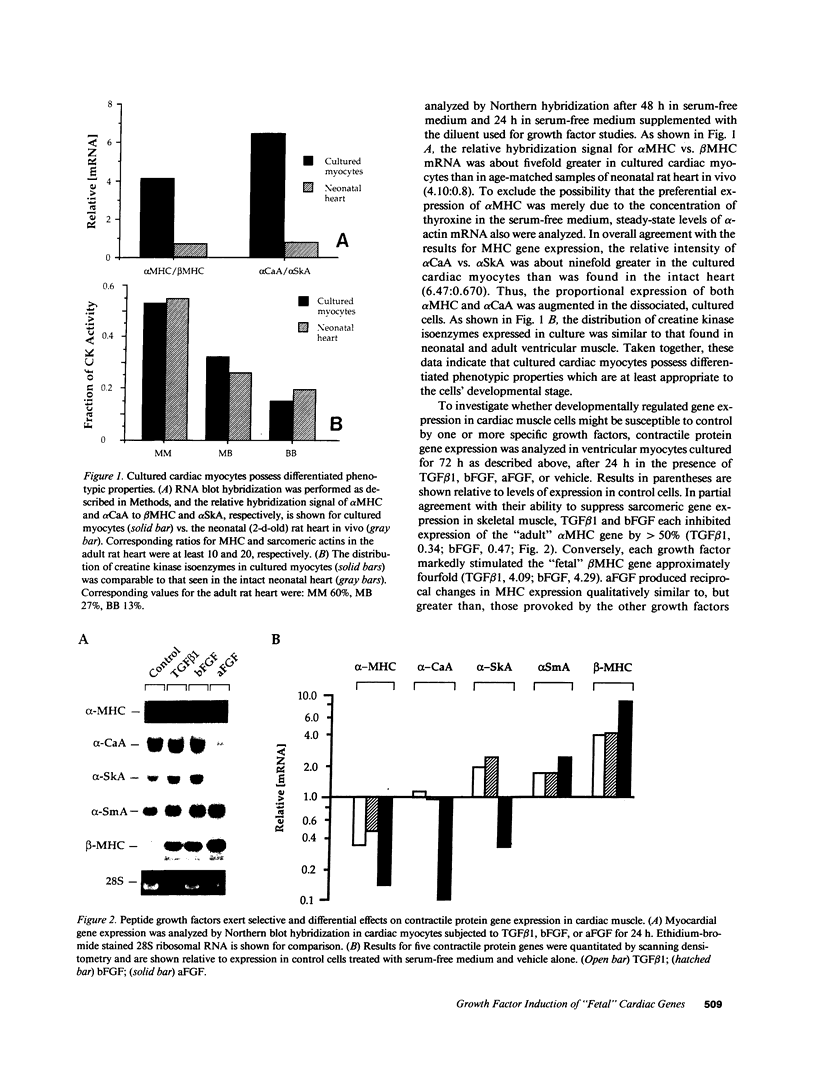
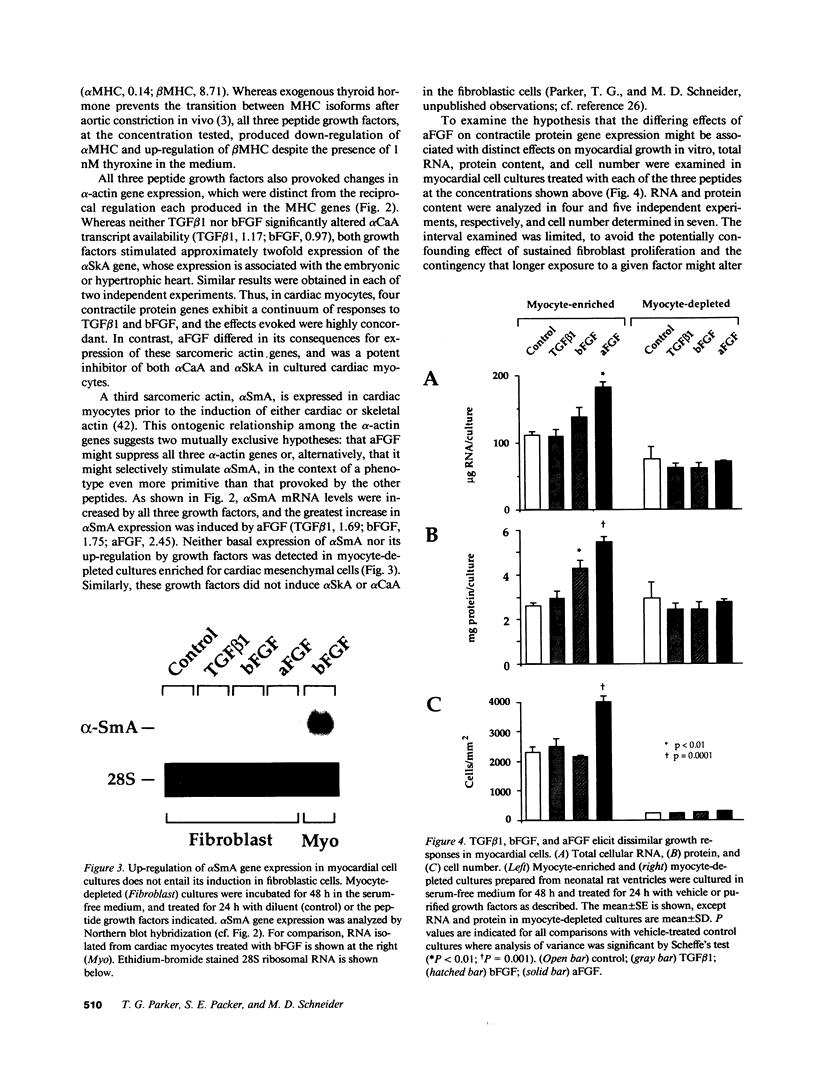
Abstract
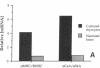
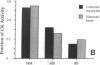
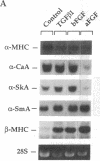
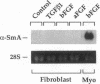
Cardiac-specific gene expression is intricately regulated in response to developmental, hormonal, and hemodynamic stimuli. To test whether cardiac muscle might be a target for regulation by peptide growth factors, the effect of three growth factors on the actin and myosin gene families was investigated by Northern blot analysis in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF beta 1, 1 ng/ml) and basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF, 25 ng/ml) elicited changes corresponding to those induced by hemodynamic load. The "fetal" beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC) was up-regulated about four-fold, whereas the "adult" alpha MHC was inhibited greater than 50-60%; expression of alpha-skeletal actin increased approximately two-fold, with little or no change in alpha-cardiac actin. Thus, peptide growth factors alter the program of differentiated gene expression in cardiac myocytes, and are sufficient to provoke fetal contractile protein gene expression, characteristic of pressure-overload hypertrophy. Acidic FGF (25 ng/ml) produced seven- to eightfold reciprocal changes in MHC expression but, unlike either TGF-beta 1 or basic FGF, inhibited both striated alpha-actin genes by 70-90%. Expression of vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin, the earliest alpha-actin induced during cardiac myogenesis, was increased by all three growth factors. Thus, three alpha-actin genes demonstrate distinct responses to acidic vs. basic FGF.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishopric N. H., Simpson P. C., Ordahl C. P. Induction of the skeletal alpha-actin gene in alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated hypertrophy of rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1194–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI113179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey J. M., Brown A. M., Schneider M. D. Ca2+ and Na+ currents in developing skeletal myoblasts are expressed in a sequential program: reversible suppression by transforming growth factor beta-1, an inhibitor of the myogenic pathway. J Neurosci. 1989 Oct;9(10):3443–3453. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-10-03443.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey J. M., Brown A. M., Schneider M. D. Mitogens and oncogenes can block the induction of specific voltage-gated ion channels. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):570–573. doi: 10.1126/science.2437651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Linkhart T. A., Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Growth factor control of skeletal muscle differentiation: commitment to terminal differentiation occurs in G1 phase and is repressed by fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):949–956. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clubb F. J., Jr, Bishop S. P. Formation of binucleated myocardial cells in the neonatal rat. An index for growth hypertrophy. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):571–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Barr P. J., Cousens L. S., Fretto L. J., Williams L. T. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors stimulate tyrosine kinase activity in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):988–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of c-myc during myogenesis: its mRNA remains inducible in differentiated cells and does not suppress the differentiated phenotype. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1412–1421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Spizz G., Olson E. N., Florini J. R. Decrease in transforming growth factor-beta binding and action during differentiation in muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):4029–4032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Roberts A. B., Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta. A very potent inhibitor of myoblast differentiation, identical to the differentiation inhibitor secreted by Buffalo rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16509–16513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Ferrara N., Schweigerer L., Neufeld G. Structural characterization and biological functions of fibroblast growth factor. Endocr Rev. 1987 May;8(2):95–114. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Markham B. E., Morkin E. Effects of thyroid hormone on alpha-actin and myosin heavy chain gene expression in cardiac and skeletal muscles of the rat: measurement of mRNA content using synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Circ Res. 1986 Aug;59(2):194–201. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. L., Wieben E., Markert C. L. Molecular signals for initiating protein synthesis in organ hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2455–2459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Lompré A. M., Matsuoka R., Koren G., Schwartz K., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Myosin heavy chain messenger RNA and protein isoform transitions during cardiac hypertrophy. Interaction between hemodynamic and thyroid hormone-induced signals. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):970–977. doi: 10.1172/JCI112908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. Synergistic induction of mesoderm by FGF and TGF-beta and the identification of an mRNA coding for FGF in the early Xenopus embryo. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro I., Kurabayashi M., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Expression of cellular oncogenes in the myocardium during the developmental stage and pressure-overloaded hypertrophy of the rat heart. Circ Res. 1988 Jun;62(6):1075–1079. doi: 10.1161/01.res.62.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Drobes B. L., Menke S. L., Taparowsky E. J. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation by the H-ras oncogene is associated with the down regulation of the MyoD1 gene. Oncogene. 1989 Apr;4(4):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Thayer M. J., Overell R. W., Weintraub H. Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop B., Olson E., Glaser L. Control by fibroblast growth factor of differentiation in the BC3H1 muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1540–1547. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Schwartz K., d'Albis A., Lacombe G., Van Thiem N., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzyme redistribution in chronic heart overload. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):105–107. doi: 10.1038/282105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Type beta transforming growth factor is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh K. M., Lessard J. L. The nucleotide sequence of a rat vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4167–4167. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvagh S. L., Michael L. H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. A hemodynamic load in vivo induces cardiac expression of the cellular oncogene, c-myc. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 15;147(2):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90977-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Behrens J., Nussbaumer U., Böhlen P., Birchmeier W. Inhibitory action of transforming growth factor beta on endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5600–5604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversibility of muscle differentiation in the absence of commitment: analysis of a myogenic cell line temperature-sensitive for commitment. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):281–293. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Spizz G., Tainsky M. A. The oncogenic forms of N-ras or H-ras prevent skeletal myoblast differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2104–2111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Sternberg E., Hu J. S., Spizz G., Wilcox C. Regulation of myogenic differentiation by type beta transforming growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1799–1805. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Cell surface fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptors are permanently lost during skeletal muscle terminal differentiation in culture. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):761–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne P. A., Olson E. N., Hsiau P., Roberts R., Perryman M. B., Schneider M. D. An activated c-Ha-ras allele blocks the induction of muscle-specific genes whose expression is contingent on mitogen withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8956–8960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinney D. F., Pearson-White S. H., Konieczny S. F., Latham K. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Myogenic lineage determination and differentiation: evidence for a regulatory gene pathway. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):781–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90095-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts J. D., Runyan R. B. Epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation in the embryonic heart can be mediated, in part, by transforming growth factor beta. Dev Biol. 1989 Aug;134(2):392–401. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosalki S. B. An improved procedure for serum creatine phosphokinase determination. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):696–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumyantsev P. P. Interrelations of the proliferation and differentiation processes during cardiact myogenesis and regeneration. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;51:186–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka D. L., Schwartz R. J. Sequential activation of alpha-actin genes during avian cardiogenesis: vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin gene transcripts mark the onset of cardiomyocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2575–2586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors promote stable neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation in cultures of PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3639–3653. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03639.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. D., Olson E. N. Control of myogenic differentiation by cellular oncogenes. Mol Neurobiol. 1988 Spring;2(1):1–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02935631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., Lecarpentier Y., Martin J. L., Lompré A. M., Mercadier J. J., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzymic distribution correlates with speed of myocardial contraction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1981 Dec;13(12):1071–1075. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(81)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., de la Bastie D., Bouveret P., Oliviéro P., Alonso S., Buckingham M. Alpha-skeletal muscle actin mRNA's accumulate in hypertrophied adult rat hearts. Circ Res. 1986 Nov;59(5):551–555. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Dunnmon P., Henderson S. A., Gerard R. D., Chien K. R. Terminally differentiated neonatal rat myocardial cells proliferate and maintain specific differentiated functions following expression of SV40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19132–19136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. C. Proto-oncogenes and cardiac hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:189–202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Darlington B. G., Heath J. K., Godsave S. F. Mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos by heparin-binding growth factors. Nature. 1987 Mar 12;326(6109):197–200. doi: 10.1038/326197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation by fibroblast growth factor or type beta transforming growth factor does not require persistent c-myc expression. Dev Biol. 1987 Oct;123(2):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starksen N. F., Simpson P. C., Bishopric N., Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Cardiac myocyte hypertrophy is associated with c-myc protooncogene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8348–8350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swynghedauw B. Developmental and functional adaptation of contractile proteins in cardiac and skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):710–771. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Bazoberry F., Speir E. H., Casscells W., Ferrans V. J., Flanders K. C., Kondaiah P., Geiser A. G., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta-1 in acute myocardial infarction in rats. Growth Factors. 1988;1(1):91–99. doi: 10.3109/08977198809000251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Flanders K. C., Smith J. M., Ellingsworth L. R., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in specific cells and tissues of adult and neonatal mice. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):661–669. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Perryman M. B., Roberts R., Schneider M. D. Differentiation of cardiac myocytes after mitogen withdrawal exhibits three sequential states of the ventricular growth response. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1911–1918. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya T. B., Rhodes S. J., Taparowsky E. J., Konieczny S. F. Fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta repress transcription of the myogenic regulatory gene MyoD1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3576–3579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner H. L., Swain J. L. Acidic fibroblast growth factor mRNA is expressed by cardiac myocytes in culture and the protein is localized to the extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2683–2687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]