Abstract
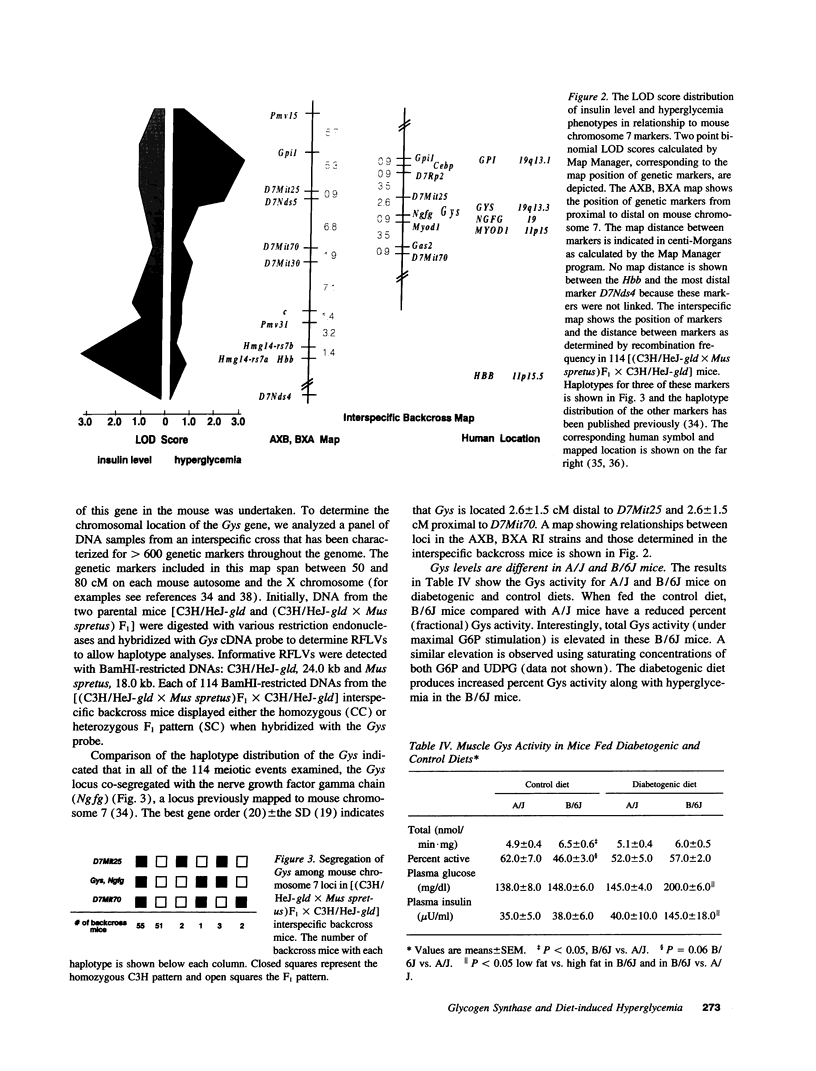
Inbred mouse strains fed a diabetogenic diet have different propensities to develop features analogous to type 2 diabetes mellitus. To define chromosomal locations that control these characteristics, recombinant inbred strains from diabetes-prone C57BL/6J (B/6J) and diabetes-resistant A/J strains were studied. Insulin levels and hyperglycemia correlated with two different regions of mouse chromosome 7 (two point LOD scores > 3.0). For insulin levels, 15 of 16 recombinant inbred strains were concordant with a region that contains the tubby mutation that results in hyperinsulinemia. For hyperglycemia, 19 of 23 strains were concordant with the D7Mit25 marker and 20 of 23 strains with the Gpi-1 locus on proximal mouse chromosome 7. Using more stringent criteria for hyperglycemia, 10 of 11 strains characterized as A/J or B/6J like were concordant with D7Mit25. This putative susceptibility locus is consistent with that of the glycogen synthase gene (Gys) recently suggested as a candidate locus by analyses of type 2 diabetes patients. Fractional glycogen synthase activity in isolated muscle was significantly lower in normal B/6J diabetic-prone mice compared with normal diabetic-resistant A/J mice, a finding similar to that reported in relatives of human patients with type 2 diabetes. These data, taken together, raise the possibility that defects in the Gys gene may in part be responsible for the propensity to develop type 2 diabetes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop D. T. The information content of phase-known matings for ordering genetic loci. Genet Epidemiol. 1985;2(4):349–361. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Harper M. E., Franchini G., Nesbitt M. N., Simon M. I. Chromosomal mapping of murine c-fes and c-src genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):978–981. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browner M. F., Nakano K., Bang A. G., Fletterick R. J. Human muscle glycogen synthase cDNA sequence: a negatively charged protein with an asymmetric charge distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. L., Eicher E. M. Fat (fat) and tubby (tub): two autosomal recessive mutations causing obesity syndromes in the mouse. J Hered. 1990 Nov-Dec;81(6):424–427. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W., Katz H., Lincoln S. E., Shin H. S., Friedman J., Dracopoli N. C., Lander E. S. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics. 1992 Jun;131(2):423–447. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisler J. S., Warden C. H., Pace M. J., Lusis A. J. BSB: a new mouse model of multigenic obesity. Obes Res. 1993 Jul;1(4):271–280. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1993.tb00621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel W. N., Stoye J. P., Taylor B. A., Coffin J. M. Genetic identification of endogenous polytropic proviruses by using recombinant inbred mice. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3810–3821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3810-3821.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite T. L., Martinson D. R., Tseng L. F., Hagen T. C., Menahan L. A. A longitudinal hormonal profile of the genetically obese mouse. Endocrinology. 1980 Sep;107(3):671–676. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-3-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groop L. C., Kankuri M., Schalin-Jäntti C., Ekstrand A., Nikula-Ijäs P., Widén E., Kuismanen E., Eriksson J., Franssila-Kallunki A., Saloranta C. Association between polymorphism of the glycogen synthase gene and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 7;328(1):10–14. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301073280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howles P. N., Dickinson D. P., DiCaprio L. L., Woodworth-Gutai M., Gross K. W. Use of a cDNA recombinant for the gamma-subunit of mouse nerve growth factor to localize members of this multigene family near the TAM-1 locus on chromosome 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2791–2805. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. R., Cook S. A., Bustin M., Davisson M. T. Genetic mapping of the murine gene and 14 related sequences encoding chromosomal protein HMG-14. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(11):625–632. doi: 10.1007/BF00352479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. M., Meisler M. H., Seldin M. F., Lee B. K., Eicher E. M. Localization of insulin-2 (Ins-2) and the obesity mutant tubby (tub) to distinct regions of mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):197–199. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C., van Heyningen V., Evans G., Little P., Mannens M. Report of the second chromosome 11 workshop. Genomics. 1992 Mar;12(3):620–625. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90461-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Mandarino L. J. Hyperglycemia normalizes insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose oxidation and storage in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1999–2007. doi: 10.1172/JCI114935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kida Y., Raz I., Maeda R., Nyomba B. L., Stone K., Bogardus C., Sommercorn J., Mott D. M. Defective insulin response of phosphorylase phosphatase in insulin-resistant humans. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):610–617. doi: 10.1172/JCI115627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Bonner-Weir S., Weir G. C. Beta-cell dysfunction induced by chronic hyperglycemia. Current ideas on mechanism of impaired glucose-induced insulin secretion. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):442–455. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto M., Stoffel M., Groop L., Espinosa R., 3rd, Le Beau M. M., Bell G. I. Assignment of the gene encoding glycogen synthase (GYS) to human chromosome 19, band q13.3. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):460–461. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly K. F. A Macintosh program for storage and analysis of experimental genetic mapping data. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(6):303–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00357089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. D., Mu J. L., Cheah Y. C., Nesbitt M. N., Frankel W. N., Paigen B. The AXB and BXA set of recombinant inbred mouse strains. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(12):669–680. doi: 10.1007/BF00444361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleer M. A., Aitman T. J., Cornall R. J., Ghosh S., Hall J. R., Hearne C. M., Love J. M., Prins J. B., Ramachandran S., Rodrigues N. Linkage analysis of 84 microsatellite markers in intra- and interspecific backcrosses. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(8):457–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00356156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills E., Kuhn C. M., Feinglos M. N., Surwit R. Hypertension in CB57BL/6J mouse model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):R73–R78. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.1.R73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mu J. L., Cheah Y. C., Paigen B. Strain distribution pattern of 25 simple sequence length polymorphisms in the AXB and BXA recombinant inbred strains. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(12):705–708. doi: 10.1007/BF00444366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt M. N., Skamene E. Recombinant inbred mouse strains derived from A/J and C57BL/6J: a tool for the study of genetic mechanisms in host resistance to infection and malignancy. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Sep;36(3):357–364. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann P. E. Three-locus linkage analysis using recombinant inbred strains and Bayes' theorem. Genetics. 1991 Jul;128(3):631–638. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann P. E. Two-locus linkage analysis using recombinant inbred strains and Bayes' theorem. Genetics. 1990 Sep;126(1):277–284. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuttall F. Q., Barbosa J., Gannon M. C. The glycogen synthase system in skeletal muscle of normal humans and patients with myotonic dystrophy: effect of glucose and insulin administration. Metabolism. 1974 Jun;23(6):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo M., Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Mott D. M. Glucose-6-phosphate stimulation of human muscle glycogen synthase phosphatase. Metabolism. 1988 Dec;37(12):1171–1176. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(88)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piehl K., Karlsson J. Glycogen synthetase and phosphorylase activity in slow and fast twitch skeletal muscle fibres in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jun;100(2):210–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Control of glycogen synthase by hierarchal protein phosphorylation. FASEB J. 1990 Sep;4(12):2961–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Seldin M. F. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 7. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):525–535. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalin-Jäntti C., Härkonen M., Groop L. C. Impaired activation of glycogen synthase in people at increased risk for developing NIDDM. Diabetes. 1992 May;41(5):598–604. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin M. F., Morse H. C., 3rd, Reeves J. P., Scribner C. L., LeBoeuf R. C., Steinberg A. D. Genetic analysis of autoimmune gld mice. I. Identification of a restriction fragment length polymorphism closely linked to the gld mutation within a conserved linkage group. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):688–693. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J. Confidence limits for estimates of gene linkage based on analysis of recombinant inbred strains. J Hered. 1985 Nov-Dec;76(6):436–440. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a110140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surwit R. S., Feinglos M. N., Livingston E. G., Kuhn C. M., McCubbin J. A. Behavioral manipulation of the diabetic phenotype in ob/ob mice. Diabetes. 1984 Jul;33(7):616–618. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.7.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surwit R. S., Feinglos M. N. Stress and autonomic nervous system in type II diabetes. A hypothesis. Diabetes Care. 1988 Jan;11(1):83–85. doi: 10.2337/diacare.11.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surwit R. S., Kuhn C. M., Cochrane C., McCubbin J. A., Feinglos M. N. Diet-induced type II diabetes in C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1163–1167. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surwit R. S., Seldin M. F., Kuhn C. M., Cochrane C., Feinglos M. N. Control of expression of insulin resistance and hyperglycemia by different genetic factors in diabetic C57BL/6J mice. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):82–87. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorburn A. W., Gumbiner B., Bulacan F., Brechtel G., Henry R. R. Multiple defects in muscle glycogen synthase activity contribute to reduced glycogen synthesis in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):489–495. doi: 10.1172/JCI115022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaag A., Henriksen J. E., Beck-Nielsen H. Decreased insulin activation of glycogen synthase in skeletal muscles in young nonobese Caucasian first-degree relatives of patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):782–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI115656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard H., Lund S., Larsen F. S., Bjerrum O. J., Pedersen O. Glycogen synthase and phosphofructokinase protein and mRNA levels in skeletal muscle from insulin-resistant patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2342–2350. doi: 10.1172/JCI116466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden C. H., Fisler J. S., Pace M. J., Svenson K. L., Lusis A. J. Coincidence of genetic loci for plasma cholesterol levels and obesity in a multifactorial mouse model. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):773–779. doi: 10.1172/JCI116649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. L., D'Eustachio P., Mock B. A., Steinberg A. D., Morse H. C., 3rd, Oakey R. J., Howard T. A., Rochelle J. M., Seldin M. F. A linkage map of mouse chromosome 1 using an interspecific cross segregating for the gld autoimmunity mutation. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(3):158–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00302874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- le Marchand-Brustel Y., Freychet P. Alteration of glycogen synthase activation by insulin in soleus muscles of obese mice. FEBS Lett. 1980 Nov 3;120(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



