Abstract
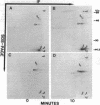
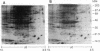
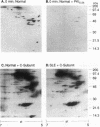
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disorder of indeterminate etiology characterized by a dysfunctional cellular immune response. We have previously identified a metabolic disorder of the adenylate cyclase/cAMP/protein kinase A (AC/cAMP/PKA) pathway characterized by impaired cAMP-inducible, PKA-catalyzed protein phosphorylation in intact T lymphocytes from subjects with severe SLE disease activity. Because this metabolic disorder may contribute to abnormal T cell immune effector functions, we tested the hypothesis that impaired PKA-dependent protein phosphorylation is the result of a PKA isozyme deficiency in SLE T lymphocytes. Compared with healthy and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) controls, subjects with severe SLE activity exhibited reduced PKA-catalyzed phosphorylation of proteins in the T lymphocyte plasma membrane where the type I isozyme of PKA (PKA-I) is predominantly localized. Both silver staining and biosynthetic labeling of membrane-associated proteins with [35S]methionine demonstrated that reduced protein phosphorylation was not due to either an altered distribution of or absence of proteins. Moreover, phosphorylation of SLE membrane-associated proteins with the PKA catalytic (C) subunit showed a similar distribution and extent of phosphorylation compared with membrane proteins from healthy T cells, suggesting that SLE T cell membrane proteins could be phosphorylated. Sequential column chromatography of the type I and type II isozymes of PKA (PKA-I, PKA-II) demonstrated a deficiency of PKA-I isozyme activity. Compared with a ratio of PKA-I to PKA-II activity of 4.2:1 in healthy T cells, the activity ratio in T cells from subjects with severe SLE disease activity was 0.99:1 (P = 0.01, SLE versus healthy controls for PKA-I). The deficient PKA-I activity was associated with a significant increase of free C-subunit activity (P = 0.04, SLE versus healthy controls for C-subunit). T cells from subjects with mild/moderate SLE disease activity also exhibited diminished PKA-I activity, yielding a ratio of PKA-I to PKA-II activity of 2.4:1. By contrast, T cells from RA controls possessed increased PKA-I, PKA-II, and free C-subunit activities compared with healthy controls, resulting in a ratio of PKA-I to PKA-II activity of 3.6:1. We conclude that the reduced PKA-catalyzed protein phosphorylation in the plasma membrane of SLE T cells is the result of deficient PKA-I isozyme activity. This is the first identification of a deficiency of PKA activity in SLE T lymphocytes; the deficiency, resulting in diminished protein phosphorylation, may alter cellular homeostasis, contributing to the cellular immune dysfunctions observed in SLE.
Full text
PDF

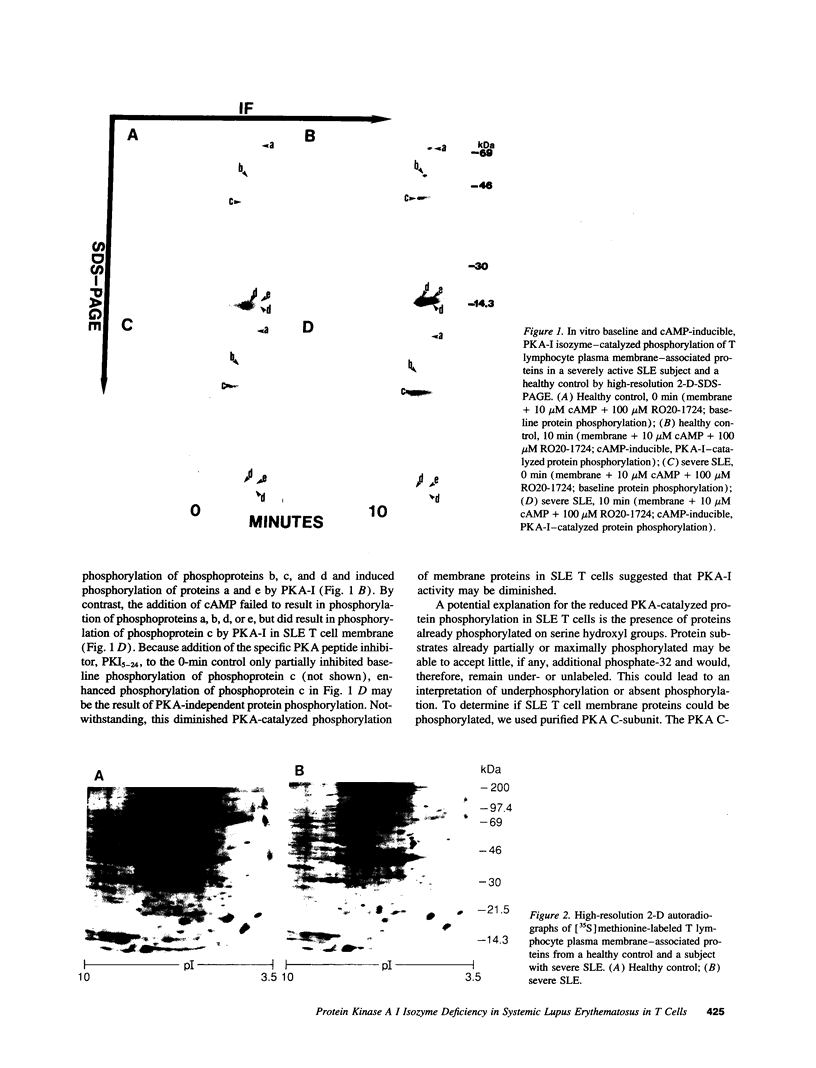

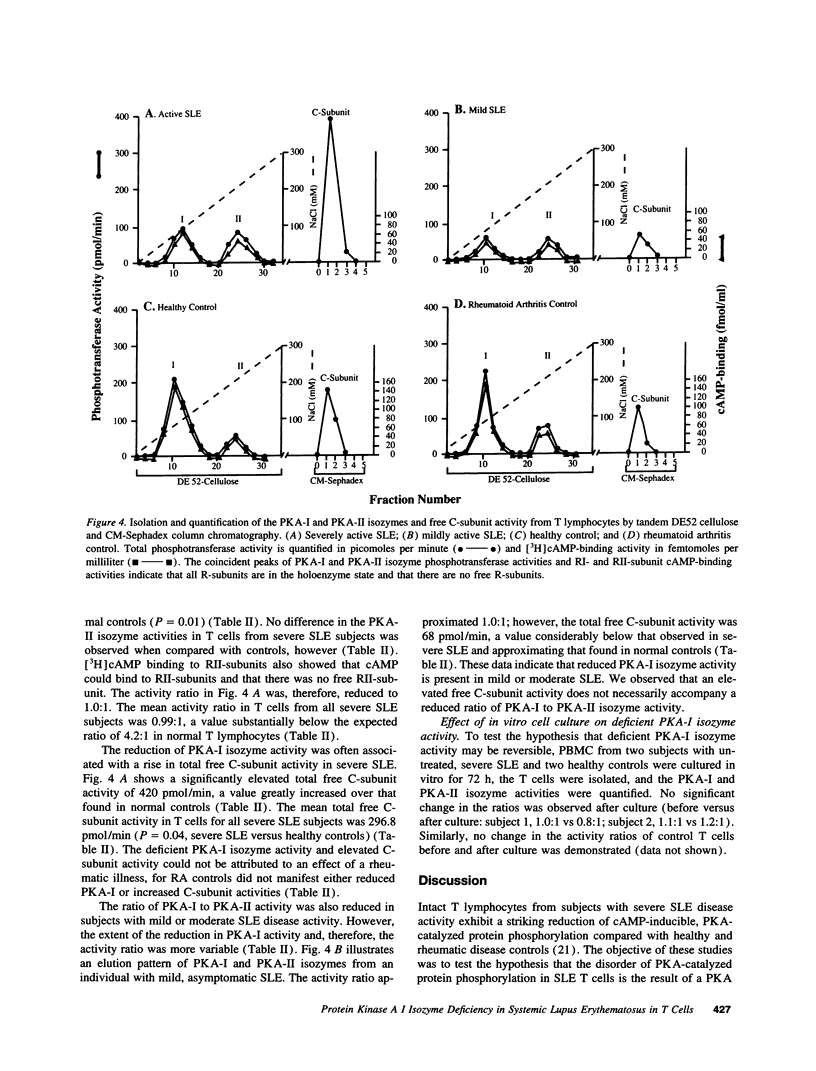



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averill L. E., Stein R. L., Kammer G. M. Control of human T-lymphocyte interleukin-2 production by a cAMP-dependent pathway. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):88–99. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and T cell activation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubis J., Neitzel J. J., Saraswat L. D., Taylor S. S. A point mutation abolishes binding of cAMP to site A in the regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9668–9673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S. Role of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in growth, differentiation, and suppression of malignancy: new approaches to therapy. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 15;50(22):7093–7100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. B., Lahita R. G., Chiorazzi N., Kunkel H. G. Immune function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Impairment of in vitro T-cell proliferation and in vivo antibody response to exogenous antigen. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):885–892. doi: 10.1172/JCI109388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler P., Moore J. J., Kammer G. M. Human T lymphocyte cAMP-dependent protein kinase: subcellular distributions and activity ranges of type I and type II isozymes. FASEB J. 1992 Jun;6(9):2735–2741. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.9.1319361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler P., Schultz L. A., Kammer G. M. Defective cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of intact T lymphocytes in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1978–1982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inghirami G., Simon J., Balow J. E., Tsokos G. C. Activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induce B cells to produce immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1988 Jul-Sep;6(3):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Impaired immunoregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: defective adenosine-induced suppressor T lymphocyte generation. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Boehm C. A., Rudolph S. A. Role of adenylate cyclase in human T-lymphocyte surface antigen capping. Cell Immunol. 1986 Aug;101(1):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Boehm C. A., Rudolph S. A., Schultz L. A. Mobility of the human T lymphocyte surface molecules CD3, CD4, and CD8: regulation by a cAMP-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):792–796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Haqqi T. M., Hasler P., Malemud C. J. The effect of circulating serum factors from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus on protein kinase A (PKA) activity and PKA-dependent protein phosphorylation in T lymphocytes. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Apr;67(1):8–16. doi: 10.1006/clin.1993.1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. Impaired T cell capping and receptor regeneration in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Evidence for a disorder intrinsic to the T lymphocyte. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1686–1697. doi: 10.1172/JCI111128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Mitchell E. Impaired mobility of human T lymphocyte surface molecules during inactive systemic lupus erythematosus. Relationship to a defective cAMP pathway. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):88–98. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Stein R. L. T lymphocyte immune dysfunctions in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Mar;115(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M. The adenylate cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A pathway and regulation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):222–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B., House C. M. Pseudosubstrate-based peptide inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:287–304. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxminarayana D., Berrada A., Kammer G. M. Early events of human T lymphocyte activation are associated with type I protein kinase A activity. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2207–2214. doi: 10.1172/JCI116823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Kuret J., Johnson K. E., Powers S., Cameron S., Michaeli T., Wigler M., Zoller M. J. A mutation in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase that disrupts regulation. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2832943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H., Kammer G. M., Rudolph S. A. Abnormal adenosine-induced immunosuppression and cAMP metabolism in T lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak T. J., Rothenberg E. V. cAMP inhibits induction of interleukin 2 but not of interleukin 4 in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9353–9357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phi N. C., Takáts A., Binh V. H., Vien C. V., González-Cabello R., Gergely P. Cyclic AMP level of lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and its relation to disease activity. Immunol Lett. 1989 Nov;23(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehfuss R. P., Walton K. M., Loriaux M. M., Goodman R. H. The cAMP-regulated enhancer-binding protein ATF-1 activates transcription in response to cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18431–18434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Agard D. A. Studies on the phosphorylation and synthesis of type I regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in intact S49 mouse lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11356–11364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Agard D. A. Turnover of regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in S49 mouse lymphoma cells. Regulation by catalytic subunit and analogs of cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10731–10734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Gorman K. B., Ogreid D., Døskeland S. O., Weber I. T. Mutations that alter the charge of type I regulatory subunit and modify activation properties of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from S49 mouse lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3547–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. Radiolabeling and detection methods for studying metabolism of regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase I in intact cultured cells. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:233–243. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suciu-Foca N., Buda J. A., Thiem T., Reemtsma K. Impaired responsiveness of lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Chen P., Hunter M., Taffs R., Sitkovsky M. The dual role of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase C alpha subunit in T-cell receptor-triggered T-lymphocytes effector functions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25256–25263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C. Biochemical and molecular abnormalities in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991 Sep-Oct;9(5):533–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Shenker A. G protein mutations in human disease. Clin Biochem. 1993 Oct;26(5):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(93)90109-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]