Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C14H12ClNO2, the two aromatic rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 5.92 (7)°. An intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond results in the formation of a nearly planar six-membered ring, which is oriented at dihedral angles of 1.55 (4) and 5.95 (4)° with respect to the phenol and chlorophenyl rings, respectively. In the crystal structure, weak intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Özek et al. (2007 ▶); Odabaşoğlu, Büyükgüngör et al. (2007 ▶); Odabaşoğlu, Arslan et al. (2007 ▶); Albayrak et al. (2005 ▶); Elerman et al. (1995 ▶). For general background, see: Friesner (2005 ▶); Liu et al. (2004 ▶).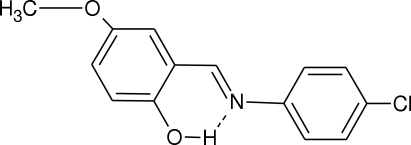
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H12ClNO2
M r = 261.70
Monoclinic,

a = 21.2642 (19) Å
b = 4.7101 (3) Å
c = 12.2175 (12) Å
β = 93.361 (8)°
V = 1221.56 (18) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.30 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.68 × 0.44 × 0.21 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDSII diffractometer
Absorption correction: integration (X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.825, T max = 0.925
10205 measured reflections
2364 independent reflections
1789 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.080
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.099
S = 1.00
2364 reflections
167 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-RED32 (Stoe & Cie, 2002 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and GAUSSIAN (Frisch et al., 2004 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808023416/hk2503sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808023416/hk2503Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N1 | 0.88 (3) | 1.79 (3) | 2.6210 (18) | 157 (2) |
| C7—H7C⋯O2i | 0.96 | 2.56 | 3.495 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Table 2. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °) calculated with X-RAY, AM1, PM3, HF and DFT .
| Parameters | X-RAY | AM1 | PM3 | HFa | DFT/B3LYPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—N1 | 1.276 (19) | 1.292 | 1.302 | 1.262 | 1.293 |
| C2—O1 | 1.355418) | 1.368 | 1.357 | 1.336 | 1.344 |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (2) | 1.406 | 1.401 | 1.393 | 1.406 |
| C1—C8 | 1.448 (2) | 1.466 | 1.459 | 1.467 | 1.449 |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (2) | 1.408 | 1.411 | 1.402 | 1.423 |
| N1—C9 | 1.418 (19) | 1.409 | 1.431 | 1.408 | 1.406 |
| C9—C10 | 1.384 (2) | 1.414 | 1.401 | 1.391 | 1.403 |
| C12—Cl1 | 1.734 (15) | 1.699 | 1.684 | 1.743 | 1.758 |
| C5—O2 | 1.3756 (18) | 1.385 | 1.386 | 1.355 | 1.371 |
| C11—C12—Cl1 | 120.72 (12) | 119.860 | 119.505 | 119.595 | 119.538 |
| C6—C5—O2 | 115.56 (14) | 114.847 | 113.926 | 116.374 | 116.232 |
| C6—C1—C8 | 119.18 (13) | 116.153 | 118.078 | 118.004 | 119.327 |
| C9—N1 —C8 | 121.22 (13) | 121.780 | 122.176 | 120.342 | 121.253 |
| C14—C9—N1 | 124.68 (13) | 123.445 | 122.813 | 122.881 | 123.392 |
| N1—C8—C1 | 122.35 (14) | 123.800 | 119.635 | 123.408 | 122.250 |
| N1—C9—C10 | 117.10 (13) | 117.991 | 116.829 | 118.015 | 117.770 |
| C8—C1—C2—O1 | −0.9 (2) | −0.050 | −0.030 | −0.111 | −0.085 |
| C6—C5—O2—C7 | −172.96 (15) | 179.476 | 179.983 | 179.698 | −179.874 |
| C10—C9—N1—C8 | −172.84 (13) | −149.450 | 179.999 | 62.793 | −147.450 |
| N1—C8—C1—C6 | 177.90 (14) | −177.484 | −0.066 | −179.307 | −179.448 |
| C1—C8—N1—C9 | −178.85 (13) | −179.157 | 179.991 | −178.540 | −177.303 |
Notes: (a) 6-31G(d,p).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Ondokuz Mayıs University, Turkey, for the use of the Stoe IPDSII diffractometer (purchased under grant No. F.279 of the University Research Fund).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The present work is part of a structural study of Schiff bases Özek et al., 2007; Odabaşoğlu, Büyükgüngör et al., 2007; Odabaşoğlu, Arslan et al., 2007). We report herein the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
In general, O-hydroxy Schiff bases exhibit two possible tautomeric forms, the phenol-imine (or benzenoid) and keto-amine (or quinoid) forms. Depending on the tautomers, two types of intramolecular hydrogen bonds are possible: O-H···N in benzenoid and N-H···O in quinoid tautomers. The H atom in (I) is located on atom O1, thus the phenol-imine tautomer is favored over the keto-amine form, as indicated by the C2-O1, C8-N1, C1-C8 and C1-C2 bonds (Fig. 1 and Table 2). The O1-C2 bond has single-bond character, whereas the N1-C8 bond has a high degree of double-bond character as in 2-(3-methoxysalicylideneamino)-1H-benzimidazole- monohydrate, (II) [where the corresponding values are C-O = 1.357 (2) Å, C-N = 1.285 (2) Å, Albayrak et al., 2005]. It is known that Schiff bases may exhibit thermochromism or photochromism, depending on the planarity or non-planarity of the molecule, respectively. Therefore, one can expect thermochromic properties in (I) caused by the planarity of the molecule; the dihedral angle between rings A (C1-C6) and B (C9-C14) is 5.92 (7)°. The intramolecular O-H···N hydrogen bond (Table 1) results in the formation of a nearly planar six-membered ring C (O1/H1/N1/C1/C2/C8), in which it is oriented with respect to rings A and B at dihedral angles of A/C = 1.55 (4)° and B/C = 5.95 (4)°. So, it is coplanar with the adjacent ring A. It generates an S(6) ring motif. The O1···N1 [2.621 (2) Å] distance is comparable to those observed for analogous ones in N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)salicylaldimine, (III) [2.675 (7) Å; Elerman et al., 1995] and in three(E)-2-[(bromophenyl)iminomethyl]-4-methoxyphenols, (IV) [2.603 (2), 2.638 (7) and 2.577 (4) Å;Özek et al., 2007].
In the crystal structure, weak intermolecular C-H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into a three-dimensional network (Fig. 2), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure.
Ab-initio Hartree-Fock (HF), density-functional theory (DFT) and semi-empirical (AM1 and PM3) calculations and full-geometry optimizations were performed by means of GAUSSIAN 03 W package (Frisch et al., 2004). The selected bond lengths and angles together with the torsion angles are compared with the obtained ones from semi-empirical, ab-initio HF and DFT/B3LYP methods (Table 2). We observe an acceptable general agreement between them. Although the DFT molecular orbital theory was considered as the most accurate method for geometry optimization for free and complex ligands (Friesner, 2005; Liu et al., 2004), the HF method led to better results in regard to the bond lengths and angles.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by refluxing a mixture of a solution containing 5-methoxysalicylaldehyde (0.5 g 3.3 mmol) in ethanol (20 ml) and a solution containing 4-chloraniline (0.420 g 3.3 mmol) in ethanol (20 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h under reflux. The crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained from ethanol by slow evaporation (yield; 76%, m.p. 378-379 K).
Refinement
H1 atom (for OH) was located in difference syntheses and refined isotropically [O-H = 0.88 (3) Å and Uiso(H) = 0.112 (9) Å2]. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C-H = 0.93 and 0.96 Å for aromatic and methyl H, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Hydrogen bond is shown as dashed line.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of (I) [symmetry codes: (i) 1 - x, y - 1/2, 3/2 - z; (ii) 1 - x, y + 1/2, 3/2 - z]. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C14H12ClNO2 | F000 = 544 |
| Mr = 261.70 | Dx = 1.423 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 10205 reflections |
| a = 21.2642 (19) Å | θ = 1.7–27.2º |
| b = 4.7101 (3) Å | µ = 0.31 mm−1 |
| c = 12.2175 (12) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 93.361 (8)º | Prismatic long stick, red |
| V = 1221.56 (18) Å3 | 0.68 × 0.44 × 0.21 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDSII diffractometer | 2364 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1789 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: plane graphite | Rint = 0.080 |
| Detector resolution: 6.67 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0º |
| T = 296 K | θmin = 1.9º |
| ω scans | h = −26→26 |
| Absorption correction: integration(X-RED32; Stoe & Cie, 2002) | k = −5→5 |
| Tmin = 0.825, Tmax = 0.925 | l = −14→14 |
| 10205 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.099 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0641P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2364 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 167 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Experimental. 225 frames, detector distance = 120 mm |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.03208 (2) | 1.40379 (9) | 0.66121 (4) | 0.06631 (18) | |
| O1 | 0.26185 (6) | 0.2746 (3) | 0.35438 (10) | 0.0677 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.2404 (12) | 0.393 (5) | 0.394 (2) | 0.112 (9)* | |
| O2 | 0.42346 (6) | −0.2199 (3) | 0.66813 (10) | 0.0676 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.21631 (6) | 0.5615 (3) | 0.51562 (10) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.29911 (7) | 0.2216 (3) | 0.54240 (12) | 0.0428 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.30182 (7) | 0.1541 (3) | 0.43144 (12) | 0.0480 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.34597 (8) | −0.0395 (4) | 0.39932 (13) | 0.0575 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.3478 | −0.0841 | 0.3254 | 0.069* | |
| C4 | 0.38738 (8) | −0.1674 (4) | 0.47512 (14) | 0.0551 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.4170 | −0.2964 | 0.4521 | 0.066* | |
| C5 | 0.38493 (7) | −0.1042 (3) | 0.58541 (13) | 0.0493 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.34078 (7) | 0.0873 (3) | 0.61831 (13) | 0.0484 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.3387 | 0.1278 | 0.6925 | 0.058* | |
| C7 | 0.47390 (9) | −0.3918 (4) | 0.63688 (19) | 0.0753 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.5012 | −0.2819 | 0.5936 | 0.090* | |
| H7B | 0.4576 | −0.5499 | 0.5945 | 0.090* | |
| H7C | 0.4971 | −0.4604 | 0.7013 | 0.090* | |
| C8 | 0.25442 (7) | 0.4252 (3) | 0.58089 (12) | 0.0461 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.2534 | 0.4579 | 0.6558 | 0.055* | |
| C9 | 0.17376 (7) | 0.7637 (3) | 0.55533 (12) | 0.0436 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.12943 (7) | 0.8772 (3) | 0.48017 (13) | 0.0522 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.1291 | 0.8199 | 0.4073 | 0.063* | |
| C11 | 0.08576 (8) | 1.0737 (3) | 0.51122 (14) | 0.0550 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.0561 | 1.1474 | 0.4599 | 0.066* | |
| C12 | 0.08649 (7) | 1.1592 (3) | 0.61875 (14) | 0.0496 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.13070 (8) | 1.0524 (4) | 0.69489 (14) | 0.0557 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.1312 | 1.1129 | 0.7674 | 0.067* | |
| C14 | 0.17395 (7) | 0.8564 (3) | 0.66347 (13) | 0.0531 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.2037 | 0.7848 | 0.7151 | 0.064* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0617 (3) | 0.0529 (2) | 0.0864 (3) | 0.01245 (18) | 0.0222 (2) | 0.0027 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0789 (8) | 0.0846 (9) | 0.0392 (6) | 0.0278 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0658 (7) | 0.0785 (8) | 0.0577 (7) | 0.0260 (6) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0012 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0442 (6) | 0.0448 (7) | 0.0018 (5) | 0.0049 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0448 (7) | 0.0422 (7) | 0.0418 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0068 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0521 (8) | 0.0535 (9) | 0.0387 (8) | 0.0048 (6) | 0.0045 (7) | 0.0015 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0654 (10) | 0.0667 (10) | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0101 (8) | 0.0104 (7) | −0.0051 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0548 (9) | 0.0571 (9) | 0.0545 (10) | 0.0100 (7) | 0.0114 (8) | −0.0039 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0484 (8) | 0.0499 (8) | 0.0495 (8) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0531 (8) | 0.0507 (8) | 0.0414 (8) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0031 (7) | −0.0039 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0683 (11) | 0.0716 (12) | 0.0849 (14) | 0.0251 (10) | −0.0049 (10) | 0.0002 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0505 (8) | 0.0467 (8) | 0.0415 (8) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0060 (7) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0439 (7) | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0468 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0061 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0572 (9) | 0.0534 (9) | 0.0458 (9) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0021 (7) | −0.0005 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0535 (9) | 0.0532 (9) | 0.0579 (10) | 0.0075 (7) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0058 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0464 (8) | 0.0404 (7) | 0.0632 (10) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0133 (7) | 0.0026 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0614 (9) | 0.0561 (9) | 0.0500 (9) | 0.0054 (7) | 0.0074 (8) | −0.0058 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0548 (9) | 0.0558 (9) | 0.0482 (9) | 0.0106 (7) | −0.0002 (7) | −0.0019 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—H1 | 0.88 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (2) | C8—N1 | 1.2763 (19) |
| C1—C2 | 1.397 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C8 | 1.448 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.384 (2) |
| C2—O1 | 1.3554 (18) | C9—C14 | 1.391 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.382 (2) | C9—N1 | 1.4186 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.379 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.380 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.384 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.373 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C5—O2 | 1.3756 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.379 (2) | C12—Cl1 | 1.7337 (15) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.374 (2) |
| C7—O2 | 1.414 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9600 | ||
| C2—O1—H1 | 102.0 (17) | O2—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C5—O2—C7 | 117.19 (14) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—C9 | 121.22 (13) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 118.74 (14) | N1—C8—C1 | 122.35 (14) |
| C6—C1—C8 | 119.18 (13) | N1—C8—H8 | 118.8 |
| C2—C1—C8 | 122.08 (13) | C1—C8—H8 | 118.8 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 119.19 (14) | C10—C9—C14 | 118.22 (14) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 121.27 (14) | C10—C9—N1 | 117.10 (13) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.54 (14) | C14—C9—N1 | 124.68 (13) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.03 (15) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.32 (15) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.05 (15) | C12—C11—C10 | 119.31 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.3 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.3 |
| O2—C5—C6 | 115.56 (14) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.51 (15) |
| O2—C5—C4 | 125.11 (15) | C11—C12—Cl1 | 120.72 (12) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.33 (14) | C13—C12—Cl1 | 118.77 (13) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.29 (14) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.87 (15) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.4 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| O2—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C13—C14—C9 | 120.76 (14) |
| O2—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C9—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | 178.95 (14) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.0 (2) |
| C8—C1—C2—O1 | −0.9 (2) | N1—C9—C10—C11 | 179.50 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.9 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.3 (2) |
| C8—C1—C2—C3 | 179.23 (14) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (2) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.82 (16) | C10—C11—C12—Cl1 | −179.55 (12) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.8 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (3) | Cl1—C12—C13—C14 | 179.40 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—O2 | 179.54 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (2) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.9 (2) |
| O2—C5—C6—C1 | 179.51 (14) | N1—C9—C14—C13 | −179.70 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.9 (2) | C1—C8—N1—C9 | −178.85 (13) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.4 (2) | C10—C9—N1—C8 | −172.84 (13) |
| C8—C1—C6—C5 | −178.79 (14) | C14—C9—N1—C8 | 7.7 (2) |
| C6—C1—C8—N1 | 177.90 (14) | C6—C5—O2—C7 | −172.96 (15) |
| C2—C1—C8—N1 | −2.3 (2) | C4—C5—O2—C7 | 7.5 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N1 | 0.88 (3) | 1.79 (3) | 2.6210 (18) | 157 (2) |
| C7—H7C···O2i | 0.96 | 2.56 | 3.495 (2) | 164 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
Table 2 Selected geometric parameters (Å, °) calculated with X-RAY, AM1, PM3, HF and DFT
| Parameters | X-RAY | AM1 | PM3 | HFa | DFT/B3LYPa |
| C8 N1 | 1.276 (19) | 1.292 | 1.302 | 1.262 | 1.293 |
| C2 O1 | 1.355418) | 1.368 | 1.357 | 1.336 | 1.344 |
| C1 C6 | 1.396 (2) | 1.406 | 1.401 | 1.393 | 1.406 |
| C1 C8 | 1.448 (2) | 1.466 | 1.459 | 1.467 | 1.449 |
| C1 C2 | 1.397 (2) | 1.408 | 1.411 | 1.402 | 1.423 |
| N1 C9 | 1.418 (19) | 1.409 | 1.431 | 1.408 | 1.406 |
| C9 C10 | 1.384 (2) | 1.414 | 1.401 | 1.391 | 1.403 |
| C12 Cl1 | 1.734 (15) | 1.699 | 1.684 | 1.743 | 1.758 |
| C5 O2 | 1.3756 (18) | 1.385 | 1.386 | 1.355 | 1.371 |
| C11 C12 Cl1 | 120.72 (12) | 119.860 | 119.505 | 119.595 | 119.538 |
| C6 C5 O2 | 115.56 (14) | 114.847 | 113.926 | 116.374 | 116.232 |
| C6 C1 C8 | 119.18 (13) | 116.153 | 118.078 | 118.004 | 119.327 |
| C9 N1 C8 | 121.22 (13) | 121.780 | 122.176 | 120.342 | 121.253 |
| C14 C9 N1 | 124.68 (13) | 123.445 | 122.813 | 122.881 | 123.392 |
| N1 C8 C1 | 122.35 (14) | 123.800 | 119.635 | 123.408 | 122.250 |
| N1 C9 C10 | 117.10 (13) | 117.991 | 116.829 | 118.015 | 117.770 |
| C8 C1 C2 O1 | -0.9 (2) | -0.050 | -0.030 | -0.111 | -0.085 |
| C6 C5 O2 C7 | -172.96 (15) | 179.476 | 179.983 | 179.698 | -179.874 |
| C10 C9 N1 C8 | -172.84 (13) | -149.450 | 179.999 | 62.793 | -147.450 |
| N1 C8 C1 C6 | 177.90 (14) | -177.484 | -0.066 | -179.307 | -179.448 |
| C1 C8 N1 C9 | -178.85 (13) | -179.157 | 179.991 | -178.540 | -177.303 |
Notes: (a) 6-31G(d,p).
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2503).
References
- Albayrak, Ç., Odabaşoğlu, M. & Büyükgüngör, O (2005). Acta Cryst. E61, o423–o424. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elerman, Y., Elmali, A., Atakol, O. & Svoboda, I. (1995). Acta Cryst. C51, 2344–2346.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Friesner, R. A. (2005). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 6648–6653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M. J., et al. (2004). GAUSSIAN03 Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT 06492, USA.
- Liu, H., Bandeira, N. A. G., Calhorda, M. J., Drew, M. G. B., Felix, V., Novosad, J., De Biani, F. F. & Zanello, P. (2004). J. Organomet. Chem.689, 2808–2819.
- Odabaşoğlu, M., Arslan, F., Ölmez, H. & Büyükgüngör, O. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3654.
- Odabaşoğlu, M., Büyükgüngör, O., Narayana, B., Vijesh, A. M. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1916–o1918.
- Özek, A., Albayrak, Ç., Odabaşoğlu, M. & Büyükgüngör, O. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o177–o180. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2002). X-AREA and X-RED32 Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808023416/hk2503sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808023416/hk2503Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




