Abstract
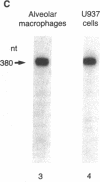
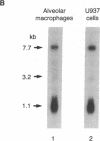
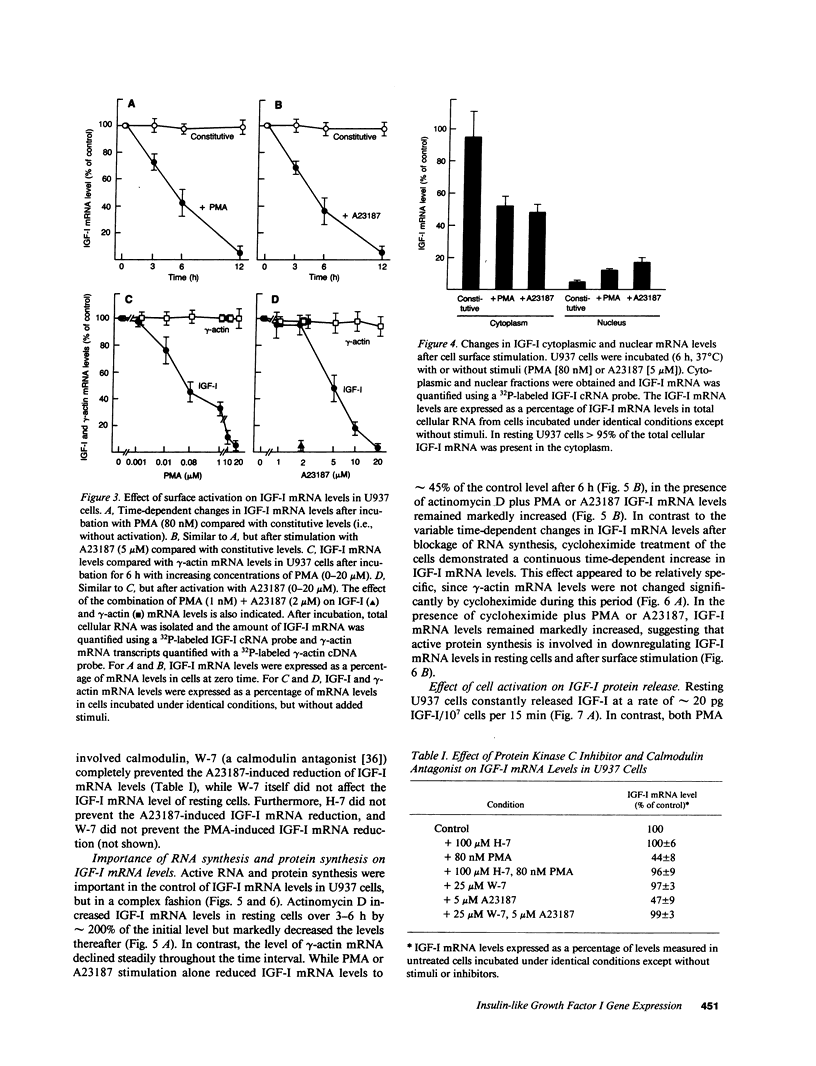
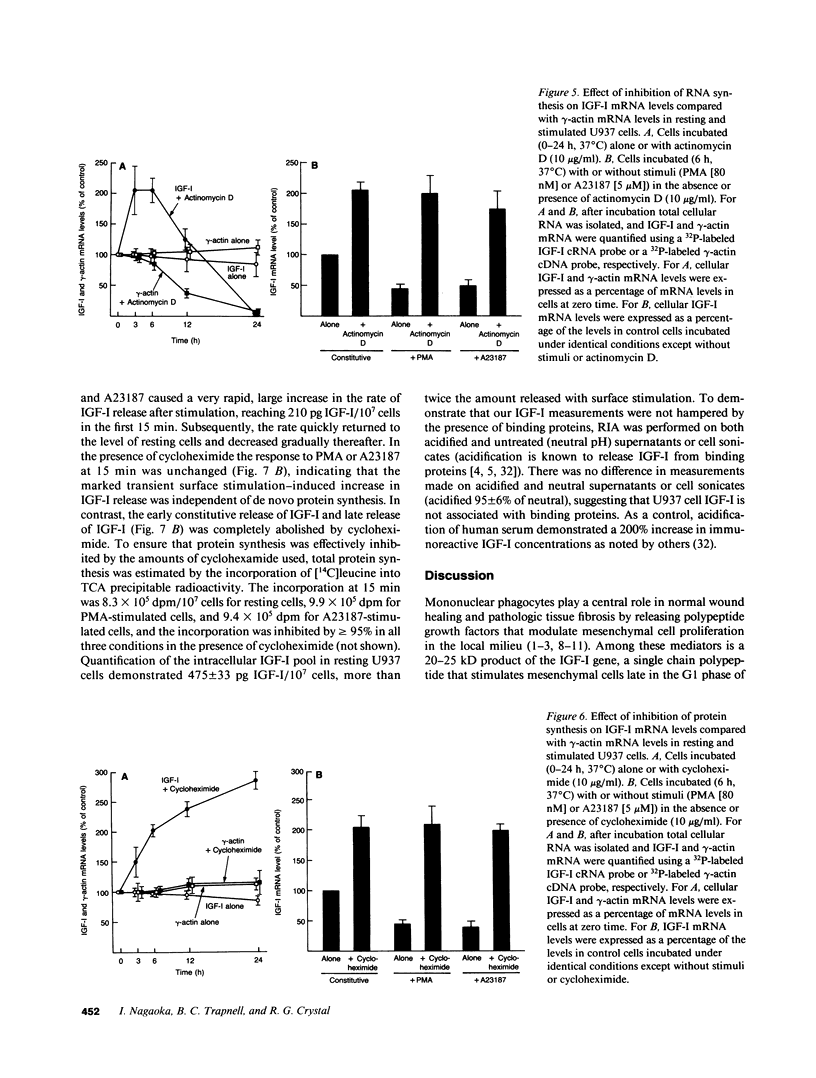
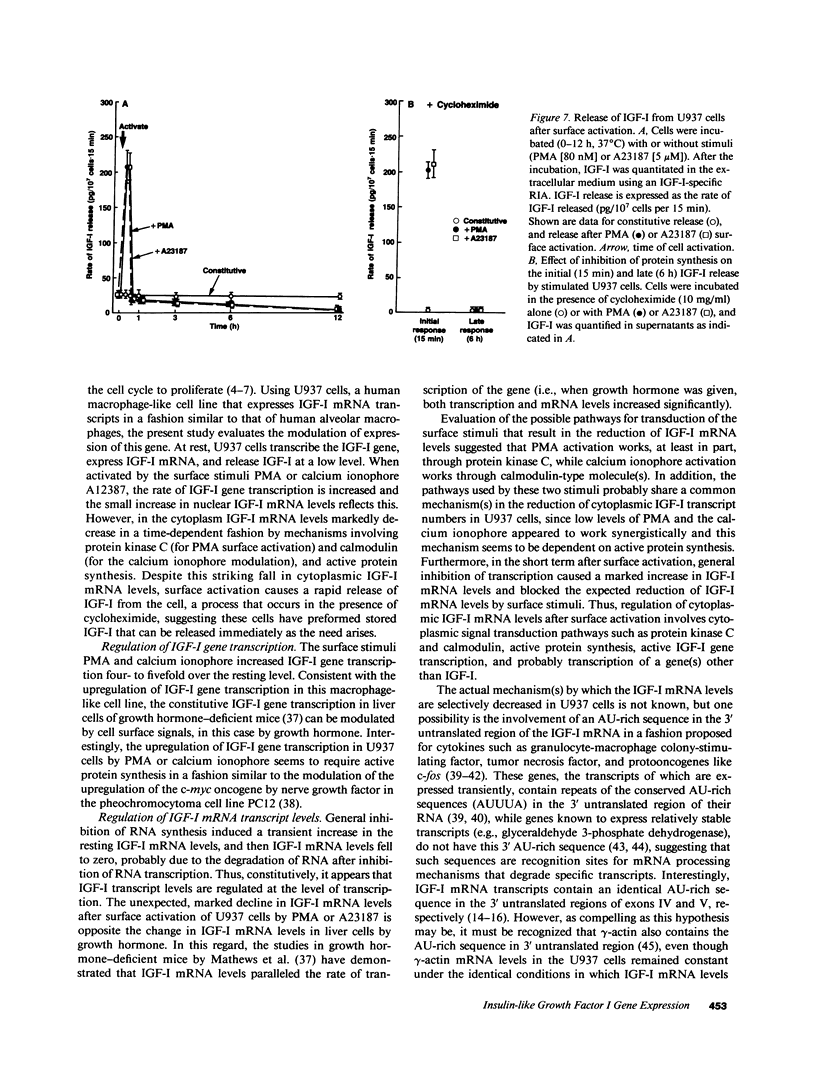
Activated macrophages release tissue forms of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), 20-25-kD products of the IGF-I gene, thus providing an extracellular growth and differentiation signal at sites of inflammation. To examine the control of IGF-I gene expression in mononuclear phagocytes, the human macrophage-like cell line U937 was evaluated at rest and after surface activation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or Ca2+ ionophore. Northern analysis and RNAse protection analysis with 32P-labeled IGF-I-specific probes demonstrated that the IGF-I mRNA transcripts of resting U937 cells were similar in size and amount to those of resting human alveolar macrophages, mononuclear phagocytes known to express the IGF-I gene. Nuclear run-off assays demonstrated that surface activation of U937 cells increased the transcription rate of the IGF-I gene four- to fivefold, a process that was inhibited by cycloheximide, suggesting that active protein synthesis was involved in the activation pathway. Despite this, cytoplasmic IGF-I mRNA levels after surface activation declined markedly, a process blocked by a protein kinase C inhibitor (for PMA activation) or a calmodulin antagonist (for Ca2+ ionophore activation). Like the increased transcription of the IGF-I gene, modulation of IGF-I mRNA transcript levels required active protein synthesis; in the presence of cycloheximide constitutive IGF-I mRNA levels increased and surface activation no longer caused a decrease in transcript number. Interestingly, surface activation caused a rapid release of IGF-I, even in the presence of a protein synthesis inhibitor, suggesting that mononuclear phagocytes have a preformed, stored, releasable pool of IGF-I. Together these observations demonstrate that IGF-I gene expression is complex and probably involves control of transcription rate, cytoplasmic mRNA levels possibly mediated through protein kinase C, calcium influx and calmodulin, and finally, release of preformed IGF-I from a storage pool.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agelli M., Wahl S. M. Cytokines and fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1986 Oct-Dec;4(4):379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashendel C. L. The phorbol ester receptor: a phospholipid-regulated protein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 9;822(2):219–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakouche O., Brown D. C., Lachman L. B. Subcellular localization of human monocyte interleukin 1: evidence for an inactive precursor molecule and a possible mechanism for IL 1 release. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4249–4255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach L. L., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Regulation of human histone gene expression: transcriptional and posttranscriptional control in the coupling of histone messenger RNA stability with DNA replication. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6178–6187. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Adelberg S., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Spontaneous release of the alveolar macrophage-derived growth factor in the interstitial lung disorders. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1801–1813. doi: 10.1172/JCI111140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., Dani C., Chambard J. C., Franchi A., Pouyssegur J., Jeanteur P. c-myc gene is transcribed at high rate in G0-arrested fibroblasts and is post-transcriptionally regulated in response to growth factors. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):443–445. doi: 10.1038/317443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brissenden J. E., Ullrich A., Francke U. Human chromosomal mapping of genes for insulin-like growth factors I and II and epidermal growth factor. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):781–784. doi: 10.1038/310781a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain P. G., Van Wyk J., Copeland K. C., Blethen S. L., Underwood L. E. Effect of in vitro action of serum proteases or exposure to acid on measurable immunoreactive somatomedin-C in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Feb;56(2):376–383. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-2-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Shaw D. S. Purification and biologic properties of fibroblast somatomedin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10293–10298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erba H. P., Eddy R., Shows T., Kedes L., Gunning P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human gamma-actin gene: differential evolution, location, and expression of the cytoskeletal beta- and gamma-actin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1775–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Mandel J. L. The glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase gene family: structure of a human cDNA and of an X chromosome linked pseudogene; amazing complexity of the gene family in mouse. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2627–2633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Ralph P. Human leukemic models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and U937 cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Apr;37(4):407–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen M., van Schaik F. M., Ricker A. T., Bullock B., Woods D. E., Gabbay K. H., Nussbaum A. L., Sussenbach J. S., Van den Brande J. L. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):609–611. doi: 10.1038/306609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A profusion of controls. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):1–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Beller D. I., Mizel S. B., Unanue E. R. Identification of a membrane-associated interleukin 1 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. The role of the macrophage in wound repair. A study with hydrocortisone and antimacrophage serum. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):71–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9343–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Taguchi M., Kovacs E. J., Young H. A., Oppenheim J. J. Intracellular localization of human monocyte associated interleukin 1 (IL 1) activity and release of biologically active IL 1 from monocytes by trypsin and plasmin. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2883–2891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Henning-Chubb C., Huberman E., Verma I. M. c-fos expression is neither sufficient nor obligatory for differentiation of monomyelocytes to macrophages. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90281-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. Induction of DNA synthesis in BALB/c 3T3 cells by serum components: reevaluation of the commitment process. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4481–4485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Basset P., Fells G. A., Nukiwa T., Trapnell B. C., Crysal R. G. Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1685–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI113781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Cantin A., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the lower respiratory tract inflammation of nonsmoking individuals with interstitial lung disease associated with chronic inhalation of inorganic dusts. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Dec;136(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.6.1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Folz R. J., Gordon J. I. Biosynthesis of human insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). The primary translation product of IGF-I mRNA contains an unusual 48-amino acid signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11807–11812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Pollock K. M., Didier D. K., Krivi G. G. Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4828–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P. Two insulin-like growth factor I messenger RNAs are expressed in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hance A. J., Ferrans V. J., Basset F., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Accurate quantification of cells recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):650–658. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. P., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Kierszenbaum A. L., Tres L. L. Partial characterization of a somatomedin-like peptide from the medium of cultured rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):186–193. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Hidaka H. Hydrophobic regions function in calmodulin-enzyme(s) interactions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11078–11080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricoli J. V., Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Shows T. B. Localization of insulin-like growth factor genes to human chromosomes 11 and 12. 1984 Aug 30-Sep 5Nature. 310(5980):784–786. doi: 10.1038/310784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]