Abstract
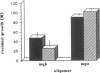
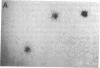
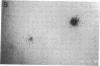
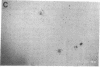
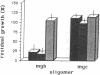
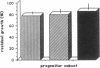
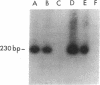
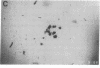
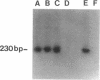
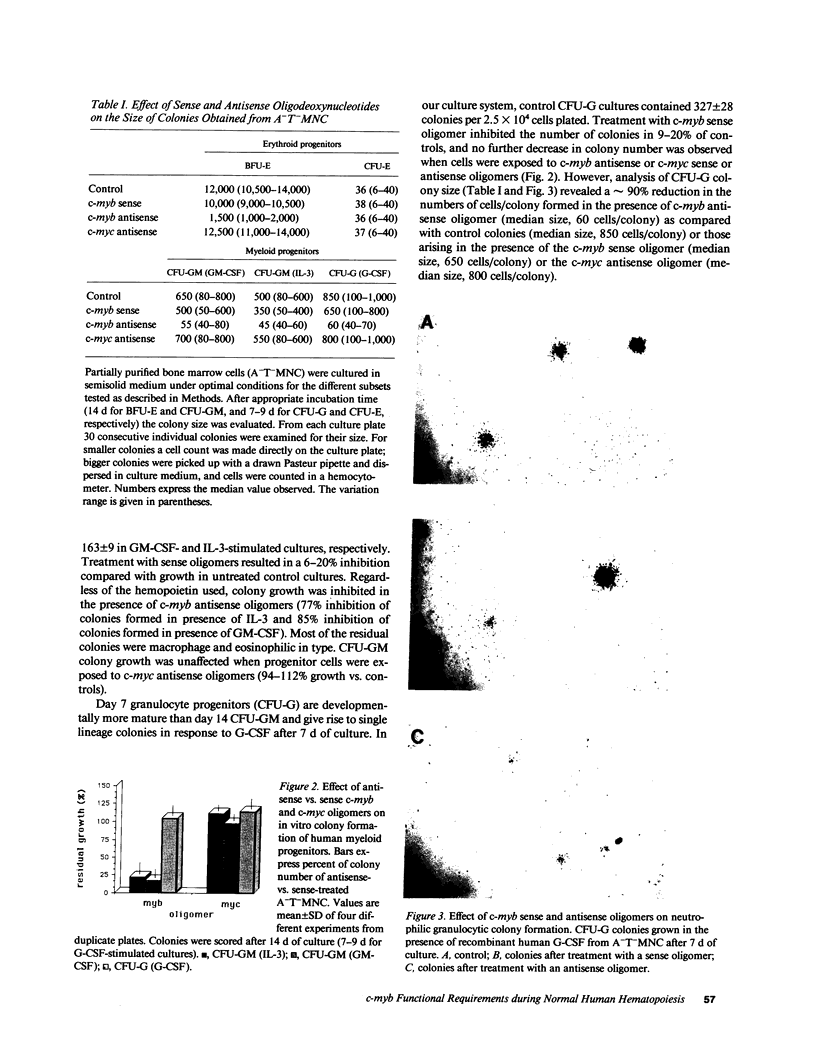
To determine if MYB protein is preferentially required during specific stages of normal human hematopoiesis we incubated normal marrow mononuclear cells (MNC) with c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Treated cells were cultured in semisolid medium under conditions designed to favor the growth of specific progenitor cell types. Compared with untreated controls, granulocyte-macrophage (GM) CFU-derived colonies decreased 77% when driven by recombinant human (rH) IL-3, and 85% when stimulated by rH GM colony-stimulating factor (CSF); erythroid burst-forming unit (BFU-E)- and CFU-E-derived colonies decreased 48 and 78%, respectively. In contrast, numbers of G-CSF-stimulated granulocyte colonies derived from antisense treated MNC were unchanged from controls, though the numbers of cells composing these colonies decreased approximately 90%. Similar results were obtained when MY10+ cells were exposed to c-myb antisense oligomers. When compared with untreated controls, numbers of CFU-GM and BFU-E colonies derived from MY10+ cells were unchanged, but the numbers of cells composing these colonies were reduced approximately 75 and greater than 90%, respectively, in comparison with controls. c-myc sense and antisense oligomers were without significant effect in these assays. Using the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, c-myb mRNA was detected in developing hematopoietic cells on days 0-8. At day 14 c-myb expression was no longer detectable using this technique. These results suggest that c-myb is required for proliferation of intermediate-late myeloid and erythroid progenitors, but is less important for lineage commitment and early progenitor cell amplification.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfossi G., Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. An oligomer complementary to c-myb-encoded mRNA inhibits proliferation of human myeloid leukemia cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3379–3383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley T. R., Metcalf D. The growth of mouse bone marrow cells in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1966 Jun;44(3):287–299. doi: 10.1038/icb.1966.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Baird N., Lu L., Srour E., Hoffman R. Characterization of a human hematopoietic progenitor cell capable of forming blast cell containing colonies in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1017–1027. doi: 10.1172/JCI113658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caracciolo D., Shirsat N., Wong G. G., Lange B., Clark S., Rovera G. Recombinant human macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) requires subliminal concentrations of granulocyte/macrophage (GM)-CSF for optimal stimulation of human macrophage colony formation in vitro. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1851–1860. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caracciolo D., Valtieri M., Venturelli D., Peschle C., Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. Lineage-specific requirement of c-abl function in normal hematopoiesis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1107–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.2672339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civin C. I., Strauss L. C., Brovall C., Fackler M. J., Schwartz J. F., Shaper J. H. Antigenic analysis of hematopoiesis. III. A hematopoietic progenitor cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody raised against KG-1a cells. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Kamen R. The human hematopoietic colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1229–1237. doi: 10.1126/science.3296190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Kukowska-Latallo J. F., Westin E., Smith M., Prochownik E. V. Constitutive expression of a c-myb cDNA blocks Friend murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):884–892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P., Lotan I., Knapp M., Kandel E. R., Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrero D., Broxmeyer H. E., Pagliardi G. L., Venuta S., Lange B., Pessano S., Rovera G. Antigenically distinct subpopulations of myeloid progenitor cells (CFU-GM) in human peripheral blood and marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4114–4118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Anfossi G., Venturelli D., Valpreda S., Sims R., Calabretta B. G1/S transition in normal human T-lymphocytes requires the nuclear protein encoded by c-myb. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):180–183. doi: 10.1126/science.2665077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. A c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits normal human hematopoiesis in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2461588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Metcalf D. Expression of myb, myc and fos proto-oncogenes during the differentiation of a murine myeloid leukaemia. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):249–251. doi: 10.1038/310249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R., Schwab G., Wickstrom E., Loke S. L., Pluznik D. H., Watt R., Neckers L. M. A c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits entry into S phase but not progress from G0 to G1. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):445–449. doi: 10.1038/328445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Redner R. L., Nienhuis A. W. An oligomer complementary to c-myc mRNA inhibits proliferation of HL-60 promyelocytic cells and induces differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):963–973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. In vitro control of the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):488–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N. The role of erythropoietin in regulation of population size and cell cycling of early and late erythroid precursors in mouse bone marrow. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1977 Jul;10(4):323–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1977.tb00300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Slamon D. J., Civin C. I. Expression of protooncogene c-myb in normal human hematopoietic cells. Blood. 1989 May 1;73(6):1444–1451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton J. M., Kudisch M., Nathan D. G. Response of three classes of human erythroid progenitors to the absence of erythropoietin in vitro as a measure of progenitor maturity. Exp Hematol. 1981 Nov;9(10):1035–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Kenyon L. C., Dalla-Favera R. Human c-myb protooncogene: nucleotide sequence of cDNA and organization of the genomic locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9636–9640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochownik E. V., Kukowska J., Rodgers C. c-myc antisense transcripts accelerate differentiation and inhibit G1 progression in murine erythroleukemia cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3683–3695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Mark D., Banda M. J., Werb Z. Wound macrophages express TGF-alpha and other growth factors in vivo: analysis by mRNA phenotyping. Science. 1988 Aug 5;241(4866):708–712. doi: 10.1126/science.3041594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. The molecular control of blood cell development. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1374–1379. doi: 10.1126/science.3317831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieff C. A. Hematopoietic growth factors. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI112988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebbi K., Rubin S., Cowan D. H., McCulloch E. A. A comparison of granulopoiesis in culture from blood and marrow cells of nonleukemic individuals and patients with acute leukemia. Blood. 1976 Aug;48(2):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Hemopoietic stem cell differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 26;605(4):431–459. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R., Stanton L. W., Marcu K. B., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M., Rovera G. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA of human c-myc oncogene. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):725–728. doi: 10.1038/303725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The action of oncogenes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.2997917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin E. H., Gallo R. C., Arya S. K., Eva A., Souza L. M., Baluda M. A., Aaronson S. A., Wong-Staal F. Differential expression of the amv gene in human hematopoietic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Goodchild J., Taguchi Y., Sarin P. S. Inhibition of replication and expression of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III in cultured cells by exogenous synthetic oligonucleotides complementary to viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4143–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]