Abstract
The crystal structure of the title compound, C11H12O2, consists of dimers which are formed due to intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonding. The dimers are linked to each other by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, where C—H belongs to the benzene ring and the O atom is of a carbonyl group of an adjoining molecule. There exist two intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds which form five-membered rings. There exist two π–π interactions between the benzene rings. The perpendicular distance in these interactions are 3.006 and 3.396 Å. There also exist C—H⋯π and C—O⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶); Liu et al. (1999 ▶); Muhammad et al. (2007 ▶); Natella et al. (1999 ▶); Niaz et al. (2008 ▶); Parez-Alvarez et al. (2001 ▶); Wiesner et al. (2001 ▶).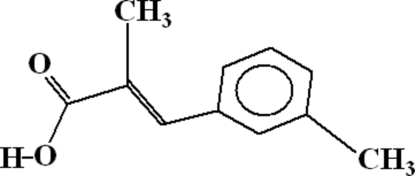
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H12O2
M r = 176.21
Monoclinic,

a = 7.4430 (9) Å
b = 13.4094 (16) Å
c = 10.2746 (12) Å
β = 110.745 (4)°
V = 959.0 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.26 × 0.18 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.980, T max = 0.986
11342 measured reflections
2820 independent reflections
1075 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.056
wR(F 2) = 0.185
S = 1.02
2820 reflections
120 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX publication routines (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808019545/at2580sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808019545/at2580Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C4–C9 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O2i | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.611 (3) | 160 |
| C3—H3⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.27 | 2.703 (3) | 108 |
| C8—H8⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.394 (3) | 145 |
| C10—H10A⋯O2 | 0.96 | 2.31 | 2.783 (3) | 109 |
| C10—H10C⋯Cgiii | 0.96 | 2.75 | 3.610 (3) | 149 |
| C1—O2⋯Cgiv | 1.25 (1) | 3.57 (1) | 3.895 (3) | 95 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan, for funding the purchase of the diffractometer at GCU, Lahore, and for financial support to NM for PhD studies under the Indigenous Scholarship Scheme.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Cinnamic acids and their derivatives have been studied for their pharmacological properties, including hepatoprotactive (Parez-Alvarez et al., 2001), antimalarial (Wiesner et al., 2001), antioxident (Natella et al., 1999) and antihyperglycemic activities (Liu et al., 1999). In continuation of our efforts to synthesize various derivatives of cinamic acids (Niaz et al., 2008) and their complexes, we herein report the structure of the title compound (I).
The crystal structure of 3-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylacrylic acid (Muhammad et al., 2007) has been reported. The title compound (I) have a similar environment about the carboxylate group but the attachement of methyl instead of Br-atom is at meta-position instead of para-position.
In the crystal structure of the title compound, the C—C bonds are in the range 1.462 (3)–1.500 (3) Å, and C═C have a value of 1.339 (3) Å. The resonant C—O bonds have values of 1.250 (3) and 1.271 (3) Å. In the asymmetric unit, there are two interamolecular H-bonds of C—H···O type (Table 2, Fig 1). Due to these H-bonds, two five membered rings (O1/C1/C2/C3/H3···O1) and (O2/C1/C2/C10/H10A···O2) are formed. The intermolecular (O1—H1···O2i [symmetry code: i = -x, -y, -z + 1]) hydrogen bond forces the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers, forming a R22(8) motif (Bernstein et al. 1995). These dimers are linked to each other by the second intermolecular H-bonding, C8—H8···O2ii [symmetry code: ii = -x + 1, y + 1/2, -z + 1/2] as shown in Fig 2. There exist π–π interactions between the centroids (Cg) of benzene (C4—C9) rings of adjacent molecules. The Cg···Cgiii [symmetry code: iii = x, -y + 1/2, z - 1/2] and Cg···Cgiv [symmetry code: iv = x, -y + 1/2, z + 1/2] have a perpendicular distance of 3.006 and 3.396 Å, respectively. There exist also C10—H10C···Cgiv interaction, with a distance of 3.610 (3) Å between C10 and Cgiv. Similarly another π-interaction is present between C1–O2 and Cgv [symmetry code: v = x - 1, y, z] with a distance of 3.895 (3) Å between C1 and Cgv. The detail of these interactions is also included in Table 1.
Experimental
Compound (I) was prepared according to our previously reported method (Muhammad et al., 2007). A mixture of 3-methylbenzaldehyde (10 mmol, 1.18 ml), methylmalonic acid (2.36 g, 20 mmol) and piperidine (20 mmol, 1.98 ml) in pyridine (12.5 ml) solution was heated on a steam-bath for 24 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and added to a mixture of 25 ml of concentrated HCl and 50 g of ice. The precipitate formed in the acidified mixture was filtered off and washed with ice-cold water. The product was recrystallized from ethanol [yield; 90%, m.p. 321 K].
Refinement
All H-atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96 Å for aromatic and methyl H-atoms, respectively, and O—H = 0.82 Å for hydroxyl O-atom, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms. The thermal parameters of methyl and hydroxyl H-atoms was taken 1.5 times while for all other H-atoms it was taken 1.2 times of the parent atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP drawing of the title compound, with the atom numbering scheme. The thermal ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H-atoms are shown by small circles of arbitrary radii. The intramolecular H-bonds are shown by doted lines.
Fig. 2.
The packing figure (PLATON: Spek, 2003) which shows the dimeric nature of the compound and the interlinkages of the dimers.
Crystal data
| C11H12O2 | F000 = 376 |
| Mr = 176.21 | Dx = 1.220 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2820 reflections |
| a = 7.4430 (9) Å | θ = 2.6–30.2º |
| b = 13.4094 (16) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 10.2746 (12) Å | T = 296 (2) K |
| β = 110.745 (4)º | Prismatic, colourless |
| V = 959.0 (2) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.18 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker KAPPA APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2820 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1075 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.047 |
| Detector resolution: 7.2 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 30.2º |
| T = 296(2) K | θmin = 2.6º |
| ω scans | h = −10→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −18→13 |
| Tmin = 0.980, Tmax = 0.986 | l = −10→14 |
| 11342 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0657P)2 + 0.191P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.185 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.02 | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 2820 reflections | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 120 parameters | Extinction correction: empirical, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.006 (2) |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.1630 (3) | −0.00578 (12) | 0.4174 (2) | 0.0795 (8) | |
| O2 | 0.0675 (2) | 0.12222 (11) | 0.51106 (18) | 0.0699 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.1639 (3) | 0.08682 (17) | 0.4441 (2) | 0.0515 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.2797 (3) | 0.15393 (16) | 0.3911 (2) | 0.0484 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.4010 (3) | 0.11136 (17) | 0.3377 (2) | 0.0533 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.5340 (3) | 0.15354 (16) | 0.2764 (2) | 0.0497 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.6214 (3) | 0.08770 (17) | 0.2126 (2) | 0.0534 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.7448 (3) | 0.11877 (18) | 0.1461 (2) | 0.0553 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.7829 (4) | 0.21882 (19) | 0.1470 (3) | 0.0637 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.7031 (4) | 0.2856 (2) | 0.2118 (3) | 0.0699 (10) | |
| C9 | 0.5794 (4) | 0.25412 (17) | 0.2757 (3) | 0.0646 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.2492 (3) | 0.26372 (17) | 0.4024 (3) | 0.0658 (10) | |
| C11 | 0.8342 (4) | 0.0464 (2) | 0.0760 (3) | 0.0788 (11) | |
| H1 | 0.10360 | −0.03595 | 0.45872 | 0.0954* | |
| H3 | 0.40046 | 0.04203 | 0.33992 | 0.0639* | |
| H5 | 0.59610 | 0.01991 | 0.21458 | 0.0640* | |
| H7 | 0.86445 | 0.24181 | 0.10285 | 0.0764* | |
| H8 | 0.73305 | 0.35299 | 0.21244 | 0.0838* | |
| H9 | 0.52556 | 0.30031 | 0.31872 | 0.0774* | |
| H10A | 0.15463 | 0.27413 | 0.44482 | 0.0988* | |
| H10B | 0.20537 | 0.29296 | 0.31123 | 0.0988* | |
| H10C | 0.36802 | 0.29433 | 0.45849 | 0.0988* | |
| H11A | 0.79146 | −0.01992 | 0.08522 | 0.1182* | |
| H11B | 0.97157 | 0.04960 | 0.11877 | 0.1182* | |
| H11C | 0.79701 | 0.06301 | −0.02083 | 0.1182* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.1052 (15) | 0.0487 (10) | 0.1240 (17) | −0.0062 (9) | 0.0893 (13) | −0.0004 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0786 (12) | 0.0602 (11) | 0.0958 (13) | −0.0042 (8) | 0.0617 (11) | −0.0100 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0479 (13) | 0.0629 (15) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0330 (12) | −0.0028 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0460 (12) | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0570 (14) | −0.0032 (10) | 0.0239 (11) | 0.0020 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0583 (14) | 0.0481 (12) | 0.0634 (15) | −0.0046 (11) | 0.0339 (12) | 0.0003 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0510 (13) | 0.0508 (12) | 0.0549 (14) | −0.0052 (10) | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0009 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0525 (14) | 0.0513 (13) | 0.0611 (15) | −0.0035 (10) | 0.0261 (12) | 0.0021 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0490 (13) | 0.0649 (16) | 0.0589 (15) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0278 (12) | 0.0047 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0631 (15) | 0.0742 (17) | 0.0646 (16) | −0.0139 (13) | 0.0358 (14) | 0.0053 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0812 (19) | 0.0581 (15) | 0.0849 (19) | −0.0194 (13) | 0.0475 (17) | −0.0021 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0767 (17) | 0.0525 (14) | 0.0804 (18) | −0.0098 (12) | 0.0475 (15) | −0.0045 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0574 (15) | 0.0538 (15) | 0.097 (2) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0408 (15) | −0.0017 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0757 (18) | 0.088 (2) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0014 (15) | 0.0521 (17) | −0.0051 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.271 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.373 (4) |
| O2—C1 | 1.250 (3) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O1—H1 | 0.8200 | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.477 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C10 | 1.500 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.339 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.462 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.391 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.391 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.389 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.371 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C11 | 1.498 (4) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.370 (4) | ||
| C1—O1—H1 | 109.00 | C4—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| O1—C1—O2 | 122.0 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 118.3 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.00 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 119.7 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.00 |
| C1—C2—C10 | 116.4 (2) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C3—C2—C10 | 126.3 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 117.2 (2) | C4—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 132.0 (2) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 125.5 (2) | C2—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 117.3 (2) | C2—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 117.3 (2) | C2—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.9 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| C5—C6—C11 | 121.8 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 120.8 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.5 (2) | C6—C11—H11A | 109.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.2 (3) | C6—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.7 (2) | C6—C11—H11C | 110.00 |
| C4—C9—C8 | 120.4 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 114.00 | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 114.00 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.00 |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −10.6 (3) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | −2.0 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C10 | 169.3 (2) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | −178.4 (2) |
| O2—C1—C2—C3 | 170.7 (2) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | 1.2 (4) |
| O2—C1—C2—C10 | −9.4 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.6 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C11 | −178.9 (2) |
| C10—C2—C3—C4 | −0.3 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −171.3 (2) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | −179.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | 8.3 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −1.2 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 177.54 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.4 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2i | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.611 (3) | 160 |
| C3—H3···O1 | 0.93 | 2.27 | 2.703 (3) | 108 |
| C8—H8···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.394 (3) | 145 |
| C10—H10A···O2 | 0.96 | 2.31 | 2.783 (3) | 109 |
| C10—H10C···Cgiii | 0.9600 | 2.75 | 3.610 (3) | 149.00 |
| C1—O2···Cgiv | 1.250 (3) | 3.574 (2) | 3.895 (3) | 95.38 (13) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iv) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: AT2580).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Liu, I. M., Chi, T. C., Hsu, F. L., Chen, C. F. & Cheng, J. T. (1999). Planta Med.65, 712–714. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N., Zia-ur-Rehman,, Ali, S. & Meetsma, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2174–o2175.
- Natella, F., Nardini, M., Felico, D. M. & Scaccini, C. (1999). J. Agric. Food Chem.47, 1453–1459. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Niaz, M., Tahir, M. N., Zia-ur-Rehman,, Ali, S. & Khan, I. U. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Parez-Alvarez, V., Bobaddilla, R. A. & Muriel, P. (2001). J. Appl. Toxicol.21, 527–531. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Wiesner, J., Mitsch, A., Wissner, P., Jomaa, H. & Schlitzer, M. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.11, 423–424. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808019545/at2580sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808019545/at2580Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




