Abstract
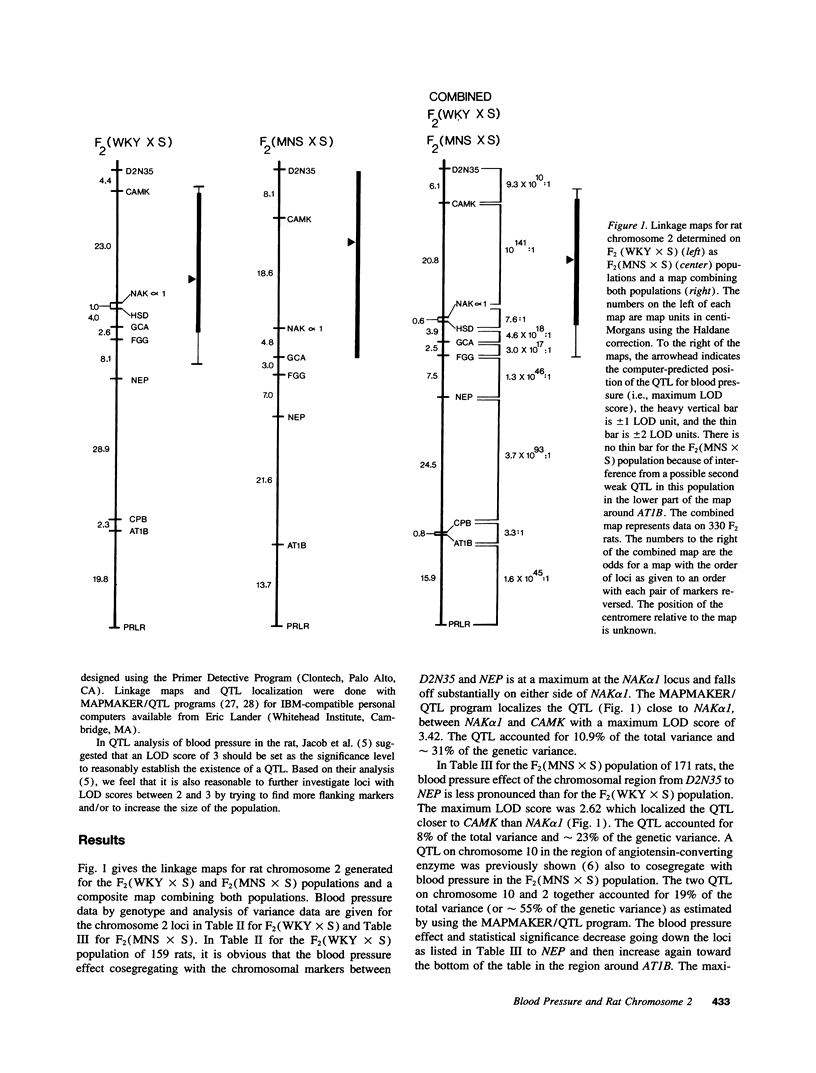
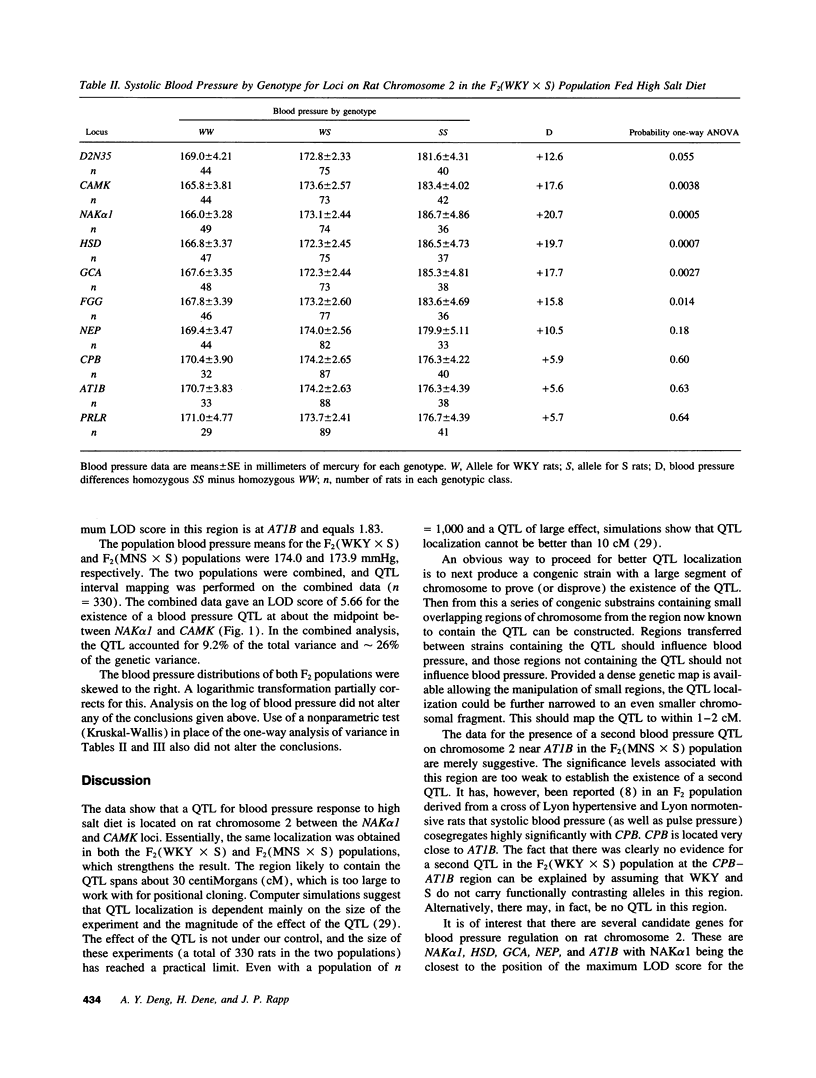
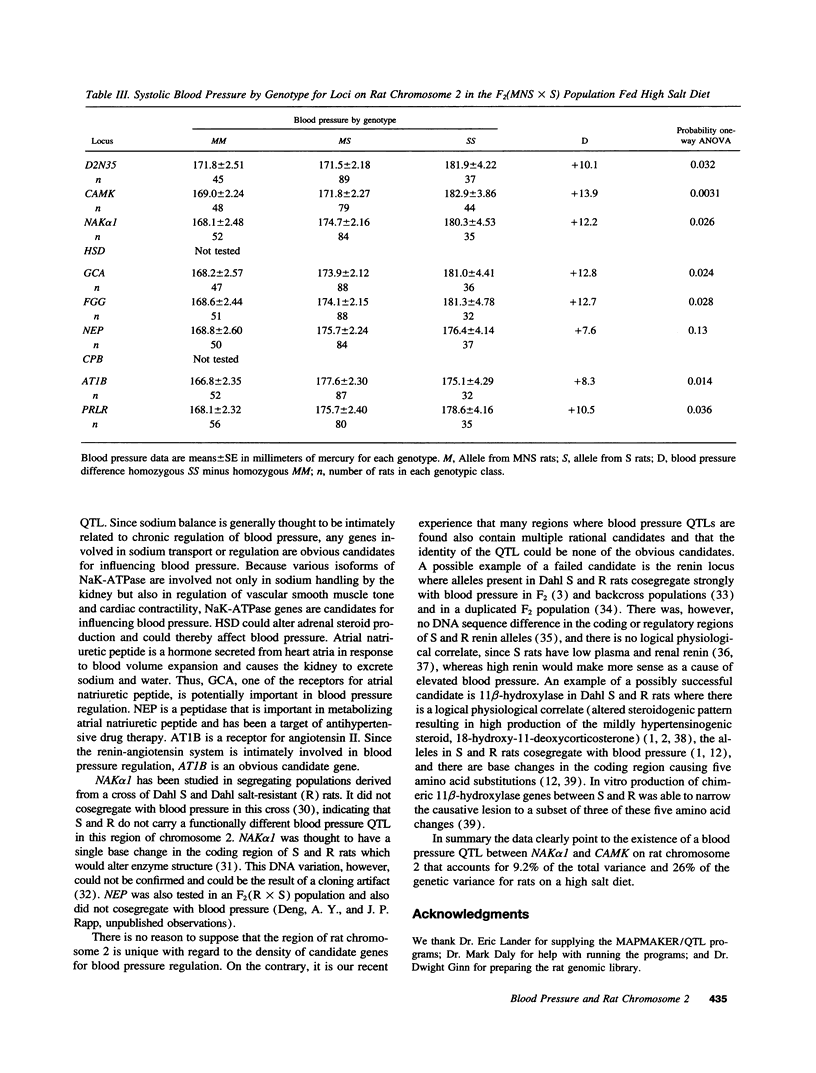
A genetic map for rat chromosome 2 that includes five candidate genes for blood pressure regulation was constructed in a region containing a quantitative trait locus (QTL) for blood pressure. Two F2 populations of male rats raised on high salt (8% NaCI) diet from weaning were studied: F2(WKY x S), derived from a cross of Dahl salt-sensitive rats (S) and Wistar-Kyoto rats (WKY); and F2(MNS x S), derived from a cross of S rats and Milan normotensive strain (MNS). In both populations a blood pressure QTL was localized between Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 isoform and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-delta loci. The LOD score for existence of this blood pressure QTL based on the combined populations (n = 330) was 5.66 and accounted for 9.2% of the total variance and 26% of the genetic variance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam K. Y., Wang Y., Dene H., Rapp J. P. Renin gene nucleotide sequence of coding and regulatory regions in Dahl rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1993 May;15(3):599–614. doi: 10.3109/10641969309041632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A. The rise and fall of positional cloning? Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):277–279. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buñag R. D., Butterfield J. Tail-cuff blood pressure measurement without external preheating in awake rats. Hypertension. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):898–903. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.4.6.898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicila G. T., Rapp J. P., Wang J. M., St Lezin E., Ng S. C., Kurtz T. W. Linkage of 11 beta-hydroxylase mutations with altered steroid biosynthesis and blood pressure in the Dahl rat. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):346–353. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Positional cloning: let's not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darvasi A., Weinreb A., Minke V., Weller J. I., Soller M. Detecting marker-QTL linkage and estimating QTL gene effect and map location using a saturated genetic map. Genetics. 1993 Jul;134(3):943–951. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.3.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dene H., McIlwain C., Rapp J. P. Quantitation of renal renin and renin mRNA in Dahl rats in response to provocative stimuli. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1989;11(8):1585–1594. doi: 10.3109/10641968909038184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Y., Rapp J. P. Cosegregation of blood pressure with angiotensin converting enzyme and atrial natriuretic peptide receptor genes using Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):267–272. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay C., Vincent M., Samani N. J., Hilbert P., Kaiser M. A., Beressi J. P., Kotelevtsev Y., Beckmann J. S., Soubrier F., Sassard J. Genetic determinants of diastolic and pulse pressure map to different loci in Lyon hypertensive rats. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):354–357. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. L., Dene H., Rapp J. P. SA gene and blood pressure cosegregation using Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Hypertens. 1993 Apr;6(4):330–334. doi: 10.1093/ajh/6.4.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera V. L., Ruiz-Opazo N. Alteration of alpha 1 Na+,K(+)-ATPase 86Rb+ influx by a single amino acid substitution. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1023–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.1975705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilbert P., Lindpaintner K., Beckmann J. S., Serikawa T., Soubrier F., Dubay C., Cartwright P., De Gouyon B., Julier C., Takahasi S. Chromosomal mapping of two genetic loci associated with blood-pressure regulation in hereditary hypertensive rats. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):521–529. doi: 10.1038/353521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwai N., Inagami T. Identification of a candidate gene responsible for the high blood pressure of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens. 1992 Oct;10(10):1155–1157. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199210000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunieda T., Kobayashi E., Tachibana M., Ikadai H., Imamichi T. Polymorphic microsatellite loci of the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Mamm Genome. 1992;3(10):564–567. doi: 10.1007/BF00350622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Green P., Abrahamson J., Barlow A., Daly M. J., Lincoln S. E., Newberg L. A., Newburg L. MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):174–181. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindpaintner K., Hilbert P., Ganten D., Nadal-Ginard B., Inagami T., Iwai N. Molecular genetics of the SA-gene: cosegregation with hypertension and mapping to rat chromosome 1. J Hypertens. 1993 Jan;11(1):19–23. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199301000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Schofield P. R., Kuang W. J., Seeburg P. H., Mason A. J., Henzel W. J. Molecular cloning and amino acid sequence of rat enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80475-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukawa N., Nonaka Y., Higaki J., Nagano M., Mikami H., Ogihara T., Okamoto M. Dahl's salt-resistant normotensive rat has mutations in cytochrome P450(11 beta), but the salt-sensitive hypertensive rat does not. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):9117–9121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dahl L. K. Mendelian inheritance of 18- and ll beta-steroid hydroxylase activities in the adrenals of rats genetically susceptible or resistant to hypertension. Endocrinology. 1972 Jun;90(6):1435–1446. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-6-1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dahl L. K. Mutant forms of cytochrome P-450 controlling both 18- and 11beta-steroid hydroxylation in the rat. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1235–1242. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dahl L. K. Possible role of 18-hydroxy-deoxycorticosterone in hypertension. Nature. 1972 Jun 9;237(5354):338–339. doi: 10.1038/237338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dene H. Development and characteristics of inbred strains of Dahl salt-sensitive and salt-resistant rats. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):340–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Dene H. Failure of alleles at the Na+, K(+)-ATPase alpha 1 locus to cosegregate with blood pressure in Dahl rats. J Hypertens. 1990 May;8(5):457–462. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199005000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Tan S. Y., Margolius H. S. Plasma mineralocorticoids, plasma renin, and urinary kallikrein in salt-sensitive and salt-resistant rats. Endocr Res Commun. 1978;5(1):35–41. doi: 10.3109/07435807809073634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Wang S. M., Dene H. A genetic polymorphism in the renin gene of Dahl rats cosegregates with blood pressure. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):542–544. doi: 10.1126/science.2563177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp J. P., Wang S. M., Dene H. Effect of genetic background on cosegregation of renin alleles and blood pressure in Dahl rats. Am J Hypertens. 1990 May;3(5 Pt 1):391–396. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.5.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samani N. J., Lodwick D., Vincent M., Dubay C., Kaiser M. A., Kelly M. P., Lo M., Harris J., Sassard J., Lathrop M. A gene differentially expressed in the kidney of the spontaneously hypertensive rat cosegregates with increased blood pressure. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):1099–1103. doi: 10.1172/JCI116616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg K., Ji H., Clark A. J., Shapira H., Catt K. J. Cloning and expression of a novel angiotensin II receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9455–9458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serikawa T., Kuramoto T., Hilbert P., Mori M., Yamada J., Dubay C. J., Lindpainter K., Ganten D., Guénet J. L., Lathrop G. M. Rat gene mapping using PCR-analyzed microsatellites. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):701–721. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet L., St Lezin E., Kurtz T. W. Sequence analysis of the alpha 1 Na+,K(+)-ATPase gene in the Dahl salt-sensitive rat. Hypertension. 1991 Nov;18(5):689–693. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.5.689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienen W., Entzeroth M. Effects on binding characteristics and renal function of the novel, non-peptide angiotensin II antagonist BIBR277 in the rat. J Hypertens. 1994 Feb;12(2):119–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Rutledge L. J., Garbers D. L. The primary structure of the rat guanylyl cyclase A/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20414–20420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zha H., Wilder R. L., Goldmuntz E. A., Cash J. M., Crofford L. J., Mathern P., Remmers E. F. Linkage map of 10 polymorphic markers on rat chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1993;63(2):117–123. doi: 10.1159/000133514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



