Abstract
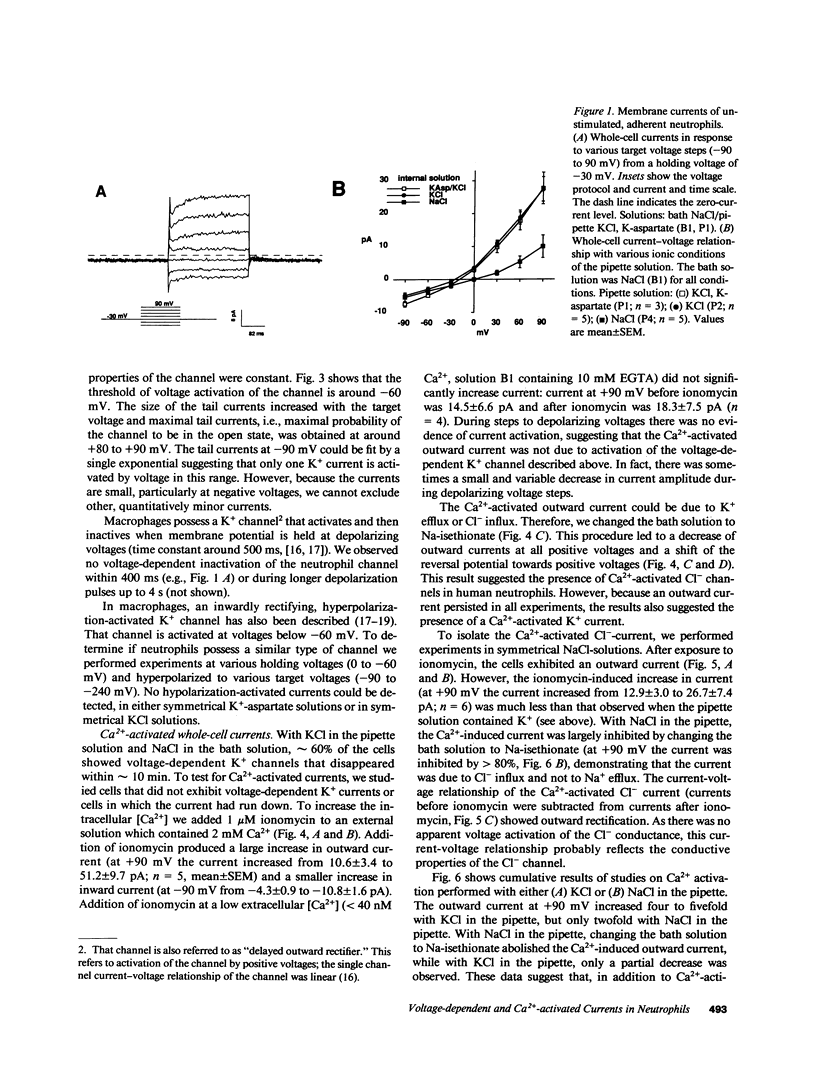
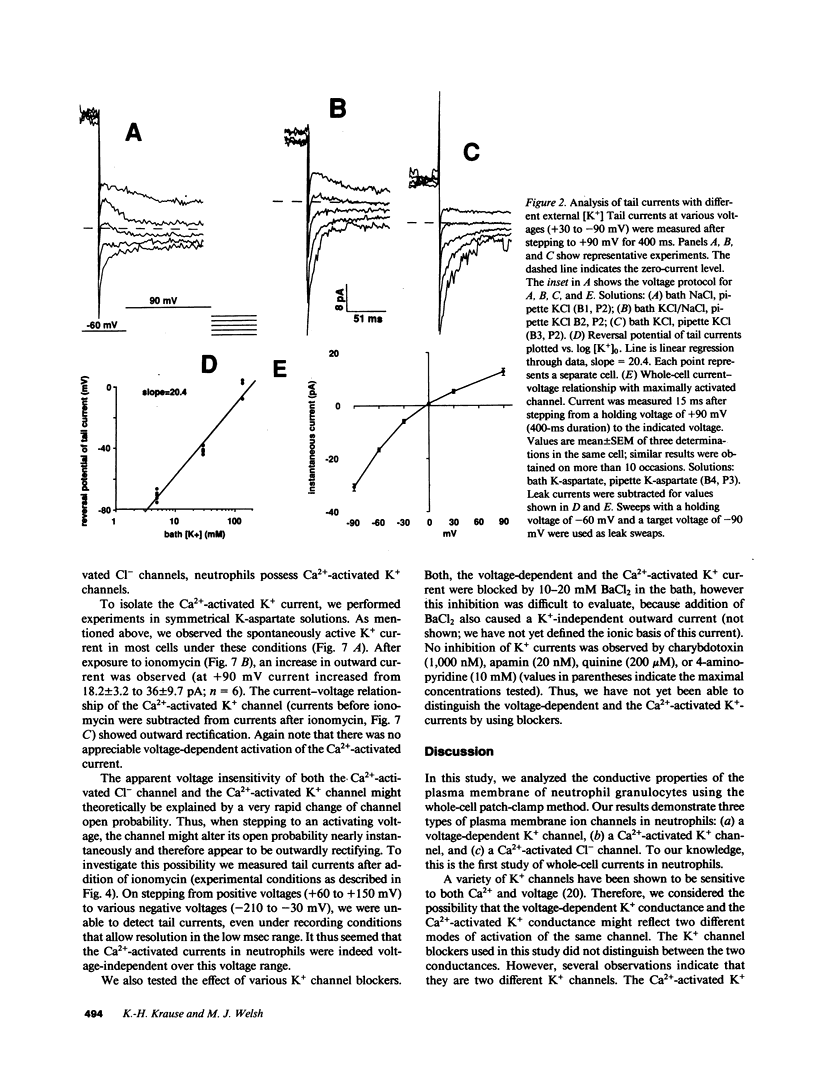
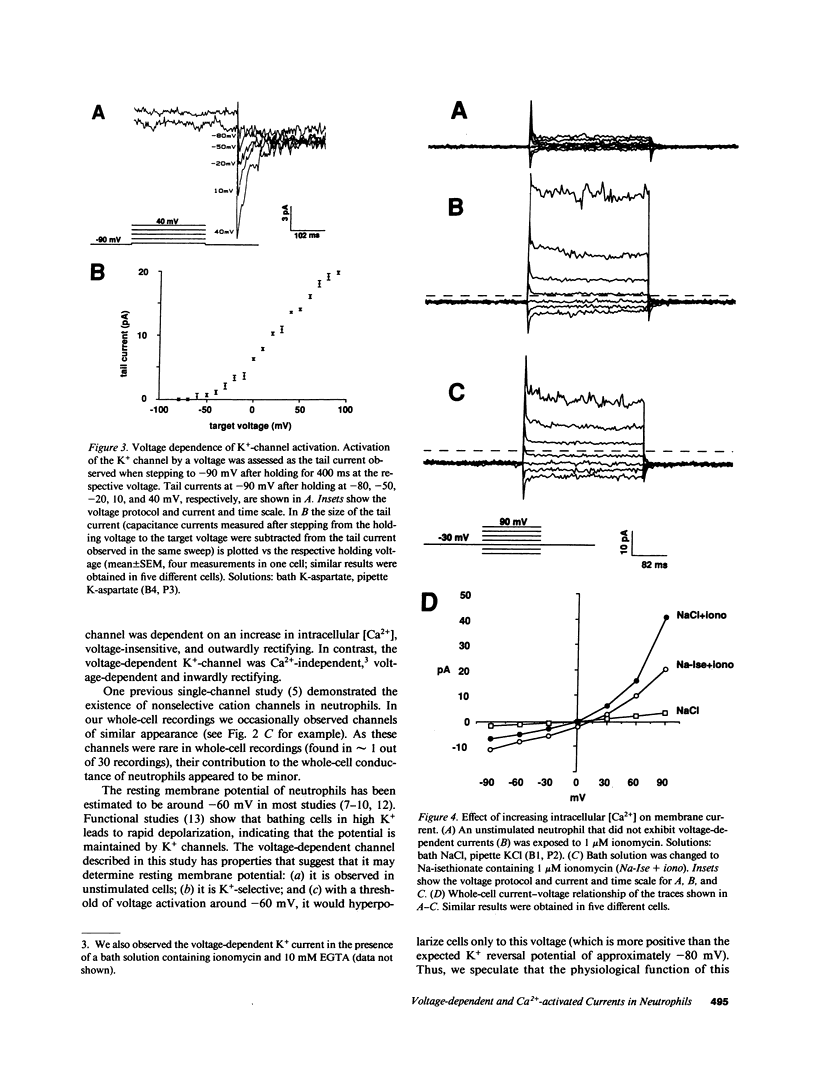
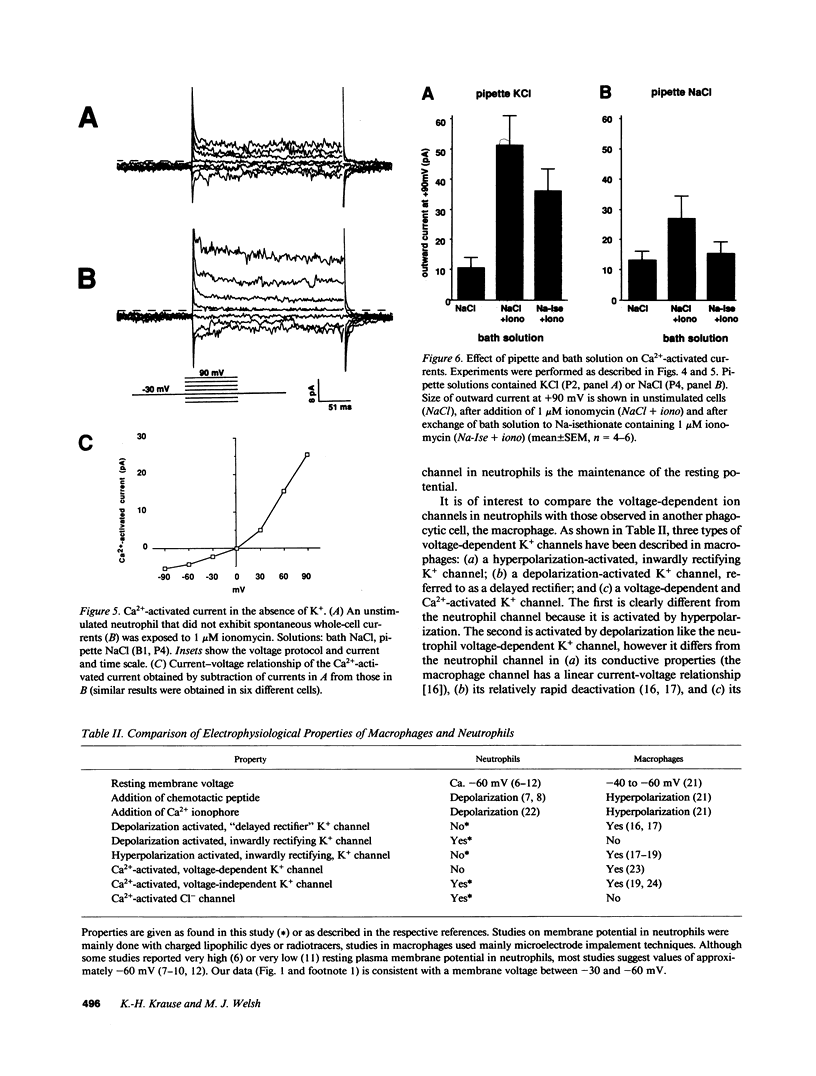
To investigate the regulation of membrane voltage and transmembrane ion fluxes in human neutrophils, we studied plasma membrane currents using the whole-cell patch-clamp method. We observed three distinct ion channel currents: (a) a voltage-dependent K+ current, (b) a Ca2(+)-activated K+ current, and (c) a Ca2(+)-activated Cl- current. The voltage-dependent K+ current was found in cells at rest. Its conductive properties suggested an inwardly rectifying channel. The channel was activated at membrane potentials more positive than -60 mV, suggesting that it may determine the resting membrane potential of neutrophils. Activation of neutrophils by the Ca2+ ionophore ionomycin led to an increase in whole-cell K+ and Cl- currents. The Ca2(+)-activated K+ channel differed from the voltage-dependent K+ channel because it was insensitive to voltage, because it rectified outwardly, and because the voltage-sensitive K+ channel was Ca2(+)-independent. The Ca2(+)-activated Cl- channel showed outward rectification and no apparent voltage dependency. The Ca2(+)-activated K+ and Cl- channels may play a role in cell volume homeostasis and/or cellular activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashford C. L., Pasternak C. A. Plasma membrane potential of neutrophils generated by the Na+ pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 11;817(1):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90080-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen O. Mediation of cell volume regulation by Ca2+ influx through stretch-activated channels. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):66–68. doi: 10.1038/330066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Lew P. D., Andersson T., Pozzan T. Plasma membrane potential modulates chemotactic peptide-stimulated cytosolic free Ca2+ changes in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4574–4579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Calcium- and voltage-activated potassium channels in human macrophages. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):821–825. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84080-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Electrophysiological properties of macrophages. Fed Proc. 1984 Jun;43(9):2385–2389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., McKinney L. C. Potassium conductances in macrophages. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1988;43:315–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K., Sheehy P. A. Differential expression of inward and outward potassium currents in the macrophage-like cell line J774.1. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:475–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin E. K. Voltage clamp studies in macrophages from mouse spleen cultures. Science. 1981 Oct 23;214(4519):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.7291986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Clarke C. A., Dupre A., Rothstein A. Volume-induced increase of anion permeability in human lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Dec;80(6):801–823. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.6.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. M., Chappell J. B., Jones O. T. The superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils is electrogenic and associated with an H+ channel. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):325–329. doi: 10.1042/bj2460325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Changes in membrane potential of human granulocytes antecede the metabolic responses to surface stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Lew D. P. Bacterial toxins and neutrophil activation. Semin Hematol. 1988 Apr;25(2):112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B., Andersson T., Waldvogel F. A., Lew P. D. Chemotactic peptide activation of human neutrophils and HL-60 cells. Pertussis toxin reveals correlation between inositol trisphosphate generation, calcium ion transients, and cellular activation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Kamo N., Kobatake Y., Okimasu E., Utsumi K. Measurement of membrane potential in polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its changes during surface stimulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 22;693(2):326–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90439-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Nauseef W. M., Clark R. A. Depolarization blunts the oxidative burst of human neutrophils. Parallel effects of monoclonal antibodies, depolarizing buffers, and glycolytic inhibitors. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3928–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omann G. M., Allen R. A., Bokoch G. M., Painter R. G., Traynor A. E., Sklar L. A. Signal transduction and cytoskeletal activation in the neutrophil. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jan;67(1):285–322. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriamampita C., Trautmann A. Ionic channels in murine macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):761–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann B. E., Gallin E. K., Martin D. L., Shain W., Gallin J. I. Interaction of chemotactic factors with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: studies using a membrane potential-sensitive cyanine dye. J Membr Biol. 1980;52(3):257–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01869194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., De Weer P. Chloride movements in human neutrophils. Diffusion, exchange, and active transport. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Aug;88(2):167–194. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Green J., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Characterization of volume-sensitive, calcium-permeating pathways in the osteosarcoma cell line UMR-106-01. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4383–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypey D. L., Clapham D. E. Development of a delayed outward-rectifying K+ conductance in cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Prod'hom B., Baggiolini M., Reuter H. Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):369–372. doi: 10.1038/324369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



