Abstract
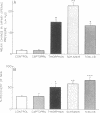
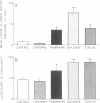
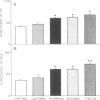
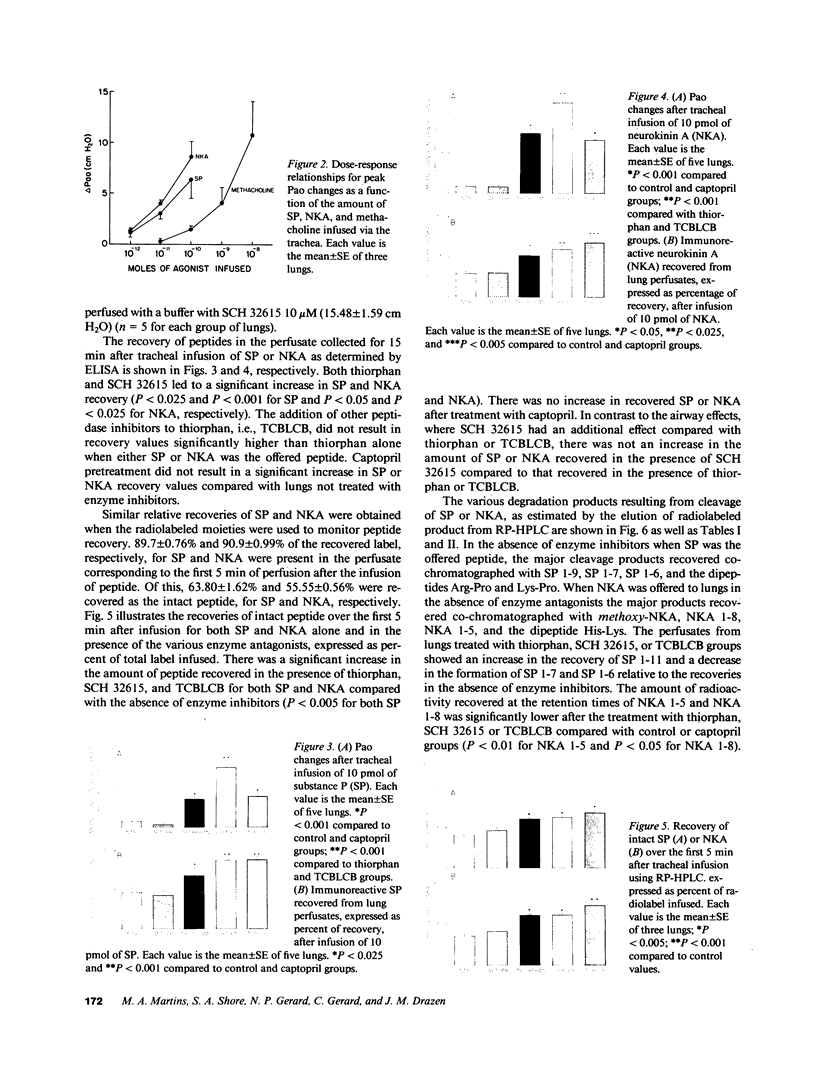
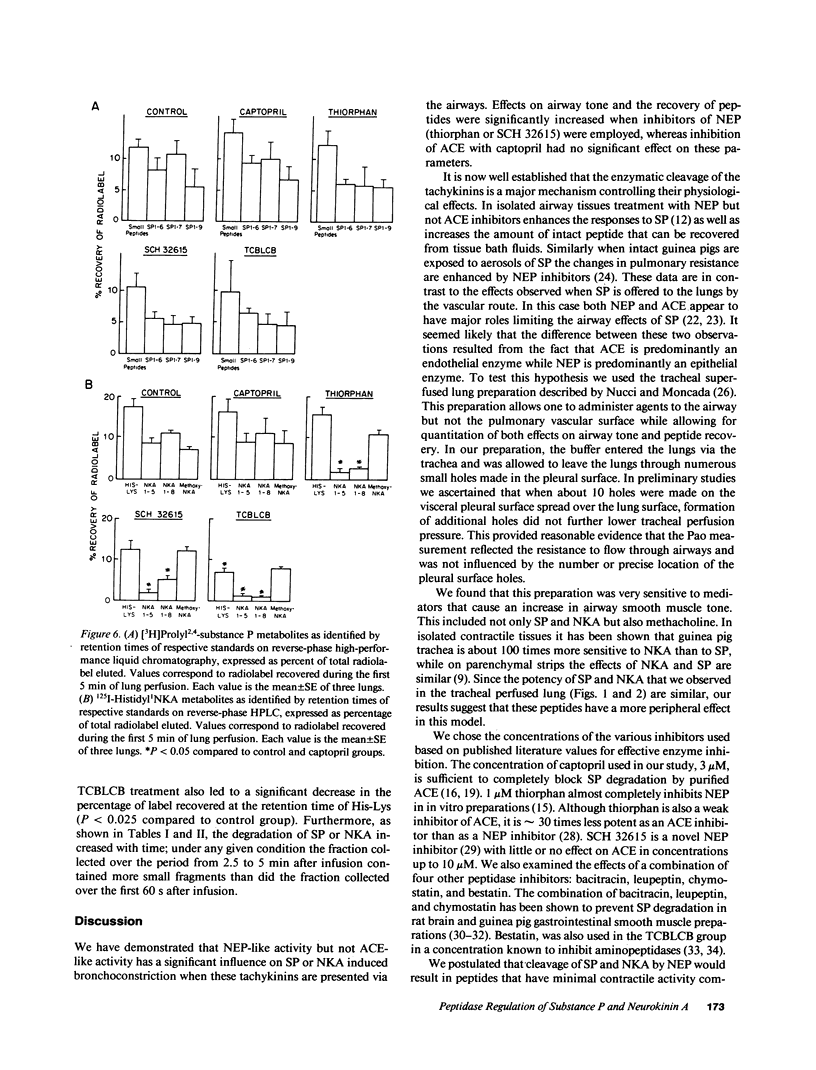
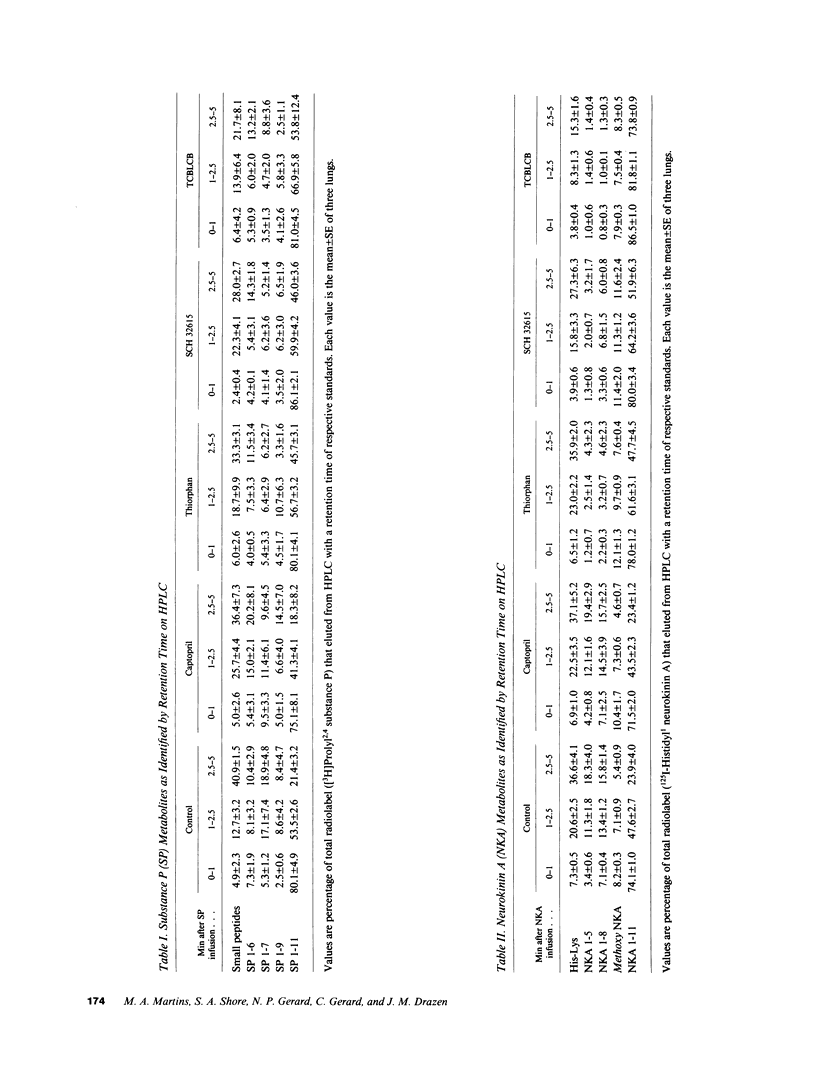
The effects of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor captopril and the neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitors thiorphan and SCH 32615 on the changes in airway opening pressure (PaO) and the recovery of offered peptide were studied after intratracheal administration of substance P (SP) and neurokinin A (NKA) in isolated guinea pig lungs superfused through the trachea. Pao changes and the recovery of offered peptide were significantly greater in NEP inhibitor-treated lungs than in control lungs. Captopril did not cause a significant change in the physiological effects or the recovery of SP and NKA. HPLC analysis of [3H]Pro2,4-SP and 125I-Histidyl1-NKA perfused through the airways showed major cleavage products consistent with NEP action. We conclude that there is significant degradation of both SP and NKA after tracheal infusion of peptides by NEP-like but not by ACE activity; this effect significantly influences the physiological effects of these peptides.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Bazzaz F. J., Kelsey J. G., Kaage W. D. Substance P stimulation of chloride secretion by canine tracheal mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;131(1):86–89. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borson D. B., Corrales R., Varsano S., Gold M., Viro N., Caughey G., Ramachandran J., Nadel J. A. Enkephalinase inhibitors potentiate substance P-induced secretion of 35SO4-macromolecules from ferret trachea. Exp Lung Res. 1987;12(1):21–36. doi: 10.3109/01902148709068812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of multiple tachykinin binding sites in gastrointestinal tract and bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):819–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Bull H. G., Mumford R. A., Patchett A. A., Thornberry N. A., Liang T. Carboxyl-terminal tripeptidyl hydrolysis of substance P by purified rabbit lung angiotensin-converting enzyme and the potentiation of substance P activity in vivo by captopril and MK-422. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):287–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Chicchi G. G., Liang T. Demonstration of two distinct tachykinin receptors in rat brain cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipkin R. E., Berger J. G., Billard W., Iorio L. C., Chapman R., Barnett A. Pharmacology of SCH 34826, an orally active enkephalinase inhibitor analgesic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):829–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couture R., Regoli D. Inactivation of substance P and its C-terminal fragments in rat plasma and its inhibition by Captopril. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;59(6):621–625. doi: 10.1139/y81-096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Shore S. A., Gerard N. P. Substance P-induced effects in guinea pig lungs: effects of thiorphan and captopril. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Mar;66(3):1364–1372. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.3.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Umeno E., Graf P. D., Djokic T., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Airway neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme modulates tachykinin-induced bronchoconstriction in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2585–2591. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. M., Gordon T., Sheppard D. Epithelium removal alters responsiveness of guinea pig trachea to substance P. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jan;66(1):232–237. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkesson R., Neil A., Terenius L. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of substance P and its metabolite SP 1-7. A comparison with RIA. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Aug;14(3):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gashi A. A., Borson D. B., Finkbeiner W. E., Nadel J. A., Basbaum C. B. Neuropeptides degranulate serous cells of ferret tracheal glands. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 1):C223–C229. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.2.C223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard N. P. Characterization of substance P contractile activity on isolated guinea pig lung tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):901–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. Neurokinin A (substance K) is a substrate for endopeptidase-24.11 but not for peptidyl dipeptidase A (angiotensin-converting enzyme). Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):357–361. doi: 10.1042/bj2310357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua X. Y., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Brodin E., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T. Multiple tachykinins (neurokinin A, neuropeptide K and substance P) in capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the guinea-pig. Regul Pept. 1985 Dec;13(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(85)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudgin R. L., Charleson S. E., Zimmerman M., Mumford R., Wood P. L. Enkephalinase: selective peptide inhibitors. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 21;29(25):2593–2601. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90632-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Ashton J., Schulz W. W., Erdös E. G. Neutral metalloendopeptidase in human lung tissue and cultured cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Sep;132(3):564–568. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.3.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Brodin E., Saria A. Effects and distribution of vagal capsaicin-sensitive substance P neurons with special reference to the trachea and lungs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Nov;119(3):243–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A., Brodin E., Rosell S., Folkers K. A substance P antagonist inhibits vagally induced increase in vascular permeability and bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo P. E., Wasserman M. A., Torphy T. J., Parris D. J., Pfeiffer D. F. Characterization of substance P-induced contractions of guinea-pig trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):782–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Fulcher I. S., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. Substance P and [Leu]enkephalin are hydrolyzed by an enzyme in pig caudate synaptic membranes that is identical with the endopeptidase of kidney microvilli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. The metabolism of neuropeptides. The hydrolysis of peptides, including enkephalins, tachykinins and their analogues, by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem J. 1984 Oct 15;223(2):433–440. doi: 10.1042/bj2230433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau R., Schäfer G., Deacon C. F., Cole T., Agoston D. V., Conlon J. M. Proteolytic inactivation of substance P and neurokinin A in the longitudinal muscle layer of guinea pig small intestine. J Neurochem. 1986 Sep;47(3):856–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Malfroy B., De La Baume S. Biological inactivation of enkephalins and the role of enkephalin-dipeptidyl-carboxypeptidase ("enkephalinase") as neuropeptidase. Life Sci. 1981 Oct 26;29(17):1715–1740. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Tamaoki J., Nadel J. A., Borson D. B. Enkephalinase inhibitor potentiates substance P- and electrically induced contraction in ferret trachea. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Oct;63(4):1401–1405. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.4.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sertl K., Wiedermann C. J., Kowalski M. L., Hurtado S., Plutchok J., Linnoila I., Pert C. B., Kaliner M. A. Substance P: the relationship between receptor distribution in rat lung and the capacity of substance P to stimulate vascular permeability. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jul;138(1):151–159. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. A., Stimler-Gerard N. P., Coats S. R., Drazen J. M. Substance P-induced bronchoconstriction in the guinea pig. Enhancement by inhibitors of neutral metalloendopeptidase and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):331–336. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shults C. W., Quirion R., Chronwall B., Chase T. N., O'Donohue T. L. A comparison of the anatomical distribution of substance P and substance P receptors in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1984 Nov-Dec;5(6):1097–1128. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidgel R. A., Engelbrecht S., Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Hydrolysis of substance p and neurotensin by converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):769–776. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimler-Gerard N. P. Neutral endopeptidase-like enzyme controls the contractile activity of substance P in guinea pig lung. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1819–1825. doi: 10.1172/JCI113023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele E. A., Strittmatter S. M., Snyder S. H. Substance K and substance P as possible endogenous substrates of angiotensin converting enzyme in the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91681-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. E., Sheppard D. Phosphoramidon potentiates the increase in lung resistance mediated by tachykinins in guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Feb;137(2):337–340. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Nomura A., Ohtsuka M., Hasegawa S., Goto K., Kimura S., Sugita Y., Uchiyama Y. Neurokinin A as a potent bronchoconstrictor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Sep;136(3):718–721. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.3.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Endo S., Ohgaki Y., Maeyama J., Ishii S. Hydrolysis of substance P and its analogs by angiotensin-converting enzyme from rat lung. Characterization of endopeptidase activity of the enzyme. J Biochem. 1985 Nov;98(5):1293–1299. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Moncada S. Release of vasoactive substances from guinea pig isolated lungs perfused via the trachea. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jun;135(6 Pt 2):S39–S41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.6P2.S39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]