Abstract
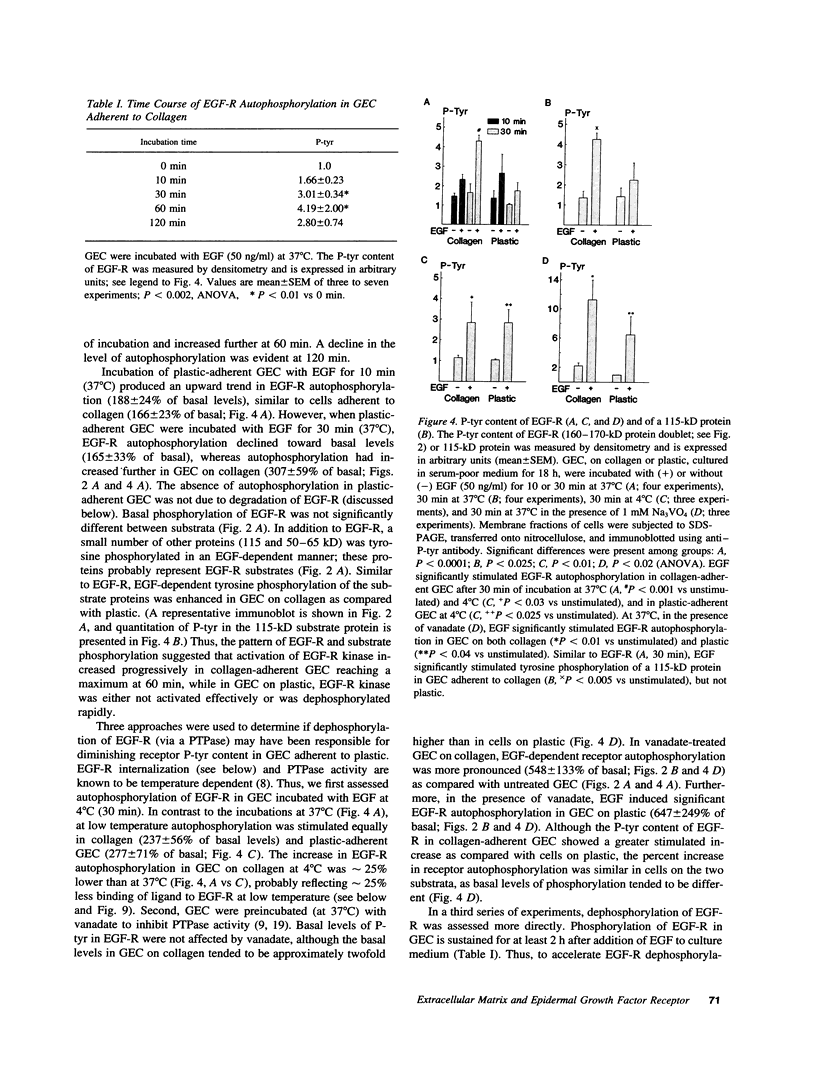
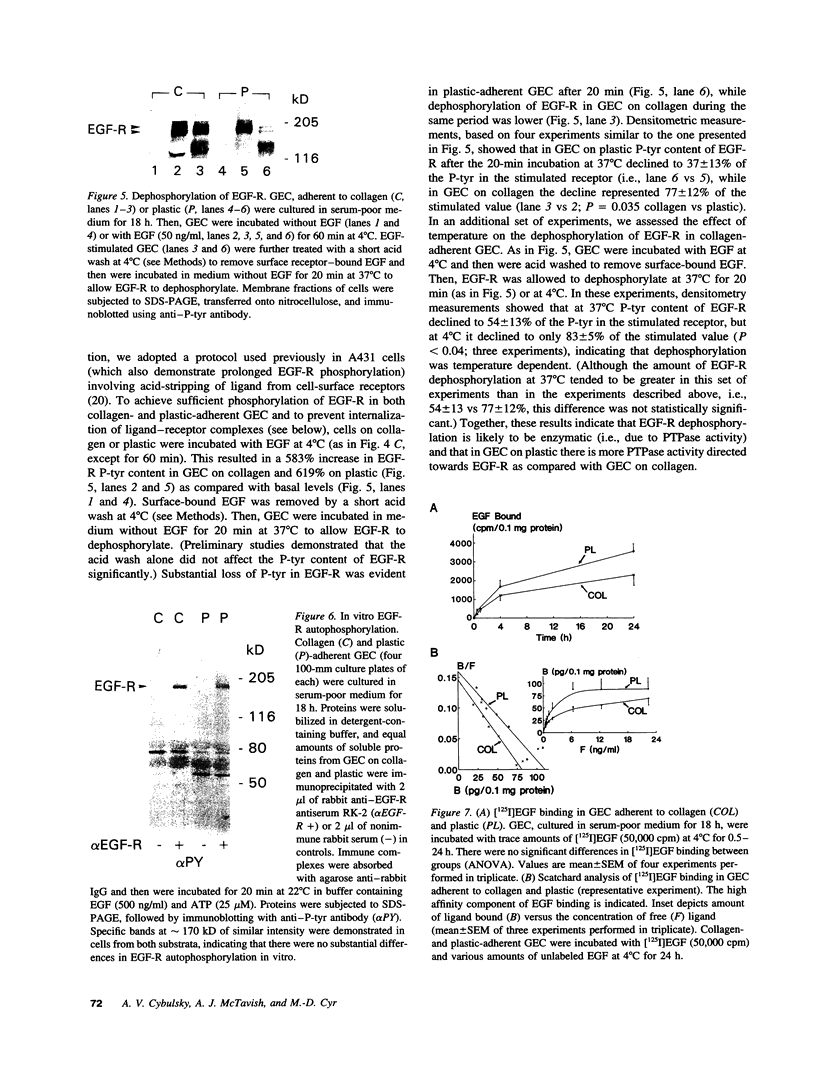
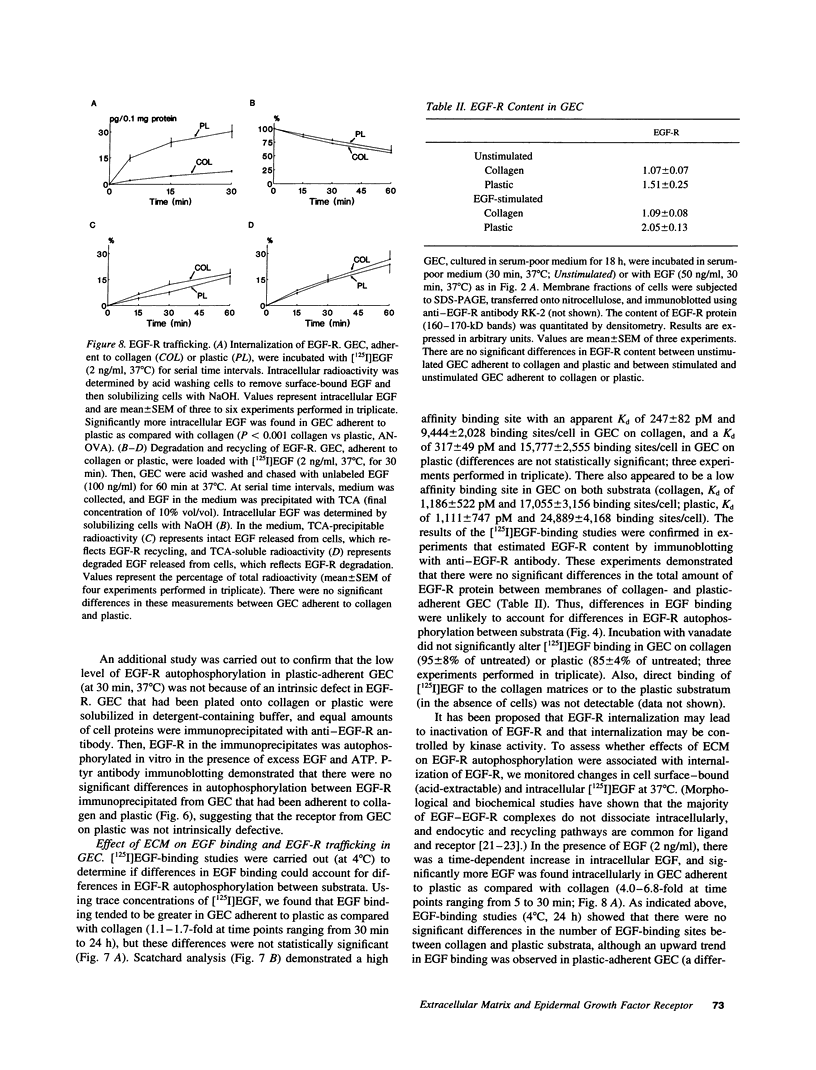
To understand how glomerular epithelial cell (GEC) proliferation may be regulated in health and disease, we studied the effects of type I collagen extracellular matrices (ECM) on EGF receptor (EGF-R) activation in cultured rat GEC. EGF stimulated proliferation of GEC adherent to ECM, but not of GEC on a plastic substratum. Significant and prolonged EGF-R tyrosine autophosphorylation (which reflects receptor kinase activation) was induced by EGF in GEC adherent to collagen, but EGF did not stimulate EGF-R autophosphorylation in GEC on plastic (at 37 degrees C). However, EGF-R autophosphorylation increased significantly in plastic-adherent GEC that were stimulated with EGF at 4 degrees C or in the presence of vanadate, an inhibitor of phosphotyrosine phosphatases. Furthermore, dephosphorylation of EGF-R was enhanced in GEC on plastic as compared with collagen. At 4 degrees C, [125I]EGF binding was not different between substrata, and there was negligible accumulation of intracellular [125I]EGF (which reflects EGF-R internalization). At 37 degrees C, EGF-R internalization was reduced significantly in collagen-adherent GEC as compared with GEC on plastic. Thus, contact with ECM facilitates proliferation and EGF-R activation in GEC. The enhanced activity of EGF-R tyrosine kinase may be due to ECM-induced reduction in EGF-R internalization and dephosphorylation by phosphotyrosine phosphatase(s). Signals from ECM to growth factor receptors may regulate cell turnover in the glomerulus under normal conditions and during immune glomerular injury.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler S. Heparin alters epidermal growth factor metabolism in cultured rat glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):169–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Lund K. A., Welsh J. B., Chang C. P., Walton G. M., Der C. J., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky A. V., Bonventre J. V., Quigg R. J., Wolfe L. S., Salant D. J. Extracellular matrix regulates proliferation and phospholipid turnover in glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):F326–F337. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.2.F326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky A. V., Goodyer P. R., Cyr M. D., McTavish A. J. Eicosanoids enhance epidermal growth factor receptor activation and proliferation in glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):F639–F646. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.4.F639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky A. V., Stewart D. J., Cybulsky M. I. Glomerular epithelial cells produce endothelin-1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993 Jan;3(7):1398–1404. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V371398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dike L. E., Farmer S. R. Cell adhesion induces expression of growth-associated genes in suspension-arrested fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6792–6796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure R., Baquiran G., Bergeron J. J., Posner B. I. The dephosphorylation of insulin and epidermal growth factor receptors. Role of endosome-associated phosphotyrosine phosphatase(s). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11215–11221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder S., Miller K., Moehren G., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Hopkins C. R. Kinase activity controls the sorting of the epidermal growth factor receptor within the multivesicular body. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90474-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E. H., Charbonneau H., Tonks N. K. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: a diverse family of intracellular and transmembrane enzymes. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):401–406. doi: 10.1126/science.1650499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Johnson R. J., Alpers C. E., Fatemi-Nainie S., Richardson C. A., Gordon K., Couser W. G. Visceral glomerular epithelial cells can proliferate in vivo and synthesize platelet-derived growth factor B-chain. Am J Pathol. 1993 Feb;142(2):637–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Zokas L., Kamps M. P. Monoclonal antibodies to phosphotyrosine. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90253-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyer P. R., Fata J., Goodyer C. G. Excretion of epidermal growth factor-like material in acute Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. 1990 Mar;4(2):101–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00858818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A. Use of vanadate as protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Bifunctional role of glycosphingolipids. Modulators for transmembrane signaling and mediators for cellular interactions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18713–18716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. E., Folkman J. How does extracellular matrix control capillary morphogenesis? Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):803–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90928-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai W. H., Cameron P. H., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Posner B. I., Bergeron J. J. Ligand-mediated autophosphorylation activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor during internalization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2751–2760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai W. H., Cameron P. H., Wada I., Doherty J. J., 2nd, Kay D. G., Posner B. I., Bergeron J. J. Ligand-mediated internalization, recycling, and downregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2741–2749. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Williams L. K., Rieser G. D. Association of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeleton of A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1341–1350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtner R. B., Wiedemuth M., Kittmann A., Ullrich A., Schirrmacher V., Khazaie K. Ligand-induced activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in intact rat mammary adenocarcinoma cells without detectable receptor phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11872–11880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. C., Grinnell F. Decreased level of PDGF-stimulated receptor autophosphorylation by fibroblasts in mechanically relaxed collagen matrices. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):663–672. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Sakariassen K. S., Assoian R. K., Sporn M. B., Bell G. I., Ross R. Induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in activated human alveolar macrophages. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magni M., Pandiella A., Helin K., Meldolesi J., Beguinot L. Transmembrane signalling at the epidermal growth factor receptor. Positive regulation by the C-terminal phosphotyrosine residues. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 15;277(Pt 2):305–311. doi: 10.1042/bj2770305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. L., Lax I., Kris R., Dombalagian M., Honegger A. M., Howk R., Givol D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. All autophosphorylation sites of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor and HER2/neu are located in their carboxyl-terminal tails. Identification of a novel site in EGF receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10667–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune B. K., Earp H. S. The epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase in liver epithelial cells. The effect of ligand-dependent changes in cellular location. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15501–15507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Suzuki Y., Churg J. Structure and development of the glomerular crescent. Am J Pathol. 1973 Sep;72(3):349–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pot D. A., Dixon J. E. A thousand and two protein tyrosine phosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jul 22;1136(1):35–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90082-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Proteoglycans in cell regulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13369–13372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Helin K., Waters C. M., Carpenter G., Beguinot L. Multiple autophosphorylation sites of the epidermal growth factor receptor are essential for receptor kinase activity and internalization. Contrasting significance of tyrosine 992 in the native and truncated receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8672–8678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Waters C., Overholser K. A., Carpenter G. Multiple autophosphorylation site mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Analysis of kinase activity and endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8355–8362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturani E., Zippel R., Toschi L., Morello L., Comoglio P. M., Alberghina L. Kinetics and regulation of the tyrosine phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor in intact A431 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1345–1351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hartigh J. C., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. The EGF receptor is an actin-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;119(2):349–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belzen N., Spaargaren M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Interaction of epidermal growth factor receptors with the cytoskeleton is related to receptor clustering. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Nov;145(2):365–375. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]