å−3 |
| 67 constraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.009 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.8369 (3) | 0.4866 (3) | 0.14992 (11) | 0.0493 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.6966 (4) | 0.5970 (3) | 0.34443 (12) | 0.0453 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.7800 (4) | 0.5422 (3) | 0.39763 (13) | 0.0538 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.8605 | 0.4733 | 0.3920 | 0.065* | |
| C3 | 0.7440 (5) | 0.5893 (4) | 0.45891 (14) | 0.0640 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.7997 | 0.5513 | 0.4942 | 0.077* | |
| C4 | 0.6258 (5) | 0.6926 (4) | 0.46804 (14) | 0.0678 (10) | |
| H4 | 0.6016 | 0.7238 | 0.5093 | 0.081* | |
| C5 | 0.5439 (5) | 0.7489 (3) | 0.41549 (13) | 0.0621 (9) | |
| H5 | 0.4649 | 0.8188 | 0.4214 | 0.074* | |
| C6 | 0.5788 (4) | 0.7021 (3) | 0.35440 (13) | 0.0493 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.5232 | 0.7409 | 0.3193 | 0.059* | |
| C7 | 0.8147 (4) | 0.7190 (3) | 0.11564 (12) | 0.0448 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.9118 (4) | 0.6959 (3) | 0.06060 (13) | 0.0562 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.9718 | 0.6147 | 0.0562 | 0.067* | |
| C9 | 0.9206 (5) | 0.7918 (3) | 0.01228 (14) | 0.0647 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.9870 | 0.7750 | −0.0242 | 0.078* | |
| C10 | 0.8318 (5) | 0.9124 (3) | 0.01757 (15) | 0.0638 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.8375 | 0.9767 | −0.0152 | 0.077* | |
| C11 | 0.7347 (4) | 0.9371 (3) | 0.07175 (14) | 0.0592 (9) | |
| H11 | 0.6745 | 1.0182 | 0.0758 | 0.071* | |
| C12 | 0.7268 (4) | 0.8410 (3) | 0.12009 (13) | 0.0524 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.6608 | 0.8586 | 0.1565 | 0.063* | |
| C13 | 0.7370 (3) | 0.5530 (3) | 0.27752 (13) | 0.0434 (7) | |
| C14 | 0.7596 (3) | 0.4139 (3) | 0.25973 (13) | 0.0448 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.7277 (4) | 0.3018 (3) | 0.30025 (13) | 0.0492 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.6855 | 0.3175 | 0.3415 | 0.059* | |
| C16 | 0.7564 (4) | 0.1704 (3) | 0.28110 (15) | 0.0522 (8) | |
| C17 | 0.8282 (4) | 0.1481 (3) | 0.22001 (14) | 0.0559 (8) | |
| H17 | 0.8570 | 0.0602 | 0.2077 | 0.067* | |
| C18 | 0.8566 (4) | 0.2523 (3) | 0.17834 (14) | 0.0545 (8) | |
| H18 | 0.9014 | 0.2342 | 0.1377 | 0.065* | |
| C19 | 0.8189 (4) | 0.3880 (3) | 0.19587 (13) | 0.0454 (7) | |
| C20 | 0.8015 (4) | 0.6132 (3) | 0.16636 (13) | 0.0447 (7) | |
| C21 | 0.7571 (4) | 0.6497 (3) | 0.23033 (12) | 0.0472 (7) | |
| H21 | 0.7413 | 0.7407 | 0.2406 | 0.057* | |
| C22 | 0.7120 (5) | 0.0522 (3) | 0.32401 (16) | 0.0677 (10) | |
| H22A | 0.6644 | 0.0853 | 0.3637 | 0.102* | |
| H22B | 0.8141 | 0.0007 | 0.3329 | 0.102* | |
| H22C | 0.6291 | −0.0046 | 0.3028 | 0.102* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0537 (14) | 0.0477 (15) | 0.0465 (14) | 0.0033 (13) | 0.0026 (11) | −0.0044 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0542 (16) | 0.0405 (15) | 0.0412 (15) | −0.0047 (14) | −0.0011 (13) | −0.0024 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0665 (19) | 0.0507 (18) | 0.0444 (16) | −0.0062 (16) | −0.0071 (14) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C3 | 0.086 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0436 (16) | −0.012 (2) | −0.0136 (16) | −0.0016 (16) |
| C4 | 0.094 (3) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0423 (17) | −0.014 (2) | 0.0028 (17) | −0.0100 (16) |
| C5 | 0.076 (2) | 0.0515 (19) | 0.0586 (18) | −0.0029 (18) | 0.0090 (17) | −0.0136 (17) |
| C6 | 0.0576 (17) | 0.0474 (17) | 0.0429 (15) | −0.0015 (16) | 0.0037 (13) | −0.0029 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0497 (16) | 0.0444 (17) | 0.0404 (14) | 0.0003 (14) | −0.0010 (13) | −0.0034 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0662 (19) | 0.0513 (19) | 0.0512 (17) | 0.0081 (17) | 0.0083 (15) | −0.0005 (15) |
| C9 | 0.084 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0465 (17) | 0.002 (2) | 0.0151 (16) | 0.0002 (17) |
| C10 | 0.092 (2) | 0.052 (2) | 0.0480 (18) | −0.004 (2) | −0.0054 (18) | 0.0059 (16) |
| C11 | 0.075 (2) | 0.0471 (18) | 0.0557 (18) | 0.0086 (18) | −0.0039 (16) | 0.0001 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0601 (17) | 0.0519 (18) | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0038 (16) | 0.0013 (14) | −0.0036 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0448 (16) | 0.0426 (16) | 0.0428 (14) | −0.0009 (14) | −0.0007 (13) | −0.0007 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0447 (16) | 0.0441 (16) | 0.0455 (15) | 0.0025 (14) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0017 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0521 (17) | 0.0498 (18) | 0.0458 (15) | −0.0017 (15) | −0.0033 (13) | 0.0019 (13) |
| C16 | 0.0533 (18) | 0.0454 (18) | 0.0579 (17) | 0.0014 (15) | −0.0086 (15) | 0.0009 (15) |
| C17 | 0.0617 (18) | 0.0445 (18) | 0.0616 (19) | 0.0077 (16) | −0.0076 (16) | −0.0066 (16) |
| C18 | 0.0588 (18) | 0.0524 (19) | 0.0522 (18) | 0.0091 (17) | 0.0026 (14) | −0.0061 (17) |
| C19 | 0.0471 (15) | 0.0438 (17) | 0.0453 (15) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0005 (13) | −0.0021 (13) |
| C20 | 0.0452 (15) | 0.0453 (17) | 0.0437 (15) | −0.0013 (14) | −0.0009 (12) | −0.0006 (13) |
| C21 | 0.0549 (17) | 0.0417 (16) | 0.0451 (15) | 0.0032 (14) | 0.0004 (14) | −0.0040 (14) |
| C22 | 0.079 (2) | 0.0488 (19) | 0.076 (2) | −0.0005 (18) | −0.0066 (19) | 0.0077 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C20 | 1.322 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C19 | 1.369 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.381 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.390 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C13 | 1.489 (4) | C13—C21 | 1.375 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.430 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.410 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.384 (5) | C14—C19 | 1.426 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.373 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.403 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (3) | C16—C22 | 1.506 (4) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.361 (4) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C12 | 1.385 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.416 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.388 (4) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C20 | 1.485 (4) | C20—C21 | 1.418 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.380 (4) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C22—H22A | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.378 (5) | C22—H22B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C22—H22C | 0.9600 |
| C10—C11 | 1.376 (4) | ||
| C20—N1—C19 | 118.0 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.4 (3) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| C2—C1—C13 | 122.0 (3) | C21—C13—C14 | 117.8 (2) |
| C6—C1—C13 | 119.5 (2) | C21—C13—C1 | 119.1 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.4 (3) | C14—C13—C1 | 123.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C15—C14—C19 | 118.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.8 | C15—C14—C13 | 125.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.5 (3) | C19—C14—C13 | 116.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C16—C15—C14 | 122.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.8 | C16—C15—H15 | 118.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.6 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 118.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C15—C16—C17 | 118.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C15—C16—C22 | 121.4 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.2 (3) | C17—C16—C22 | 120.3 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C18—C17—C16 | 121.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.9 (3) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.3 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C17—C18—C19 | 121.0 (3) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 117.7 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C12—C7—C20 | 121.8 (2) | N1—C19—C18 | 118.0 (2) |
| C8—C7—C20 | 120.4 (3) | N1—C19—C14 | 123.6 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.9 (3) | C18—C19—C14 | 118.3 (3) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.6 | N1—C20—C21 | 122.1 (3) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 | N1—C20—C7 | 117.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.5 (3) | C21—C20—C7 | 120.2 (3) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C13—C21—C20 | 121.3 (3) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C13—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.4 (3) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.4 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.3 | C16—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.3 | C16—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.8 (3) | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 | C16—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C7 | 121.6 (3) | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.2 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −178.1 (3) |
| C13—C1—C2—C3 | 177.5 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 3.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (5) | C14—C15—C16—C22 | −176.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.2 (5) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −5.1 (5) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.4 (5) | C22—C16—C17—C18 | 174.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.2 (5) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.8 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.0 (4) | C20—N1—C19—C18 | 179.9 (3) |
| C13—C1—C6—C5 | −177.3 (3) | C20—N1—C19—C14 | 1.8 (4) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.3 (4) | C17—C18—C19—N1 | −174.7 (3) |
| C20—C7—C8—C9 | 178.0 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | 3.5 (5) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.5 (5) | C15—C14—C19—N1 | 172.8 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.4 (5) | C13—C14—C19—N1 | −7.1 (4) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (5) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | −5.3 (4) |
| C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.0 (5) | C13—C14—C19—C18 | 174.8 (3) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.1 (4) | C19—N1—C20—C21 | 4.1 (4) |
| C20—C7—C12—C11 | −177.7 (3) | C19—N1—C20—C7 | −177.7 (2) |
| C2—C1—C13—C21 | −135.1 (3) | C12—C7—C20—N1 | 157.1 (3) |
| C6—C1—C13—C21 | 41.1 (4) | C8—C7—C20—N1 | −20.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—C13—C14 | 43.6 (4) | C12—C7—C20—C21 | −24.7 (4) |
| C6—C1—C13—C14 | −140.2 (3) | C8—C7—C20—C21 | 157.8 (3) |
| C21—C13—C14—C15 | −173.5 (3) | C14—C13—C21—C20 | −1.0 (4) |
| C1—C13—C14—C15 | 7.8 (4) | C1—C13—C21—C20 | 177.8 (2) |
| C21—C13—C14—C19 | 6.3 (4) | N1—C20—C21—C13 | −4.6 (4) |
| C1—C13—C14—C19 | −172.4 (3) | C7—C20—C21—C13 | 177.2 (3) |
| C19—C14—C15—C16 | 2.0 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···Cg3i | 0.93 | 2.75 | 3.551 (3) | 145 |
| C11—H11···Cg2i | 0.93 | 2.92 | 3.726 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+3/2, −y+1/2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FB2095).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Park, S. B. & Alper, H. (2005). Chem. Commun. pp. 1315–1317. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, L., Tu, Y.-Q., Wang, M., Zhang, F.-M. & Fan, C.-A. (2004). Org. Lett.6, 1001–1003. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Skraup, H. (1880). Chem. Ber.13, 2086–2087.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015651/fb2095sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808015651/fb2095Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report