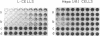Abstract
Reovirus type 1, strain Lang (1/L), can infect hepatocytes in vivo only after hepatocellular damage is induced by hepatotoxins, surgical trauma, resection, or profound immunosuppression. To examine the role of cell cycle and cellular differentiation on liver cell susceptibility to reovirus infection, a murine hepatocarcinoma cell line, Hepa 1/A1, was infected with reovirus and assayed for the presence of infectious virus or reovirus antigen in cells. Despite a > 95% binding of reovirus to hepatocarcinoma cells as indicated by cytometric analysis; only 10% of hepatoma cells contained infectious virus by infectious center assay. In comparison, 100% of L cells were infected. Analysis of intracellular reovirus antigen revealed its presence in dividing but not in quiescent hepatocytes. This correlation of cellular division and cell capacity to support viral replication suggests that induction of hepatocyte proliferation may be a mechanism for liver susceptibility to reovirus infection.
Full text
PDF




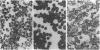
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Graham A. F. Persistent infections in L cells with temperature-sensitive mutants of reovirus. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):250–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.250-262.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanc P., Etienne H., Daujat M., Fabre I., Zindy F., Domergue J., Astre C., Saint Aubert B., Michel H., Maurel P. Mitotic responsiveness of cultured adult human hepatocytes to epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor alpha, and human serum. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1340–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brillanti S., Masci C., Siringo S., Di Febo G., Miglioli M., Barbara L. Serological and histological aspects of hepatitis C virus infection in alcoholic patients. J Hepatol. 1991 Nov;13(3):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90079-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington G. J., Bernhard H. P., Miller R. A., Ruddle F. H. Expression of liver phenotypes in cultured mouse hepatoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Apr;64(4):809–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollard S. C., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Regulation of the human papillomavirus type 11 E6 promoter by viral and host transcription factors in primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1721–1726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1721-1726.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein R. L., Powers M. L., Rogart R. B., Weiner H. L. Binding of 125I-labeled reovirus to cell surface receptors. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):46–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A., Cebra J. J. Responses of single germinal-center B cells in T-cell-dependent microculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A., Kost S. I., Witzleben C. L., Cebra J. J., Rubin D. H. Reovirus-induced liver disease in severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. A model for the study of viral infection, pathogenesis, and clearance. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):929–934. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass M. J., Summers D. F. Identification of a trans-acting activity from liver that stimulates hepatitis A virus translation in vitro. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):1047–1050. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glibetic M. D., Baumann H. Influence of chronic inflammation on the level of mRNA for acute-phase reactants in the mouse liver. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1616–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripon P., Diot C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Reproducible high level infection of cultured adult human hepatocytes by hepatitis B virus: effect of polyethylene glycol on adsorption and penetration. Virology. 1993 Feb;192(2):534–540. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripon P., Diot C., Thézé N., Fourel I., Loreal O., Brechot C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. Hepatitis B virus infection of adult human hepatocytes cultured in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4136–4143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4136-4143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J. Characterization of the growth inhibited substate induced in murine hepatic tumor cells during in vitro exposure to dimethylsulfoxide. Int J Cancer. 1986 Dec 15;38(6):889–899. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., O'Donnell P. V. Dimethylsulfoxide-induced alterations in the growth properties and protein composition of in vitro-propagated murine hepatoma cells. Oncology. 1982;39(5):325–330. doi: 10.1159/000225662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J. Response of mouse liver tumor cells to the differentiation-inducing agent dimethylsulfoxide. Pharmacology. 1982;25(3):170–176. doi: 10.1159/000137739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Kinane T. B., West K., Soper B. W., Karga H., Ausiello D. A., Ercolani L. Transcriptional regulation of G-protein alpha i subunit genes in LLC-PK1 renal cells and characterization of the porcine G alpha 1-3 gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3964–3975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiki Y., Ohnishi H., Muto Y., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. Direct evidence that hepatocyte growth factor is a hepatotrophic factor for liver regeneration and has a potent antihepatitis effect in vivo. Hepatology. 1992 Nov;16(5):1227–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K. Studies on the effect of chymotrypsin on reovirions. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):700–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jérôme V., Vourc'h C., Baulieu E. E., Catelli M. G. Cell cycle regulation of the chicken hsp90 alpha expression. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Mar;205(1):44–51. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccoli D. A., Witzleben C. L., Guico C. J., Morrison A., Rubin D. H. Synergism between hepatic injuries and a nonhepatotropic reovirus in mice. Enhanced hepatic infection and death. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1038–1045. doi: 10.1172/JCI114806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porta C., Moroni M., Nastasi G., Ricci G., Casagranda I. Anti-HCV antibodies and hepatocellular carcinoma. Relationship in a medium-risk population. Ups J Med Sci. 1992;97(3):261–266. doi: 10.3109/03009739209179300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst T., Propst A., Dietze O., Judmaier G., Braunsteiner H., Vogel W. High prevalence of viral infection in adults with homozygous and heterozygous alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency and chronic liver disease. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Oct 15;117(8):641–645. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-8-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridinger D. N., Spendlove R. S., Barnett B. B., George D. B., Roth J. C. Evaluation of cell lines and immunofluorescence and plaque assay procedures for quantifying reoviruses in sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):740–746. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.740-746.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosman A. S., Paronetto F., Galvin K., Williams R. J., Lieber C. S. Hepatitis C virus antibody in alcoholic patients. Association with the presence of portal and/or lobular hepatitis. Arch Intern Med. 1993 Apr 26;153(8):965–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Eaton M. A., Anderson A. O. Reovirus infection in adult mice: the virus hemagglutinin determines the site of intestinal disease. Microb Pathog. 1986 Feb;1(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90034-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Fields B. N. Molecular basis of reovirus virulence. Role of the M2 gene. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):853–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Kornstein M. J., Anderson A. O. Reovirus serotype 1 intestinal infection: a novel replicative cycle with ileal disease. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):391–398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.391-398.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Morrison A. H., Witzleben C. L., Guico C. J., Piccoli D. A. Site of reovirus replication in liver is determined by the type of hepatocellular insult. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4593–4597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4593-4597.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H. Reovirus serotype 1 binds to the basolateral membrane of intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1987 Sep;3(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Weiner D. B., Dworkin C., Greene M. I., Maul G. G., Williams W. V. Receptor utilization by reovirus type 3: distinct binding sites on thymoma and fibroblast cell lines result in differential compartmentalization of virions. Microb Pathog. 1992 May;12(5):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. H., Wetzel J. D., Williams W. V., Cohen J. A., Dworkin C., Dermody T. S. Binding of type 3 reovirus by a domain of the sigma 1 protein important for hemagglutination leads to infection of murine erythroleukemia cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2536–2542. doi: 10.1172/JCI116147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Polypeptide components of virions, top component and cores of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):791–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Powers M. L., Weiner H. L. Age dependent susceptibility to Reovirus type 3 encephalitis: role of viral and host factors. Ann Neurol. 1983 Jun;13(6):602–607. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thean E. T., Toh B. H. Western immunoblotting: temperature-dependent reduction in background staining. Anal Biochem. 1989 Mar;177(2):256–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Girard K., Williams W. V., McPhillips T., Rubin D. H. Reovirus type 1 and type 3 differ in their binding to isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jul;5(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh C. H., Ting L. P. Differentiated liver cell specificity of the second enhancer of hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.142-149.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]