Abstract
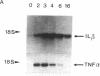
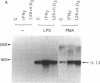
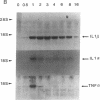
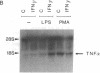
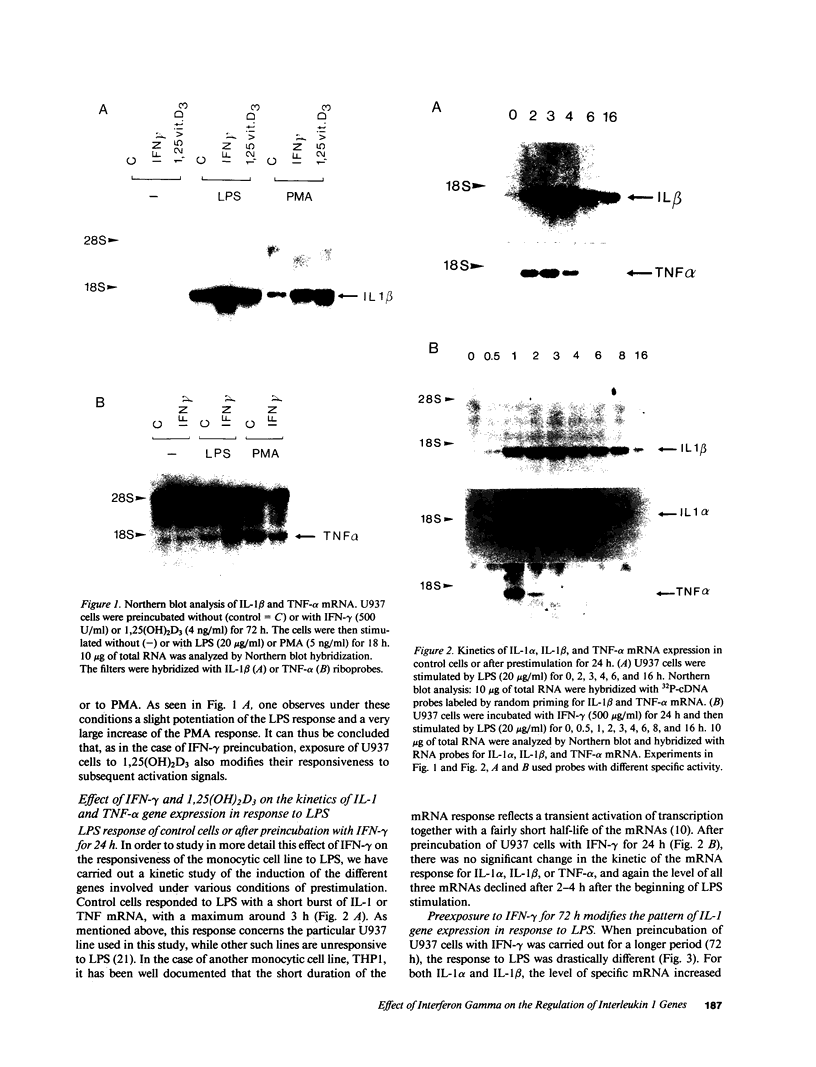
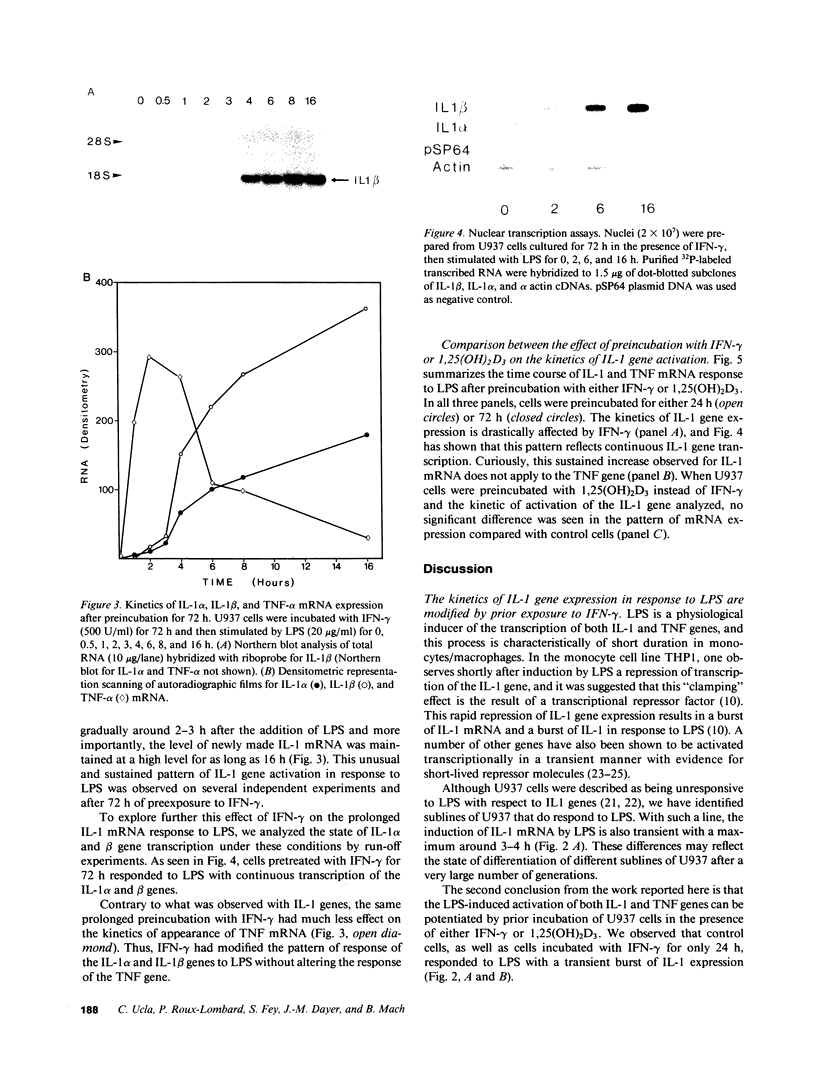
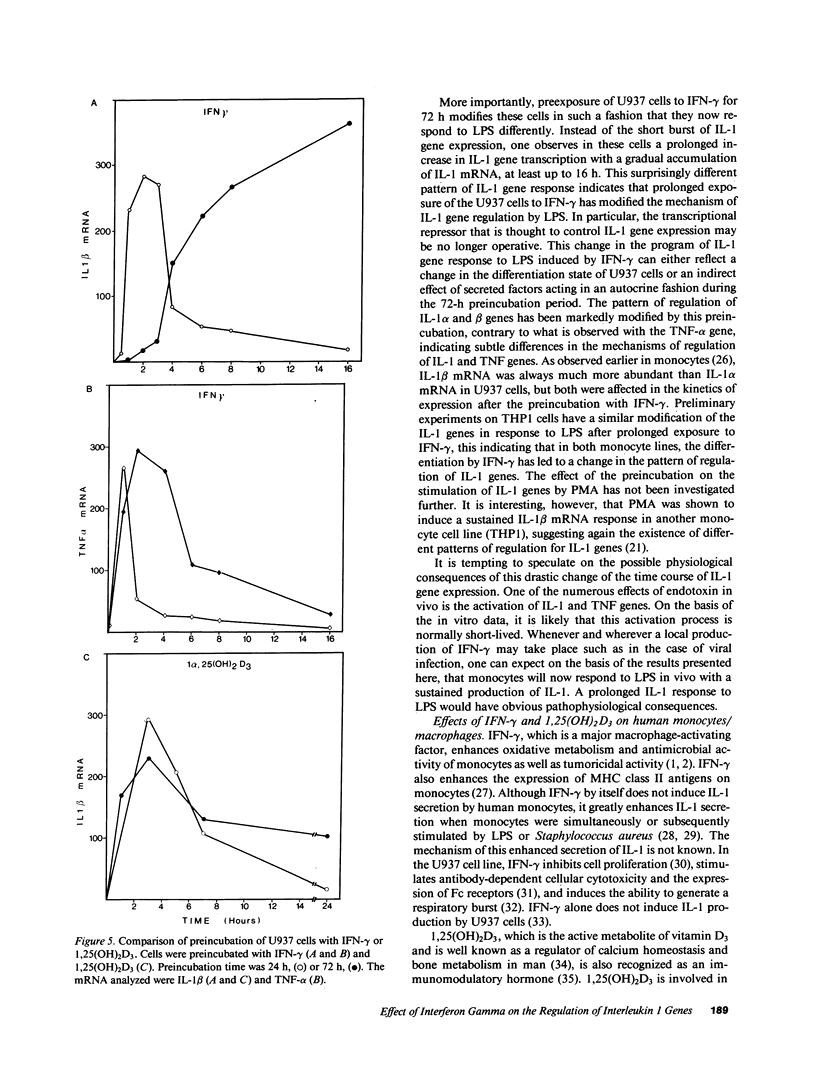
IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) gene expression is induced by LPS (endotoxin) in monocytes/macrophages and in some monocytic cell lines. IFN gamma and 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25[OH]2D3) are important macrophage-activating factors. They induce changes in the human monocyte cell line U937 that reflect cellular differentiation. We have studied the effect of IFN-gamma and of 1,25(OH)2D3 on the expression of IL-1 and TNF-alpha messenger RNA in response to LPS. The induction of these genes by LPS is immediate and transient, with a maximum in 3 h. Preincubation of the cells with IFN-gamma or with 1,25(OH)2D3 increases these mRNA responses to LPS about fourfold. More importantly, cells exposed to IFN-gamma for 72 h exhibit a drastically different and unexpected pattern of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta gene response to LPS. Instead of the normal transient response, one then observes a sustained increase in IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta gene expression over at least 16 h after LPS stimulation. This was measured both at the level of mRNA and by direct transcription assays (run-off). This striking effect of IFN-gamma on the kinetics of IL-1 gene response does not apply to the TNF-alpha gene. Interestingly, 1,25(OH)2D3, which shares with IFN-gamma a number of important effects on monocytes/macrophages, does not affect the kinetics of IL-1 gene response to LPS. In view of the biological relevance of endotoxin as a macrophage activator, the potential clinical implication of this prolonged induction of IL-1 gene expression is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. Molecular transductional mechanisms by which IFN gamma and other signals regulate macrophage development. Immunol Rev. 1987 Jun;97:5–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. O., Hamilton T. A. The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:283–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Bhalla A. K., Kurnick J. T., Kradin R. L., Clemens T. L., Holick S. A., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces maturation of the human monocyte cell line U937, and, in association with a factor from human T lymphocytes, augments production of the monokine, mononuclear cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):731–739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Kurnick J. T., Krane S. M. Interleukin 1 production by the human monocyte cell line U937 requires a lymphokine induction signal distinct from interleukin 2 or interferons. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):350–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P. Vitamin D and the immune system. Steroids. 1987 Jan-Mar;49(1-3):55–72. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L., Fiers W. Interferons as macrophage-activating factors. III. Preferential effects of interferon-gamma on the interleukin 1 secretory potential of fresh or aged human monocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2444–2448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Krane S. M. Differential effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human lymphocytes and monocyte/macrophages: inhibition of interleukin-2 and augmentation of interleukin-1 production. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Beutler B. The role of cachectin/TNF in endotoxic shock and cachexia. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–31. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Lehmeyer J. E. Regulation of the growth and differentiation of a human monocytic cell line by lymphokines. I. Induction of superoxide anion production and chemiluminescence. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2763–2766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Mesler D. E., Snipes R. G., Gray T. K. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 activates secretion of hydrogen peroxide by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1049–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F., Schnoes H. K. Vitamin D: recent advances. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:411–439. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demczuk S., Baumberger C., Mach B., Dayer J. M. Expression of human IL 1 alpha and beta messenger RNAs and IL 1 activity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1987;3(5):255–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Multiple biological properties of recombinant human interleukin 1 (beta). Immunobiology. 1986 Sep;172(3-5):301–315. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton M. J., Clark B. D., Collins K. L., Webb A. C., Rich A., Auron P. E. Transcriptional regulation of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3972–3979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton M. J., Vermeulen M. W., Clark B. D., Webb A. C., Auron P. E. Human pro-IL-1 beta gene expression in monocytic cells is regulated by two distinct pathways. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2267–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard T. L., Siegel J. P., Dyer D. R., Zoon K. C. Differential effects of interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma on interleukin 1 secretion by monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2535–2540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring S. R., Amento E. P., Roelke M. S., Krane S. M. The adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate response to prostaglandin E2 is altered in U937 cells in association with maturational events induced by activated T lymphocytes and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3461–3466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr Current concepts: immunology. Monocytes and macrophages. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):747–752. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Moore J. O., Metzgar R. S. Preparation and characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) from acute monocytic and myelomonocytic leukemia cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Nov;41(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(78)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Fischer D. G., Anderson S. J., Koren H. S. Characterization of a human macrophage-like cell line stimulated in vitro: a model of macrophage functions. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmenout A., Fransen L., Tavernier J., Van der Heyden J., Tizard R., Kawashima E., Shaw A., Johnson M. J., Semon D., Müller R. Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor necrosis factor and comparison with mouse tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):515–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F., Shen L., Ball E. D., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Differentiation of a human monocytic cell line by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol): a morphologic, phenotypic, and functional analysis. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1110–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F. The immunobiology of vitamin D. Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Lombard P., Cruchaud A., Dayer J. M. Effect of interferon-gamma and 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on superoxide anion, prostaglandins E2, and mononuclear cell factor production by U937 cells. Cell Immunol. 1986 Feb;97(2):286–296. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90399-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Direct stimulation of ADCC by cloned gamma interferon is not ablated by glucocorticoids: studies using a human monocyte-like cell line (U-937). Mol Immunol. 1984 Feb;21(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztein M. B., Steeg P. S., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of human peripheral blood monocyte DR antigen expression in vitro by lymphokines and recombinant interferons. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):556–565. doi: 10.1172/JCI111243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield P., Payton M., Graber P., Rose K., Dayer J. M., Shaw A. R., Schmeissner U. Purification and characterization of human interleukin-1 alpha produced in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):537–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield P., Payton M., Tavernier J., Barnes M., Shaw A., Rose K., Simona M. G., Demczuk S., Williamson K., Dayer J. M. Purification and characterization of human interleukin-1 beta expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]