Abstract
The title compound, C17H16N2O3S, crystallizes in the thioamide form with an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond across the thiourea system. Molecules are connected in chains parallel to [10 ] by hydrogen bonds from the second thiourea N—H group to the benzoate C=O function.
] by hydrogen bonds from the second thiourea N—H group to the benzoate C=O function.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Huebner et al. (1953 ▶); Xu et al. (2004 ▶); Xue et al. (2003 ▶); Zeng et al. (2003 ▶); Zheng et al. (2004 ▶); Douglas & Dains (1934 ▶); Glasser & Doughty (1964 ▶); Morales et al. (2000 ▶); D’hooghe et al. (2005 ▶); Dušek (1985 ▶).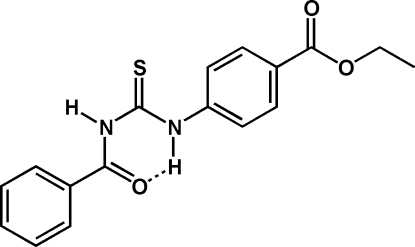
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H16N2O3S
M r = 328.38
Monoclinic,
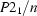
a = 9.6018 (3) Å
b = 8.3882 (3) Å
c = 19.3199 (6) Å
β = 91.393 (4)°
V = 1555.60 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.23 mm−1
T = 100 (2) K
0.38 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur S diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.943, T max = 1.000 (expected range = 0.916–0.971)
31428 measured reflections
5103 independent reflections
3676 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 0.94
5103 reflections
217 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED; data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP (Siemens, 1994 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017856/im2071sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017856/im2071Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H02⋯O1 | 0.85 (2) | 1.89 (2) | 2.618 (1) | 143 (1) |
| N1—H01⋯O2i | 0.85 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 3.099 (1) | 162 (1) |
| C3—H3⋯Sii | 0.95 | 3.04 | 3.763 (1) | 134 |
| C17—H17C⋯Siii | 0.98 | 2.88 | 3.677 (1) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 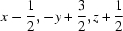 ; (ii)
; (ii) 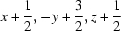 ; (iii)
; (iii) 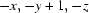 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad, Pakistan, and Institut für Anorganische und Analytische Chemie, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany, for the research facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
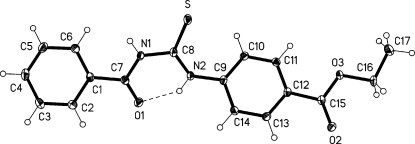
Epoxy resins have the combination of good thermal and dimensional stability, excellent chemical and corrosion resistance, high tensile strength and modulus, and ease of handling and processability, ensuring their wide application in the aerospace and electronic industries in the form of structural adhesives, advanced composite matrices, and packaging materials (Dušek, 1985). The properties of cured epoxy polymers largely depend on the nature of the chemical structure of the starting resins and curing agents. The title compound (I) is a precursor in an attempt to synthesize imidazole derivatives and transition metal complexes as epoxy resin curing agents and accelerators. Substituted thioureas are an important class of compounds, precursors or intermediates towards the synthesis of a variety of heterocyclic systems such as imidazole-2-thiones (Zeng et al., 2003), 2-imino-1, 3-thiazolines (D'hooghe et al., 2005), pyrimidine-2-thiones and (benzothiazolyl)-4-quinazolinones. Thioureas are also known to exhibit a wide range of biological activities including antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antitubercular, antithyroidal, herbicidal and insecticidal activities (Huebner et al., 1953) and as agrochemicals (Xu.Y et al., 2004). One example are 1-benzoyl-3-(4,5-disubstituted-pyrimidine-2-yl) thioureas, which have excellent herbicidal activity (W.Zheng et al., 2004). Thioureas are also well known chelating agents for transition metals (Xue et al.,2003). N,N-Dialkyl-N'-benzoyl thioureas act as selective complexing agents for the enrichment of platinum metals even from strongly interfacing matrixes.The complexes of thiourea derivatives also show various biological activities (Glasser et al., 1964). Thioureas and substituted thioureas are also known as epoxy resin curing agents. We became interested in the synthesis of N-Aroyl, N'-arylthioureas as intermediates towards some new novel heterocycles and for the systematic study of their bioactive complexes and epoxy resin curing agents. In this article, we describe the spectroscopy and crystal structure of ethyl 4-(3-benzoylthioureido)-benzoate (I) as a typical representative of N-aroyl, N'-arylthioureas. Compound (I) crystallizes in the thioamide form. The conformation of the molecule with respect to the carbonyl and thiocarbonyl part is essentially planar, as reflected by the torsional angles O1—C7—N1—C8, C7—N1—C8—S and C7—N1—C8—N2 of 0.7 (2), -177.97 (9) and 1.0 (2) °, respectively. However, there is rotation about the various moieties as indicated by e.g. C6—C1—C7—N1 34.7 (2) and C8—N2—C9—C14 136.9 (1) °. Apart from the atoms O1, N1, C8 and S, the molecule is planar (mean deviation of non-H atoms is 0.055 Å). The C7—O1, C8—S and C15—O2 bonds show a typical double bond character with bond lengths of 1.226 (1), 1.659 (1) and 1.215 (1) Å, respectively. All of the C—N bonds, C9—N2 1.415 (1), C7—N1 1.385 (1), C8—N2 1.339 (2), and C8—N1 1.401 (1) Å also indicate partial double bond character. Among the three latter C—N bonds, C7—N1 is the longest, indicating an C(sp2)—N(sp2) single bond, while C8—N2 is the shortest bond with more double bond character. This demonstrates that there is π conjugation in the system S—C8—N2 but not along O1—C7—N1 and C7—N1—C8, as found in 1-(3-methoxybenzoyl)-3,3-diethylthiourea (Moraless et al., 2000).
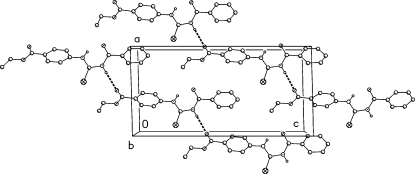
There is a strong intramolecular hydrogen bond N2—H02···O1, with distances H2···O1 1.89 (2) and N2···O1 2.618 (1) Å, resulting in a 6-membered ring. Molecules are connected in chains parallel to [101] by the classical H bond N1—H01···O2; weak C—H···S interactions are observed interconecting the chains (Table 1).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by a slight modification of the published procedure (Douglas et al., 1934). A solution of benzoyl chloride (0.1 mol) in anhydrous acetone (70 ml) was added dropwise to a suspension of ammonium thiocyanate (0.1 mol) in anhydrous acetone (50 ml) and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 45 minutes. After cooling to room temperature, a solution of p-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester (0.1 mol) in anhydrous acetone (25 ml) was added and the resulting mixture refluxed for 1.5 hrs. The reaction mixture was poured into five times its volume of cold water where the thiourea precipitated as a solid. The product was recrystallized from ethyl acetate as pale yellow crystals (3.55 g, 85%). m.p. 425 K. Elemental analysis for C17H16N2O3S (M=328.38) calc. C 62.19, H 4.87, N 8.53, S 9.75, found C 62.16, H 4.93, N 8.58, S 9.76. FTIR (KBr pellet) [cm-1]: 1276 (C=S), 1676 (C=O amide), 1700 (C=O ester), 3346 (free N—H), 3208 (assoc. N—H). 1H-NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6) [ppm]: 1.34 (3H, t, CH3); 4.32 (2H, q, CH2); 7.51–7.56 (2H, m, CHar), 7.63–7.68 (2H, m, CHar), 7.90–8.00 (5H, m, CHar); 11.63 (1H, s, broad, NH); 12.80 (1H, s, broad, NH). 13C-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6) [ppm]: 14.14 (CH3); 60.70 (CH2); 127.83(C), 128.72(C), 128.81(C), 129.72(C), 132.06(C), 133.17(C); 165.08(C=O amide); 168.20 (C=O ester), 178.99 (C=S thioamide).
Refinement
H atoms of NH groups were refined freely. Methyl H atoms were included on the basis of idealized rigid groups (C—H 0.98 Å, H—C—H 109.5°) allowed to rotate but not tip. Other hydrogen atoms were included using a riding model with C—H 0.95 (aromatic) or 0.99 (methylene) Å. U(H) values were fixed at 1.5Uiso(C) of the parent C atom for methyl H, 1.2Uiso(C) for other H.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecule of the title compound in the crystal. Ellipsoids represent 50% probability levels.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of I showing classical H bonds as thick dashed bonds. H atoms not involved in H bonds are omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C17H16N2O3S | F000 = 688 |
| Mr = 328.38 | Dx = 1.402 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 11202 reflections |
| a = 9.6018 (3) Å | θ = 2.6–32.1º |
| b = 8.3882 (3) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| c = 19.3199 (6) Å | T = 100 (2) K |
| β = 91.393 (4)º | Tablet, colourless |
| V = 1555.60 (9) Å3 | 0.38 × 0.24 × 0.13 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur S diffractometer | 5103 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 3676 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1057 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 32.2º |
| T = 100(2) K | θmin = 2.7º |
| ω scans | h = −14→13 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2008) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.943, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −27→28 |
| 31428 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0546P)2 |
| S = 0.94 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 5103 reflections | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 217 parameters | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Experimental. CrysAlis RED, Oxford Diffraction Ltd., Version 1.171.32.15 (release 10-01-2008 CrysAlis171 .NET) (compiled Jan 10 2008,16:37:18) |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S | 0.10457 (3) | 0.58015 (4) | 0.231857 (14) | 0.01866 (8) | |
| O1 | 0.51573 (9) | 0.70720 (10) | 0.34044 (4) | 0.01821 (18) | |
| O2 | 0.50845 (9) | 0.81469 (9) | −0.09004 (4) | 0.01765 (18) | |
| O3 | 0.35152 (9) | 0.61785 (9) | −0.10425 (4) | 0.01525 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.28549 (11) | 0.63504 (11) | 0.33385 (5) | 0.01329 (19) | |
| H01 | 0.2098 (15) | 0.6256 (15) | 0.3555 (7) | 0.020 (4)* | |
| N2 | 0.37602 (11) | 0.65342 (11) | 0.22473 (5) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H02 | 0.4445 (16) | 0.6886 (17) | 0.2488 (7) | 0.028 (4)* | |
| C1 | 0.39896 (12) | 0.67621 (12) | 0.44636 (5) | 0.0126 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.48431 (13) | 0.78318 (13) | 0.48262 (6) | 0.0171 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.5431 | 0.8536 | 0.4582 | 0.021* | |
| C3 | 0.48347 (13) | 0.78691 (14) | 0.55439 (6) | 0.0196 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.5392 | 0.8624 | 0.5791 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.40113 (13) | 0.68031 (14) | 0.59006 (6) | 0.0190 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.4013 | 0.6822 | 0.6392 | 0.023* | |
| C5 | 0.31886 (13) | 0.57135 (14) | 0.55422 (6) | 0.0188 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.2644 | 0.4969 | 0.5789 | 0.023* | |
| C6 | 0.31562 (12) | 0.57034 (13) | 0.48250 (6) | 0.0158 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.2567 | 0.4977 | 0.4580 | 0.019* | |
| C7 | 0.40746 (12) | 0.67435 (12) | 0.36961 (5) | 0.0131 (2) | |
| C8 | 0.26324 (12) | 0.62392 (12) | 0.26210 (5) | 0.0128 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.38365 (12) | 0.66358 (13) | 0.15181 (5) | 0.0125 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.32131 (12) | 0.55175 (13) | 0.10741 (5) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| H10 | 0.2696 | 0.4656 | 0.1257 | 0.017* | |
| C11 | 0.33527 (12) | 0.56701 (13) | 0.03650 (5) | 0.0130 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.2917 | 0.4920 | 0.0061 | 0.016* | |
| C12 | 0.41293 (11) | 0.69188 (12) | 0.00951 (5) | 0.0117 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.47771 (12) | 0.80015 (13) | 0.05441 (5) | 0.0139 (2) | |
| H13 | 0.5328 | 0.8837 | 0.0363 | 0.017* | |
| C14 | 0.46254 (12) | 0.78708 (13) | 0.12517 (5) | 0.0146 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.5059 | 0.8623 | 0.1555 | 0.018* | |
| C15 | 0.43123 (12) | 0.71552 (12) | −0.06585 (5) | 0.0123 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.36048 (13) | 0.63785 (14) | −0.17859 (5) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| H16A | 0.4578 | 0.6239 | −0.1932 | 0.021* | |
| H16B | 0.3287 | 0.7458 | −0.1924 | 0.021* | |
| C17 | 0.26837 (14) | 0.51324 (15) | −0.21156 (6) | 0.0235 (3) | |
| H17A | 0.3001 | 0.4072 | −0.1968 | 0.035* | |
| H17B | 0.2728 | 0.5216 | −0.2621 | 0.035* | |
| H17C | 0.1722 | 0.5295 | −0.1973 | 0.035* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S | 0.01261 (15) | 0.03287 (18) | 0.01044 (13) | −0.00304 (12) | −0.00088 (10) | 0.00021 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0142 (4) | 0.0261 (5) | 0.0143 (4) | −0.0035 (3) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0017 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0229 (5) | 0.0169 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | −0.0043 (3) | 0.0029 (3) | 0.0005 (3) |
| O3 | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0195 (4) | 0.0094 (3) | −0.0034 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0005 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0090 (4) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0001 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0205 (5) | 0.0092 (4) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0002 (4) | −0.0004 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0106 (5) | 0.0026 (4) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C2 | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0155 (5) | −0.0030 (5) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0151 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | −0.0037 (5) | −0.0043 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0264 (6) | 0.0110 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | −0.0003 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0254 (6) | 0.0141 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0046 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0136 (5) | −0.0018 (4) | −0.0023 (4) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0142 (6) | 0.0128 (5) | 0.0121 (5) | 0.0007 (4) | −0.0016 (4) | 0.0000 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0099 (5) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0000 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C9 | 0.0118 (5) | 0.0158 (5) | 0.0098 (5) | 0.0019 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | 0.0002 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0146 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | −0.0013 (4) | 0.0027 (4) | 0.0001 (4) |
| C11 | 0.0126 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0125 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | 0.0008 (4) | −0.0026 (4) |
| C12 | 0.0113 (5) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0103 (5) | 0.0029 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0135 (5) | −0.0011 (4) | 0.0017 (4) | 0.0004 (4) |
| C14 | 0.0147 (6) | 0.0171 (5) | 0.0121 (5) | −0.0017 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | −0.0025 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0129 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0107 (5) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0224 (6) | 0.0216 (6) | 0.0078 (5) | −0.0010 (5) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0311 (7) | 0.0161 (6) | −0.0049 (5) | −0.0019 (5) | −0.0042 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S—C8 | 1.6594 (12) | C12—C13 | 1.3921 (15) |
| O1—C7 | 1.2259 (14) | C12—C15 | 1.4839 (14) |
| O2—C15 | 1.2153 (13) | C13—C14 | 1.3827 (14) |
| O3—C15 | 1.3342 (13) | C16—C17 | 1.5010 (16) |
| O3—C16 | 1.4505 (12) | N1—H01 | 0.852 (15) |
| N1—C7 | 1.3850 (14) | N2—H02 | 0.849 (15) |
| N1—C8 | 1.4005 (13) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C8 | 1.3391 (15) | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C9 | 1.4151 (13) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3926 (15) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3941 (15) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C7 | 1.4871 (14) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.3872 (15) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3879 (17) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3829 (17) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3852 (15) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C9—C14 | 1.3895 (15) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C9—C10 | 1.3961 (15) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.3857 (14) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C11—C12 | 1.3943 (15) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C15—O3—C16 | 115.63 (9) | C8—N1—H01 | 111.7 (9) |
| C7—N1—C8 | 128.05 (10) | C8—N2—H02 | 113.3 (10) |
| C8—N2—C9 | 127.59 (10) | C9—N2—H02 | 117.8 (10) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.77 (10) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.0 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 117.54 (10) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.0 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 122.59 (10) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.97 (11) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.94 (11) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.17 (10) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.24 (11) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.85 (10) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 122.71 (10) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 121.58 (10) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.1 |
| N1—C7—C1 | 115.70 (10) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| N2—C8—N1 | 114.55 (10) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| N2—C8—S | 126.77 (8) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| N1—C8—S | 118.68 (8) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C14—C9—C10 | 120.19 (10) | C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C14—C9—N2 | 117.10 (9) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C10—C9—N2 | 122.64 (10) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.67 (10) | C9—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.31 (10) | O3—C16—H16A | 110.3 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.47 (10) | C17—C16—H16A | 110.3 |
| C13—C12—C15 | 117.54 (10) | O3—C16—H16B | 110.3 |
| C11—C12—C15 | 122.99 (9) | C17—C16—H16B | 110.3 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.54 (10) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.6 |
| C13—C14—C9 | 119.78 (10) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C15—O3 | 123.60 (9) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O2—C15—C12 | 123.83 (10) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O3—C15—C12 | 112.56 (9) | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3—C16—C17 | 106.93 (9) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—N1—H01 | 119.9 (9) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.67 (17) | C8—N2—C9—C10 | −46.16 (17) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −178.22 (10) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.79 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.21 (18) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | −178.66 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.63 (18) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.00 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.51 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.73 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 2.04 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C15 | −179.62 (10) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.45 (17) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.70 (17) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | 175.92 (10) | C15—C12—C13—C14 | 178.63 (10) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | 0.74 (17) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.92 (17) |
| C8—N1—C7—C1 | −179.93 (10) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.83 (17) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | 30.47 (15) | N2—C9—C14—C13 | 177.88 (10) |
| C6—C1—C7—O1 | −145.97 (11) | C16—O3—C15—O2 | −0.79 (16) |
| C2—C1—C7—N1 | −148.86 (10) | C16—O3—C15—C12 | 178.03 (9) |
| C6—C1—C7—N1 | 34.69 (15) | C13—C12—C15—O2 | 6.55 (16) |
| C9—N2—C8—N1 | −174.63 (10) | C11—C12—C15—O2 | −173.11 (11) |
| C9—N2—C8—S | 4.22 (17) | C13—C12—C15—O3 | −172.27 (10) |
| C7—N1—C8—N2 | 0.99 (16) | C11—C12—C15—O3 | 8.07 (15) |
| C7—N1—C8—S | −177.97 (9) | C15—O3—C16—C17 | 177.67 (10) |
| C8—N2—C9—C14 | 136.88 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H02···O1 | 0.85 (2) | 1.89 (2) | 2.618 (1) | 143 (1) |
| N1—H01···O2i | 0.85 (2) | 2.28 (2) | 3.099 (1) | 162 (1) |
| C3—H3···Sii | 0.95 | 3.04 | 3.763 (1) | 134 |
| C17—H17C···Siii | 0.98 | 2.88 | 3.677 (1) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IM2071).
References
- D’hooghe, M., Waterinckx, A. & De Kimpe, N. (2005). J. Org. Chem.70, 227–232. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Douglas, I. B. & Dains, F. B. (1934). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 56, 719–721.
- Dušek, K. (1985). Adv. Polym. Sci.78 , 115–118.
- Glasser, A. C. & Doughty, R. M. (1964). J. Pharm. Soc. 53,40–42. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Huebner, O. F., Marsh, J. L., Mizzoni, R. H., Mull, R. P., Schrooder, D. C., Troxell, H. A. & Scholz, C. R. (1953). J. Am. Chem. Soc.75, 2274–2275.
- Morales, A. D., Novoa de Armas, H., Blaton, N. M., Peeters, O. M., De Ranter, C. J., Márquez, H. & Pomés Hernández, R. (2000). Acta Cryst. C56, 503–504. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2008). CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siemens (1994). XP Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Xu, Y., Hua, W., Liu, X. & Zhu, D. (2004). Chin. J. Org. Chem.24, 1217–1222.
- Xue, S., Duan, L., Ke, S. & Jia, L. (2003). Chemistry Magazine, 5, 67–70.
- Zeng, R. S., Zou, J. P., Zchen, S. J. & Shen, Q. (2003). Org. Lett.61, 1657–1659. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W., Yates, S. R., Papiernik, S. K. & Guo, M. (2004). Environ. Sci. Technol.38, 6855–6860. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017856/im2071sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808017856/im2071Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report