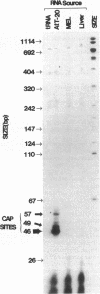
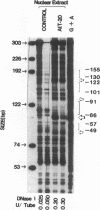
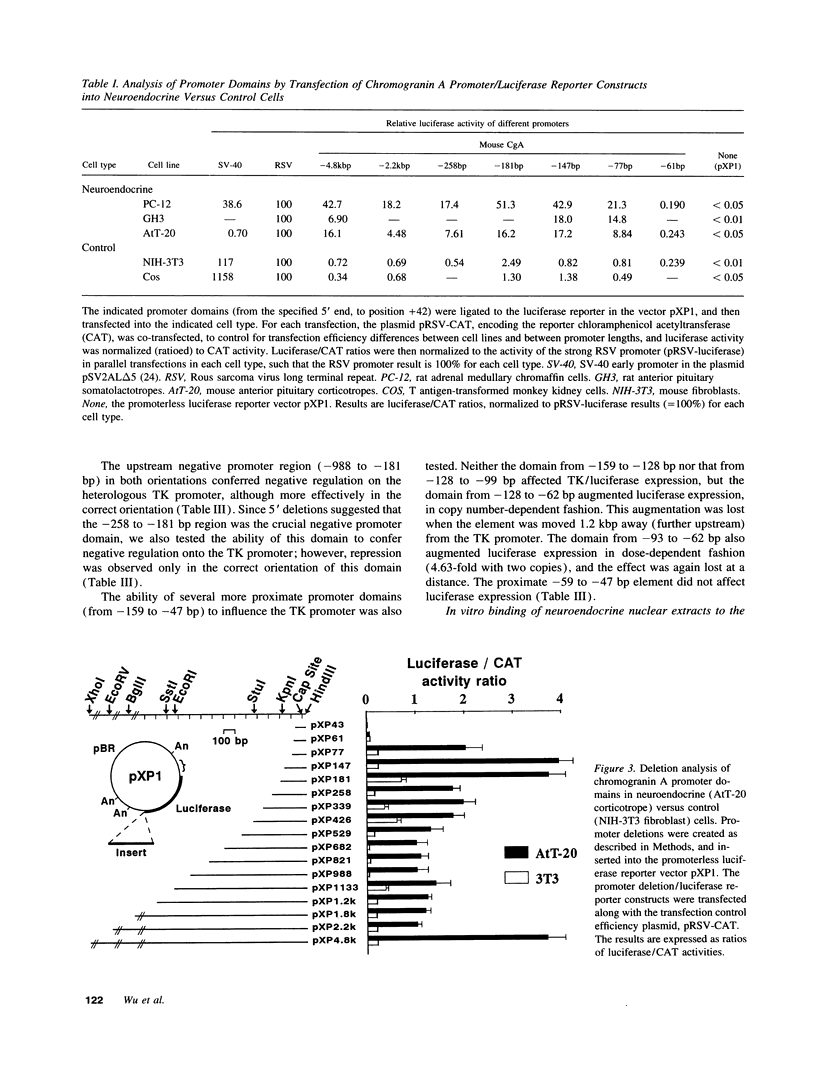
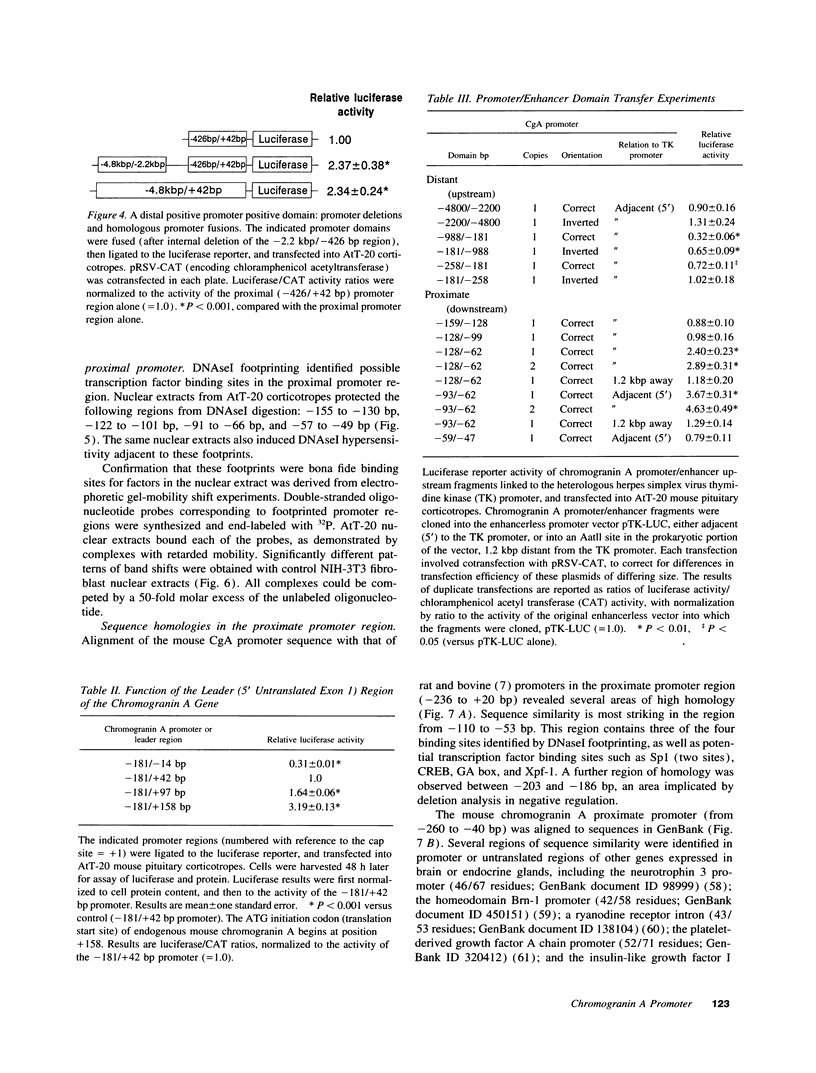
Abstract
The acidic secretory protein chromogranin A universally occurs in amine and peptide hormone and neurotransmitter storage granules throughout the neuroendocrine system. What factors govern the activity of the chromogranin A gene, to yield such a widespread yet neuroendocrine-selective pattern of expression? To address this question, we isolated the mouse chromogranin A gene promoter. The promoter conferred cell type-specific expression in several neuroendocrine cell types (adrenal medullary chromaffin cells, anterior pituitary corticotropes, and anterior pituitary somatolactotropes) but not in control (fibroblast or kidney) cells. In neuroendocrine cells, analysis of promoter deletions established both positive and negative transcriptional regulatory domains. A distal positive domain (-4.8/-2.2 kbp) was discovered, as well as negative (-258/-181 bp) and positive (-147/-61 bp) domains in the proximate promoter. The proximate promoter contained a minimal neuroendocrine-specific element between -77 and -61 bp. Sequence alignment of the mouse promoter with corresponding regions in rat and bovine clones indicated that the mouse sequence shares over 85% homology with rat and 52% with bovine promoters. DNaseI footprinting and electrophoretic gel mobility shift assays demonstrated the presence of nuclear factors in neuroendocrine cells that recognized the proximate promoter. We conclude that the chromogranin A promoter contains both positive and negative domains governing its cell type-specific pattern of transcription, and that a small proximate region of the promoter, containing novel as well as previously described elements, interacts specifically with neuroendocrine nuclear proteins, and is thereby sufficient to ensure widespread neuroendocrine expression of the gene.
Full text
PDF




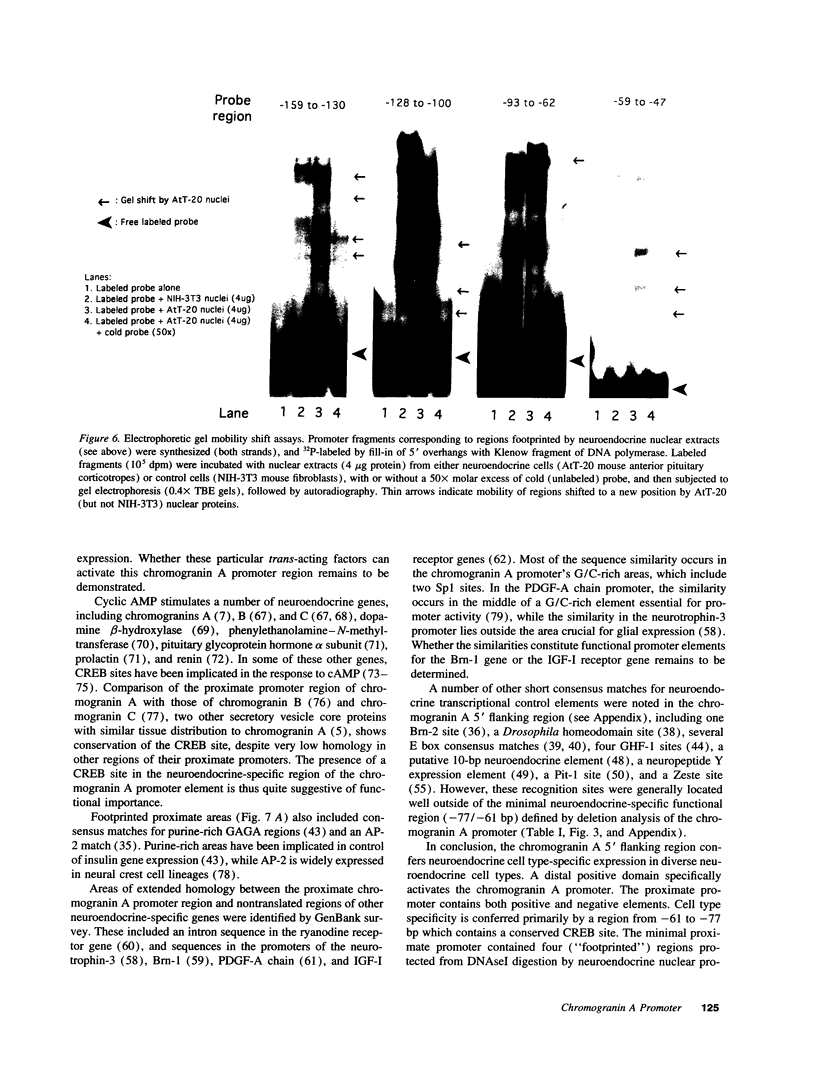
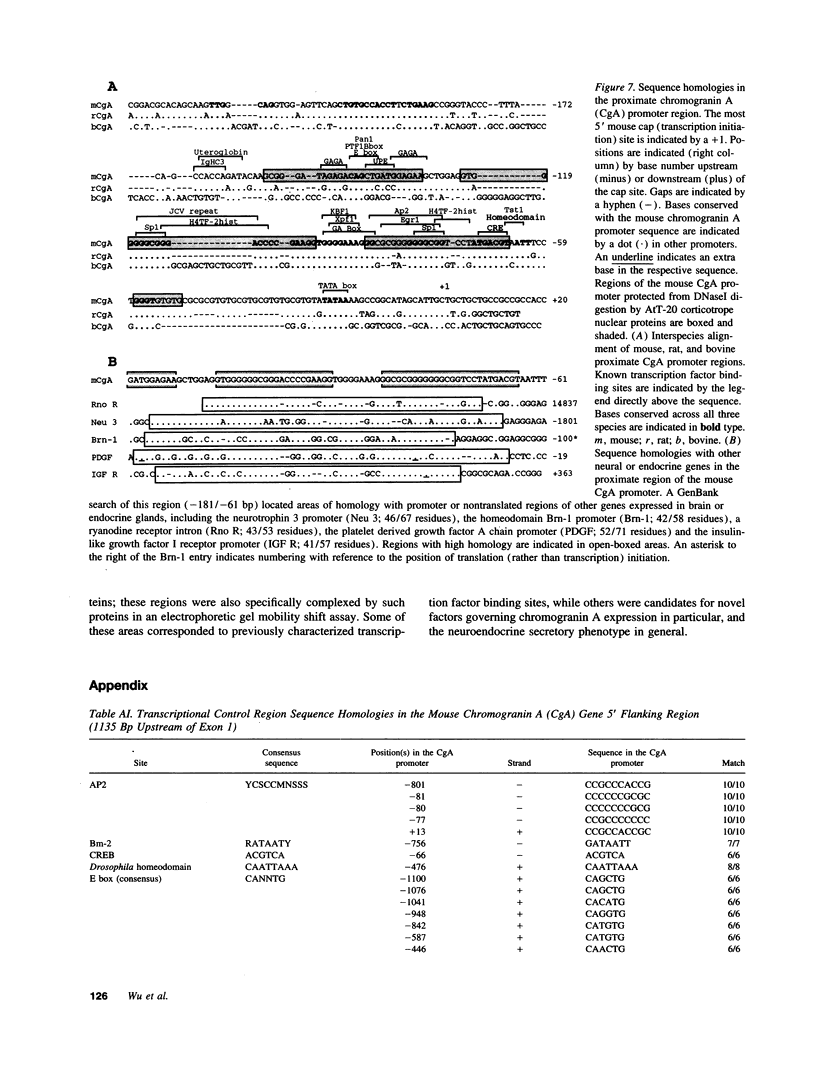
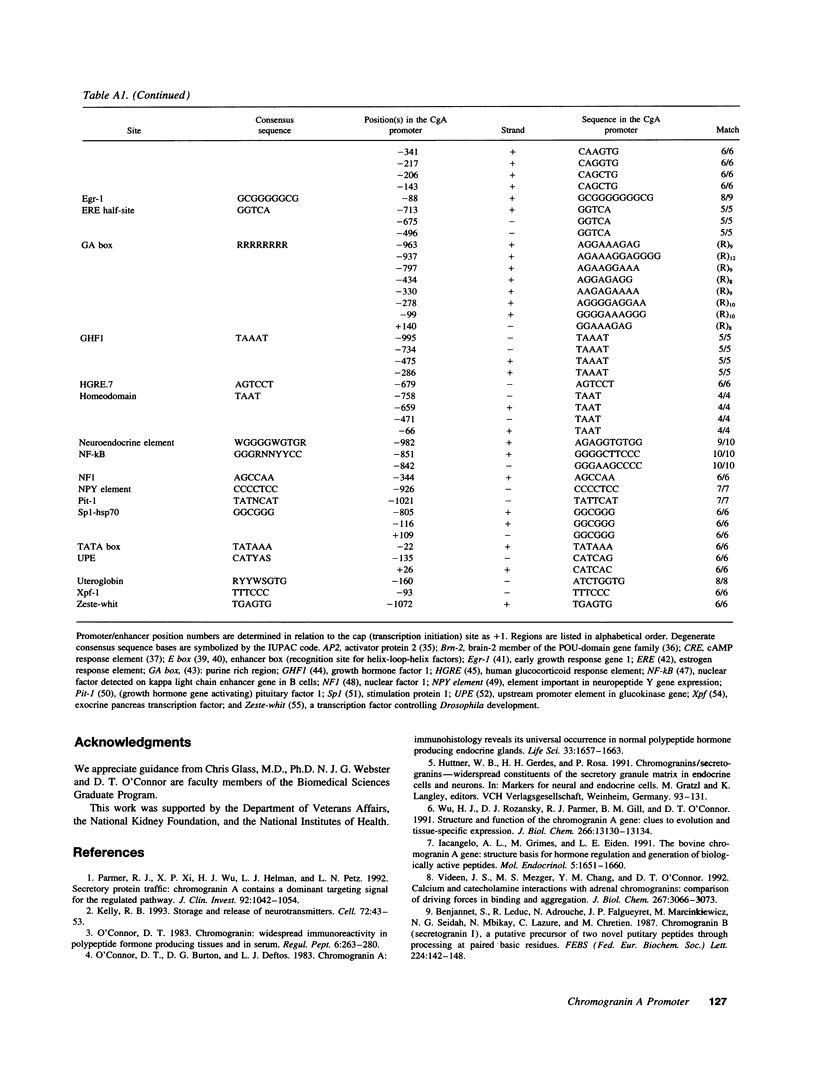


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbosa J. A., Gill B. M., Takiyyuddin M. A., O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin A: posttranslational modifications in secretory granules. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):174–190. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjannet S., Leduc R., Adrouche N., Falgueyret J. P., Marcinkiewicz M., Seidah N. G., Mbikay M., Lazure C., Chretien M. Chromogranin B (secretogranin I), a putative precursor of two novel pituitary peptides through processing at paired basic residues. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors and the control of Drosophila development. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenig B., Brem G. Genomic organization and analysis of the 5' end of the porcine ryanodine receptor gene (ryr1). FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):277–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80076-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Geisse S., Wenz M., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The nucleotide sequences recognized by the glucocorticoid receptor in the rabbit uteroglobin gene region are located far upstream from the initiation of transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2771–2778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02208.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Schnermann J., Smart A. M., Brosius F. C., Killen P. D., Briggs J. P. Cyclic AMP selectively increases renin mRNA stability in cultured juxtaglomerular granular cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24138–24144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson I. M., Mains R. E. Cell-type specific posttranslational processing of peptides by different pituitary cell lines. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):133–140. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz A. B., Neibergs H. L., Womack J. E. Assignment of eight loci to bovine syntenic groups by use of PCR: extension of a comparative gene map. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(2):106–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00431254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillen L., Miserez B., Claeys M., Aunis D., De Potter W. Posttranslational processing of proenkephalins and chromogranins/secretogranins. Neurochem Int. 1993 Apr;22(4):315–352. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Lewis K., Rothenberg B. E. High efficiency vectors for cosmid microcloning and genomic analysis. Gene. 1989 Jun 30;79(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90088-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Wahl G. M. Cosmid vectors for genomic walking and rapid restriction mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:604–610. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasciotto B. H., Gorr S. U., Bourdeau A. M., Cohn D. V. Autocrine regulation of parathyroid secretion: inhibition of secretion by chromogranin-A (secretory protein-I) and potentiation of secretion by chromogranin-A and pancreastatin antibodies. Endocrinology. 1990 Sep;127(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-3-1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Gutierrez J., Hsu C. M., Iacangelo A., Eiden L. E. Sequence analysis, tissue distribution and regulation by cell depolarization, and second messengers of bovine secretogranin II (chromogranin C) mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9208–9213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. P., Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M. Sequences that direct rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression. J Neurochem. 1992 Jun;58(6):2044–2052. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm S., Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription factor NF-kappa B: structure-function relationship of its protein subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):297–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2900297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haisenleder D. J., Yasin M., Marshall J. C. Enhanced effectiveness of pulsatile 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate in stimulating prolactin and alpha-subunit gene expression. Endocrinology. 1992 Dec;131(6):3027–3033. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.6.1280210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara Y., Rovescalli A. C., Kim Y., Nirenberg M. Structure and evolution of four POU domain genes expressed in mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3280–3284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Grimes M., Eiden L. E. The bovine chromogranin A gene: structural basis for hormone regulation and generation of biologically active peptides. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1651–1660. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Okayama H., Eiden L. E. Primary structure of rat chromogranin A and distribution of its mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro H., Kim K. T., Joh T. H., Kim K. S. Neuron-specific expression of the human dopamine beta-hydroxylase gene requires both the cAMP-response element and a silencer region. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17987–17994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen K., Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Espel E., Janich S., Cato A. C., Mugele K., Beato M. Partial overlapping of binding sequences for steroid hormone receptors and DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the rabbit uteroglobin gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4535–4552. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung Y. K., Kunczt C. J., Pearson R. K., Dixon J. E., Fricker L. D. Structural characterization of the rat carboxypeptidase-E gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Sep;5(9):1257–1268. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-9-1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapiloff M. S., Farkash Y., Wegner M., Rosenfeld M. G. Variable effects of phosphorylation of Pit-1 dictated by the DNA response elements. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):786–789. doi: 10.1126/science.1652153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay T. W., Jameson J. L. Identification of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone-responsive region in the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1767–1773. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1282668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Storage and release of neurotransmitters. Cell. 1993 Jan;72 (Suppl):43–53. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy G. C., Rutter W. J. Pur-1, a zinc-finger protein that binds to purine-rich sequences, transactivates an insulin promoter in heterologous cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11498–11502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre C., Imagawa M., Dana S., Grindlay J., Bodner M., Karin M. Tissue-specific expression of the human growth hormone gene is conferred in part by the binding of a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):971–981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson M. A., Jetton T. L. Evolutionary conservation of elements in the upstream glucokinase promoter. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Feb;21(1):160–163. doi: 10.1042/bst0210160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula P. W., Goldfine I. D. Cloning and characterization of the human insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene 5'-flanking region. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):43–50. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel G., McKinnon D. Molecular basis of neural-specific gene expression. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:323–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A., Sabban E. L. Regulation of expression of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in PC12 cells by glucocorticoids and cyclic AMP analogues. J Neurochem. 1992 Dec;59(6):2040–2047. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minth C. D., Dixon J. E. Expression of the human neuropeptide Y gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12933–12939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Timmons P. M., Hébert J. M., Rigby P. W., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-2 is expressed in neural crest cell lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):105–119. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi W. S., Levine M. A., Seuanez H. N., Dean M., O'Brien S. J. The human chromogranin A gene: chromosome assignment and RFLP analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Nov;45(5):814–818. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M., Bartlett P. F. Molecular regulation of neural crest development. Mol Neurobiol. 1993 Summer;7(2):111–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02935639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray S. S., Deaven L. L., Burton D. W., O'Connor D. I., Mellon P. L., Deftos L. J. The gene for human chromogranin A (CgA) is located on chromosome 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 15;142(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Chromogranin A: immunohistology reveals its universal occurrence in normal polypeptide hormone producing endocrine glands. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 24;33(17):1657–1663. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90721-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin: widespread immunoreactivity in polypeptide hormone producing tissues and in serum. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmer R. J., Miles L. A., Xi X. P., Gill B. M., Wu H. J., O'Connor D. T. Processing of chromaffin granule proteins: a profusion of proteases? Neurochem Int. 1993 Apr;22(4):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(93)90018-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmer R. J., Xi X. P., Wu H. J., Helman L. J., Petz L. N. Secretory protein traffic. Chromogranin A contains a dominant targeting signal for the regulated pathway. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):1042–1054. doi: 10.1172/JCI116609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl T. M., Phillips E., Song K. Y., Gerdes H. H., Huttner W. B., Rüther U. The organisation of the mouse chromogranin B (secretogranin I) gene. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80194-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain transcription factors: pou-er-ful developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):897–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel A., Bräunling O., Rüther U., Huttner W. B., Gerdes H. H. The organisation of the mouse secretogranin II gene. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81509-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shintani A., Ono Y., Kaisho Y., Sasada R., Igarashi K. Identification of the functional regulatory region of the neurotrophin-3 gene promoter. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Jan;17(1-2):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90081-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon-Chazottes D., Wu H., Parmer R. J., Rozansky D. J., Szpirer J., Levan G., Kurtz T. W., Szpirer C., Guenet J. L., O'Connor D. T. Assignment of the chromogranin A (Chga) locus to homologous regions on mouse chromosome 12 and rat chromosome 6. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):252–255. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler D., Rupprecht R., Van L. P., Holsboer F. Identification and characterization of a 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-responsive element in the human corticotropin-releasing hormone gene promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Nov;6(11):1931–1941. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.11.1480179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto Y., Wang Z. Y., Kobler K., Deuel T. F. Promoter region of the human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1686–1690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. E., Zimmer W. E., Wear L. B., MacMillan L. A., Thompson W. J., Huttner W. B., Hidaka H., Scammell J. G. Differential regulation of chromogranin B/secretogranin I and secretogranin II by forskolin in PC12 cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Jan;12(1-3):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90084-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro M., Pawlak A., Jost J. P. Positive and negative regulatory elements of chicken vitellogenin II gene characterized by in vitro transcription competition assays in a homologous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3047–3051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Videen J. S., Mezger M. S., Chang Y. M., O'Connor D. T. Calcium and catecholamine interactions with adrenal chromogranins. Comparison of driving forces in binding and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3066–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D. C., Marley P. D., Livett B. G. Coordinate and differential regulation of proenkephalin A and PNMT mRNA expression in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: responses to cAMP elevation and phorbol esters. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90138-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Lin X. H., Qiu Q. Q., Deuel T. F. Modulation of transcription of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene by a promoter region sensitive to S1 nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):17022–17031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schmid K. W., Feichtinger H., Bussolati G., Grimelius L., Krisch K., Kerl H., O'Connor D., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the occurrence and properties of chromogranin A and B and secretogranin II in endocrine tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Nov;12(11):877–884. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198811000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrich S. L., Meister A., Rutter W. J. Exocrine pancreas transcription factor 1 binds to a bipartite enhancer element and activates transcription of acinar genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4985–4997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience. 1992 Aug;49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Oliver G., De Robertis E. M. Vertebrate homeodomain proteins: families of region-specific transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. J., Rozansky D. J., Parmer R. J., Gill B. M., O'Connor D. T. Structure and function of the chromogranin A gene. Clues to evolution and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13130–13134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S. O., Chikaraishi D. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the rat tyrosine hydroxylase gene requires synergy between an AP-1 motif and an overlapping E box-containing dyad. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]