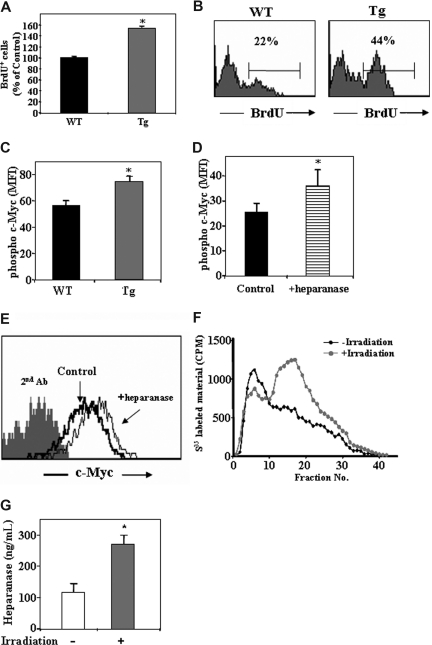
Figure 5.
Heparanase is involved in progenitor cell proliferation.(A) BrdU uptake in the primitive c-Kit+/Lin− cells obtained from control WT or hpa-Tg mice, as detected by flow cytometry. Data are means plus or minus SE; n = 4 samples. (B) Representative histogram plot of BrdU+ cells among the c-Kit+/Lin− population obtained from WT or hpa-Tg mice. (C) Phosphorylated c-Myc expression in the primitive cKit+/Lin− BM cells obtained from the BM of WT or hpa-Tg mice. (D) Phosphorylated c-Myc expression in the primitive c-Kit+/Lin− cells following exogenous in vitro treatment with heparanase (compared with control nontreated cells). Data are means plus or minus SE; n = 3 samples. (E) Representative histogram plot of phosphorylated c-Myc expression levels among the primitive c-Kit+/Lin− cells following in vitro treatment with or without exogenous heparanase. (F) Heparanase activity (determined by the ability to degrade sulfate-labeled heparan-sulfate) in lysates of cells collected from the BM of irradiated (24 hours after irradiation) or nonirradiated mice. Data are means plus or minus SE; n = 3 mice. (G) Heparanase levels in BM supernatant of WT and hpa-Tg mice as determined by ELISA. Data are means plus or minus SE; n = 7 mice (*P < .05).