Abstract
Encapsulating cells in biodegradable hydrogels offers numerous attractive features for tissue engineering, including ease of handling, a highly hydrated tissue-like environment for cell and tissue growth, and the ability to form in vivo. Many properties important to the design of a hydrogel scaffold, such as swelling, mechanical properties, degradation, and diffusion, are closely linked to the crosslinked structure of the hydrogel, which is controlled through a variety of different processing conditions. Degradation may be tuned by incorporating hydrolytically or enzymatically labile segments into the hydrogel or by using natural biopolymers that are susceptible to enzymatic degradation. Because cells are present during the gelation process, the number of suitable chemistries and formulations are limited. In this review, we describe important considerations for designing biodegradable hydrogels for cell encapsulation and highlight recent advances in material design and their applications in tissue engineering.
Introduction
One of the primary goals of tissue engineering is to develop strategies that regenerate living, healthy, and functional tissues that can be used as tissue grafts or even organ replacements. The general approach is to utilize three-dimensional (3D) scaffolds that serve as temporary supports for cell growth and new tissue development. The scaffold may be designed as purely a structural support providing passive cues to the cells or with biological cues incorporated into the scaffold to guide cell and tissue growth. There are two main strategies in utilizing scaffolds for tissue engineering: (i) cells are seeded onto prefabricated porous scaffolds or (ii) cells are encapsulated during scaffold formation. In the former strategy, a wide range of hydrophilic and/or hydrophobic precursors can be used, and the fabrication process may involve harsh solvents and/or reactants, as long as the final product is cell friendly. In cell encapsulation strategies, the process by which scaffolds form must be cytocompatible, which significantly limits the number of suitable materials and formulations. This strategy, however, offers several advantages. Because the encapsulation process is mild, this strategy is often employable as an injectable system where cells suspended in a liquid precursor solution are delivered in vivo to the site of interest. In addition, by curing the hydrogel directly at the site of interest, the precursor solution can diffuse into the adjacent tissue, leading to enhanced adhesion of the scaffold to the tissue without requiring glue or sutures.1
Hydrogels are attractive biomaterials for numerous medical applications—in particular, scaffolds for tissue engineering.2 Hydrogels are water swellable, yet water insoluble, crosslinked networks that exhibit high water contents and tissue-like elastic properties. These attributes make them ideal candidates as scaffolds for growing cells and tissues. A subset of hydrogels, which are formed from biocompatible macromolecular precursors and mild gelation conditions, has been developed. As a result, hydrogels are used to encapsulate cells in 3D scaffolds. The earliest work in cell encapsulation utilized naturally forming and biodegradable hydrogels prepared from collagen, fibrin, or alginate.3–7 Although these studies demonstrated early successes in growing tissues, the gelation process, mechanical properties, and degradation rates are difficult to control. Ultimately, tissue engineering aims to engineer living tissues with structural and biochemical similarity to the native tissue such that the engineered tissue can function properly in vivo. For this reason, there is a need to better control gelation conditions for cell encapsulation and in vivo formation and to tailor the hydrogel chemistry, macroscopic properties, and degradation to promote functional tissue growth. Toward this goal, many recent strategies have focused on synthetic hydrogels, which afford greater control over each of these aspects, while the addition of natural chemistries into synthetic-based gels has been explored to create bioactive hydrogels.
This review describes important considerations in designing a suitable biodegradable hydrogel for cell encapsulation based on lessons learned. We also highlight recent advances in hydrogel design for cell encapsulation and recent progress made toward regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Hydrogel Design Considerations For Cell Encapsulation
In designing a suitable hydrogel for cell encapsulation, there are several criteria that must be considered. Cells are suspended in a liquid precursor solution prior to encapsulation. The process by which gelation occurs must be mild and cell friendly. The hydrogel structure and chemistry must be suitable for cell survival and tissue formation, while its degradation must closely follow tissue growth. Finally, the degradation products must not adversely affect the encapsulated cells. These steps are depicted in Figure 1. If the hydrogel is to be formed in vivo, biocompatibility of precursors and degradation products as well as changes in degradation kinetics due to the in vivo environment must be considered. Of equal importance is designing an encapsulation process that can be approved by the FDA and be clinically acceptable by patients and surgeons. Together, these stringent requirements limit the number of suitable chemistries and formulations that can be used to encapsulate cells. However, as we gain a better understanding of the criteria involved in cell encapsulation strategies, more and more successful systems are being developed. Table 1 lists several examples of recent materials that have been developed and successfully used to encapsulate cells for a range of tissue engineering applications. We include their precursors, crosslinking and degradation mechanisms, and cells encapsulated.
FIG. 1.
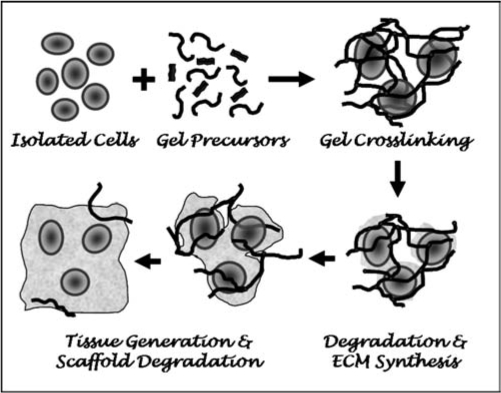
Cell encapsulation strategies involve mixing cells with precursors in a liquid solution followed by gelation and encapsulation of cells. The crosslinked structure will largely dictate diffusion of newly synthesized ECM molecules, and therefore, degradation of the scaffold must closely follow ECM synthesis and macroscopic tissue development. The gel precursors, gelation mechanisms, and degradation products must be cytocompatible.
Table 1.
Recent Biodegradable Hydrogels Used in Cell Encapsulation Strategies for Tissue Engineeringa
| Material | Gel precursors | Crosslink mechanism | Degradation mechanism | Cells encapsulated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan | Macromer(s): chitosan grafted with lactic acid and methacrylate | Covalent | Enzymatic (lysozyme) | Chondrocytes12 |
| Initiator: APS/TEMDA | Hydrolyticb | |||
| Macromer(s): chitosan-g-azidobenzoic acid and acryloyl-PEG-RGD | Covalent | Enzymatic (lysozyme) | Cardiomyocytes98 | |
| Alginate-co-Gelatin | Macromer(s): alginate dialdehyde and gelatin | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Hepatocytes90 |
| Crosslinking agent: Boraxc | ||||
| Styrenated gelatin | Macromer(s): styrenated gelatin | Covalent | Enzymatic | Chondrocytes72 |
| Initiator: camphorquinone | ||||
| HA | Macromer(s): methacrylated HA | Covalent | Enzymatic (Hyaluronidase) | Valvular interstitial cells,59 chondrocytes,106,134 fibroblasts135 |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Macromers(s): acrylated HA and PEG-(SH)4 | Covalent | Enzymatic (Hyaluronidase) | Human MSCs26 | |
| Other: triethanolamine (pH 8.0) | ||||
| Macromers(s): thiol-modified HA and PEG diacrylate | Covalent | Enzymatic (Hyaluronidase)b | Adipocyte-stem cells,109 chick dorsal root ganglia110 | |
| Chondroitin sulfate | Macromers(s): methacrylated chondroitin sulfate | Covalent | Enzymatic (Chondroitinase) | Chondrocytes61,62 |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Synthetic ECM analogs | Macromer(s): thiol-modified HA or thiol-modified chondroitin sulfate, thiol-modified gelatin and PEG diacrylate | Covalent | Enzymaticb | Murine fibroblasts,28 MSCs113 |
| PEGylated fibrinogen | Macromers(s): fibrinogen-g-PEGacryloyl and PEG diacrylate | Covalent | Enzymatic (plasmin, MMPs) | Bone marrow stromal cells85 |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Self-assembled peptide gels | Macromer(s): self-assembling peptide | Physical | Dissolution or enzymaticd | Human MSCs,75 preosteoblastes,84 endothelial cells,136 cardiomyocytes,137 embryonic SCs137 |
| Other: electrolyte solutions (e.g., sucrose, DMEM) | ||||
| Elastin-like polypeptide | Macromer(s): genetically engineered ELP | Covalent | Enzymatic | Chondrocytes,77 adipose-derived SCs78 |
| Other: tissue transglutaminase and calcium chloride | ||||
| Macromer(s): PLA-b-PEG-b-PLA dimethacrylate | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Osteoblasts,39 neural precursor cells138 | |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Poly(ethylene glycol) based | Macromer(s): PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL dimethacrylate | Covalent | Enzymatic (lipase) Hydrolytic | Chondrocytes139 |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Macromer(s): PEG-(poly(glycerol succinic acidmethacrylate4))2 | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Chondrocytes37 | |
| Initiator: Eosin-Y, NVP, triethanolamine | ||||
| Macromer(s): OPF and NVP | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Chondrocytes126 | |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Polyfumarate based | Macromer(s): poly(lactide-co-ethylene oxide-co-fumarate) and MMP-diacrylate | Covalent | Hydrolytic Enzymatic (MMPs) | Bone marrow stromal cells133 |
| Initiator: APS/TEMDA | ||||
| Macromer(s): poly(ethylene glycol) di-[ethyl phosphatidyl (ethylene glycol) methacrylate] | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Goat MSCs51 | |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 | ||||
| Phosphoester | Macromer(s): poly(6-aminohexyl propylene phosphate)-acrylate | Covalent | Hydrolytic | Goat MSCs125 |
| Initiator: Irgacure 2959 |
Studies published prior to 2005 were not included.
Degradation may also occur via hydrolysis.
In addition to Borax, gel also forms crosslinks between amine groups on gelatin and dialdehyde groups on alginate.
Not confirmed.
APS: ammonium persulfate; TEMDA: N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine; PEG: poly(ethylene glycol); HA: hyaluronic acid; Irgacure 2959: 2-hydroxy-1-[4-(hydroxyethoxy) phenol]-2-methyl-1-propanone; ECM: extracellular matrix; MSCs: mesenchymal stem cells; MMPs: metalloproteinases; DMEM: Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium; ELP: Elastin-like peptides; PLA: poly(lactic acid); PCL: poly(8-caprolactone); NVP: N-vinylpyrrolidone; OPF: oligo(polyethylene glycol) fumarate.
Liquid precursors and gelation mechanisms
Hydrogels are formed through a variety of gelation mechanisms where polymer chains are crosslinked by covalent, ionic, or physical bonds. Naturally forming hydrogels are typically formed by either physical or ionic crosslinks. Covalently crosslinked hydrogels have become more attractive, because they offer tunability of many of the hydrogel properties, such as mechanical properties and degradation. However, they introduce additional components into the system that must be examined for cytocompatibility.
Because cells are suspended in a liquid precursor solution prior to the encapsulation process, the choice of precursors is limited to water-soluble components. In addition, the aqueous solution must be buffered with appropriate osmolality to prevent cell lysis. Cell encapsulation strategies involving covalently crosslinked hydrogels are typically fabricated from macromolecular monomers (i.e., macromers) derived from biocompatible polymers rather than low-molecular-weight monomers, which are generally cytotoxic.8,9 In general, macromers with molecular weight of 3 kDa or greater are used when encapsulating cells.
The most common mechanisms to create covalently crosslinked hydrogels for cell encapsulation are through radical chain polymerizations and chemical crosslinking. The combination of radical and step growth polymerization, termed mixed-mode polymerization, has recently been explored for cell encapsulation. Each mechanism utilizes a unique set of liquid precursors containing multifunctional macromers to enable crosslinking. Together, these components must be examined for cytocompatibility, and each system exhibits limitations with respect to its suitability for cell encapsulation.
Radical chain polymerization
Biocompatible polymers (synthetic and natural) have been modified to contain two or more vinyl groups [e.g., (meth)acrylate or fumarate] to create multifunctional macromers. In the presence of an initiator and in certain systems an initiating signal (e.g., a change in temperature or exposure to light), radicals are generated that propagate through multiple carbon–carbon double bonds to form high-molecular-weight kinetic chains that are covalently crosslinked in the network. The presence of initiators, which are typically small molecules, and generation of radicals, however, may be toxic to cells. Radical concentration will be dependent on several factors, including initiator chemistry and concentration, degree of the initiating signal (e.g., light intensity), and polymerization kinetics. Therefore, careful consideration must be taken in choosing the appropriate initiating conditions to minimize exposure to potentially damaging photoinitiator molecules and radicals. Nonetheless, radical chain polymerizations are attractive for encapsulating cells, because the polymerization reaction is fast, on the order of seconds to several minutes.
Thermal,10 redox,11,12 and photoinitiating conditions13,14 have been successfully used to encapsulate a range of cells (Table 1).Redox-initiating systems are comprised of a two-component initiator system consisting of, for example, a peroxide oxidizing agent and an amine reducing agent, which when mixed form active centers to initiate polymerization. The redox system, ammonium persulfate and N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine, has been used to encapsulate bone marrow stromal stem cells and chondrocytes.11,12 Cytotoxicity of several redox-initiating systems was examined, and their toxicity was primarily dependent on the pH of the individual initiators and to a lesser degree on the active centers produced by combining the two initiators.15 Cytotoxicity of several photoinitiators has also been examined where the initiator chemistry and concentration influenced cell viability, which was found to be dependent on cell division rate.16,17 In addition to initiator chemistry and concentration, radical concentration and length of exposure to radicals will have a profound effect on cell viability. For example, two photoinitiators, 2,2-demethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone (DMPA) and 2-hydroxy-1-[4-(hydroxyethoxy)phenyl]-2-methyl-1-propanone (Irgacure 2959, a trademark name of Ciba Specialty Chemical, Newport, Delaware) at concentrations deemed cytocompatible were employed to encapsulate bovine chondrocytes in poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) hydrogels by UV exposure for 6 min.17 Cell survival was high when Irgacure 2959 was used, but few cells survived using DMPA. However, Mann et al.18 successfully photoencapsulated rat aortic smooth muscle cells in a biodegradable poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogel using DMPA in N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP) when a short 20-s UV exposure was used. These findings suggest that radical chemistry, photoinitiator efficiency (i.e., the ability of a photoinitiator to produce radicals), and exposure time dramatically affect cell viability. Visible light photoinitiating conditions have also been used to encapsulate cells to minimize the potentially damaging effects of UV irradiation. Several common visible light photoinitiating systems used in cell encapsulation include eosin-Y and triethanolamine and camphorquinone.19,20,21 Together, these studies illustrate the importance of choosing the appropriate initiator(s) and initiating conditions for cell encapsulation strategies, which involve radical chain polymerizations.
Chemical crosslinking
Alternative strategies have been employed to encapsulate cells in hydrogels fabricated by chemical crosslinking or step-growth polymerization. One attractive feature of this type of crosslinking mechanism is that it does not require any additional components, such as an initiator.22 For example, hyaluronic acid (HA) has been modified with thiol side groups, which in the presence of air form a disulfide crosslink.23 This mechanism was used to successfully encapsulate fibroblasts; however, the gelation process required several hours.23 Alternatively, Michael-type addition reactions have been explored for cell encapsulation, which exhibit gelation times on the order of minutes.22,24 Michael-type addition involves the reaction between a nucleophilic thiolate, the reactive form of the thiol, and an electrophile, such as unsaturated ester, to form a thioether linkage. Typically, thiolates form under slightly basic conditions (e.g., pH 8.0), but the pKa of the thiol can be adjusted by altering the chemistry adjacent to the thiol to increase its reactivity at neutral pH.24,25 Multifunctional macromers containing vinyl sulfones and acrylates have been used as the unsaturated ester macromer for cell encapsulation strategies.22,26,27 Thiol containing polysaccharides and proteins or peptides containing cysteine amino acid residues have been used in cell encapsulation strategies.22,24,28 These studies demonstrate that the basic environment, as well as the thiolate reactive species, does not adversely affect cells. Unlike chain polymerizations that produce kinetic chains as a result of the polymerization, chemical crosslinking does not produce any additional components during polymerization; therefore, no additional components are produced during degradation.29 However, the gelation rates are typically slower compared to radical chain polymerizations.
Mixed-mode polymerizations
More recently, a mixed-mode gelation scheme of chain and step-growth polymerization reactions was employed based on multifunctional macromers containing thiols and acrylate macromers where the reaction is mediated by radicals in the presence or absence of an initiator.30,31 This reaction scheme involves the step-growth reaction between a thiol and acrylate to form thioether linkages and the homopolymerization of acrylates to form kinetic chains. The molar ratio of thiol to acrylates in the reaction mixture controls many of the network properties, and presence of thiols reduces the molecular weight of the resulting kinetic chains.32,33 Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were successfully encapsulated in a mixed-mode reaction (step and chain polymerizations) from PEG diacrylate and multithiol containing peptides.31 The authors noted that when high concentrations of unreacted thiol remained in the network, significant cell death occurred, which was attributed to changes in pH.31 Several advantages for using mixed-mode polymerization reactions for cell encapsulation include faster polymerization times compared to step-growth polymerization or chemical crosslinking, shorter kinetic chains (which will be important in tuning degradation), and the ease with which peptides may be incorporated into the network.
Hydrogel structure and chemistry
The ability to control the molecular structure of the hydrogel enables tuning of many hydrogel macroscopic properties important in scaffold design, for example, swelling, mechanical properties, diffusion, and degradation. These properties are closely related to the degree of crosslinking where an increase in the crosslinking density results in gels with higher mechanical strengths, but lower swelling capabilities and decreased mesh sizes. The mesh size is a measure of the distance between crosslinks and influences diffusive properties through the hydrogel. In designing hydrogels for tissue engineering, there are competing factors in the design. For example, a hydrogel with high mechanical strength is attractive when the gel will experience large stresses, for example, in situ placement for articular cartilage tissue engineering. However, swelling and diffusional capabilities are sacrificed. Therefore, there is a fine balance in designing a hydrogel with appropriate properties that exhibit sufficient mechanical integrity without sacrificing cell viability and tissue growth. Chondrocytes have been successfully encapsulated in high-moduli biodegradable PEG gels that exhibit initial compressive moduli of ∼900 kPa, which is in the range of native cartilage.34 A recent review by Peppas et al.2 describes the theoretical approaches for determining network structure of crosslinked hydrogels using equilibrium-swelling and rubber-elasticity theories.
An important aspect in cell encapsulation strategies is the fact that cells are entrapped in a 3D structure. The mesh size is significantly smaller than the size of a cell and therefore acts to retain the cells inside the gel. Typical mesh sizes for crosslinked PEG hydrogels used in cell encapsulation are in the range of ∼40 to 200 Å, which was estimated from equilibrium-swelling theory.35 The mesh size will not only control diffusion of nutrients and other biological signaling molecules (e.g., growth factors) from the surrounding medium to the entrapped cells, but will also control diffusion of tissue-specific molecules secreted by the cells. Several studies have demonstrated that the hydrogel structure dramatically influences distribution of newly synthesized matrix molecules within the hydrogel, playing a pivotal role in 3D macroscopic tissue development.14,36,37
In addition to the structure, hydrogel chemistry plays an important role in cell function and initially cell survival. Hydrophilic polymers, such as PEG, resist protein adsorption and cell adhesion. Chondrocytes and osteoblasts encapsulated in PEG hydrogels survive well without the addition of any biological signals.38,39 However, many cell types are attachment dependent and require cell adhesion sites to survive. For example, human MSCs encapsulated in PEG hydrogels require the addition of a cell adhesion component, such as the oligopeptide sequence Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD), for cell survival.31,40 Rat marrow stromal cells encapsulated in biodegradable oligo(polyethylene glycol) fumarate (OPF) hydrogels, however, survived without any cell adhesion moieties.11 The incorporation of other biological cues into synthetic hydrogels has also been investigated to control cellular functions and promote tissue growth.41–43 Alternatively, strategies have developed natural hydrogel environments by mimicking the native extracellular matrix (ECM), which not only promote cell-matrix interactions with the hydrogel but also sequester important growth factors that can augment tissue growth.28,44
Gel degradation
There are a number of factors that influence hydrogel degradation including the number of degradable linkages as well as its chemistry presence of cells and the in vivo environment. Biodegradable hydrogels formed via ionic or physical crosslinks may break down by processes that reverse the gelation mechanism. For example solutes present in the in vivo environment and/or deposition of new tissue can lead to exchange of divalent cations for monovalent cations in alginate gels leading to dissolution of polymer chains or the disruption of hydrogen bonds associated with physical crosslinks. In many cases hydrogels are designed with explicit degradable sequences programmed into the crosslinked structure which enable control and tuning of the degradation rate and profile. These gels are designed to degrade by hydrolysis, enzyme-mediated processes, or a combination.
Unlike porous prefabricated scaffolds where significant tissue can fill the large open pores (typically ∼200 μm in diameter) prior to scaffold degradation tissue evolution and hydrogel degradation are closely linked in cell encapsulation strategies. Specifically, the gel mesh size, which controls ECM diffusion increases with degradation and therefore must closely match secretion of newly synthesized ECM. If degradation occurs too quickly the cell-laden hydrogel will simply dissolve. If degradation is too slow, a buildup of ECM will occur in the pericellular regions. The latter event will not only affect tissue growth, but may also influence cell function. For instance, many ECM proteins bind to cell surface receptors to initiate a cascade of intracellular signaling events that may ultimately affect the type of tissue produced.45
During degradation, hydrolytically or enzymatically susceptible linkages are broken, and when a certain number of linkages are broken (depending on the structure of the gel), mass is eroded from the gel. A typical plot of mass loss versus time for crosslinked hydrogels is shown in Figure 2. There are several characteristic features of the mass loss profile. As linkages are cleaved, mass loss increases with time until there are no longer a sufficient number of cross-links to maintain a 3D network, at which time the remaining highly branched chains dissolve. At this point, a sharp increase in mass loss is observed, and this phenomenon is referred to as reverse gelation. The degradation profile can be controlled through a variety of mechanisms.46 Degradation kinetics can be controlled through the chemistry of the degradable linker; for example, ester linkages associated with lactic acid degrade much more rapidly than ester linkages of caprolactone,47 while enzymatically susceptible linkages having slightly different amino acid sequences can have different reactivities toward the same enzyme.48 The structure of the gel can also influence the degradation profile where more highly crosslinked gels lead to overall longer degradation times.46 In radical chain polymerization reactions, the kinetic chain length also influences mass loss profiles. When longer kinetic chains are present, more crosslinks must be broken before the chains are eroded from the gel, which increases overall degradation time and delays reverse gelation.46,49
FIG. 2.
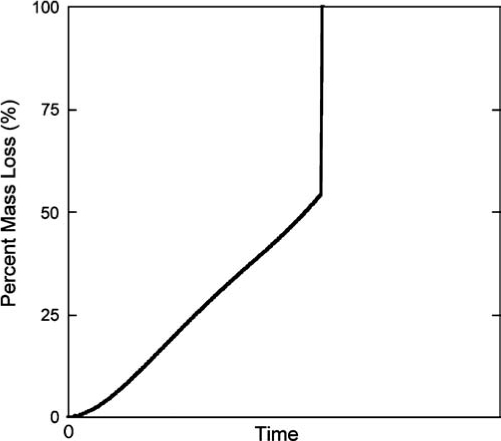
A typical plot of mass loss versus degradation time for a crosslinked hydrogel. A characteristic feature of the degradation profile is the point where there are fewer than two crosslinks per polymer chain and the highly branched polymer chains dissolve. This point is referred to as reverse gelation. A number of factors influence the degradation rate and profile, including the chemistry, as well as the number of degradable linkages present in the hydrogel and the crosslinking density of the hydrogel.
The majority of hydrogels engineered to degrade hydrolytically typically hydrolyze via an ester linkage located in the crosslink or backbone of the hydrogel. Examples of hydrolytically labile linkages used in hydrogels for cell encapsulation include α-hydroxy esters (e.g., lactic acid and epsilon-caprolactone),36,39 fumarate,11,50 and phosphoesters.51,52 In hydrolytically degradable hydrogels, degradation immediately begins when the linkages are exposed to an aqueous environment, and therefore, degradation rate and overall time must be tuned for each cell type and tissue application. Figure 3A and B illustrates the impact of tuning the degradation of a hydrolytically degradable gel on cell–cell interactions for osteogenesis of human MSCs.53 When encapsulated in PEG hydrogels, MSCs adopted a spherical morphology. However, with sufficient degradation, cells were able to migrate toward one another to form cell–cell junctions and adopt a more osteoblastic phenotype. Bimodal degradation schemes have also been investigated to tune degradation and gel structure for enhanced tissue deposition.54–56 For example, bimodal degradable hydrogels were prepared by copolymerizing biodegradable PEG and PVA macromers, which exhibit different degradation kinetics for cartilage tissue engineering (Fig. 3C, D).56 The fast-degrading linkages associated with PVA enabled significant deposition of the cartilage-specific matrix molecules in the hydrogel after 2 weeks in vitro. Interestingly, void spaces were present, which was attributed to the fast degradation of the PVA chains, but by 6 weeks, cells and tissue had completely filled these gaps and a macroscopic tissue containing glycosaminoglycans and collagen was present.
FIG. 3.
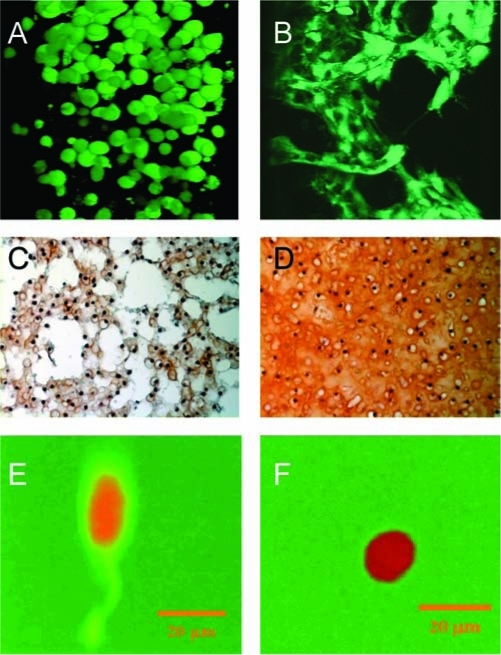
(A, B) Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) encapsulated in a photopolymerized hydrolytically biodegradable PEG hydrogel and cultured in osteogenic medium. After encapsulation and when limited degradation has occurred, hMSCs adopt a spherical morphology (A). With sufficient degradation, hMSCs are able to migrate and form cell–cell junctions and adopt a more osteogenic-like phenotype (B). Reproduced with permission from Cushing et al.53 (C, D) Engineered cartilage after 2 (C) and 6 (D) weeks in vitro culture (glycosaminoglycans stained red). Chondrocytes were encapsulated in a biodegradable PEG-co-PVA hydrogel exhibiting bimodal degradation. Reprinted with permission from Martens et al.56 (E, F) Fibroblasts encapsulated in an enzymatically degradable PEG hydrogel. When crosslinks are degraded, fluorescence is emitted at the degradation site enabling spatial visualization of the degrading gel. After 7 days postencapsulation, cell-mediated degradation was observed only in the direction of the extended process (E); however, when treated with an MMP inhibitor, no cell-mediated degradation was observed (F). Reproduced with permission from Lee et al.64 Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/ten.
Alternatively, hydrogels have been engineered where their degradation is cell mediated, leading to localized degradation of the gel. This process may provide a means to maintain mechanical integrity of the hydrogel during degradation. There are two common strategies for creating enzymatically degradable hydrogels. Hydrogels may be fabricated from natural biopolymers, for example, HA, which degrades by cell-secreted enzymes, for example, hyaluronidase.23,57 The other strategy is to program short amino acid sequences into the hydrogel network, which are susceptible to enzymatic cleavage.58 Examples of enzymatically degradable segments used in cell encapsulation strategies include polysaccharide-based gels (e.g., HA24,57,59,60 and chondroitin sulfate28,61,62) and peptide-based linkages that are susceptible to plasmin63 or matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).22 Figure 3E and F illustrates localized degradation of aproteolytically degradable PEG hydrogel in the immediate region of an encapsulated fibroblast.64 The authors incorporated a collagenase-sensitive fluorgenic substrate into PEG hydrogels to enable visualization at the site of degradation. In the presence of an MMP inhibitor, no lamellipodia projecting from the edge of the cell or fluorescent activity was observed.
The presence of cells, as well as the in vivo environment, will also impact degradation kinetics of the hydrogel. Martens et al.56 demonstrated that overall degradation time was significantly less when biodegradable PEG hydrogels containing poly(lactic acid) (PLA)–degradable linkages were cultured in serum containing cell culture medium compared to a phosphate-buffered saline solution. This study demonstrates that the complex mixture of proteins present in serum, including bovine serum albumin, which has previously been shown to degrade PLA,65,66 significantly enhances degradation of hydrolytically labile PEG-PLA–based hydrogels. On the contrary, this effect was not observed in PEG-based hydrogels containing fumarate as the degradable linker, suggesting the fumarate ester linkage may not be as susceptible to serum containing proteases.10 Interestingly, Bryant et al.36 demonstrated that the presence of cells slowed degradation of biodegradable PEG gels containing PLA as the degradable linkage. This finding was attributed, in part, to differences in water contents between the cell-free and cell-laden gels. The in vivo environment is known to accelerate cleavage of ester bonds65,66 and, for example, significantly accelerated degradation of hydrolytically biodegradable PEG-PLA–based gels.36 In tuning the degradation of the hydrogel, there are many factors that must be considered, including the type and length of the degradable linker as well as the culture environment. These factors will directly influence the structural evolution of the hydrogel, which subsequently impact the spatial deposition of newly synthesized tissues.
Practical considerations
Ultimately for a cell encapsulation strategy to be successful, a number of practical factors must be considered in addition to the fundamental design criteria described above. The process must be easily scaled up for manufacturing; marketable; accepted by surgeons, patients, and healthcare providers; and receive FDA approval.67–70 If the encapsulation process is to be performed in situ, additional considerations are necessary. The starting materials must be easy to handle. For example, a viscous solution injected in vivo will remain in place more easily than a low viscosity solution. The encapsulation process must be fast, on the order of seconds to minutes to be clinically accepted. A recent review by Prestwich describes a “user-driven design criteria” approach to tissue engineering and highlights many of these practical considerations.70 Incorporating these considerations into the early stages of the design will significantly enhance the translation of a cell encapsulation strategy from the bench to the clinic.70
Hydrogels Used in Cell Encapsulation and Their Applications in Tissue Engineering
There are two main categories of hydrogels: (i) naturally forming hydrogels, such as collagen, fibrin, and alginate, where all components are natural polymers and (ii) synthetic hydrogels. The latter category encompasses a wide array of hydrogels, including purely synthetic polymers, natural biopolymers that have been modified or synthetically built, and biomimetic hydrogels that incorporate bioactivity into synthetic hydrogels. Synthetic-based hydrogels afford greater control over gelation and polymerization conditions, final macroscopic structure of the hydrogel, and degradation kinetics. In addition, the synthetic approach enables incorporation of biological signals into the network in a highly controlled and reproducible fashion. These attributes are particularly desirable when tuning a cell encapsulation strategy for a specific application. Here, we present several recent advances in synthetic-based hydrogels, which we categorize into three areas: (i) naturally derived hydrogels, (ii) synthetic hydrogels, and (iii) biomimetic hydrogels.
Naturally derived hydrogels
DNA-based gels
Recently, a new class of biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogels was fabricated entirely from synthesized branched DNA molecules. These multibranched DNA macromers are designed to self-assemble, and in the presence of DNA ligase, covalent linkages are formed between the ends of the branches, which lead a crosslinked hydrogel.71 The mechanical properties were tuned through the degree of DNA branching and ranged from 1 to 40 kPa. As a proof of concept, Chinese hamster ovary cells were successfully encapsulated in the DNA crosslinked hydrogel.71
Protein-based gels
Proteins are attractive materials for designing bioactive scaffolds, because cells recognize and bind to specific sites within proteins, as well as secrete enzymes that may degrade specific amino acid sequences. Although many naturally forming protein-based gels, like collagen and fibrin, exhibit these qualities, the gels are not easily tailored. There have been significant advances in peptide-based hydrogels aimed at harnessing these attractive qualities, which are inherent to proteins, but in ways that are tailorable. For example, Ahmed et al.21 explored the use of exogenously delivering inhibitors to control degradation of cell-mediated fibrin gels, which led to enhanced accumulation of tissue. Hoshikawa et al.72 created covalently crosslinked gelatin hydrogels by modifying gelatin with styrene groups, which enabled photocrosslinking. Crosslinking minimized gel shrinkage, which is typically observed with physically crosslinked collagen gels; however, the crosslinking resulted in a marked decrease in cell proliferation when compared to traditional collagen gels.72
As an alternative to natural proteins, several groups have explored synthetic peptides that are relatively short ∼15- to 20-mer amino acid sequences designed to self-assemble into a hydrogel under certain environmental conditions.73–79 One strategy was recently developed based on an amphiphilic peptide containing positively charged lysine residues.75 At neutral pH, the positively charged lysine residues facilitate dissolution in aqueous mediums of low ionic strengths. However, when the peptide solution was mixed with cell culture medium containing a high concentration of electrolytes, the lysine residues become shielded, causing the hydrophobic regions of the peptide to rapidly assemble and form a crosslinked hydrogel. An interesting attribute of this peptide gel is the fact that under a shear stress, the crosslinked gel undergoes shear thinning resulting in a viscous gel, but fully recovers to its original solid network when the stress is relieved. This process enables an already formed cell-laden gel to be delivered in situ through a syringe and was successfully demonstrated with encapsulated MSCs.75
Elastin-like peptides (ELPs) have been genetically engineered with precisely controlled sequences, molecular weights, and gelation temperatures to create a suite of protein-based hydrogels for tissue engineering.78,80,81 When human adipose-derived adult stem cells were encapsulated in ELP hydrogels, the ELP environment was sufficient to promote chondrogenesis without the addition of chondrogenic medium, suggesting that cues from the hydrogel matrix are sufficient to induce stem cell differentiation.78 Self-assembling peptide amphiphile nanofibers have also been designed to include bioactive sequences and have been used in tissue engineering applications.79,82–84 In particular, these nanofibers self-assemble to form hydrogel matrices that support cell encapsulation and have been explored as a preosteoblastic cell carrier for bone regeneration.84
In another study, fibrinogen and its fragments were reacted with PEG diacrylate via Michael-type addition to create a crosslinkable peptide where the core peptide was flanked with multiple PEG tethers each endcapped with an acrylate to create a multivinyl peptide macromer.85 The incorporation of fibrinogen introduces proteolytic and cell adhesion sites into the PEG hydrogel. The properties of the hydrogel and its degradation rates were controlled through the molecular weight of the core fibrinogen fragment. When bovine aortic smooth muscle cells were encapsulated in PEG–fibrinogen gels, cells exhibited spreading and attachment to the gel, whereas in pure PEG gels, cells remained rounded showing no signs of interaction with the gel.
Synthetic peptides hold great promise in designing hydrogel carriers with a wealth of bioactive signals programmed directly into the hydrogel matrix. For example, one could envision incorporation of cell adhesion moieties, biochemical cues to promote tissue deposition, and specific enzyme-sensitive sequences for cell-mediated degradation. However, one of the drawbacks of self-assembled peptides is their weak mechanical properties.74
Polysaccharide-based gels
Several nonmammalian and mammalian polysaccharides have been explored for cell encapsulation, and they include alginate, chitosan, HA, and chondroitin sulfate. Alginate and chitosan form crosslinked hydrogels under certain solution conditions, while HA and chondroitin sulfate must be modified to contain crosslinkable groups to form a hydrogel.
Alginate is a natural, nonmammalian, polysaccharide that forms a gel in the presence of divalent cations via ionic crosslinking. Although the properties of the hydrogel can be controlled to some degree through changes in the alginate precursor (molecular weight, composition, and macromer concentration),86 alginate does not degrade, but rather dissolves when the divalent cations are replaced by monovalent ions. In addition, alginate does not promote cell interactions.87 To overcome these limitations, a biodegradable alginate macromer was synthesized by partial oxidation where the degree of oxidation controlled overall degradation time.88 Cell adhesion has been incorporated into the alginate network either through the addition of RGD, a cell adhesion oligopeptide,87,89 or by copolymerizing alginate with gelatin.90 Oxidized alginate copolymerized with gelatin was recently examined for liver tissue engineering where the gel supported hepatocyte encapsulation and function as seen by an increase in albumin secretion with culture time and complete degradation of the gel occurred in 5 weeks in a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution.90 Light-activated gelation of alginate91 was recently employed to encapsulate rat bone marrow cells through the release of calcium chloride from light-sensitive liposomes suspended in the alginate–cell solution.92
Chitosan is made by partially deacetylating chitin, a natural nonmammalian polysaccharide, which exhibits a close resemblance to mammalian polysaccharides making it attractive for cell encapsulation.93 Chitosan degrades predominantly by lysozyme through hydrolysis of the acetylated residues.94 Higher degrees of deacetylation lead to slower degradation times, but better cell adhesion due to increased hydrophobicity.95 Under dilute acid conditions (pH < 6), chitosan is positively charged and water soluble, while at physiological pH, chitosan is neutral and hydrophobic, leading to the formation of a solid physically crosslinked hydrogel. The addition of polyol salts has been used to enable encapsulation of cells at neutral pH, where gelation becomes temperature dependent.96 Several approaches have explored methods to covalently crosslink chitosan to better control the macroscopic gel properties. Chitosan has a plethora of amine and hydroxyl groups that can be readily modified. For example, Hong et al.12 modified chitosan by grafting methacrylic acid to create a crosslinkable macromer while also grafting lactic acid to enhance its water solubility at physiological pH. This crosslinked chitosan hydrogel readily degraded in the presence of lysozyme and showed signs of degradation in the presence of chondrocytes without exogenous delivery of the enzyme. In a separate study, a photopolymerizable chitosan macromer was synthesized by modifying chitosan with photoreactive azidobenzoic acid groups.97,98 Upon exposure to UV in the absence of any initiator, reactive nitrene groups are formed that react with each other or other amine groups on the chitosan to form an azo crosslink.97,98 The addition of RGD was necessary to promote myoblast cell attachment, and cardiomyocytes were successfully encapsulated in this crosslinked gel.98 In a separate study, polylysine was grafted to chitosan to enhance the microenvironment for neural cell growth.99 When fetal mouse cortical cells were encapsulated in chitosan-g-polylysine gels, neurite extensions were observed in the 3D gel cultures and the number of cells expressing neurite extensions was dependent on the amount of grafted polylysine.99
Chondroitin sulfate makes up a large percentage of structural proteoglycans found in many tissues, including skin, cartilage, tendons, and heart valves, making it an attractive biopolymer for a range of tissue engineering applications. Photocrosslinked chondroitin sulfate hydrogels have been prepared by modifying chondroitin sulfate with methacrylate groups.61,100 The hydrogel properties were readily controlled by the degree of methacrylate substitution and macromer concentration in solution prior to polymerization.100 Further, the negatively charged polymer creates increased swelling pressures allowing the gel to imbibe more water without sacrificing its mechanical properties.61,100 Crosslinked chondroitin sulfate remained susceptible to chondroitinase, an enzyme produced by mammalian cells, which specifically targets its degradation.61,100 Interestingly, when chondrocytes were encapsulated in chondroitin sulfate hydrogel, there was no evidence of glycosaminoglycan or collagen production after 6 weeks in vitro.62 However, the addition of PEG into the crosslinked network supported ECM deposition, suggesting that pure chondroitin sulfate has an inhibitory effect on chondrocyte bioactivity.62 This finding was attributed to the fact that glycosaminoglycans interact with a wide variety of proteins,101 which may prevent serum proteins from interacting with the entrapped cells and therefore negatively impacting ECM deposition. However, copolymer hydrogels comprising chondroitin sulfate and an inert polymer, such as PEG or PVA, may provide a more suitable environment for cartilage regeneration.61,62,100 Photopolymerizable chondroitin sulfate has been recently employed as an adhesive layer to enhance adhesion of the cell–hydrogel construct to the host tissue.102
HA, a glycosaminoglycan present in many tissues throughout the body, exhibits a wide range of biological activities, playing an important role in embryonic development, wound healing, and angiogenesis.103,104 In addition, HA interacts with cells through cell-surface receptors to influence intracellular signaling pathways.105 Together, these qualities make HA attractive for tissue engineering scaffolds. Recent strategies have included modifying HA with crosslinkable moieties, namely methacrylates57,59,106 and thiols,24,28 to enable cell encapsulation. Crosslinked HA gels remain susceptible to degradation by hyaluronidase, which breaks HA into oligosaccharide fragments of varying molecular weights.24,59 Interestingly, low-molecular-weight oligosaccharide HA fragments significantly enhanced valvular interstitial cell proliferation and elastin production. This study demonstrated a positive feedback mechanism where cell-mediated degradation enhanced heart valve tissue growth.59 Chung et al.106 encapsulated auricular chondrocytes in photopolymerized HA hydrogels where the gel structure was controlled by the macromer concentration and macromer molecular weight. When implanted in subcutaneous pockets of nude mice, the resulting cartilaginous tissue growth was highly dependent on the initial HA structure where the lowest macromer concentration, corresponding to the lowest crosslinking density, promoted better tissue growth while molecular weight had less of an effect. In addition, photopolymerized hyaluronan and dextran hydrogels have been recently described as environments that maintain long-term culture of undifferentiated human embryonic stem cells.107,108 The stem cells were easily extracted from the hydrogel by enzyme treatment and maintained their ability to form embryoid bodies and differentiation capability.107,108
HA hydrogels have also been fabricated through Michael-type addition reaction mechanisms where either acrylated HA is reacted with PEG-tetrathiol26 or thiol-modified HA is reacted with PEG diacrylate.24,28,109 The former reaction scheme was used to produce networks for MSC encapsulation and bone regeneration.26 In this study, new bone growth was observed in an in vivo rat calvarial defect model when the HA hydrogel containing MSCs filled the defect compared to the hydrogel alone.26 The latter reaction scheme has been used in several cell encapsulation strategies.24,28,109 For example, adipose-derived stem cells were encapsulated in these HA hydrogels in the presence or absence of a placental decellular matrix.109 Cell morphology was markedly different depending on the seeding strategy. Interestingly, cells that were allowed to adhere to the decellular matrix prior to encapsulation showed reduced ability to differentiate into adipocytes when compared to cells localized in the bulk HA gel, which retained a spherical morphology.109 A similar HA hydrogel was used to encapsulate dorsal root ganglia and which promoted neurite outgrowth.110
A new class of hydrogels has been fabricated based on click chemistry111 in which HA derivatives were synthesized to contain azide or alkyne functional groups that when reacted together form a crosslinked network suitable for cell encapsulation.112
Synthetic ECM analogs
In an effort to recapitulate the native microenvironment that surrounds cells, synthetic ECM hydrogels have been designed that incorporate both proteins and glycosaminoglycans into a single hydrogel matrix. For example, thiol-modified HA or thiol-modified chondroitin sulfate macromers were combined with thiol-modified gelatin macromers, and when reacted with PEG diacrylate, they formed a crosslinked ECM-like microenvironment.28 These synthetic ECM analogs degraded through hydrolysis of the ester bond associated with the acrylate, and the degree of degradation was dependent on the type of glycosaminoglycans employed.28 However, both gel compositions rapidly degraded in the presence of hyaluronidase and collagenase.28 MSCs were encapsulated in the synthetic ECM environments within an osteochondral defect of a rabbit model.113 The combination of MSCs and the synthetic ECMs resulted in superior tissue regeneration that captured the native zonal architecture of cartilage.113
Synthetic-based hydrogels
PEG-based hydrogels
PEG has been the most widely used synthetic polymer to create macromers for cell encapsulation. A number of studies have used poly(ethylene glycol) di(meth)acrylate to encapsulate a variety of cells.18,35,114,115 However, PEG hydrogels formed from these macromer precursors are very stable in vitro showing no signs of degradation. The ester bond linking the PEG crosslink with the kinetic chain is susceptible to degradation where degradation may occur slowly in vivo. A recent study by Stosich and Mao116 implanted human MSC–derived adipogenic cells encapsulated in PEG hydrogels into subcutaneous pockets of athymic nude mice.116 After 4 weeks postimplantation, lipid vacuoles resembling fatty tissue had formed in gels containing adipogenic cells, while undifferentiated MSCs did not produce any fatty-like tissue.116 It was noted that the slow-degrading nature of PEG gels, which were formed from PEG diacrylate precursors, was advantageous for regenerating adipose tissue.
Biodegradable PEG hydrogels have been prepared from triblock copolymers of poly(α-hydroxy esters)-b-poly (ethylene glycol)-b-poly(α-hydroxy esters) endcapped with (meth)acrylate functional groups to enable crosslinking.47 PLA and poly(8-caprolactone) (PCL) have been the most commonly used poly(α-hydroxy esters) in creating biodegradable PEG macromers for cell encapsulation. The degradation profile and rate are controlled through the length of the degradable block and the chemistry.47,117 The ester bonds may also degrade by esterases present in serum, which accelerates degradation.56 The degradation of PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL hydrogels was temporally controlled by exogenously delivering lipase to match tissue growth for cartilage tissue engineering.118 Osteoblasts encapsulated in partially degrading PEG gels produced higher amounts of osteopontin and collagen type I gene expression with greater mineralization deposition compared to nondegradable gels.39 Neural cells encapsulated in PLA-b-PEG-b-PLA hydrogels formed microtissues within the construct consisting of multiple cells, and when significant degradation had occurred, neurite processes extending radially from the microtissues were visible.119 Together, these studies demonstrate the importance of degradation in macroscopic tissue growth.
More recently, biodegradable PEG hydrogels were fabricated from precursors of PEG-bis-[2-acryloyloxy propanoate], which completely degraded in ∼5 weeks in PBS at physiological temperatures.120 The suitability of these new degradable PEG hydrogels for use in tissue engineering applications was demonstrated by encapsulation of fibroblasts. Interestingly, when linear HA was incorporated into these gels to produce semi-interpenetrating networks, the morphology of the encapsulated fibroblasts was markedly different. In PEG gels, a rounded morphology was observed; however, with increasing HA, there was an increase in fibroblast spreading.120
As an alternative to linear PEG macromers, PEG-based dendrimers of poly(glycerol-succinic acid)-PEG were developed, which contain multiple reactive vinyl groups per PEG molecule.121 An attractive feature of these materials is the ability to control the degree of branching, which consequently affects the overall structural properties of the hydrogel and its degradation. Degradation will occur through the ester linkages present in the dendrimer backbone.37 These systems were recently used to encapsulate chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering where gels with lowest crosslinking density enabled the greatest amount of tissue deposition compared to gels with higher crosslinking densities.37
Polyfumarate-based hydrogels
A relatively new class of biodegradable synthetic hydrogels has been developed, which is based on a natural compound, fumarate.50,122–124,125 Polyfumarate is particularly attractive, because it contains polymerizable vinyl groups and ester linkages that are susceptible to hydrolytic degradation and which break down into fumarate making it an ideal candidate for creating crosslinked and biodegradable hydrogels.10,11 In a recent study by Dadsetan et al.,126 activity of encapsulated chondrogenic cells was examined as a function of crosslinking density, which was controlled by changes in OPF or NVP concentrations prior to polymerization. Increasing NVP and/or OPF concentration resulted in increased mechanical strength, decreased swelling, and longer degradation times. Gel crosslinking significantly impacted chondrocyte gene expression and tissue production, where gels with the highest crosslinking density impeded tissue growth. To create a more native environment in these synthetic hydrogels, MSCs were initially entrapped in gelatin microparticles prior to encapsulation in OPF gels.127 This strategy was employed for cartilage tissue engineering and led to an increase in cartilage-specific matrix gene expression and matrix production when compared to MSCs entrapped directly in OPF gels.127
Phosphoester
Another class of biodegradable hydrogels has been recently developed based on polyphosphoesters or polyphosphates where the phosphoester linkage is susceptible to hydrolytic degradation resulting in the release of phosphate.51,52,125,128 For example, a phosphoester was incorporated into the backbone of a crosslinkable PEG macromer, poly(ethylene glycol)-di-[ethylphosphatidyl (ethylene glycol) methacrylate] (PhosPEG-dMA), to form a biodegradable hydrogel that was partially degraded when placed in PBS at 37°C for 9 weeks.52 Interestingly, the addition of alkaline phosphatase, an ECM component synthesized by bone cells, enhanced degradation, indicating an enzymatic degradation mechanism.51 Another interesting attribute of this hydrogel is its degradation product, phosphoric acid, which readily reacts with calcium ions in the medium to produce insoluble calcium phosphate inducing autocalcification within the hydrogels.51 More recently, poly(6-aminoethyl propylene phosphate), a polyphosphoester, was modified with methacrylates to create multivinyl macromers where the degradation rate was controlled by the degree of derivitization of the polyphosphoester polymer.125 Goat MSCs were successfully encapsulated in this gel, and in the presence of osteogenic medium, mineralization was present throughout the hydrogel.125 These gels are particularly attractive for bone tissue engineering where the degradation products facilitate bone deposition in the construct, which may subsequently influence cellular functions.
Biomimetic hydrogels
Synthetic hydrogels are hydrophilic and generally inert polymers, which resist protein adhesion and do not support cell interactions with the hydrogel. Therefore, synthetic hydrogels offer a great platform with which to create a structural 3D support system where bioactive cues may be incorporated into the hydrogel in a highly controlled manner. Many studies have incorporated bioactive moieties into synthetic networks by the addition of larger molecules, such as whole proteins, or short oligopeptides. The latter method eliminates the need to maintain the protein's bioactive structure during modification (e.g., during the addition of reactive groups to the peptide to enable covalent linking into the network) and allows for better control over cellular signals presented in the hydrogel.
The incorporation of short bioactive oligopeptide sequences into biodegradable hydrogels has been achieved through several mechanisms. For radical chain polymerizations, peptides have been tethered to a monovinyl group by reacting free amines on the peptide with acryloyl-PEG-N-hydroxysuccinimide.129 Alternatively, oligopeptides have been synthesized with thiol containing cysteine residues, which readily react with vinyl groups through Michael-type addition to enable incorporation into the network. For example, RGD containing a single cysteine enables tethering of RGD to the network,130 while multiple cysteines enable RGD to be embedded in the crosslink.31 The cell adhesion oligopeptide RGD has been the most widely studied. Other bioactive functionalities have been incorporated into the network to target a specific cellular function. For example, dexamethasone was tethered to a PEG hydrogel through hydrolytically degradable PLA linkages for controlled and localized release of osteogenic factors for MSC differentiation.43 When a collagen adhesive oligopeptide sequence was incorporated into synthetic PEG hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering, matrix production was significantly enhanced when compared to pure PEG hydrogels.131 This finding was attributed to an enhanced localization of collagen in the pericellular matrix, which led to a more native environment surrounding the cell.131
Cells naturally produce proteolytic enzymes, which play key roles in cell migration and tissue remodeling. Several approaches have been used to incorporate cell-mediated degradation sequences into the crosslinks of synthetic hydrogels. Oligopeptides that are susceptible to enzyme degradation, for example, by matrix MMPs or plasmin, have been modified with multiple reactive moieties to enable crosslinking into the network either through chain poly-merization18 or step-growth polymerization.130 Lutolf and Hubbell132 incorporated a combination of cell-recognizable sequences into synthetic networks that enabled cell migration only when both RGD- and MMP-sensitive crosslinkers were present. Chondrocytes were encapsulated in a proteolytically degradable PEG hydrogel, which was formed by reacting a four- or eight-arm PEG-vinylsulfone with a dithiol MMP-sensitive crosslinker. An increase in the number of PEG arms in the PEG macromer resulted in gels with increased crosslinking density as evident by an increase in the elastic modulus and decreased swelling. Tissue was localized in the pericellular regions of the hydrogel, but was more diffuse in gels with lower crosslinking. In addition, cartilage ECM gene expression was significantly higher in lower crosslinked gels containing the MMP crosslinker, compared to gels fabricated with a nondegradable crosslinker. More recently, He and Jabbari133 developed a degradable hydrogel where poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) macromers were reacted with an MMP-degradable diacrylate crosslinker to create a bimodal degradable hydrogel for bone marrow stromal cells. Significant degradation occurred by 15 days when treated with MMP-13; however, when a non-MMP-sensitive crosslinker was employed, little hydrolytic degradation was observed by 15 days.
Summary and Future Directions
Encapsulating cells in biodegradable hydrogels offers numerous attractive features for tissue engineering, including ease of handling where cells are simply mixed in a solution prior to gelation enabling a highly uniform cell seeding, a highly hydrated tissue-like environment, and the ability to form in vivo. In addition, many of the properties important to the design of a scaffold, for example, swelling, mechanical properties, degradation, and diffusion, are closely linked to the crosslinked structure of the hydrogel, which is controlled through a variety of different processing conditions. For example, changes in the macromer molecular weight, macromer concentration in solution prior to polymerization, or macromer functionality will affect the final gel structure and its degradation. Degradation may be tuned by incorporating hydrolytically or enzymatically labile segments into the hydrogel or by employing natural biopolymers that are susceptible to enzymatic degradation. Finally, a nice attribute of hydrogels is the fact that multiple chemistries can be incorporated into the network with high fidelity through modifications with crosslinkable functionalities.
A number of cells have been encapsulated in biodegradable hydrogels for a wide range of tissue engineering applications, but the most common applications have been in cartilage and bone tissue engineering. We have learned from multiple studies that the crosslinked structure controls ECM diffusion and plays a pivotal role in macroscopic tissue development. Lower molecular weight ECM molecules secreted by the cells can diffuse into the extracellular spaces of the hydrogel and lay down the foundation for new tissue development, but it is not until sufficient degradation occurs before larger ECM molecules, namely, collagen, are able to diffuse. Therefore, a challenge that faces hydrogel designers is controlling the gel structure and closely matching its degradation to ECM secretion. Temporal control over the degradation, such as in the case of exogenously delivering enzymes to control degradation, offers the ability to control the network structure such that sufficient tissue is secreted and deposited in the hydrogel network before complete degradation. In cell-mediated degradation strategies, cells locally degrade the network, providing localized open space for new tissue deposition without degrading the bulk hydrogel. The latter two strategies may enable us to overcome many of the hurdles by promoting macroscopic tissue growth in crosslinked hydrogels. In summary, hydrogels offer great promise in designing suitable environments that provide not only a structural support for cells and new tissue growth, but also harness a variety of biological cues to promote differentiation and new tissue growth.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the NIDCR through a research grant number K22DE 016608 and Department of Education's GAANN fellowship to G.D.N. We are also grateful for the helpful comments and review from Katie Walline.
References
- 1.Peretti G.M. Campo-Ruiz V. Gonzalez S. Randolph M.A. Xu J.W. Morse K.R. Roses R.E. Yaremchuk M.J. Tissue engineered cartilage integration to live and devitalized cartilage: a study by reflectance mode confocal microscopy and standard histology. Connect. Tissue Res. 2006;47:190. doi: 10.1080/03008200600809935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Peppas N.A. Hilt J.Z. Khademhosseini A. Langer R. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2006;18:1345. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mikos A.G. Papadaki M.G. Kouvroukoglou S. Ishaug S.L. Thomson R.C. Islet transplantation to create a bioartificial pancreas—mini review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1994;43:673. doi: 10.1002/bit.260430717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cao Y.L. Rodriguez A. Vacanti M. Ibarra C. Arevalo C. Vacanti C.A. Comparative study of the use of poly(glycolic acid), calcium alginate and pluronics in the engineering of autologous porcine cartilage. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1998;9:475. doi: 10.1163/156856298x00578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sims C.D. Butler P.E. Cao Y.L. Casanova R. Randolph M.A. Black A. Vacanti C.A. Yaremchuk M.J. Tissue engineered neocartilage using plasma derived polymer substrates and chondrocytes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998;101:1580. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199805000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Perka C. Spitzer R.S. Lindenhayn K. Sittinger M. Schultz O. Matrix-mixed culture: new methodology for chondrocyte culture and preparation of cartilage transplants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000;49:305. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(20000305)49:3<305::aid-jbm2>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee K.Y. Mooney D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001;101:1869. doi: 10.1021/cr000108x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Peppas N.A. Hydrogels in Medicine and Pharmacy. Boca Raton, Fl: CRC Press; 1986. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schweikl H. Spagnuolo G. Schmalz G. Genetic and cellular toxicology of dental resin monomers. J. Dent. Res. 2006;85:870. doi: 10.1177/154405910608501001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Temenoff J.S. Park H. Jabbari E. Conway D.E. Sheffield T.L. Ambrose C.G. Mikos A.G. Thermally cross-linked oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels support osteogenic differentiation of encapsulated marrow stromal cells in vitro. Biomacromolecules. 2004;5 doi: 10.1021/bm030067p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Temenoff J.S. Park H. Jabbari E. Sheffield T.L. LeBaron R.G. Ambrose C.G. Mikos A.G. In vitro osteogenic differentiation of marrow stromal cells encapsulated in biodegradable hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2004;70A:235. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hong Y. Song H.Q. Gong Y.H. Mao Z.W. Gao C.Y. Shen J.C. Covalently crosslinked chitosan hydrogel: properties of in vitro degradation and chondrocyte encapsulation. Acta Biomater. 2007;3:23. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2006.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Williams C.G. Kim T.K. Taboas A. Malik A. Manson P. Elisseeff J. In vitro chondrogenesis of bone marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells in a photopolymerizing hydrogel. Tissue Eng. 2003;9:679. doi: 10.1089/107632703768247377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bryant S.J. Anseth K.S. Controlling the spatial distribution of ECM components in degradable PEG hydrogels for tissue engineering cartilage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003;64A:70. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.10319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Temenoff J.S. Shin H. Conway D.E. Engel P.S. Mikos A.G. In vitro cytotoxicity of redox radical initiators for cross-linking of oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) macromers. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:1605. doi: 10.1021/bm030056w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bryant S.J. Nuttelman C.R. Anseth K.S. Cyto-compatibility of ultraviolet, visible light photoinitiating systems on cultured NIH/3T3 fibroblasts in vitro. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2000;11:439. doi: 10.1163/156856200743805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Williams C.G. Malik A.N. Kim T.K. Manson P.N. Elisseeff J.H. Variable cytocompatibility of six cell lines with photoinitiators used for polymerizing hydrogels and cell encapsulation. Biomaterials. 2005;26:1211. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.04.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mann B.K. Gobin A.S. Tsai A.T. Schmedlen R.H. West J.L. Smooth muscle cell growth in photopolymerized hydrogels with cell adhesive and proteolytically degradable domains: synthetic ECM analogs for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2001;22:3045. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(01)00051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cruise G.M. Scharp D.S. Hubbell J.A. Characterization of permeability and network structure of interfacially photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 1998;19:1287. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cruise G.M. Hegre O.D. Lamberti F.V. Hager S.R. Hill R. Scharp D.S. Hubbell J.A. In vitro and in vivo performance of porcine islets encapsulated in interfacially photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate membranes. Cell Transplant. 1999;8:293. doi: 10.1177/096368979900800310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ahmed T.A.E. Griffith M. Hincke M. Characterization and inhibition of fibrin hydrogel-degrading enzymes during development of tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:1469. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Park Y. Lutolf M.P. Hubbell J.A. Hunziker E.B. Wong M. Bovine primary chondrocyte culture in synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive poly(ethylene glycol)-based hydrogels as a scaffold for cartilage repair. Tissue Eng. 2004;10:515. doi: 10.1089/107632704323061870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shu X.Z. Liu Y.C. Luo Y. Roberts M.C. Prestwich G.D. Disulfide cross-linked hyaluronan hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:1304. doi: 10.1021/bm025603c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shu X.Z. Liu Y.C. Palumbo F.S. Lu Y. Prestwich G.D. In situ crosslinkable hyaluronan hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2004;25:1339. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lutolf M.P. Tirelli N. Cerritelli S. Cavalli L. Hubbell J.A. Systematic modulation of Michael-type reactivity of thiols through the use of charged amino acids. Bioconjug. Chem. 2001;12:1051. doi: 10.1021/bc015519e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim J. Kim I.S. Cho T.H. Lee K.B. Hwang S.J. Tae G. Noh I. Lee S.H. Park Y. Sun K. Bone regeneration using hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel with bone morphogenic protein-2 and human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1830. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.11.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tae G. Kim Y.J. Choi W.I. Kim M. Stayton P.S. Hoffman A.S. Formation of a novel heparin-based hydrogel in the presence of heparin-binding biomolecules. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:1979. doi: 10.1021/bm0701189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shu X.Z. Ahmad S. Liu Y.C. Prestwich G.D. Synthesis and evaluation of injectable, in situ crosslinkable synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2006;79A:902. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Metters A. Hubbell J. Network formation and degradation behavior of hydrogels formed by Michael-type addition reactions. Biomacromolecules. 2005;6:290. doi: 10.1021/bm049607o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rydholm A.E. Bowman C.N. Anseth K.S. Degradable thiol-acrylate photopolymers: polymerization and degradation behavior of an in situ forming biomaterial. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4495. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.11.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Salinas C.N. Cole B.B. Kasko A.M. Anseth K.S. Chondrogenic differentiation potential of human mesenchymal stem cells photoencapsulated within poly(ethylene glycol)-arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-serine thiol-methacrylate mixed-mode networks. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:1025. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rydholm A.E. Reddy S.K. Anseth K.S. Bowman C.N. Controlling network structure in degradable thiolacrylate biomaterials to tune mass loss behavior. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:2827. doi: 10.1021/bm0603793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rydholm A.E. Held N.L. Bowman C.N. Anseth K.S. Gel permeation chromatography characterization of the chain length distributions in thiol-acrylate photopolymer networks. Macromolecules. 2006;39:7882. doi: 10.1021/ma060858u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Villanueva I. Hauschulz D.S. Mejic D. Bryant S.J. Static and dynamic compressive strains influence nitric oxide production and chondrocyte bioactivity when encapsulated in PEG hydrogels of different crosslinking densities. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.12.003. In Press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bryant S.J. Anseth K.S. Hydrogel properties influence ECM production by chondrocyte photoencapsulated in poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001;59:63. doi: 10.1002/jbm.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bryant S.J. Durand K.L. Anseth K.S. Manipulations in hydrogel chemistry control photoencapsulated chondrocyte behavior and their extracellular matrix production. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003;67A:1430. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.20003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sontjens S.H.M. Nettles D.L. Carnahan M.A. Setton L.A. Grinstaff M.W. Biodendrimer-based hydrogel scaffolds for cartilage tissue repair. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:310. doi: 10.1021/bm050663e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bryant S.J. Durand K.L. Anseth K.S. Manipulations in hydrogel chemistry control photoencapsulated chondrocyte behavior and their extracellular matrix production. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2003;67A:1430. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.20003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Benoit D.S.W. Durney A.R. Anseth K.S. Manipulations in hydrogel degradation behavior enhance osteoblast function and mineralized tissue formation. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:1663. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.1663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nuttelman C.R. Tripodi M.C. Anseth K.S. Synthetic hydrogel niches that promote hMSC viability. Matrix Biol. 2005;24:208. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2005.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mann B.K. Schmedlen R.H. West J.L. Tethered-TGF-beta increases extracellular matrix production of vascular smooth muscle cells. Biomaterials. 2001;22:439. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Benoit D.S.W. Nuttelman C.R. Collins S.D. Anseth K.S. Synthesis and characterization of a fluvastatin-releasing hydrogel delivery system to modulate hMSC differentiation and function for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2006;27:6102. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nuttelman C.R. Tripodi M.C. Anseth K.S. Dexamethasone-functionalized gels induce osteogenic differentiation of encapsulated hMSCs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2006;76A:183. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cai S.S. Liu Y.C. Shu X.Z. Prestwich G.D. Injectable glycosaminoglycan hydrogels for controlled release of human basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6054. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Guilak F. Alexopoulos L.G. Upton M.L. Youn I. Choi J.B. Cao L. Setton L.A. Haider M.A. The pericellular matrix as a transducer of biomechanical and biochemical signals in articular cartilage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006;1068:498. doi: 10.1196/annals.1346.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Metters A.T. Anseth K.S. Bowman C.N. A statistical kinetic model for the bulk degradation of PLA-b-PEG-b-PLA hydrogel networks: incorporating network non-idealities. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2001;105:8069. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sawhney A.S. Pathak C.P. Hubbell J.A. Bioerodible hydrogels based on photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(alpha-hydroxy acid) diacrylate macromers. Macromolecules. 1993;26:581. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lutolf M.P. Lauer-Fields J.L. Schmoekel H.G. Metters A.T. Weber F.E. Fields G.B. Hubbell J.A. Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: engineering cell-invasion characteristics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:5413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0737381100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Metters A.T. Anseth K.S. Bowman C.N. Fundamental studies of a novel, biodegradable PEG-b-PLA hydrogel. Polymer. 2000;41:3993. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fisher J.P. Jo S. Mikos A.G. Reddi A.H. Thermo-reversible hydrogel scaffolds for articular cartilage engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2004;71A:268. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang D.A. Williams C.G. Yang F. Cher N. Lee H. Elisseeff J.H. Bioresponsive phosphoester hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:201. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang D.A. Williams C.G. Li Q.A. Sharma B. Elisseeff J.H. Synthesis and characterization of a novel degradable phosphate-containing hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2003;24:3969. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cushing M.C. Anseth K.S. Hydrogel cell cultures. Science. 2007;316:1133. doi: 10.1126/science.1140171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rice M.A. Anseth K.S. Encapsulating chondrocytes in copolymer gels: bimodal degradation kinetics influence cell phenotype and extracellular matrix development. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2004;70A:560. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bryant S.J. Bender R.J. Durand K.L. Anseth K.S. Encapsulating chondrocytes in degrading PEG hydrogels with high modulus: engineering gel structural changes to facilitate cartilaginous tissue production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004;86:747. doi: 10.1002/bit.20160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Martens P.J. Bryant S.J. Anseth K.S. Tailoring the degradation of hydrogels formed from multivinyl poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(vinyl alcohol) macromers for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2003;4:283. doi: 10.1021/bm025666v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Smeds K.A. Grinstaff M.W. Photocrosslinkable polysaccharides for in situ hydrogel formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001;54:115. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(200101)54:1<115::aid-jbm14>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.West J.L. Hubbell J.A. Polymeric biomaterials with degradation sites for proteases involved in cell migration. Macromolecules. 1999;32:241. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Masters K.S. Shah D.N. Leinwand L.A. Anseth K.S. Crosslinked hyaluronan scaffolds as a biologically active carrier for valvular interstitial cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26:2517. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Burdick J.A. Chung C. Jia X.Q. Randolph M.A. Langer R. Controlled degradation and mechanical behavior of photopolymerized hyaluronic acid networks. Biomacromolecules. 2005;6:386. doi: 10.1021/bm049508a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li Q. Williams C.G. Sun D.D.N. Wang J. Leong K. Elisseeff J.H. Photocrosslinkable polysaccharides based on chondroitin sulfate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2004;68A:28. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.20007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bryant S.J. Arthur J.A. Anseth K.S. Incorporation of tissue-specific molecules alters chondrocyte metabolism and gene expression in photocrosslinked hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2005;1:243. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2004.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Halstenberg S. Panitch A. Rizzi S. Hall H. Hubbell J.A. Biologically engineered protein-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels: a cell adhesive and plasm in-degradable biosynthetic material for tissue repair. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:710. doi: 10.1021/bm015629o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lee S.H. Moon J.J. Miller J.S. West J.L. Poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels conjugated with a collagenase-sensitive fluorogenic substrate to visualize collagenase activity during three-dimensional cell migration. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3163. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Catiker E. Gumusderelioglu M. Guner A. Degradation of PLA, PLGA homo- and copolymers in the presence of serum albumin: a spectroscopic investigation. Polym. Int. 2000;49:728. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kurono Y. Maki T. Yotsuyanagi T. Ikeda K. Esterase-like activity of human-serum albumin: structure-activity-relationships for the reactions with phenyl acetates and paranitrophenyl esters. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1979;27:2781. doi: 10.1248/cpb.27.2781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Archer R. Williams D.J. Why tissue engineering needs process engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1353. doi: 10.1038/nbt1105-1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chong A.K.S. Chang J. Tissue engineering for the hand surgeon: a clinical perspective. J. Hand. Surg. [Am] 2006;31A:349. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2005.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Detamore M.S. Athanasiou K.A. Mao J. A call to action for bioengineers and dental professionals: directives for the future of TMJ bioengineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007;35:1301. doi: 10.1007/s10439-007-9298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Prestwich G.D. Simplifying the extracellular matrix for 3-d cell culture and tissue engineering: a pragmatic approach. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007;101:1370. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Um S.H. Lee J.B. Park N. Kwon S.Y. Umbach C.C. Luo D. Enzyme-catalysed assembly of DNA hydrogel. Nat. Mater. 2006;5:797. doi: 10.1038/nmat1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hoshikawa A. Nakayama Y. Matsuda T. Oda H. Nakamura K. Mabuchi K. Encapsulation of chondrocytes in photopolymerizable styrenated gelatin for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:2333. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.2333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Semino C.E. Merok J.R. Crane G.G. Panagiotakos G. Zhang S.G. Functional differentiation of hepatocyte-like spheroid structures from putative liver progenitor cells in three-dimensional peptide scaffolds. Differentiation. 2003;71:262. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.2003.7104503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kisiday J. Jin M. Kurz B. Hung H. Semino C. Zhang S. Grodzinsky A.J. Self-assembling peptide hydrogel fosters chondrocyte extracellular matrix production and cell division: implications for cartilage tissue repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:9996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.142309999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Haines-Butterick L. Rajagopal K. Branco M. Salick D. Rughani R. Pilarz M. Lamm M.S. Pochan D.J. Schneider J.P. Controlling hydrogelation kinetics by peptide design for three-dimensional encapsulation and injectable delivery of cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:7791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701980104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chilkoti A. Dreher M.R. Meyer D.E. Design of thermally responsive, recombinant polypeptide carriers for targeted drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002;54:1093. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(02)00060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.McHale M.K. Setton L.A. Chilkoti A. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of enzymatically cross-linked elastin-like polypeptide gels for cartilaginous tissue repair. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:1768. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.1768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Betre H. Ong S.R. Guilak F. Chilkoti A. Fermor B. Setton L.A. Chondrocytic differentiation of human adipose-derived adult stem cells in elastin-like polypeptide. Biomaterials. 2006;27:91. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.05.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Hartgerink J.D. Beniash E. Stupp S.I. Peptide-amphiphile nanofibers: a versatile scaffold for the preparation of self-assembling materials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.072699999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Meyer D.E. Chilkoti A. Genetically encoded synthesis of protein-based polymers with precisely specified molecular weight and sequence by recursive directional ligation: examples from the elastin-like polypeptide system. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:357. doi: 10.1021/bm015630n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Betre H. Setton L.A. Meyer D.E. Chilkoti A. Characterization of a genetically engineered elastin-like polypeptide for cartilaginous tissue repair. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:910. doi: 10.1021/bm0255037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Niece K.L. Hartgerink J.D. Donners J. Stupp S.I. Self-assembly combining two bioactive peptide-amphiphile molecules into nanofibers by electrostatic attraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:7146. doi: 10.1021/ja028215r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Storrie H. Guler M.O. Abu-Amara S.N. Volberg T. Rao M. Geiger B. Stupp S.I. Supramolecular crafting of cell adhesion. Biomaterials. 2007;28:4608. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Sargeant T.D. Guler M.O. Oppenheimer S.M. Mata A. Satcher R.L. Dunand D.C. Stupp S.I. Hybrid bone implants: self-assembly of peptide amphiphile nanofibers within porous titanium. Biomaterials. 2008;29:161. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Almany L. Seliktar D. Biosynthetic hydrogel scaffolds made from fibrinogen and polyethylene glycol for 3D cell cultures. Biomaterials. 2005;26:2467. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.06.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Augst A.D. Kong H.J. Mooney D.J. Alginate hydrogels as biomaterials. Macromol. Biosci. 2006;6:623. doi: 10.1002/mabi.200600069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Rowley J.A. Madlambayan G. Mooney D.J. Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials. Biomaterials. 1999;20:45. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(98)00107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Bouhadir K.H. Lee K.Y. Alsberg E. Damm K.L. Anderson K.W. Mooney D.J. Degradation of partially oxidized alginate and its potential application for tissue engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 2001;17:945. doi: 10.1021/bp010070p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Alsberg E. Kong H.J. Hirano Y. Smith M.K. Albeiruti A. Mooney D.J. Regulating bone formation via controlled scaffold degradation. J. Dent. Res. 2003;82:903. doi: 10.1177/154405910308201111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Balakrishnan B. Jayakrishnan A. Self-cross-linking biopolymers as injectable in situ forming biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2005;26:3941. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Westhaus E. Messersmith P.B. Triggered release of calcium from lipid vesicles: a bioinspired strategy for rapid gelation of polysaccharide and protein hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2001;22:453. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Smith A.M. Harris J.J. Shelton R.M. Perrie Y. 3D culture of bone-derived cells immobilised in alginate following light-triggered gelation. J. Control. Release. 2007;119:94. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Drury J.L. Mooney D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4337. doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(03)00340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Li J. Du Y.M. Liang H.B. Influence of molecular parameters on the degradation of chitosan by a commercial enzyme. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007;92:515. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Mao J.S. Cui Y.L. Wang X.H. Sun Y. Yin Y.J. Zhao H.M. De Yao K. A preliminary study on chitosan and gelatin polyelectrolyte complex cytocompatibility by cell cycle and apoptosis analysis. Biomaterials. 2004;25:3973. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.10.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Chenite A. Chaput C. Wang D. Combes C. Buschmann M.D. Hoemann C.D. Leroux J.C. Atkinson B.L. Binette F. Selmani A. Novel injectable neutral solutions of chitosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials. 2000;21 doi: 10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Yeo Y. Burdick J.A. Highley C.B. Marini R. Langer R. Kohane D.S. Peritoneal application of chitosan and UV-cross-linkable chitosan. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2006;78A:668. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Yeo Y. Geng W.L. Ito T. Kohane D.S. Burdick J.A. Radisic M. Photocrosslinkable hydrogel for myocyte cell culture and injection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. 2007;81B:312. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.30667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Crompton K.E. Goud J.D. Bellamkonda R.V. Gengenbach T.R. Finkelstein D.I. Horne M.K. Forsythe J.S. Polylysine-functionalised thermoresponsive chitosan hydrogel for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28:441. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.08.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bryant S.J. Davis-Arehart K.A. Luo N. Shoemaker R.K. Arthur J.A. Anseth K.S. Synthesis and characterization of photopolymerized multifunctional hydrogels: water-soluble poly(vinyl alcohol) and chondroitin sulfate macromers for chondrocyte encapsulation. Macromolecules. 2004;37:6726. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Jackson R.L. Busch S.J. Cardin A.D. Glycosaminoglycans: molecular-properties, protein interactions, and role in physiological processes. Physiol. Rev. 1991;71:481. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Wang D.A. Varghese S. Sharma B. Strehin I. Fermanian S. Gorham J. Fairbrother D.H. Cascio B. Elisseeff J.H. Multifunctional chondroitin sulphate for cartilage tissue-biomaterial integration. Nat. Mater. 2007;6:385. doi: 10.1038/nmat1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Hascall V.C. Majors A.K. de la Motte C.A. Evanko S.P. Wang A.M. Drazba J.A. Strong S.A. Wight T.N. Intracellular hyaluronan: a new frontier for inflammation? Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1673:3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Laurent T.C. Fraser J.R.E. Hyaluronan. FASEB J. 1992;6:2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Goodison S. Urquidi V. Tarin D. CD44 cell adhesion molecules. J. Clin. Pathol.—Mol. Pathol. 1999;52:189. doi: 10.1136/mp.52.4.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Chung C. Mesa J. Randolph M.A. Yaremchuk M. Burdick J.A. Influence of gel properties on neocartilage formation by auricular chondrocytes photoencapsulated in hyaluronic acid networks. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2006;77A:518. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ferreira L.S. Gerecht S. Fuller J. Shieh H.F. Vunjak-Novakovic G. Langer R. Bioactive hydrogel scaffolds for controllable vascular differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2706. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Gerecht S. Burdick J.A. Ferreira L.S. Townsend S.A. Langer R. Vunjak-Novakovic G. Hyaluronic acid hydrogen for controlled self-renewal and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:11298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703723104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Flynn L. Prestwich G.D. Semple J.L. Woodhouse K.A. Adipose tissue engineering with naturally derived scaffolds and adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3834. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Horn E.M. Beaumont M. Shu X.Z. Harvey A. Prestwich G.D. Horn K.M. Gibson A.R. Preul M.C. Panitch A. Influence of cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels on neurite outgrowth and recovery from spinal cord injury. J. Neurosurg. Spine. 2007;6:133. doi: 10.3171/spi.2007.6.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Crescenzi V. Cornelio L. Di Meo C. Nardecchia S. Lamanna R. Novel hydrogels via click chemistry: synthesis and potential biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:1844. doi: 10.1021/bm0700800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Nandivada H. Jiang X.W. Lahann J. Click chemistry: versatility and control in the hands of materials scientists. Adv. Mater. 2007;19:2197. [Google Scholar]
- 113.Liu Y.C. Shu X.Z. Prestwich G.D. Osteochondral defect repair with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in an injectable, in situ, cross-linked synthetic extracellular matrix. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:3405. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.3405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Liu V.A. Bhatia S.N. Three-dimensional photo-patterning of hydrogels containing living cells. Biomed. Microdevices. 2002;4:257. [Google Scholar]
- 115.Koh W.G. Revzin A. Pishko M.V. Poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogel microstructures encapsulating living cells. Langmuir. 2002;18:2459. doi: 10.1021/la0115740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Stosich M.S. Mao J.J. Adipose tissue engineering from human adult stem cells: clinical implications in plastic and reconstructive surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007;119:71. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000244840.80661.e7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Metters A.T. Bowman C.N. Anseth K.S. A statistical kinetic model for the bulk degradation of PLA-b-PEG-b-PLA hydrogel networks. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000;104:7043. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Rice M.A. Sanchez-Adams J. Anseth K.S. Exogenously triggered, enzymatic degradation of photopolymerized hydrogels with polycaprolactone subunits: experimental observation and modeling of mass loss behavior. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7:1968. doi: 10.1021/bm060086+. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Mahoney M.J. Anseth K.S. Three-dimensional growth and function of neural tissue in degradable polyethylene glycol hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2006;27:2265. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kutty J.K. Cho E. Lee J.S. Vyavahare N.R. Webb K. The effect of hyaluronic acid incorporation on fibroblast spreading and proliferation within PEG-diacrylate based semi-interpenetrating networks. Biomaterials. 2007;28:4928. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Carnahan M.A. Middleton C. Kim J. Kim T. Grinstaff M.W. Hybrid dendritic-linear polyester-ethers for in situ photopolymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002;124:5291. doi: 10.1021/ja025576y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Suggs L.J. Kao E.Y. Palombo L.L. Krishnan R.S. Widmer M.S. Mikos A.G. Preparation and characterization of poly(propylene fumarate-co-ethylene glycol) hydrogels. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1998;9:653. doi: 10.1163/156856298x00073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Jo S. Shin H. Shung A.K. Fisher J.P. Mikos A.G. Synthesis and characterization of oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) macromer. Macromolecules. 2001;34:2839. [Google Scholar]
- 124.Temenoff J.S. Athanasiou K.A. LeBaron R.G. Mikos A.G. Effect of poly(ethylene glycol) molecular weight on tensile and swelling properties of oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate) hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002;59:429. doi: 10.1002/jbm.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Li Q. Wang J. Shahani S. Sun D.D.N. Sharma B. Elisseeff J.H. Leong K.W. Biodegradable and photo-crosslinkable polyphosphoester hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1027. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Dadsetan M. Szatkowski J.P. Yaszemski M.J. Lu L.C. Characterization of photo-cross-linked oligo[poly (ethylene glycol) fumarate] hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:1702. doi: 10.1021/bm070052h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Park H. Temenoff J.S. Tabata Y. Caplan A.I. Mikos A.G. Injectable biodegradable hydrogel composites for rabbit marrow mesenchymal stem cell and growth factor delivery for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28:3217. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.03.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Du J.Z. Sun T.M. Weng S.Q. Chen X.S. Wang J. Synthesis and characterization of photo-cross-linked hydrogels based on biodegradable polyphosphoesters and poly (ethylene glycol) copolymers. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:3375. doi: 10.1021/bm700474b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Hern D.L. Hubbell J.A. Incorporation of adhesion peptides into nonadhesive hydrogels useful for tissue resurfacing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998;39:266. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(199802)39:2<266::aid-jbm14>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lutolf M.R. Weber F.E. Schmoekel H.G. Schense J.C. Kohler T. Muller R. Hubbell J.A. Repair of bone defects using synthetic mimetics of collagenous extracellular matrices. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003;21:513. doi: 10.1038/nbt818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Lee H.J. Lee J.S. Chansakul T. Yu C. Elisseeff J.H. Yu S.M. Collagen mimetic peptide-conjugated photo-polymerizable PEG hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2006;27:5268. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Lutolf M.P. Hubbell J.A. Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:47. doi: 10.1038/nbt1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.He X.Z. Jabbari E. Material properties and cytocompatibility of injectable MMP degradable poly(lactide ethylene oxide fumarate) hydrogel as a carrier for marrow stromal cells. Biomacromolecules. 2007;8:780. doi: 10.1021/bm060671a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Chung C. Mesa J. Miller G.J. Randolph M.A. Gill T.J. Burdick J.A. Effects of auricular chondrocyte expansion on neocartilage formation in photocrosslinked hyaluronic acid networks. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:2665. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.12.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Yeh J. Ling Y.B. Karp J.M. Gantz J. Chandawarkar A. Eng G. Blumling J. Langer R. Khademhosseini A. Micromolding of shape-controlled, harvestable cell-laden hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2006;27:5391. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Narmoneva D.A. Oni O. Sieminski A.L. Zhang S.G. Gertler J.P. Kamm R.D. Lee R.T. Self-assembling short oligopeptides and the promotion of angiogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4837. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Davis M.E. Motion J.P.M. Narmoneva D.A. Takahashi T. Hakuno D. Kamm R.D. Zhang S.G. Lee R.T. Injectable self-assembling peptide nanofibers create intra-myocardial microenvironments for endothelial cells. Circulation. 2005;111:442. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000153847.47301.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Mahoney M.J. Anseth K.S. Contrasting effects of collagen and bFGF-2 on neural cell function in degradable synthetic PEG hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2007;81A:269. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Rice M.A. Anseth K.S. Controlling cartilaginous matrix evolution in hydrogels with degradation triggered by exogenous addition of an enzyme. Tissue Eng. 2007;13:683. doi: 10.1089/ten.2006.0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


