Abstract
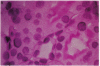
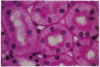
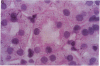
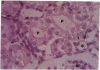
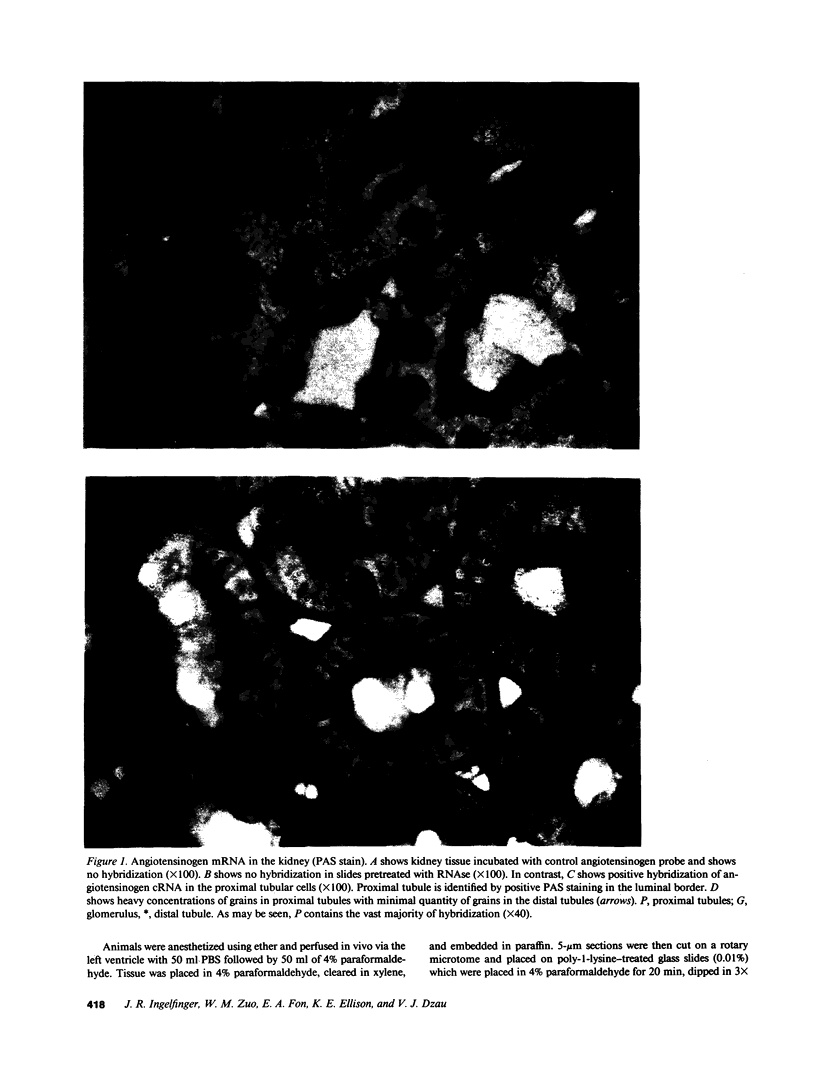
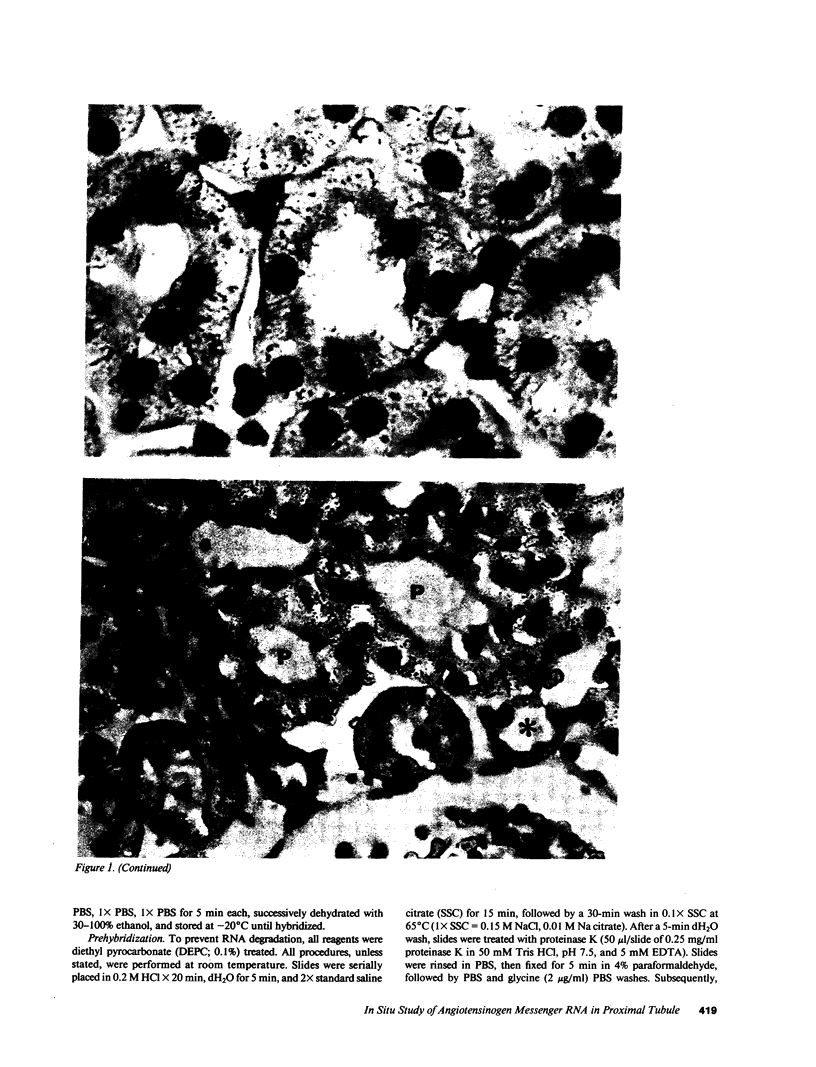
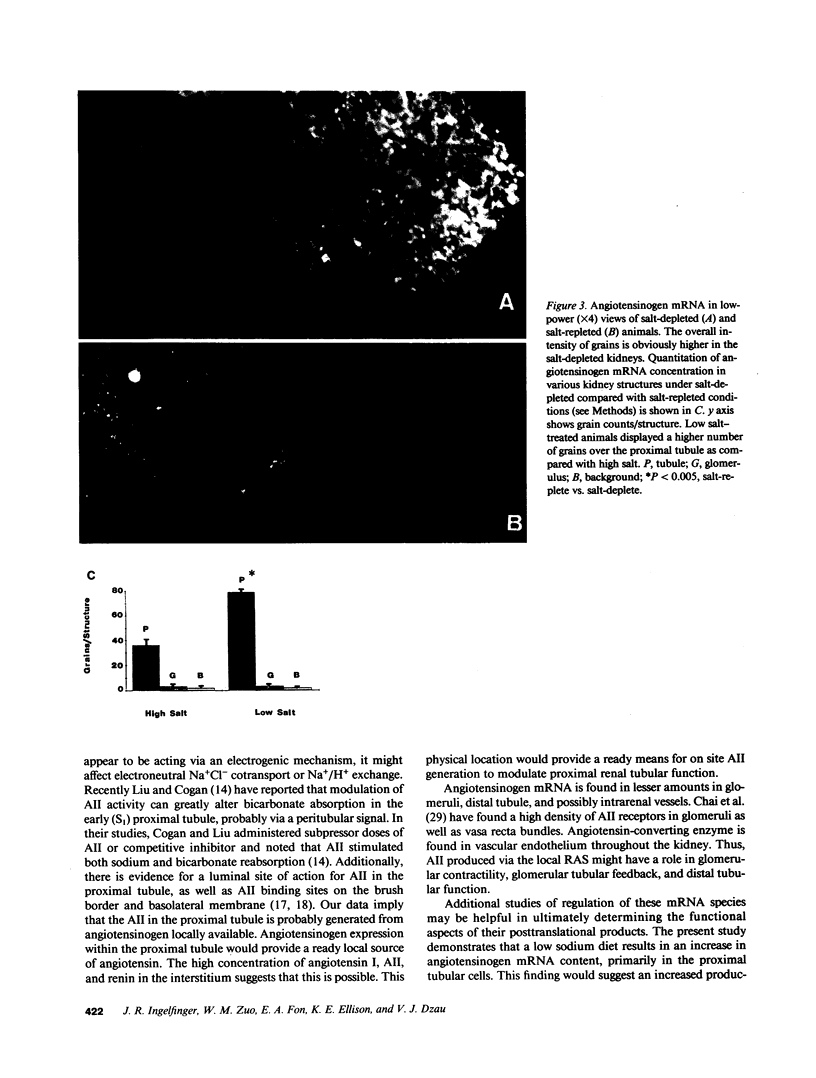
We examined angiotensinogen gene expression in rat kidney by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Using a rat cRNA probe to angiotensinogen, we demonstrated angiotensinogen mRNA to be localized predominantly in the proximal renal tubule, with considerably lesser amounts in distal tubular segments and glomerular tufts. Previous studies have localized renin immunoreactivity to the juxtaglomerular cells, glomerular tufts, and proximal tubules. Such findings provide further evidence for a local tissue renin angiotensin system within the kidney which may influence regional function. Based on our data, we hypothesize that a major site of angiotensin production is the proximal tubule. We postulate that angiotensin synthesized in and/or around the proximal tubule may directly modulate tubular transport of sodium, bicarbonate, and water. In addition to the proximal tubule, the specific localization of the renin angiotensin components elsewhere in the kidney would also support the other proposed regional functions of the intrarenal system, including modulation of tubuloglomerular balance.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch B. L'hybridation in situ: méthodologie et applications à l'analyse des phénomènes d'expression génique dans les glandes endocrines et le système nerveux. Ann Endocrinol (Paris) 1985;46(4-5):253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J. Circulating and tissue angiotensin systems. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. J., Habener J. F. Angiotensinogen gene is expressed and differentially regulated in multiple tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jul;78(1):31–39. doi: 10.1172/JCI112566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin M., Gutkowska J., Lacasse J., Ballak M., Ledoux S., Inagami T., Beuzeron J., Genest J. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of renin and angiotensin II in the juxtaglomerular cells of the ischemic kidney in experimental renal hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1984 May;115(2):212–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai S. Y., Allen A. M., Adam W. R., Mendelsohn F. A. Local actions of angiotensin II: quantitative in vitro autoradiographic localization of angiotensin II receptor binding and angiotensin converting enzyme in target tissues. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1986;8 (Suppl 10):S35–S39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper C. F., Mellon S. H., Cumin F., Baxter J. D., Ganong W. F. Analysis by immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization of renin and its mRNA in kidney, testis, adrenal, and pituitary of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7552–7556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ellison K. E., Brody T., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E. A comparative study of the distributions of renin and angiotensinogen messenger ribonucleic acids in rat and mouse tissues. Endocrinology. 1987 Jun;120(6):2334–2338. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-6-2334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzau V. J., Ingelfinger J., Pratt R. E., Ellison K. E. Identification of renin and angiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in mouse and rat brains. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):544–548. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison K. E., Ingelfinger J. R., Pivor M., Dzau V. J. Androgen regulation of rat renal angiotensinogen messenger RNA expression. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jun;83(6):1941–1945. doi: 10.1172/JCI114102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., McGowan R. A., Dickinson D. P., Gross K. W. Tissue and gene specificity of mouse renin expression. Hypertension. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):597–603. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.6.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez R. A., Lynch K. R., Chevalier R. L., Wilfong N., Everett A., Carey R. M., Peach M. J. Renin and angiotensinogen gene expression in maturing rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1988 Apr;254(4 Pt 2):F582–F587. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.4.F582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. J., Navar L. G. Tubular transport responses to angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F621–F630. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingelfinger J. R., Pratt R. E., Ellison K., Dzau V. J. Sodium regulation of angiotensinogen mRNA expression in rat kidney cortex and medulla. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1311–1315. doi: 10.1172/JCI112716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leyssac P. P. Changes in single nephron renin release are mediated by tubular fluid flow rate. Kidney Int. 1986 Sep;30(3):332–339. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly L. S., Pratt R. E., Alexander R. W., Larson D. M., Ellison K. E., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Dzau V. J. Renin expression by vascular endothelial cells in culture. Circ Res. 1985 Aug;57(2):312–318. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Cogan M. G. Angiotensin II: a potent regulator of acidification in the rat early proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):272–275. doi: 10.1172/JCI113059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. R., Simnad V. I., Ben-Ari E. T., Garrison J. C. Localization of preangiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in the rat brain. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):540–543. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn F. A. Localization and properties of angiotensin receptors. J Hypertens. 1985 Aug;3(4):307–316. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198508000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris B. J., Johnston C. I. Renin substrate in granules from rat kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj1540625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richoux J. P., Cordonnier J. L., Bouhnik J., Clauser E., Corvol P., Menard J., Grignon G. Immunocytochemical localization of angiotensinogen in rat liver and kidney. Cell Tissue Res. 1983;233(2):439–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00238309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Mechanisms of action of various hormones and vasoactive substances on glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):442–451. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Kokko J. P., Jacobson H. R. Angiotensin II directly stimulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):507–515. doi: 10.1172/JCI111237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Hackenthal E., Rix E., Nobiling R., Poulsen K. Immunocytochemistry of the renin-angiotensin system: renin, angiotensinogen, angiotensin I, angiotensin II, and converting enzyme in the kidneys of mice, rats, and tree shrews. Kidney Int Suppl. 1982 Aug;12:S33–S43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd In situ hybridization histochemical detection of neuropeptide mRNA using DNA and RNA probes. Methods Enzymol. 1989;168:702–710. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)68051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]