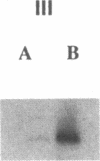
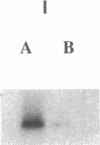
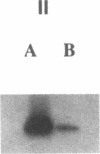
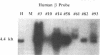
Abstract
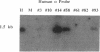
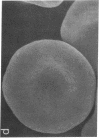
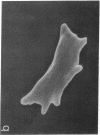
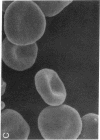
To develop an animal model for sickle cell anemia, we have created transgenic mice that express a severe naturally occurring human sickling hemoglobin, Hb S Antilles. Due to its low solubility and oxygen affinity, Hb S Antilles has a greater propensity to cause red cell sickling than Hb S. To make transgenic animals that express a high level of Hb S Antilles, the erythroid-specific DNAse I hypersensitive site II from the human beta-globin cluster was linked independently to the human alpha 2-globin gene and to the beta S Antilles gene. Embryos were injected with both constructs simultaneously and seven transgenic mice were obtained, three of which contained both the human alpha and the human beta S Antilles transgene. After crossing the human transgenes into the mouse beta-thalassemic background a transgenic mouse line was derived in which approximately half the beta-globin chains in the murine red cells were human beta S Antilles. Deoxygenation of the transgenic red cells in vitro resulted in extensive sickling. An increase of in vivo sickling was achieved by placing these transgenic mice in a low oxygen environment. This murine model for red cell sickling should help to advance our understanding of sickle cell disease and may provide a model to test therapeutic interventions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter B. P., Goff S. C., Efremov G. D., Gravely M. E., Huisman T. H. Globin chain electrophoresis: a new approach to the determination of the G gamma/A gamma ratio in fetal haemoglobin and to studies of globin synthesis. Br J Haematol. 1980 Apr;44(4):527–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behringer R. R., Ryan T. M., Reilly M. P., Asakura T., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Townes T. M. Synthesis of functional human hemoglobin in transgenic mice. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):971–973. doi: 10.1126/science.2772649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. A sensitive new prenatal test for sickle-cell anemia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):30–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner B. J., Reyes A. A., Morin C., Itakura K., Teplitz R. L., Wallace R. B. Detection of sickle cell beta S-globin allele by hybridization with synthetic oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):278–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F., Chada K., Magram J. Correction of murine beta-thalassemia by gene transfer into the germ line. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1192–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.3461564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Kantoff P., Schafer M. P., Anderson W. F., Safer B. Compensatory increase in levels of beta minor globin in murine beta-thalassemia is under translational control. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16126–16132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Liu D. P., Liu W., Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. Human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice is enhanced by a distant DNase I hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7082–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn J. B., Mann M., Meng C. K., Wong S. F., Whitehouse C. M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):64–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2675315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Fraser P., Vidal M. A., Hedges M. J., Ropers D., Luzzatto L., Grosveld F. A transgenic mouse model of sickle cell disorder. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):183–185. doi: 10.1038/343183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanscombe O., Vidal M., Kaeda J., Luzzatto L., Greaves D. R., Grosveld F. High-level, erythroid-specific expression of the human alpha-globin gene in transgenic mice and the production of human hemoglobin in murine erythrocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1572–1581. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Versatile cosmid vectors for the isolation, expression, and rescue of gene sequences: studies with the human alpha-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5225–5229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Johnson A., Wyatt J., Croisille L., Reeves J., Tycko D., Groner W. Automated quantitation of cell density distribution and hyperdense cell fraction in RBC disorders. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):442–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monplaisir N., Merault G., Poyart C., Rhoda M. D., Craescu C., Vidaud M., Galacteros F., Blouquit Y., Rosa J. Hemoglobin S Antilles: a variant with lower solubility than hemoglobin S and producing sickle cell disease in heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9363–9367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahbar S., Lee T. D., Baker J. A., Rabinowitz L. T., Asmerom Y., Legesse K., Ranney H. M. Reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography and secondary ion mass spectrometry. A strategy for identification of ten human hemoglobin variants. Hemoglobin. 1986;10(4):379–400. doi: 10.3109/03630268608996869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoda M. D., Domenget C., Vidaud M., Bardakdjian-Michau J., Rouyer-Fessard P., Rosa J., Beuzard Y. Mouse alpha chains inhibit polymerization of hemoglobin induced by human beta S or beta S Antilles chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 29;952(2):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Horness D., Kucera J., Blattner F. R. Construction of coliphage lambda Charon vectors with BamHI cloning sites. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Kan Y. W., Mohandas N. Effect of human beta (s)-globin chains on cellular properties of red cells from beta-thalassemic mice. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1129–1133. doi: 10.1172/JCI113670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Lu R. H., Cooper S., Mohandas N., Kan Y. W. Introduction and expression of the human Bs-globin gene in transgenic mice. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Apr;42(4):585–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Martin N. C., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. A single erythroid-specific DNase I super-hypersensitive site activates high levels of human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):314–323. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Townes T. M., Reilly M. P., Asakura T., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Behringer R. R. Human sickle hemoglobin in transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):566–568. doi: 10.1126/science.2154033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skow L. C., Burkhart B. A., Johnson F. M., Popp R. A., Popp D. M., Goldberg S. Z., Anderson W. F., Barnett L. B., Lewis S. E. A mouse model for beta-thalassemia. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]