Abstract
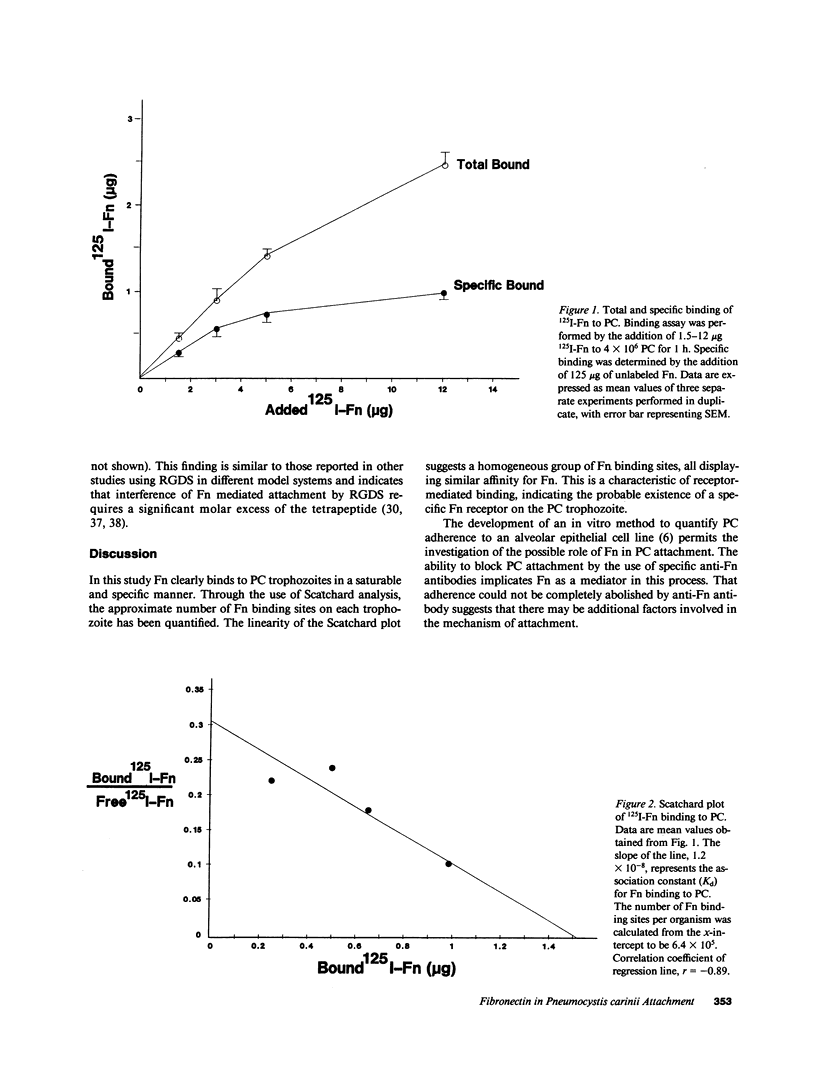
Attachment of pathogens to host cells is a prerequisite for the development of many infections. Pneumocystis carinii (PC) pneumonia is characterized by attachment of PC trophozoites to the alveolar epithelium. The mechanism of this process is unknown. Fibronectin (Fn) is a glycoprotein present in the alveolar space known to mediate cell-cell attachment, including the attachment of certain pathogens to host epithelial cells. In this study the binding of Fn to PC trophozoites has been characterized in vitro using 125I-Fn. Fn binds saturably and specifically to 6.4 x 10(5) binding sites per organism with an apparent binding constant, Kd, of 1.2 x 10(-8) M. Fn binding to PC was inhibited by the addition of Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS), a tetrapeptide containing the active site of the cell-binding domain of Fn. PC attachment to an alveolar epithelial cell line was quantified using 51Cr-labeled PC trophozoites. Attachment was decreased from 24 +/- 1.9% to 12.1 +/- 1% (P less than 0.01) by the addition of an anti-Fn antibody, an effect that could be overcome by the addition of excess free Fn. It is concluded that binding of Fn to PC may be an important initial step in the attachment of the organism to alveolar epithelial cells. Furthermore, it appears that PC recognizes and binds to the RGDS cell attachment site of Fn.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Yamada K. M. Synthetic peptides competitively inhibit both direct binding to fibroblasts and functional biological assays for the purified cell-binding domain of fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10402–10405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. New rat model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1100-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cierniewski C. S., Swiatkowska M., Poniatowski J., Niewiarowska J. Anti-(Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser) antibody and its interaction with fibronectin, fibrinogen and platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):109–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Detachment of cells from culture substrate by soluble fibronectin peptides. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1948–1954. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw N. G., Carson J. L., Collier A. M. Ultrastructural observations of Pneumocystis carinii attachment to rat lung. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):181–186. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. Molecular biology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:67–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalo A., Segal E., Sahar E., Dayan D. Interaction of Candida albicans with genital mucosal surfaces: involvement of fibronectin in adherence. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1253–1256. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Vartio T., Vuento M., Myhre E. B. Binding sites for streptococci and staphylococci in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):433–436. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.433-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. G., Smith J. S., Meier J. L. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to rat pneumocytes. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to conformationally specific determinants in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2279-2285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Jones T. C. The interaction in vitro of Pneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Physiology of fibronectin. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:561–575. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.35.020184.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouaissi M. A., Afchain D., Capron A., Grimaud J. A. Fibronectin receptors on Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes and their biological function. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):380–382. doi: 10.1038/308380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouaissi M. A., Cornette J., Afchain D., Capron A., Gras-Masse H., Tartar A. Trypanosoma cruzi infection inhibited by peptides modeled from a fibronectin cell attachment domain. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):603–607. doi: 10.1126/science.3094145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L., Shanley J. D. Glycoproteins of Pneumocystis carinii: characterization by electrophoresis and microscopy. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1353–1359. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Hayman E. G., Ruoslahti E. Location of the cell-attachment site in fibronectin with monoclonal antibodies and proteolytic fragments of the molecule. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature. 1984 May 3;309(5963):30–33. doi: 10.1038/309030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Variants of the cell recognition site of fibronectin that retain attachment-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5985–5988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor R. A., Mosher D. F., Olbrantz P. J. Fibronectin binding to Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14788–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. A 125/115-kDa cell surface receptor specific for vitronectin interacts with the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid adhesion sequence derived from fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5766–5770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Crystal R. G. Fibronectin in human bronchopulmonary lavage fluid. Elevation in patients with interstitial lung disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):113–122. doi: 10.1172/JCI110421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Production of fibronectin by the human alveolar macrophage: mechanism for the recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury in interstitial lung diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkrans W. A., Jr, Albright J. T., Hausman R. E., Penney D. P. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of fibronectin in the developing rat lung. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;234(1):165–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00217410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Farin F. M., Striker G. E., Fisher A. B. Granular pneumocytes in primary culture secrete several major components of the extracellular matrix. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2148–2155. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Adherence of group A streptococci to fibronectin on oral epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):275–279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.275-279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueishi K., Hisano S., Sumiyoshi A., Tanaka K. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic study of human pulmonary pneumocystosis. Chest. 1977 Aug;72(2):213–216. doi: 10.1378/chest.72.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., DeSimone D. W., Fonda D., Patel R. S., Buck C., Horwitz A. F., Hynes R. O. Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90744-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Fibronectin mediates Treponema pallidum cytadherence through recognition of fibronectin cell-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):514–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Sypek J. P., McDonald J. A. In vitro parasite-monocyte interactions in human leishmaniasis: possible role of fibronectin in parasite attachment. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):305–311. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.305-311.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Amino acid sequence specificities of an adhesive recognition signal. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(2):99–104. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Attachment of Pneumocystis carinii to type I alveolar cells studied by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):812–815. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.812-815.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda K., Walzer P. D. Mechanism of pulmonary alveolar injury in experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the rat. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):339–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



